Discrimination of Different Species of Dendrobium with an Electronic Nose Using Aggregated Conformal Predictor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Electronic Nose Analysis
3. Data Analysis Method
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.3. Aggregated Conformal Prediction
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Different Conformal Predictors and Simple Predictor
4.2. Validity and Efficiency of Conformal Prediction
4.3. Confidence and Credibility of Conformal Predictors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H. The rapid determination of total polyphenols content and antioxidant activity in Dendrobium officinale using near-infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4584–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlosrichok, A.; Sumkhemthong, S.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P.; Chaotham, C. A bibenzyl from Dendrobium ellipsophyllum induces apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhummaphan, N.; Pongrakhananon, V.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Cancer Stem Cell Suppressing Activity of Chrysotoxine, a bibenzyl from Dendrobium pulchellum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 364, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Qiu, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Cai, S.; Zhang, X. Antiproliferative effect of Dendrobium catenatum Lindley polypeptides against human liver, gastric and breast cancer cell lines. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandovalavila, S.; Diaz, N.F.; Gómezpinedo, U.; Canalesaguirre, A.A.; Gutiérrezmercado, Y.K.; Padillacamberos, E.; Marquezaguirre, A.L.; Díazmartínez, N.E. Neuroprotective effects of phytochemicals on dopaminergic neuron cultures. Neurologia 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengpaeng, P.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Dendrofalconerol A sensitizes anoikis and inhibits migration in lung cancer cells. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.A.T.D.; Ng, T.B. The medicinal and pharmaceutical importance of Dendrobium species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Li, Y.; Tao, S.; Wei, G.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, C. Purification, Characterization and Biological Activity of Polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale. Molecules 2016, 21, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.B.; Huang, Y.P.; Yang, L.; Liu, T.T.; Gong, W.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Sheng, J.; Hu, A.M. Structural characterization and immunomodulating activity of polysaccharide from Dendrobium officinale. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 83, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, D.D.; Zha, X.Q.; Pan, L.H.; Luo, J.P. Intestinal immunomodulating activity and structural characterization of a new polysaccharide from stems of Dendrobium officinale. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.M.; Deng, M.Z. [Effect of dendrobium mixture on hypoglycemic and the apoptosis of islet in rats with type 2 diabetic mellitus]. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2012, 35, 765. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.Y.; Yu, Z.Y.; Lu, B.; Yang, L.; Sheng, Y.C.; Fan, Y.M.; Ji, L.L.; Wang, Z.T. Ethanol extract of Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl ameliorates diabetic retinopathy and its mechanism. Vasc. Pharm. 2014, 62, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.Z.; Liang, C.Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhu, D.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.R.; Huang, S.; Lai, X.P. Dendrobium officinale Prevents Early Complications in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.H.; Lu, J.; Luo, J.P.; Zha, X.Q.; Wang, J.H. Preventive effect of a galactoglucomannan (GGM) from Dendrobium huoshanense on selenium-induced liver injury and fibrosis in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Luo, J.P.; Chen, R.; Zha, X.Q.; Wang, H. The effects of daily supplementation of Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide on ethanol-induced subacute liver injury in mice by proteomic analysis. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2020–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.C.; Zha, X.Q.; Luo, J.P. A polysaccharide from Dendrobium huoshanense prevents hepatic inflammatory response caused by carbon tetrachloride. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.S.; Lee, S.A.; Hong, S.S.; Han, X.H.; Lee, C.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, M.K. Phenanthrenes from Dendrobium nobile and their inhibition of the LPS-induced production of nitric oxide in macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3785–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, L.J.; Chun, Z.; Bao, J.K.; Zhang, G.L. Anti-inflammatory phenanthrene derivatives from stems of Dendrobium denneanum. Phytochemistry 2013, 95, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Gong, C.; Lu, B.; Yang, L.; Sheng, Y.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z. Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl. alleviates diabetic retinopathy by preventing retinal inflammation and tight junction protein decrease. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.; Cui, S.W.; Nie, S.; Phillips, G.O.; Goff, H.D.; Wang, Q. A review of isolation process, structural characteristics, and bioactivities of water-soluble polysaccharides from Dendrobium plants. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2013, 1, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gui, S.; Huang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Shun, Q.; Huang, K.; Tao, S.; Wei, G. Characteristic fingerprint analysis of Dendrobium huoshanense by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3802–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.D.; Chen, N.F.; Li, J.; Cao, C.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Huang, H.P. Similarity Evaluation of Different Origins and Species of Dendrobiums by GC-MS and FTIR Analysis of Polysaccharides. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015, 713410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Geng, P.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wen, C. Pharmacokinetic study of dendrobine in rat plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 30, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Li, G.; Kou, Z.; Feng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Determination of chrysotoxine in rat plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a rat pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 967, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, W. Application of two-dimensional near-infrared (2D-NIR) correlation spectroscopy to the discrimination of three species of Dendrobium. J. Chemom. 2010, 23, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Manuela, B. Applications and advances in electronic-nose technologies. Sensors 2009, 9, 5099–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, R.; Sivret, E.C.; Parcsi, G.; Lebrero, R.; Wang, X.; Suffet, I.M.; Stuetz, R.M. Monitoring techniques for odour abatement assessment. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5129–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebicki, J.; Dymerski, T.; Namieśnik, J. Monitoring of odour nuisance from landfill using electronic nose. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 40, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Vito, S.D.; Piga, M.; Martinotto, L.; Francia, G.D. CO, NO(2) and NO(x) urban pollution monitoring with on-field calibrated electronic nose by automatic bayesian regularization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romain, A.C.; Nicolas, J. Long term stability of metal oxide-based gas sensors for e-nose environmental applications: An overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 146, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Raj, V.B.; Kumar, J.; Mittal, U.; Mishra, M.; Nimal, A.T.; Sharma, M.U.; Gupta, V. Metal oxide SAW E-nose employing PCA and ANN for the identification of binary mixture of DMMP and methanol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 200, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębicki, J.; Dymerski, T.; Namieśnik, J. Investigation of Air Quality beside a Municipal Landfill: The Fate of Malodour Compounds as a Model VOC. Environments 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, A.K.; Magan, N.; Mcnulty, C.; Jones, J.M.; Sharp, D.; Brown, J.; Turner, A.P.F. Use of an electronic nose system for diagnoses of urinary tract infections. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodogiannis, V.S.; Lygouras, J.N.; Andrzej, T.; Chowdrey, H.S. Artificial odor discrimination system using electronic nose and neural networks for the identification of urinary tract infection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2008, 12, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covington, J.A.; Westenbrink, E.W.; Nathalie, O.; Ruth, H.; Catherine, B.; Nicola, O.; James, C.; Nigel, W.; Nwokolo, C.U.; Bardhan, K.D. Application of a novel tool for diagnosing bile acid diarrhoea. Sensors 2013, 13, 11899–11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, G.C.; Chan, A.D.C.; Dan, H.; Lin, M. Using a metal oxide sensor (MOS)-based electronic nose for discrimination of bacteria based on individual colonies in suspension. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 152, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnowski, W.; Majchrzak, T.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Portable Electronic Nose Based on Electrochemical Sensors for Food Quality Assessment. Sensors 2017, 17, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loutfi, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Mani, G.K.; Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 2015, 144, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.M.; J Enrique, A.; Antonio, G.M.; Carlos Javier, G.O.; Horacio Manuel, G.V.; Ramón, G.C. A compact and low cost electronic nose for aroma detection. Sensors 2013, 13, 5528–5541. [Google Scholar]
- Majchrzak, T.; Wojnowski, W.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Electronic noses in classification and quality control of edible oils: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Kumar, R.; Gulati, A.; Ghanshyam, C.; Kapur, P.; Bhondekar, A.P. Enhancing electronic nose performance: A novel feature selection approach using dynamic social impact theory and moving window time slicing for classification of Kangra orthodox black tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebicki, J.; Szulczynski, B.; Kaminski, M. Determination of authenticity of brand perfume using electronic nose prototypes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Guan, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Discrimination between Alternative Herbal Medicines from Different Categories with the Electronic Nose. Sensors 2018, 18, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Optimal Sensor Selection for Classifying a Set of Ginsengs Using Metal-Oxide Sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 16027–16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Miao, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, G. Conformal Prediction Based on K-Nearest Neighbors for Discrimination of Ginsengs by a Home-Made Electronic Nose. Sensors 2017, 17, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longobardi, F.; Casiello, G.; Ventrella, A.; Mazzilli, V.; Nardelli, A.; Sacco, D.; Catucci, L.; Agostiano, A. Electronic nose and isotope ratio mass spectrometry in combination with chemometrics for the characterization of the geographical origin of Italian sweet cherries. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, L.; Eklund, M.; Norinder, U. Aggregated Conformal Prediction. IFIP Adv. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2014, 437, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Vovk, V. Cross-conformal predictors. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 2015, 74, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norinder, U.; Boyer, S. Conformal Prediction Classification of a Large Data Set of Environmental Chemicals from ToxCast and Tox21 Estrogen Receptor Assays. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, M.; Norinder, U.; Boyer, S.; Carlsson, L. The application of conformal prediction to the drug discovery process. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 2015, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, M.; Karlén, A.; Norinder, U. Predicting the Rate of Skin Penetration Using an Aggregated Conformal Prediction Framework. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Xiuzhen, G.; Shukai, D.; Pengfei, J.; Lidan, W.; Chao, P.; Songlin, Z. Electronic Nose Feature Extraction Methods: A Review. Sensors 2015, 15, 27804–27831. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Vovk, V. Conditional validity of inductive conformal predictors. Mach. Learn. 2013, 92, 349–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löfström, T.; Johansson, U.; Boström, H. Effective utilization of data in inductive conformal prediction using ensembles of neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Dallas, TX, USA, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]


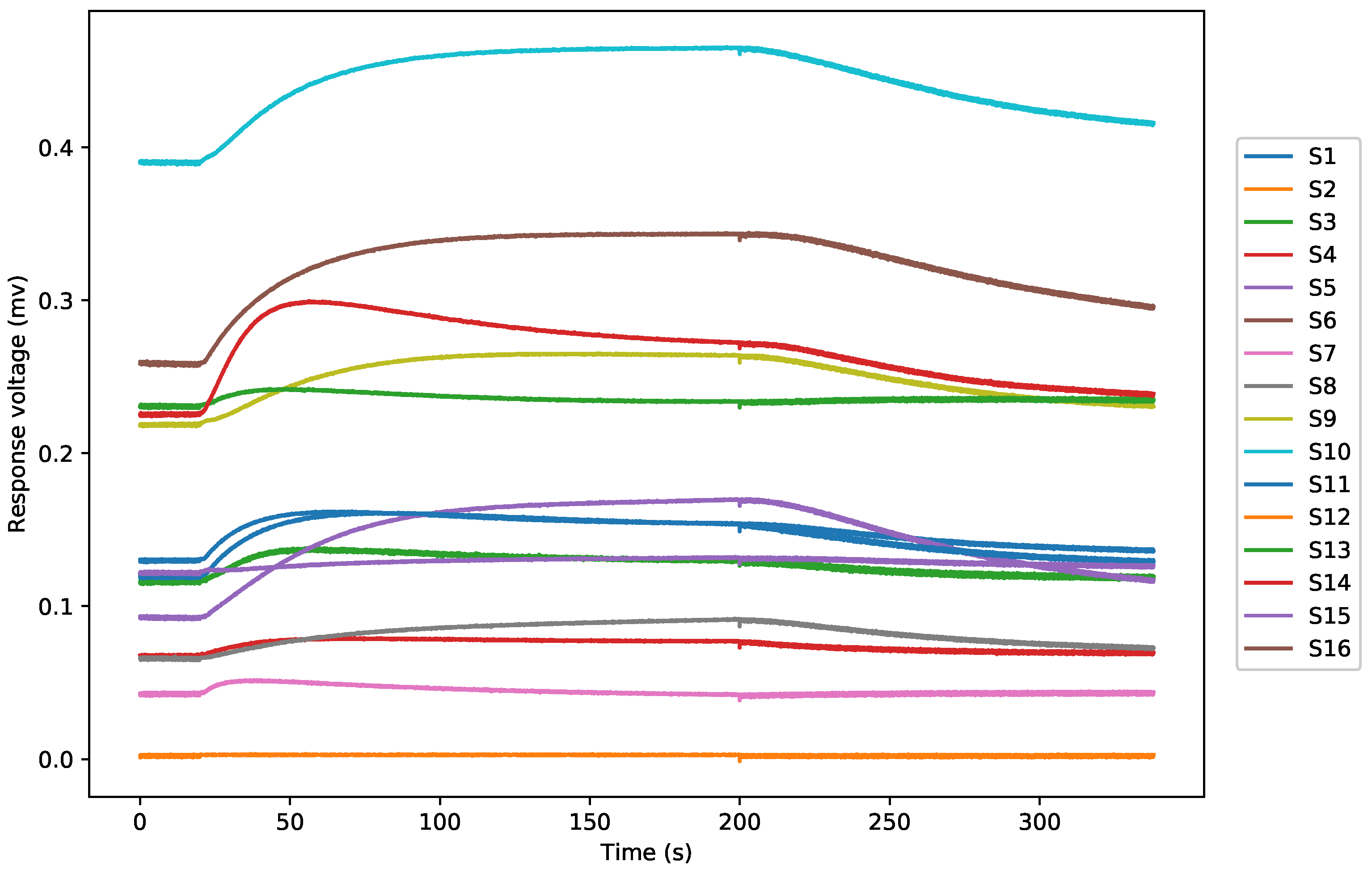
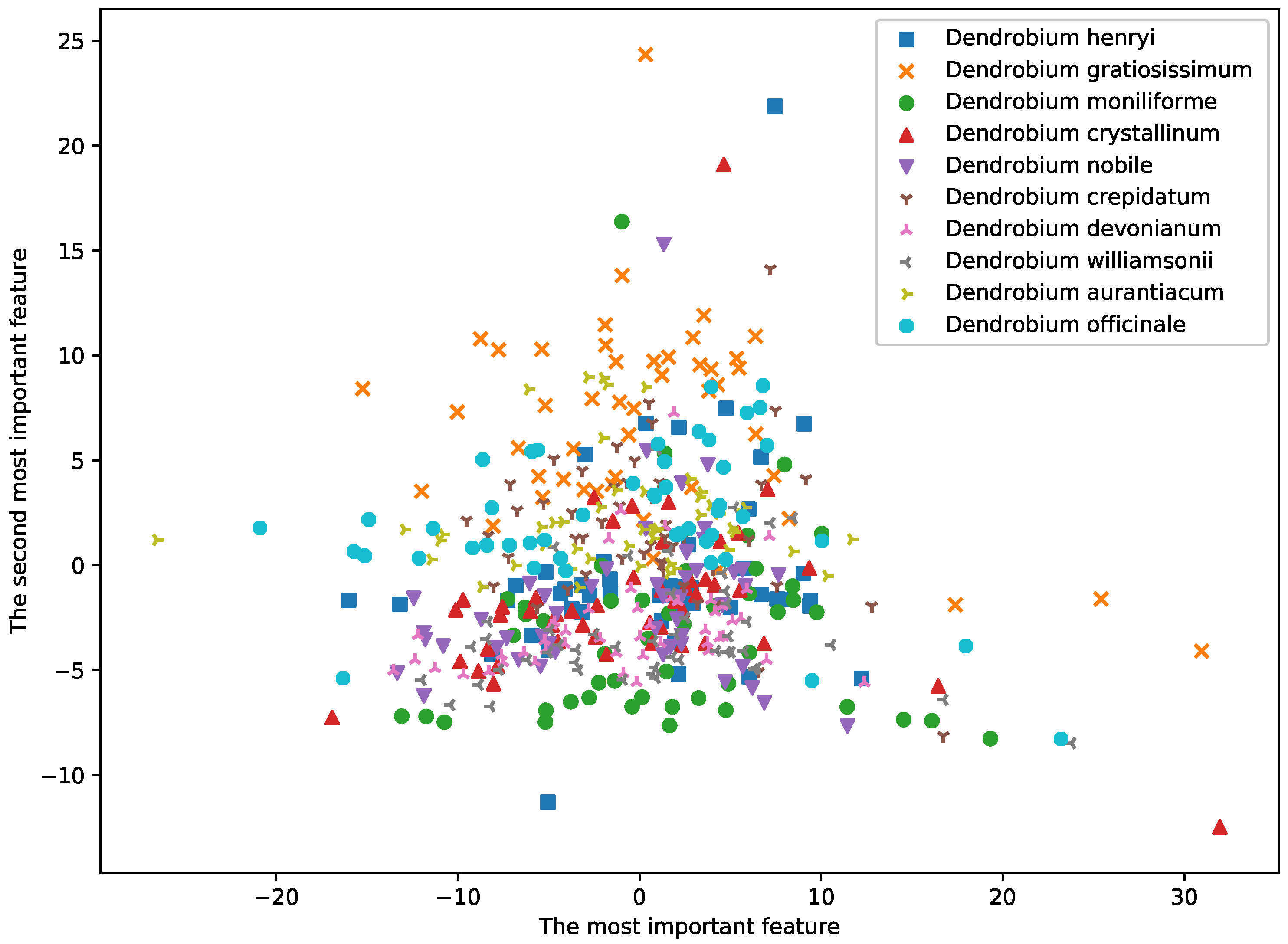
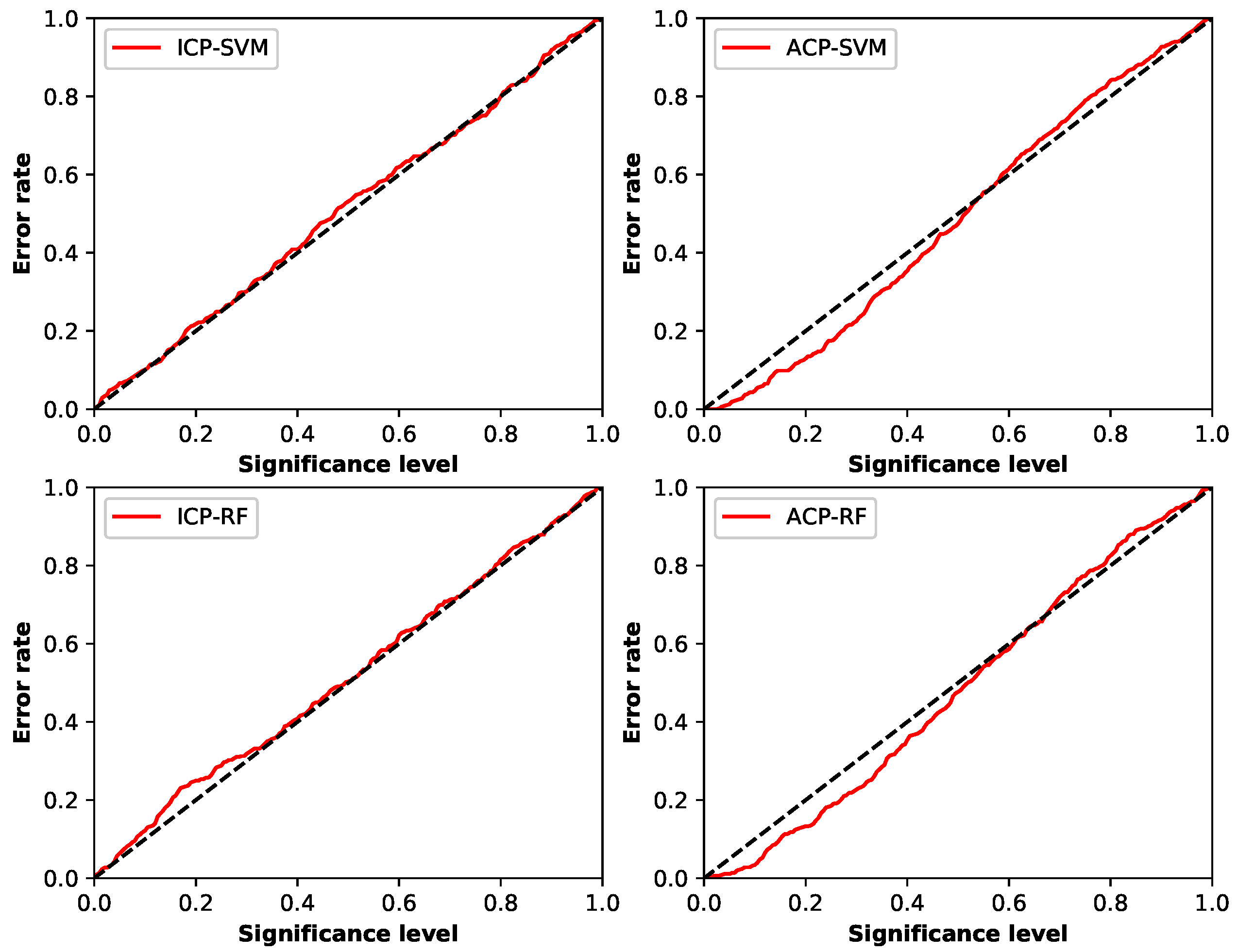

| Name of Specie | Place of Production |
|---|---|
| Dendrobium henryi | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium gratiosissimum | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium moniliforme | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium crystallinum | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium nobile | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium crepidatum | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium devonianum | Zhejiang, China |
| Dendrobium williamsonii | Yunnan, China |
| Dendrobium aurantiacum | Zhejiang, China |
| Dendrobium officinale | Zhejiang, China |
| No. | Sensor Name | Target Gases | Optimal Detection Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | TGS800 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, hydrogen, ammonia | 1–30 ppm |
| S2 | TGS813 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, hydrogen, isobutane | 500–10,000 ppm |
| S3 | TGS813 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, hydrogen, isobutane | 500–10,000 ppm |
| S4 | TGS816 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, hydrogen, isobutane | 500–10,000 ppm |
| S5 | TGS821 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, hydrogen | 30–1000 ppm |
| S6 | TGS822 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, acetone, n-Hexane, | 50–5000 ppm |
| benzene, isobutane | |||
| S7 | TGS822 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, acetone, | 50–5000 ppm |
| n-Hexane, benzene, isobutane | |||
| S8 | TGS826 | Ammonia, trimethyl amine | 30–300 ppm |
| S9 | TGS830 | Ethanol, R-12, R-11, R-22, R-113 | 100–3000 ppm |
| S10 | TGS832 | R-134a, R-12 and R-22, ethanol | 100–3000 ppm |
| S11 | TGS800 | Carbon monoxide, ethanol, methane, hydrogen, ammonia | 1–30 ppm |
| S12 | TGS2620 | Methane, Carbon monoxide, isobutane, hydrogen | 50–5000 ppm |
| S13 | TGS2600 | Carbon monoxide, hydrogen | 1–30 ppm |
| S14 | TGS2602 | Hydrogen, ammonia ethanol, hydrogen sulfide, toluene | 1–30 ppm |
| S15 | TGS2610 | Ethanol, hydrogen, methane, isobutane/propane | 500–10,000 ppm |
| S16 | TGS2611 | Ethanol, hydrogen, isobutane, methane | 500–10,000 ppm |
| Underlying Method | Framework | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple | ICP | ACP | |
| SVM | 77.4% | 70.85% | 79.4% |
| RF | 76.65% | 71.75% | 78.00% |
| Predictors | Output | Confidence | Credibility | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... | 10 | |||
| SVM | False | False | False | False | ... | True | - | - |
| ICP-SVM | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.007 | ... | 0.813 | 0.915 | 0.813 |
| ACP-SVM | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.040 | 0.012 | ... | 0.765 | 0.854 | 0.765 |
| Conformal Predictor | Confidence | Credibility | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | ST.dev. | Mean | ST.dev. | |
| ICP-SVM | 0.908 | 0.092 | 0.515 | 0.252 |
| ACP-SVM | 0.885 | 0.094 | 0.506 | 0.241 |
| ICP-RF | 0.904 | 0.090 | 0.535 | 0.244 |
| ACP-RF | 0.877 | 0.099 | 0.548 | 0.232 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Diao, J.; Sun, X.; Luo, Z.; Li, G. Discrimination of Different Species of Dendrobium with an Electronic Nose Using Aggregated Conformal Predictor. Sensors 2019, 19, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040964
Wang Y, Wang Z, Diao J, Sun X, Luo Z, Li G. Discrimination of Different Species of Dendrobium with an Electronic Nose Using Aggregated Conformal Predictor. Sensors. 2019; 19(4):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040964
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, You, Zhan Wang, Junwei Diao, Xiyang Sun, Zhiyuan Luo, and Guang Li. 2019. "Discrimination of Different Species of Dendrobium with an Electronic Nose Using Aggregated Conformal Predictor" Sensors 19, no. 4: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040964
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, Z., Diao, J., Sun, X., Luo, Z., & Li, G. (2019). Discrimination of Different Species of Dendrobium with an Electronic Nose Using Aggregated Conformal Predictor. Sensors, 19(4), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040964





