Video-Based Actigraphy for Monitoring Wake and Sleep in Healthy Infants: A Laboratory Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects and Data
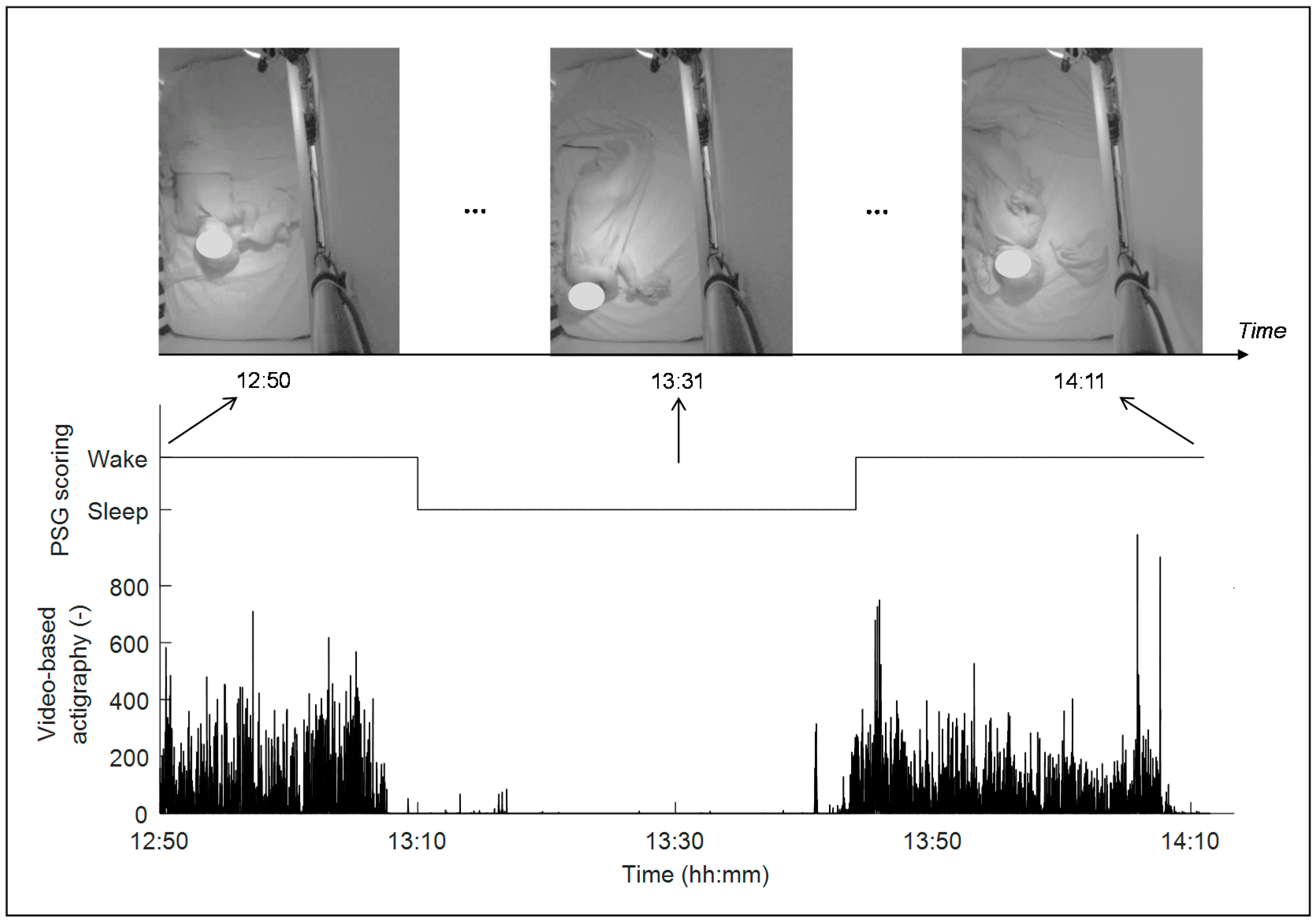
2.2. Video-Based Actigraphy
2.3. Feature Extraction and Classification Model
2.4. Validation and Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirshkowitz, M.; Whiton, K.; Albert, S.M.; Alessi, C.; Bruni, O.; DonCarlos, L.; Hazen, N.; Herman, J.; Katz, E.S.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; et al. National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: Methodology and results summary. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, R. The regulation of sleep and arousal: Development and psychopathology. Dev. Psychopathol. 1996, 8, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graven, S.N.; Browne, J.V. Sleep and Brain Development: The Critical Role of Sleep in Fetal and Early Neonatal Brain Development. Newborn Infant Nurs. Rev. 2008, 8, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, J.K.; Hiscock, H.; Hampton, A.; Wake, M.S. Sleep problems in young infants and maternal mental and physical health. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2007, 43, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindell, J.A.; Telofski, L.S.; Wiegand, B.; Kurtz, E.S. A nightly bedtime routine: Impact on sleep in young children and maternal mood. Sleep 2009, 32, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeh, A.; Tikotzky, L.; Scher, A. Parenting and infant sleep. Sleep Med. Rev. 2010, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, H.L. Reasons to bed-share: Why parents sleep with their infants. J. Repord. Infant Psychol. 2010, 4, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg-Damberger, M.; Gozal, D.; Marcus, C.L.; Quan, S.F.; Rosen, C.L.; Chervin, R.D.; Merrill, W.; Picchietti, D.L.; Sheldon, S.H.; Iber, C. The visual scoring of sleep and arousal in infants and children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2007, 3, 201–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadeh, A.; Lavie, P.; Scher, A.; Tirosh, E.; Epstein, R. Actigraphic home-monitoring sleep-disturbed and control infants and young children: A new method for pediatric assessment of sleep-wake patterns. Pediatrics 1991, 87, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Acebo, C.; Sadeh, A.; Seifer, R.; Tzischinsky, O.; Wolfson, A.R.; Hafer, A.; Carskadon, M.A. Estimating sleep patterns with activity monitoring in children and adolescents: How many nights are necessary for reliable measures? Sleep 1999, 22, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, L.; Serteyn, A.; Meftah, M.; Schellekens, M.; Vullings, R.; Bergmans, J.W.M.; Osagiator, A.; Bambang Oetomo, S. Unobtrusive ECG monitoring in the NICU using a capacitive sensing array. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.K.; Yoon, H.; Jung, D.W.; Hwang, S.H.; Park, K.S. Ballistocardiogram of baby during sleep. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7167–7170. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, A.; Oberg, P.A.; Sedin, G. Monitoring of heart and respiratory rates in newborn infants using a new photoplethysmographic technique. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 1999, 15, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubb, M.R.; Carpenter, J.; Crowe, J.A.; Teoh, J.; Marlow, N.; Ward, C.; Mann, C.; Sharkey, D.; Hayes-Gill, B.R. Forehead reflectance photoplethysmography to monitor heart rate: Preliminary results from neonatal patients. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchionni, P.; Scalise, L.; Ercoli, I.; Tomasini, E.P. An optical measurement method for the simultaneous assessment of respiration and heart rates in preterm infants. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.K.; Leonhardt, S. Intelligent neonatal monitoring based on a virtual thermal sensor. BMC Med. Imaging 2014, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarts, L.A.M.; Jeanne, V.; Cleary, J.P.; Lieber, C.; Stuart Nelson, J.; Bambang Oetomo, S.; Verkruysse, W. Non-contact heart rate monitoring utilizing camera photoplethysmography in the neonatal intensive care unit–A pilot study. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 89, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werth, J.; Atallah, L.; Andriessen, P.; Long, X.; Zwartkruis-Pelgrim, E.; Aarts, R.M. Unobtrusive sleep state measurements in preterm infants–A review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 35, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, G.; Inoue, Y. Wearable sensor systems for infants. Sensors 2015, 15, 3721–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, K.; Buckley, P.; Adamson, M.; Horne, R.S.C. Actigraphy correctly predicts sleep behavior in infants who are younger than six months, when compared with polysomnography. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Fonseca, P.; Foussier, J.; Haakma, R.; Aarts, R.M. Sleep and wake classification with actigraphy and respiratory effort using dynamic warping. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, L.J.; Montgomery-Downs, H.H.; Insana, S.P.; Walsh, C.M. Use of actigraphy for assessment in pediatric sleep research. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, A.; Aubert, X.; de Haan, G. Body movement analysis during sleep based on video motion estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Lisbon, Portugal, 9–12 October 2013; pp. 539–543. [Google Scholar]
- Tveit, D.M.; Engan, K.; Austvoll, I.; Meinich-Bache, Ø. Motion based detection of respiration rate in infants using video. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 1225–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Marcus, C.L.; Vaughn, B.V. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events–Rules, Terminology and Technical Specification, Version 2.2; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; van der Sanden, E.; Prevoo, Y.; ten Hoor, L.; den Boer, S.; Gelissen, J.; Otte, R.; Zwartkruis-Pelgrim, E. An efficient heuristic method for infant in/out of bed detection using video-derived motion estimates. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechtl, H.F. The behavioural states of the newborn infant (a review). Brain Res. 1974, 76, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, G.; Biezen, P.W.A.C. Sub-pixel motion estimation with 3-D recursive search block-matching. Signal Process. Image Commun. 1994, 6, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, A.; Geng, D.; Znamenskiy, D.; Vink, J.P.; de Haan, G. Robust and sensitive video motion detection for sleep analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilmanne, J.; Urbain, J.; Kothare, M.V.; Wouwer, A.V.; Kothare, S.V. Algorithm for sleep-wake identification using actigraphy: A comparative study and new results. J. Sleep Res. 2009, 18, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Fonseca, P.; Haakma, R.; Aarts, R.M. Actigraphy-based sleep/wake detection for insomniacs. In Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), Eindhoven, The Nethelrands, 9–12 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, P.; den Teuling, N.; Long, X.; Aarts, R.M. Cardiorespiratory sleep stage detection using conditional random fields. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolink, J.; Fonseca, P.; Long, X.; Leonhardt, S. Improving sleep/wake classification with recurrence quantification analysis features. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 49, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoman, E.B.; Whitney, M.P. Sleep states of infants monitored in the home: Individual differences, developmental trends, and origins of diurnal cyclicity. Infant Behav. Dev. 1989, 12, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, B.C.; Taylor, B.J.; Elder, D.E.; Herbison, P. Normal sleep patterns in infants and children: A systematic review of observational studies. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Metrics 1 | Feature Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| mACT | pSLP | mACT + pSLP | |
| True positive (TP) | 304 | 307 | 318 |
| False positive (FP) | 36 | 143 | 35 |
| False negative (FN) | 85 | 82 | 71 |
| True negative (TN) | 954 | 847 | 955 |
| Precision | 82.4% ± 18.3% | 61.0% ± 22.7% | 82.3% ± 16.6% |
| Sensitivity | 71.9% ± 24.4% | 82.8% ± 18.9% | 77.4% ± 22.7% |
| Specificity | 95.9% ± 2.6% | 84.8% ± 6.5% | 95.8% ± 2.6% |
| Accuracy | 91.3% ± 4.7% | 82.0% ± 7.9% | 92.0% ± 4.6% |
| Cohen’s kappa | 0.701 ± 0.227 | 0.544 ± 0.187 | 0.733 ± 0.204 |
| Infant | Epoch Number | % Wake Epochs | Accuracy | Cohen’s kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 216 | 17.6% | 91.7% | 0.664 |
| 02 | 120 | 46.7% | 90.8% | 0.816 |
| 03 | 118 | 10.2% | 93.2% | 0.629 |
| 04 | 237 | 30.8% | 93.3% | 0.837 |
| 05 | 163 | 58.3% | 91.4% | 0.826 |
| 06 | 93 | 21.5% | 97.9% | 0.939 |
| 07 | 123 | 5.7% | 98.4% | 0.866 |
| 08 | 131 | 38.2% | 91.6% | 0.817 |
| 09 | 106 | 24.5% | 89.6% | 0.716 |
| 10 | 72 | 16.7% | 81.9% | 0.220 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, X.; Otte, R.; Sanden, E.v.d.; Werth, J.; Tan, T. Video-Based Actigraphy for Monitoring Wake and Sleep in Healthy Infants: A Laboratory Study. Sensors 2019, 19, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051075
Long X, Otte R, Sanden Evd, Werth J, Tan T. Video-Based Actigraphy for Monitoring Wake and Sleep in Healthy Infants: A Laboratory Study. Sensors. 2019; 19(5):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051075
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Xi, Renée Otte, Eric van der Sanden, Jan Werth, and Tao Tan. 2019. "Video-Based Actigraphy for Monitoring Wake and Sleep in Healthy Infants: A Laboratory Study" Sensors 19, no. 5: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051075
APA StyleLong, X., Otte, R., Sanden, E. v. d., Werth, J., & Tan, T. (2019). Video-Based Actigraphy for Monitoring Wake and Sleep in Healthy Infants: A Laboratory Study. Sensors, 19(5), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051075






