An Instant Donning Multi-Channel EEG Headset (with Comb-Shaped Dry Electrodes) and BCI Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
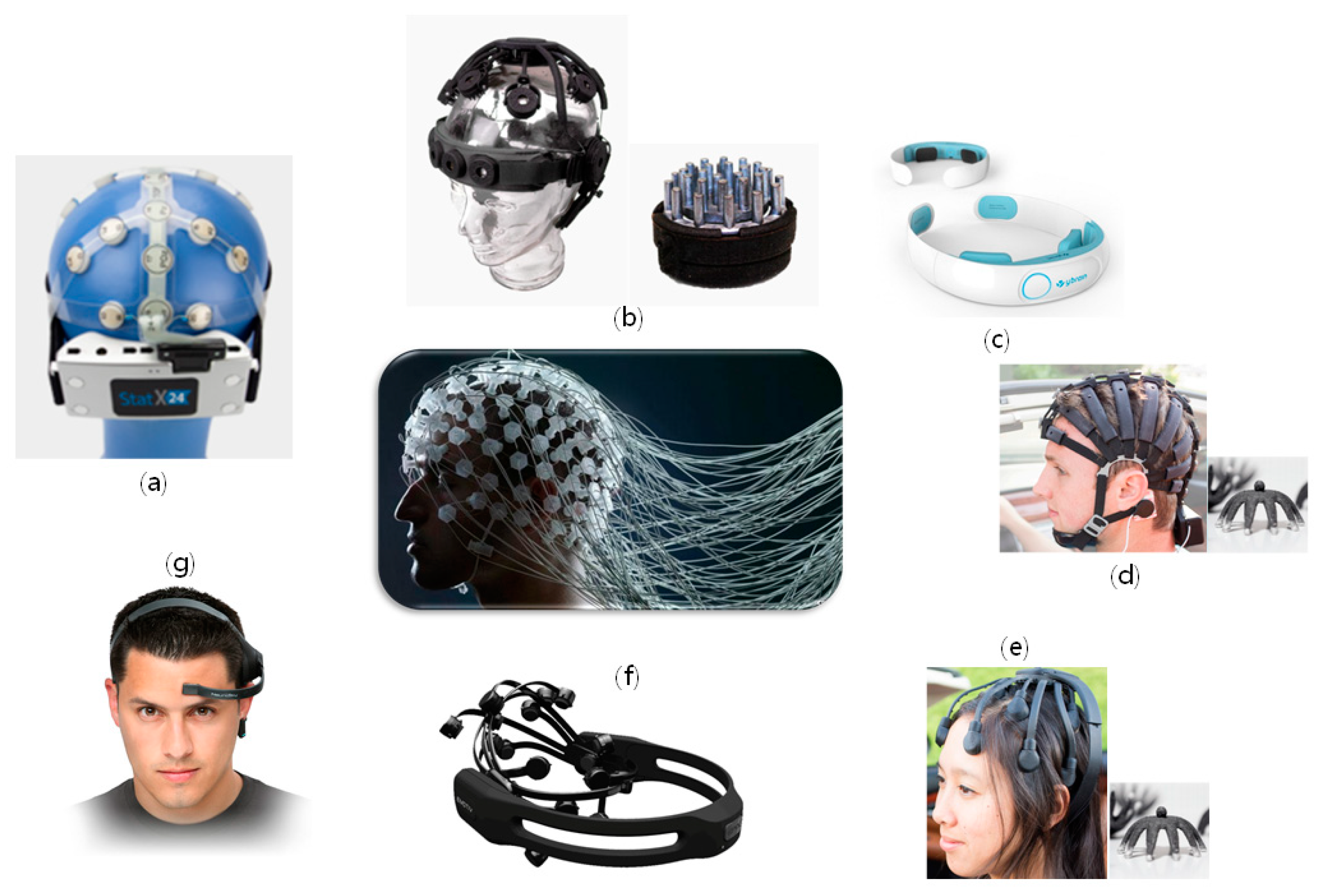
2. Materials and Methods
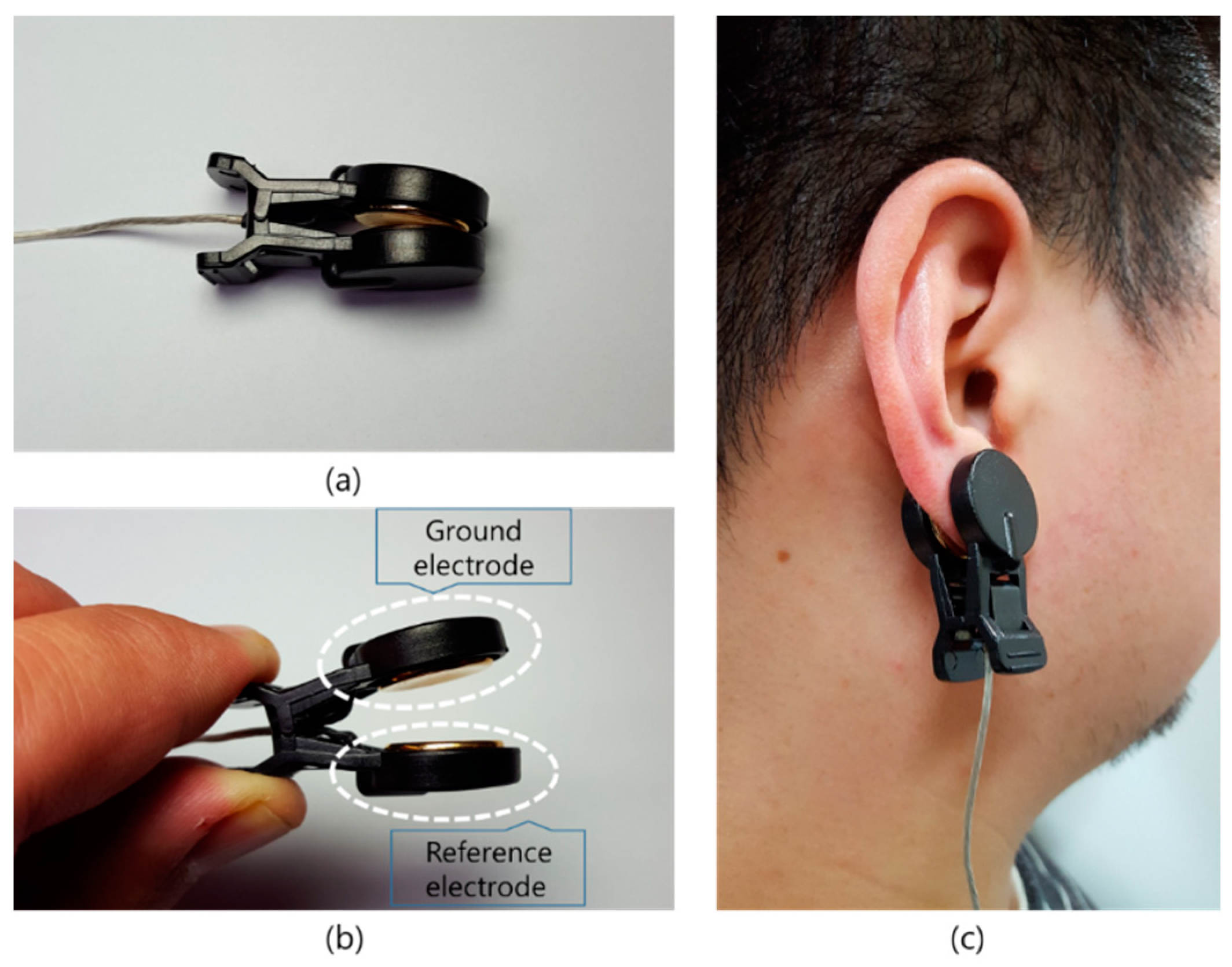
2.1. Electrodes
2.2. Headsets
3. Experiment
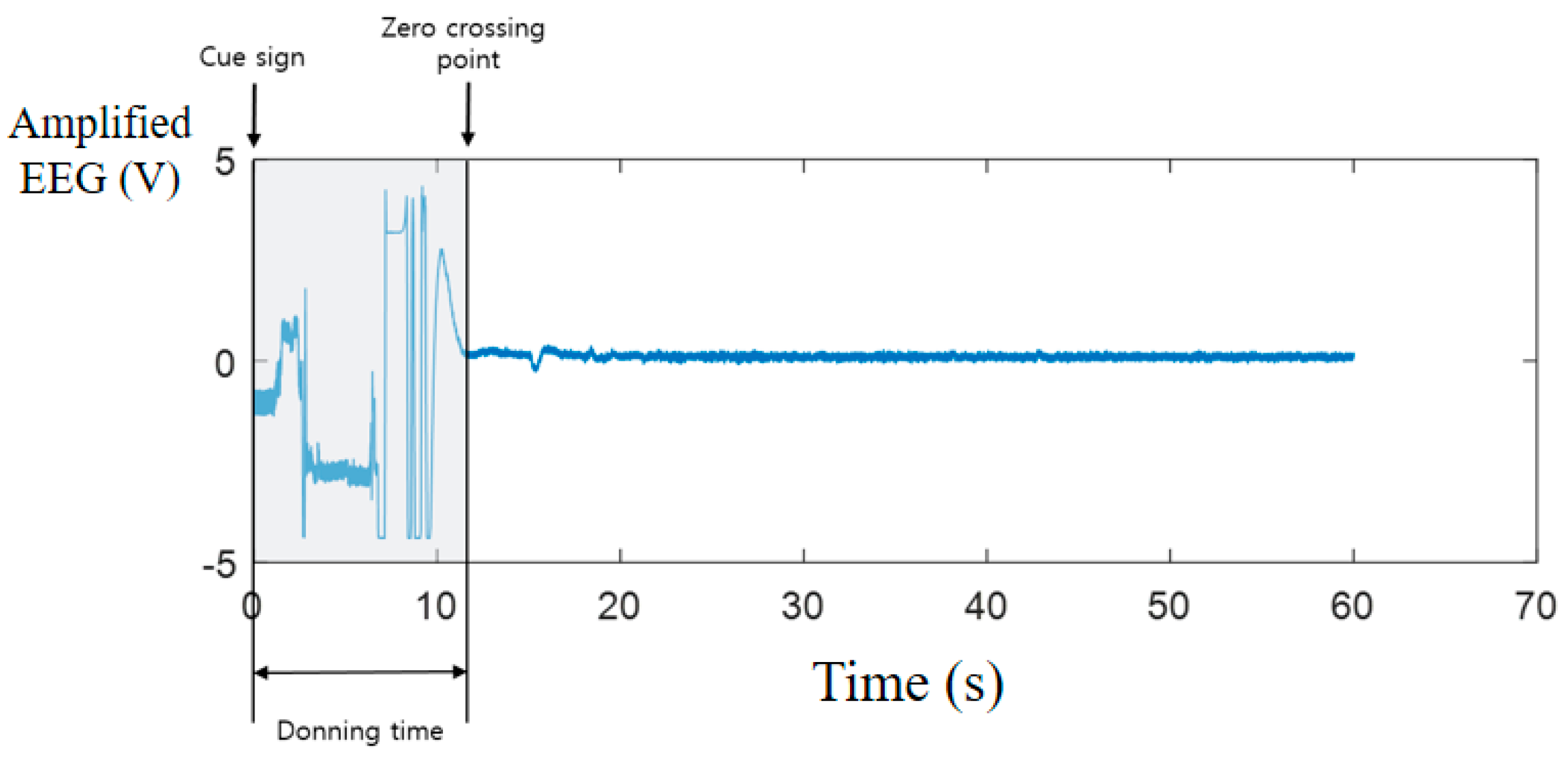
3.1. Instant Donning Experiment
3.2. Alpha-Rhythm-Based BCI Experiment
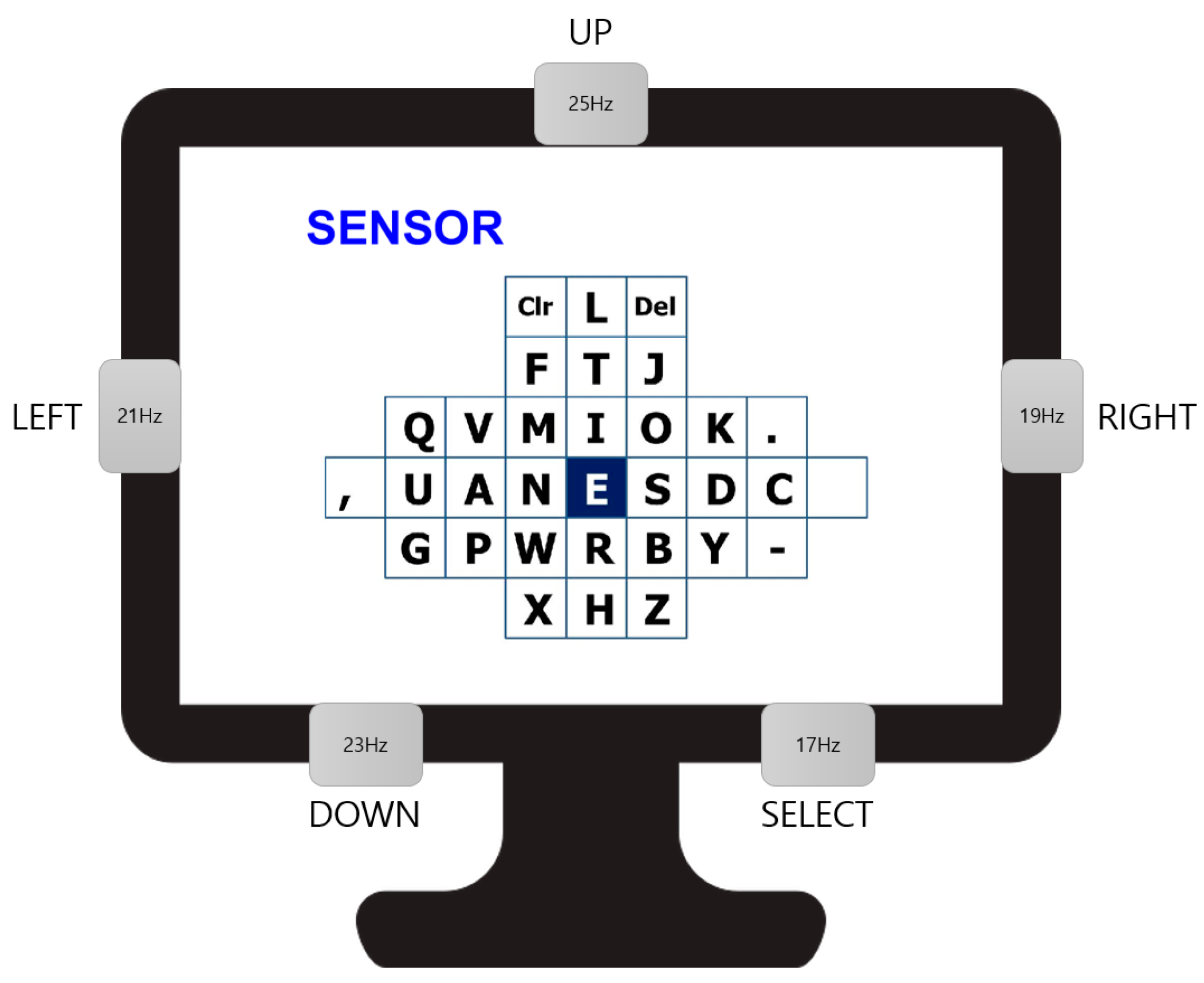
3.3. SSVEP-Based BCI Speller
3.4. ASSR-Based BCI Paradigm
4. Results
4.1. Instant Donning Experiment
4.2. Alpha-Rhythm-Based BCI Experiment
4.3. SSVEP-Based BCI Speller
4.4. ASSR-Based BCI Paradigm
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, B.C.; Ruiz-Blondet, M.V.; Khalifian, N.; Kurtz, K.J.; Jin, Z.; Laszlo, S. Brainprint: Assessing the uniqueness, collectability, and permanence of a novel method for ERP biometrics. Neurocomputing 2015, 166, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachinger, C.; Golland, P.; Kremen, W.; Fischl, B.; Reuter, M. BrainPrint: A discriminative characterization of brain morphology. NeuroImage 2015, 109, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Kim, S.K.; Yoon, H.N.; Lee, W.K.; Park, C.S.; Kim, K.K.; Park, K.S. Contrast between spectral and connectivity features for electroencephalography based authentication. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Toronto, ON, Canada, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, E.; Nazeran, H.; Nava, P.; Behbehani, K.; Burk, J.; Lucas, E. EEG feature extraction for classification of sleep stages. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004; pp. 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; McFarland, D.J. Multichannel EEG-based brain-computer communication. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 90, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghöfer, M.; Elbert, T.; Leiderer, P.; Berg, P.; Rockstroh, B. Mapping EEG-potentials on the surface of the brain: A strategy for uncovering cortical sources. Brain Topography 1997, 9, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grummett, T.; Leibbrandt, R.; Lewis, T.; DeLosAngeles, D.; Powers, D.; Willoughby, J.; Pope, K.; Fitzgibbon, S. Measurement of neural signals from inexpensive, wireless and dry EEG systems. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Companies—BNCI Horizon 2020 (List of Companies of Involved in the BCI Field). Available online: http://bnci-horizon-2020.eu/index.php/community/companies (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Lee, J.S.; Han, C.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.S. Reverse-curve-arch-shaped dry EEG electrode for increased skin-electrode contact area on hairy scalps. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 1643–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornhege, G.; Millan, J.D.; Hinterberger, T.; McFarland, D.J.; Müller, K.R. Toward Brain-Computer Interfacing; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leuthardt, E.C.; Schalk, G.; Wolpaw, J.R.; Ojemann, J.G.; Moran, D.W. A brain-computer interface using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 2004, 1, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donchin, E.; Spencer, K.M.; Wijesinghe, R. The mental prosthesis: Assessing the speed of a P300-based brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Lee, J.-C.; Park, Y.-M.; Kim, I.-Y.; Im, C.-H. Auditory brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and their practical applications. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2012, 2, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijboer, F.; Sellers, E.; Mellinger, J.; Jordan, M.; Matuz, T.; Furdea, A.; Halder, S.; Mochty, U.; Krusienski, D.J.; Vaughan, T.M. A P300-based brain-computer interface for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farwell, L.A.; Donchin, E. Talking off the top of your head: Toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1988, 70, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusienski, D.J.; Sellers, E.W.; Cabestaing, F.; Bayoudh, S.; McFarland, D.J.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. A comparison of classification techniques for the P300 Speller. J. Neural Eng. 2006, 3, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Townsend, G.; LaPallo, B.K.; Boulay, C.B.; Krusienski, D.J.; Frye, G.E.; Hauser, C.K.; Schwartz, N.E.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R.; Sellers, E.W. A novel P300-based brain-computer interface stimulus presentation paradigm: Moving beyond rows and columns. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, E.W.; Krusienski, D.J.; McFarland, D.J.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. A P300 event-related potential brain-computer interface (BCI): The effects of matrix size and inter stimulus interval on performance. Biol. Psychol. 2006, 73, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel-Rezai, R.; Ahmad, W. P300-based Brain-Computer Interface Paradigm Design. In Recent Advances in Brain-Computer Interface Systems; Fazel, R., Ed.; INTECH Open Access Publisher, IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2011; pp. 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fazel-Rezai, R.; Abhari, K. A region-based P300 speller for brain-computer interface. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2009, 34, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusienski, D.J.; Sellers, E.W.; McFarland, D.J.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. Toward enhanced P300 speller performance. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 167, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.J.; Lim, J.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.W.; Im, C.H. Development of an SSVEP-based BCI spelling system adopting a QWERTY-style LED keyboard. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 208, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Gao, X.; Hong, B.; Gao, S. Frequency and phase mixed coding in SSVEP-based brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Gao, X. Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2610–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punsawad, Y.; Wongsawat, Y. Multi-command SSVEP-based BCI system via single flickering frequency half-field stimulation pattern. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 1101–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.-L.; Sie, J.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Shu, C.-H.; Li, P.H.; Sun, C.W.; Shyu, K.K. An SSVEP-actuated brain computer interface using phase-tagged flickering sequences: A cursor system. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.-L.; Yeh, C.-L.; Cheng, J.-S.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lan, G.-Y. An SSVEP-based BCI using high duty-cycle visual flicker. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 3350–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volosyak, I. SSVEP-based Bremen-BCI interface—Boosting information transfer rates. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 036020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Sullivan, T.J. A user-friendly SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a time-domain classifier. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7, 026010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, R.C.; Puthusserypady, S.; Sun, Y. An asynchronous P300 BCI with SSVEP-based control state detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, H.; Wan, B.; Yin, T.; Liu, Z.; Ming, D. A hybrid BCI speller paradigm combining P300 potential and the SSVEP blocking feature. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, E.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Hu, D. A novel hybrid BCI speller based on the incorporation of SSVEP into the P300 paradigm. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 026012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Heo, J.; Lim, Y.G.; Park, K.S. Brain-computer interfaces using capacitive measurement of visual or auditory steady-state responses. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, G.; Gao, X.; Yan, Z.; Hong, B.; Gao, S. An online multi-channel SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a canonical correlation analysis method. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, B.; Luth, T.; Valbuena, D.; Teymourian, A.; Volosyak, I.; Graser, A. BCI demographics: How many (and what kinds of) people can use an SSVEP BCI? IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Cho, J.-H.; Hwang, H.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Im, C.-H. A vision-free brain-computer interface (BCI) paradigm based on auditory selective attention. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W.; Hwang, H.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Jung, K.-Y.; Im, C.-H. Classification of selective attention to auditory stimuli: Toward vision-free brain-computer interfacing. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 197, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Cao, T.; Wan, F.; Mak, P.U.; Mak, P.-I.; Vai, M.I. Implementation of SSVEP based BCI with Emotiv EPOC. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Virtual Environments Human-Computer Interfaces and Measurement Systems (VECIMS), Tianjin, China, 2–4 July 2012; pp. 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Halford, J.; Schalkoff, R.; Satterfield Martz, G.; Kutluay, E.; Waters, C.; Dean, B. Comparison of a novel dry electrode headset to standard routine EEG in veterans. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.-S.; Pan, J.-S.; Chu, T.-Y.; Lin, B.-S. Development of a wearable motor-imagery-based brain-computer interface. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Trial | Donning Time (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | Subject 2 | Subject 3 | Subject 4 | |
| 1 | 10.11 | 6.74 | 11.82 | 12.85 |
| 2 | 11.70 | 7.80 | 7.97 | 14.68 |
| 3 | 14.19 | 7.50 | 8.01 | 13.46 |
| 4 | 12.66 | 7.00 | 6.88 | 11.42 |
| 5 | 12.90 | 5.66 | 6.83 | 15.22 |
| 6 | 14.95 | 5.37 | 10.41 | 10.95 |
| 7 | 13.18 | 5.75 | 7.23 | 10.43 |
| 8 | 13.98 | 5.99 | 7.96 | 11.53 |
| 9 | 11.98 | 4.77 | 9.93 | 9.75 |
| 10 | 15.98 | 5.16 | 9.21 | 12.83 |
| Mean | 13.16 | 6.17 | 8.63 | 12.31 |
| STD | 1.70 | 1.03 | 1.66 | 1.80 |
| Subject | Task | Classification Results | Correct/Total | Spec | Sens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NPNPNPNPNP | NPNPNPNPNP | 10/10 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | NNNPPNNPNP | NNNPPNNPNP | 10/10 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | NNPNNPNPPN | NNPNNPNPPN | 10/10 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | NNNPPPNNPN | NNNPPPNNPN | 10/10 | 1 | 1 |
| Subject | Word | Input Results (Dhading: Wrong Result) | ACC (%) | ITR (bit/min) | LPM (letters/min) | EFF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | BRAIN | → ↓ B ↓ R ← ← A ↑ I ← N | 100 | 23.22 | 4.17 | 100 |
| SNU | → S ← ← → N ← ← ← ← → U | 83.33 | 13.38 | 2.50 | 66.67 | |
| BCI | → ↓ B → → → C ↑ I | 100 | 23.22 | 3.33 | 100 | |
| ALS | ← ← A ↑ ↑ ↑ L → S | 100 | 23.22 | 3.33 | 100 | |
| NEW | ← N E ← ↓ W | 100 | 23.22 | 5.00 | 100 | |
| SENSOR | → S E ← N → S ↑ → O ↓ R | 100 | 23.22 | 5.00 | 100 | |
| S2 | BRAIN | → ↓ B ↓ R ← ← ← → A ↑ I ← N | 92.86 | 18.08 | 3.57 | 85.71 |
| SNU | → S ← N ← ← ← U | 100 | 23.22 | 3.75 | 100 | |
| BCI | → ↓ B → → → C ↑ I | 100 | 23.22 | 3.33 | 100 | |
| ALS | ← ← A ← ↑ ↑ → ↑ L → S | 90.91 | 17.01 | 2.73 | 81.82 | |
| NEW | ← N E ← ↓ W | 100 | 23.22 | 5.00 | 100 | |
| SENSOR | → S E ← N → S ↑ → O ↓ R | 100 | 23.22 | 5.00 | 100 | |
| S3 | BRAIN | → ↓ B ↓ R ← ← A → ↑ ← I ← N | 92.86 | 18.08 | 3.57 | 85.71 |
| SNU | → S ← N ← ← ← U | 100 | 23.22 | 3.75 | 100 | |
| BCI | → ↓ B → ← → → ← → → C ↑ I | 84.62 | 13.95 | 2.31 | 69.23 | |
| ALS | → ← ← ← A ↑ ↑ ↑ L → S | 90.91 | 17.01 | 2.73 | 81.82 | |
| NEW | ← N E ← ↓ W | 100 | 23.22 | 5.00 | 100 | |
| SENSOR | → S E ← N → S ↑ → → ← O ↓ R | 92.86 | 18.08 | 4.29 | 85.71 | |
| S4 | BRAIN | → ↓ B ↓ R ← ← ← → A ↑ I ← N | 92.86 | 18.08 | 3.57 | 85.71 |
| SNU | → S ← N ← ← ← U | 100 | 23.22 | 3.75 | 100 | |
| BCI | → ↓ B → → → C ↑ ↑ ↓ I | 90.91 | 17.01 | 2.73 | 81.82 | |
| ALS | ← ← A ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ L → S | 90.91 | 17.01 | 2.73 | 81.82 | |
| NEW | ← N E ← ↓ W | 100 | 23.22 | 5.00 | 100 | |
| SENSOR | → → ← S → ← E ← N → S ↑ → O ↓ R | 93.75 | 18.60 | 3.75 | 75.00 | |
| Mean | 95.70 | 20.34 | 3.75 | 90.88 | ||
| STD | 5.01 | 3.39 | 0.89 | 11.08 |
| Subject | Task | Classification Results | Correct/Total | Spec | Sens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | RLRLRRRLRL | RRRRLRRRRRRRR | 7/10 | 0.4 | 1 |
| S2 | LRLRLRRLLR | LLLRLLRLLL | 7/10 | 1 | 0.4 |
| S3 | RLLLRRLRLR | RLRLRRLRLR | 9/10 | 0.8 | 1 |
| S4 | RLLRLRLLRR | RLLLLRLLLL | 7/10 | 1 | 0.4 |
| S5 | RRRLLRLLRL | RRRLRRLRRL | 8/10 | 0.6 | 1 |
| Mean | 7.6/10 | 0.76 | 0.76 | ||
| STD | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.33 |
| Electrode Type | Preparation Time | Number of EEG Channels | Time Window | Number of Subjects | Accuracy | BCI Paradigm | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold disk | Several minutes | 4 | 2–20 s | 6 | 84.3% | ASSR | Kim et al. (2011) [38] |
| Capacitive coupling | Several minutes | 4 | 14 s | 5 | 72.0% | ASSR | Baek et al. (2013) [34] |
| Wet felt pad | Several minutes | 14 | 6 s | 4 | 83.0% | SSVEP | Liu et al. (2012) [39] |
| Spike dry | 5.7 min | 21 | † | 21 | † | † | Halford et al. (2016) [40] |
| Spike dry | <2 min | 3 | 4 s | 10 | 81.3% | Motor imagery | Lin et al. (2016) [41] |
| Reverse-curve-arch shaped | ~10 s | 8 | 20 s | 5 | 76.0% | ASSR | This study |
| Reverse-curve-arch shaped | ~10 s | 8 | 6 s | 4 | 95.7% | SSVEP | This study |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Han, C.; Park, K. An Instant Donning Multi-Channel EEG Headset (with Comb-Shaped Dry Electrodes) and BCI Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071537
Kim J, Lee J, Han C, Park K. An Instant Donning Multi-Channel EEG Headset (with Comb-Shaped Dry Electrodes) and BCI Applications. Sensors. 2019; 19(7):1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071537
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeehoon, Jeongsu Lee, Chungmin Han, and Kwangsuk Park. 2019. "An Instant Donning Multi-Channel EEG Headset (with Comb-Shaped Dry Electrodes) and BCI Applications" Sensors 19, no. 7: 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071537
APA StyleKim, J., Lee, J., Han, C., & Park, K. (2019). An Instant Donning Multi-Channel EEG Headset (with Comb-Shaped Dry Electrodes) and BCI Applications. Sensors, 19(7), 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071537





