Secrecy Performance of TAS/SC-Based Multi-Hop Harvest-to-Transmit Cognitive WSNs Under Joint Constraint of Interference and Hardware Imperfection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a simple multi-hop MIMO relaying protocol using the TAS/SC technique for PB-UCR WSNs. The proposed protocol can obtain energy efficiency and spectrum usage efficiency, enhance the reliability of data transmission, and improve the secrecy performance.
- In almost published works related to EH and UCR (see [23,24,25]), the transmitters adjust their transmit power following the instantaneous channel state information. As a result, the transmit power is a random variable (RV), which is not feasible. In this paper, the secondary source and relay nodes are assumed to transmit the source data at fixed transmit power levels. In addition, we derive an exact closed-form expression of the average transmit power of the secondary transmitters under the joint impacts of the energy harvested, the interference constraint, and the maximum transmit power level.
- We investigate the impact of hardware impairments on the end-to-end SOP and PNSC of the proposed scheme. Indeed, the obtained results presented that the hardware imperfection has a significant impact on the secrecy performance. Moreover, the analytical results showed that different values of the hardware impairment levels of the data and eavesdropping links lead to different secrecy performance trend. Finally, it is worth noting that the proposed scheme is a generalized case of the existing schemes in which the transceiver hardware is assumed to be perfect [11,41,42,43].
- We derive new exact and asymptotic expressions of the end-to-end SOP and PNSC over Rayleigh fading channels, which are then verified by Monte Carlo simulations.
2. System Model
3. Performance Analysis
3.1. Average Transmit Power of the Secondary Transmitters
3.2. Secrecy Outage Probability (SOP)
3.3. Probability of Non-Zero Secrecy Capacity (PNSC)
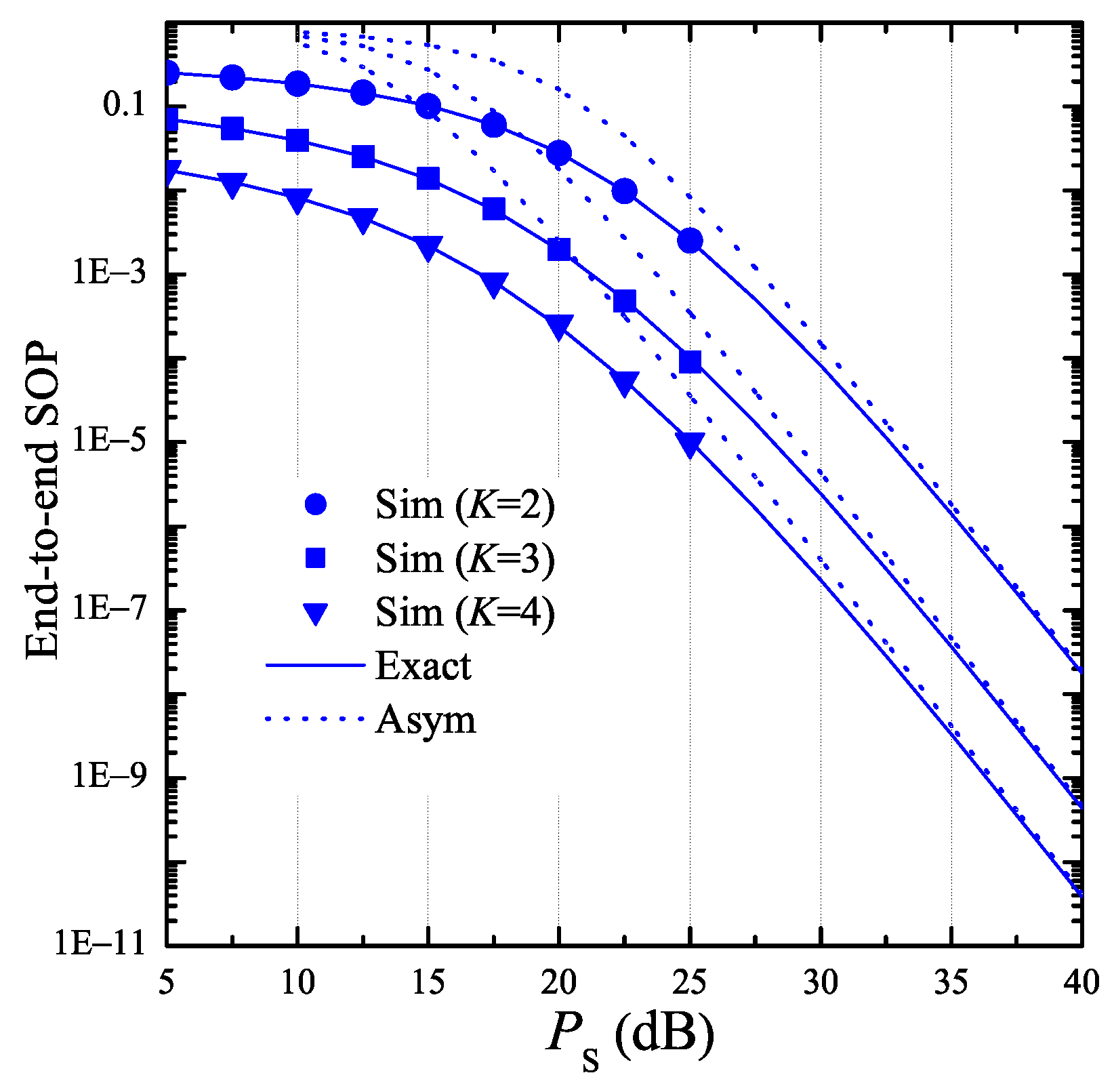
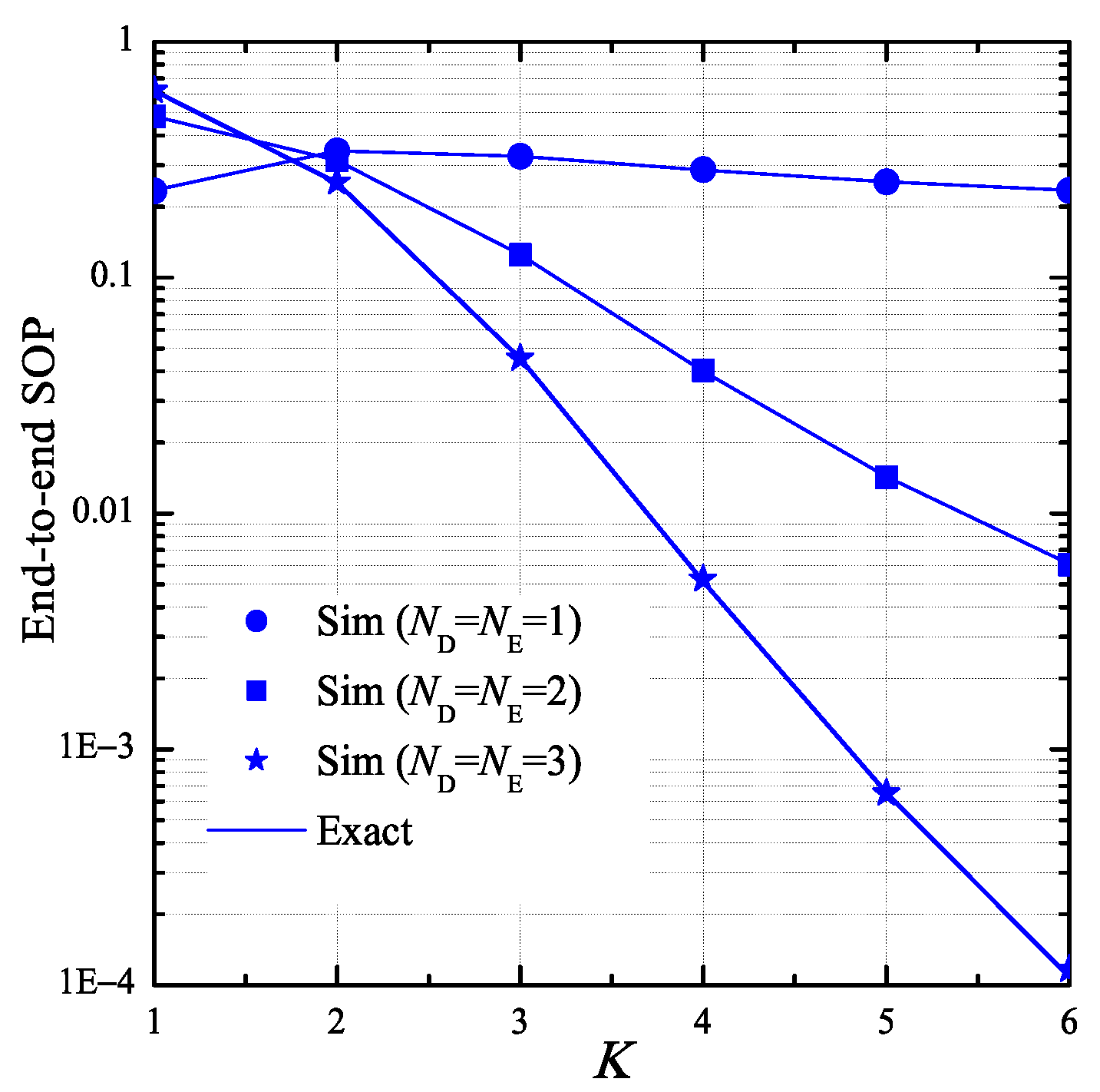
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
- The hardware impairments have a significant impact on the secrecy performance. Particularly, when the transceiver hardware of the authorized nodes is better than that of the eavesdropper, the proposed protocol obtains high secrecy performance. Otherwise, the SOP and PNSC performance is significantly degraded.
- The secrecy performance of the proposed protocol can be enhanced with higher number of antennas equipped at the authorized nodes.
- By optimally designing the number of hops and the fraction of time spent for the energy harvesting phase, the secrecy performance of the proposed protocol can be significantly improved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledwaba, L.P.I.; Hancke, G.P.; Venter, H.S.; Isaac, S.J. Performance Costs of Software Cryptography in Securing New-Generation Internet of Energy Endpoint Devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9303–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Grossschadl, J. Securing Edge Devices in the Post-Quantum Internet of Things Using Lattice-Based Cryptography. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyner, A.D. The Wire-tap Channel. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1975, 54, 1355–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszar, I.; Korner, J. Broadcast Channels With Confidential Messages. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1978, 24, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopala, P.K.; Lai, L.; Gamal, H.E. On the secrecy capacity of fading channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 4687–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jing, T.; Ma, L.; Huo, Y.; Qian, J. Worst-Case Cooperative Jamming for Secure Communications in CIoT Networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Cai, Y.; Yang, W.; Yang, W.; Chen, D.; Hu, J. Secure Transmission of Cooperative Zero-Forcing Jamming for Two-User SWIPT Sensor Networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Y.; Yang, N.; Guo, D.; Gao, B. Secure Multiuser Communications in Wireless Sensor Networks with TAS and Cooperative Jamming. Sensors 2016, 16, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Yeoh, P.L.; Elkashlan, M.; Schober, R.; Collings, I.B. Transmit Antenna Selection for Security Enhancement in MIMO Wiretap Channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Tang, Y.; Ma, D.; Xiao, P.; Wong, K.-K. Secrecy Performance Analysis for TAS-MRC System with Imperfect Feedback. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikidis, I. Opportunistic Relay Selection For Cooperative Networks with Secrecy Constraints. IET Commun. 2010, 4, 1787–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tran, T.D.; Elkashlan, M.; Duong, T.Q. Relay Selection for Security Enhancement in Cognitive Relay Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2015, 4, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duy, T.T.; Duong, T.Q.; Thanh, T.L.; Bao, V.N.Q. Secrecy Performance Analysis with Relay Selection Methods under Impact of Co-channel Interference. IET Commun. 2015, 9, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Zhang, Z. Secure Full-Duplex Two-Way Relaying Networks With Optimal Relay Selection. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhestani, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Mohammadi, M. Joint Relay Selection and Power Allocation in Large-Scale MIMO Systems With Untrusted Relays and Passive Eavesdroppers. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Tao, M.; Liu, Y. Relay Placement for Physical Layer Security: A Secure Connection Perspective. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 878–881. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Wen, H.; Wu, B.; Pan, F.; Liao, R.-F.; Song, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. Cooperative Jamming for Physical Layer Security Enhancement in Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, P. Robust MISO Beamforming with Cooperative Jamming for Secure Transmission From Perspectives of QoS and Secrecy Rate. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, J.; Wu, Q.; Cui, M.; Li, X.; Lin, F. Wireless Powered Cooperative Jamming for Secure OFDM System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Ho, C.-K. Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 4754–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.A.; Zhou, X.; Durrani, S.; Kennedy, R.A. Relaying protocols for wireless energy harvesting and information processing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 3622–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapattu, S.; Evans, J. Optimal Energy Harvesting Protocols for Wireless Relay Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 5789–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zheng, M.; Liang, W.; Yu, H.; Liang, Y.-C. Outage Performance of Underlay Multihop Cognitive Relay Networks with Energy Harvesting. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zheng, M.; Liang, W.; Yu, H.; Liang, Y.-C. End-to-end Throughput Maximization for Underlay Multi-hop Cognitive Radio Networks with RF Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, T.D.; Duy, T.T.; Dung, L.T.; Choi, S.G. Performance Evaluation of Relay Selection Schemes in Beacon-Assisted Dual-hop Cognitive Radio Wireless Sensor Networks under Impact of Hardware Noises. Sensors 2018, 18, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Liang, T.; Li, B. Secrecy Performance Analysis of Cognitive Sensor Radio Networks with an EH-Based Eavesdropper. Sensors 2017, 17, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieu, T.D.; Duy, T.T.; Kim, B.-S. Performance Enhancement for Multi-hop Harvest-to-Transmit WSNs with Path-Selection Methods in Presence of Eavesdroppers and Hardware Noises. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 5173–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Gomaa, A.; Al-Dhahir, N. OFDM AF relaying under I/Q imbalance: Performance analysis and baseband compensation. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Matthaiou, M.; Debbah, M. A new look at dual-hop relaying: Performance limits with hardware impairments. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 4512–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, S.; Upadhyay, P.K.; da Costa, D.B.; Bithas, P.S.; Kanatas, A.G.; Dias, U.S. Joint Impact of RF Hardware Impairments and Channel Estimation Errors in Spectrum Sharing Multiple-Relay Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 3809–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulogeorgos, A.A.; Karas, D.S.; Karagiannidis, G.K. How much does I/Q Imbalance affect secrecy capacity? IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ng, D.W.K.; Wang, N.; Schober, R.; Bhargava, V.K. Analysis and Design of Secure Massive MIMO Systems in the Presence of Hardware Impairments. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 2001–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-H. Full-Duplex Relay for Enhancing Physical Layer Security in Multi-Hop Relaying Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Sohn, I.; Kim, Y.-H. Transmit Power Allocation for Physical Layer Security in Cooperative Multi-Hop Full-Duplex Relay Networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. Secrecy Rate Optimization in Wireless Multi-Hop Full Duplex Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 5695–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, E.R.; Hamdi, K.A. Secure Relaying in Multihop Communication Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 1120–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, P.T.; Hung, D.T.; Duy, T.T.; Voznak, M. Analysis of Probability of Non-zero Secrecy Capacity for Multi-hop Networks in Presence of Hardware Impairments over Nakagami-m Fading Channels. Radio Eng. 2016, 25, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Liu, Y. Secrecy Rate Maximization with Outage Constraint in Multihop Relaying Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Huang, K.; Zhong, Z.; Kang, X.; Zhong, Z. Physical layer security of multi-hop aided downlink MIMO heterogeneous cellular networks. Chin. Commun. 2016, 13, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H. Confidential Multicasting Assisted by Multi-Hop Multi-Antenna DF Relays in the Presence of Multiple Eavesdroppers. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 4295–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Han, Z.; Petropulu, A.P.; Poor, H.V. Improving wireless physical layer security via cooperating relays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, V.N.Q.; Trung, N.L.; Debbah, M. Relay selection scheme for dual-hop networks under security constraints with multiple eavesdroppers. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 6076–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.N.; Tran, D.-D.; Chakchai, S.-I.; Tran, H. Secrecy Performance Analysis for Fixed-Gain Energy Harvesting in an Internet of Things with Untrusted Relays. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48247–48258. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J. Secrecy Performance of Wireless Powered Communication Networks with Multiple Eavesdroppers and Outdated CSI. IEEE Access. 2018, 6, 33774–33788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Choi, H.-H. Secure Analog Network Coding with Wireless Energy Harvesting under Multiple Eavesdroppers. IEEE Access. 2018, 6, 76289–76301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneman, J.N.; Tse, D.N.; Wornell, G.W. Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2004, 50, 3062–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaiou, M.; Papadogiannis, A. Two-way relaying under the presence of relay transceiver hardware impairments. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2013, 17, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, T.T.; Duong, Q.T.; da Costa, D.B.; Bao, V.N.Q.; Elkashlan, M. Proactive Relay Selection with Joint Impact of Hardware Impairment and Co-channel Interference. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Upadhyay, P.K. Cognitive relaying with transceiver hardware impairments under interference constraints. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tin, P.T.; Minh Nam, P.; Trung Duy, T.; Tran, P.T.; Voznak, M. Secrecy Performance of TAS/SC-Based Multi-Hop Harvest-to-Transmit Cognitive WSNs Under Joint Constraint of Interference and Hardware Imperfection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051160
Tin PT, Minh Nam P, Trung Duy T, Tran PT, Voznak M. Secrecy Performance of TAS/SC-Based Multi-Hop Harvest-to-Transmit Cognitive WSNs Under Joint Constraint of Interference and Hardware Imperfection. Sensors. 2019; 19(5):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051160
Chicago/Turabian StyleTin, Phu Tran, Pham Minh Nam, Tran Trung Duy, Phuong T. Tran, and Miroslav Voznak. 2019. "Secrecy Performance of TAS/SC-Based Multi-Hop Harvest-to-Transmit Cognitive WSNs Under Joint Constraint of Interference and Hardware Imperfection" Sensors 19, no. 5: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051160
APA StyleTin, P. T., Minh Nam, P., Trung Duy, T., Tran, P. T., & Voznak, M. (2019). Secrecy Performance of TAS/SC-Based Multi-Hop Harvest-to-Transmit Cognitive WSNs Under Joint Constraint of Interference and Hardware Imperfection. Sensors, 19(5), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051160





