Measuring Blood Pulse Wave Velocity with Bioimpedance in Different Age Groups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The ΔISTI is lower in older subjects (above 60) compared to younger subjects (below 30) from a healthy population.
- The ΔISTI decreases with increasing heart rate in older subjects (above 60).
2. Materials and Methods
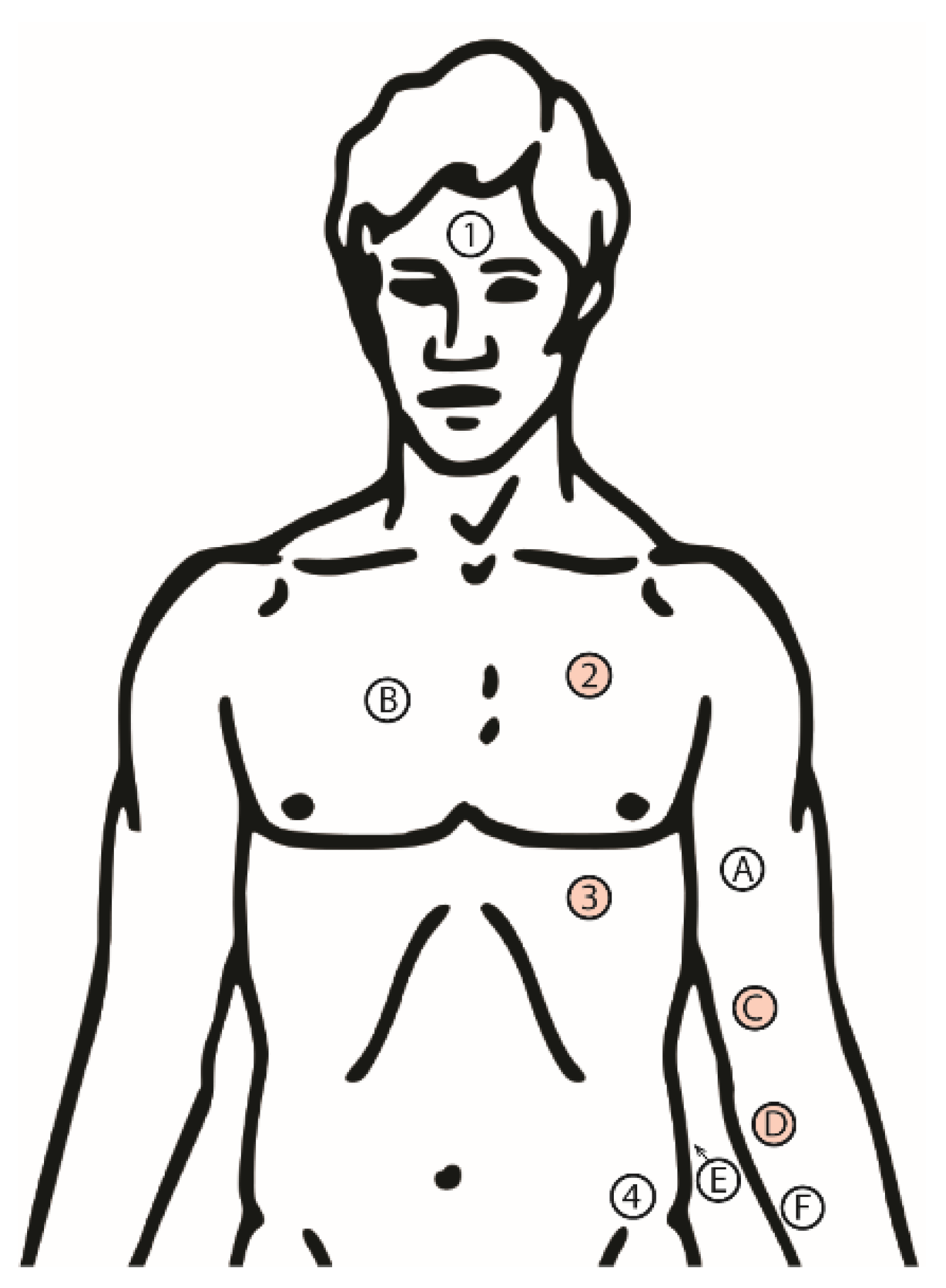
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Age and RR Interval on ΔISTIc
3.2. ΔISTIc Difference between Young and Older Subjects at High and Low Heart Rate
3.3. ΔISTIc Relation to RR for Young and Older Subjects
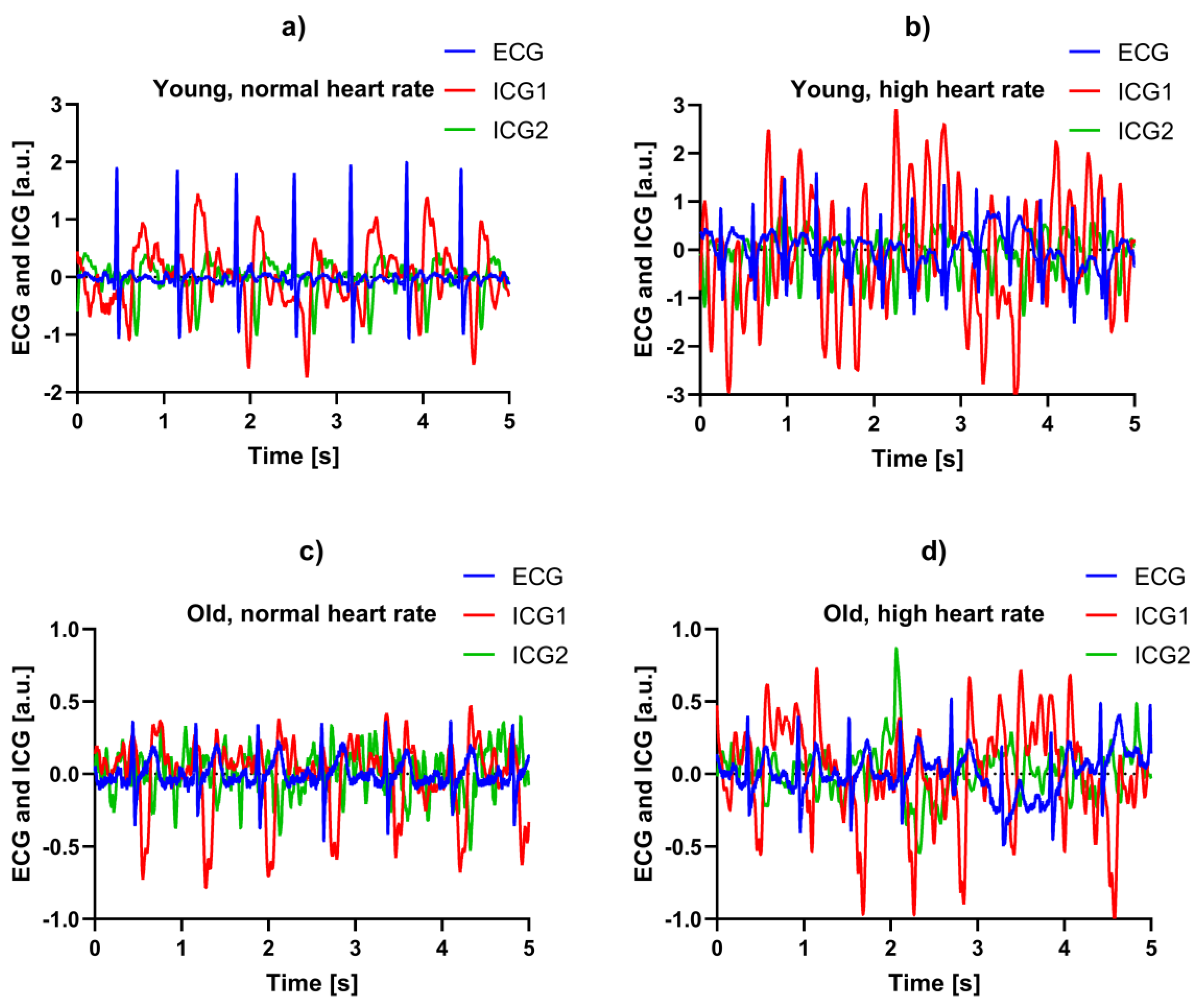
3.4. Example Recordings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McEniery, C.M.; Yasmin; Hall, I.R.; Qasem, A.; Wikinson, I.B.; Cockroft, J.R. Normal Vascular Aging: Differential Effects on Wave Reflection and Aortic Pulse Wave Velocity: The Anglo-Cardiff Collaborative Trial (ACCT). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Cruickshank, J.K.; De Backer, T.; Filipovsky, J.; Huybrechts, S.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Protogerou, A.D.; et al. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westerhof, N.; Westerhof, B.E. A review of methods to determine the functional arterial parameters stiffness and resistance. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, M.E. A Short Insight on 2 Different Aspects of Arterial Stiffness. Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerhof, N.; Westerhof, B.E. Aortic wave speed: Two-point and peripheral pressure methods compared with the gold standard. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Correia, C.; Cardoso, J.J. Novel Methods for Pulse Wave Velocity Measurement. Med. Biol. Eng. 2015, 35, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, T.; Santos, I.; Oliveira, T.; Vaz, P.; Pereira, T.; Santos, H.; Pereira, H.; Correira, C.; Cardoso, J. Pulse pressure waveform estimation using distension profiling with contactless optical probe. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, P.; Lio, G.; Labat, C.; Ricci, E.; Pannier, B.; Benetos, A.J. Validation of a new non-invasive portable tonometer for determining arterial pressure wave and pulse wave velocity: The PulsePen device. Hypertension 2004, 22, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztrymf, B.; Jacobs, F.; Chemla, D.; Richard, C.; Millasseau, S.C. Validation of the new Complior sensor to record pressure signals non-invasively. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2013, 27, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butlin, M.; Qasem, A. Large Artery Stiffness Assessment Using SphygmoCor Technology. Pulse 2017, 4, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulmann, J.; Schillings, U.; Rickert, S.; Uen, S.; Düsing, R.; Illyes, M.; Cziraki, A.; Nickenig, G.; Mengden, T.J. A new oscillometric method for assessment of arterial stiffness: Comparison with tonometric and piezo-electronic methods. Hypertension 2008, 26, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.M.; Bailey, M.C.; Griffin, K.J.; Scott, J.A. Pulse wave velocity and the non-invasive methods used to assess it: Complior, SphygmoCor, Arteriograph and Vicorder. Vascular 2012, 20, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimnes, S.; Martinsen, Ø.G. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eijnatten, M.A.J.M.; van Rijssel, M.J.; Peters, R.J.A.; Verdaasdonk, R.M.; Meijer, J.H. Comparison of cardiac time intervals between echocardiography and impedance cardiography at various heart rates. J. Electr. Bioimped. 2014, 5, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, J.H.; Boesveldt, S.; Elbertse, E.; Berendse, H.W. Method to measure autonomic control of cardiac function using time interval parameters from impedance cardiography. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, S383–S391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimnes, S.; Martinsen, Ø.G. Sources of error in tetrapolar impedance measurements on biomaterials and other ionic conductors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tsorrero, J.F.S.; Tardio-Fernandez, M.; Valverde-Valverde, J.M.; Duque-Carrillo, F.; Vega-Fernandez, J.M.; Joya-Vazquez, P.; Vega-Fernandez, J. Pulse Wave Velocity in Four Extremities for Assessing Cardiovascular Risk Using a New Device. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2014, 16, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, W.W. Clinical measurement of arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 3S–10S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantelme, P.; Mestre, C.; Lievre, M.; Gressard, A.; Milon, H. Heart Rate: An Important Confounder of Pulse Wave Velocity Assessment. Hypertension 2002, 39, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Spronck, B.; Kiat, H.; Barin, E.; Koen, D.; Reesink, K.D.; Delhaas, T.; Avolio, A.P.; Butlin, M. Heart Rate Dependency of Large Artery Stiffness. Hypertension 2016, 68, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, H.; Tan, I.; Butlin, M.; Li, D.; Avolio, A.P. Arterial viscoelasticity: Role in the dependency of pulse wave velocity on heart rate in conduit arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H1185–H1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, H.; Yamashina, A.; Arai, T.; Hirose, K.; Koji, Y.; Chikamori, T.; Hori, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hinohara, S. Influences of age and gender on results of noninvasive brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity measurement—A survey of 12 517 subjects. Atherosclerosis 2003, 166, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusche, R.; Klimach, P.; Ryschka, M. A Multichannel Real-Time Bioimpedance Measurement Device for Pulse Wave Analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group | Male | Female | Age (years) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Younger | 5 | 5 | 24.6 ± 2.3 | 176.4 ± 7.2 | 71.3 ± 13.6 |
| Older | 5 | 5 | 68.2 ± 5.9 | 174.6 ± 8.7 | 75.7 ± 8.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aria, S.; Elfarri, Y.; Elvegård, M.; Gottfridsson, A.; Grønaas, H.S.; Harang, S.; Jansen, A.; Madland, T.E.R.; Martins, I.B.; Olstad, M.W.; et al. Measuring Blood Pulse Wave Velocity with Bioimpedance in Different Age Groups. Sensors 2019, 19, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040850
Aria S, Elfarri Y, Elvegård M, Gottfridsson A, Grønaas HS, Harang S, Jansen A, Madland TER, Martins IB, Olstad MW, et al. Measuring Blood Pulse Wave Velocity with Bioimpedance in Different Age Groups. Sensors. 2019; 19(4):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040850
Chicago/Turabian StyleAria, Shafa, Yassine Elfarri, Marius Elvegård, Adam Gottfridsson, Halvor S. Grønaas, Sigve Harang, Anders Jansen, Thomas Emil Rolland Madland, Ivar Bruvik Martins, Marius Wilhelm Olstad, and et al. 2019. "Measuring Blood Pulse Wave Velocity with Bioimpedance in Different Age Groups" Sensors 19, no. 4: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040850
APA StyleAria, S., Elfarri, Y., Elvegård, M., Gottfridsson, A., Grønaas, H. S., Harang, S., Jansen, A., Madland, T. E. R., Martins, I. B., Olstad, M. W., Ryan, T. L., Shaban, A. N., Svenningsen, Ø. L., Sørensen, A. D., Ulvestad, E. H., Vister, O. M., Øvergaard, M. B., Kalvøy, H., Pettersen, F. J., ... Martinsen, Ø. G. (2019). Measuring Blood Pulse Wave Velocity with Bioimpedance in Different Age Groups. Sensors, 19(4), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040850






