Non-Enzymatic Impedimetric Sensor Based on 3-Aminophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Glucose Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation and Apparatus
2.3. Functionalization and Characterization of the SPCE
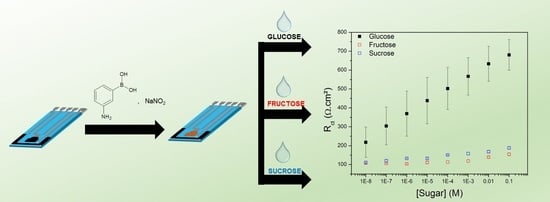
2.4. Selective Detection of Glucose by EIS
2.5. Evaluation of Sensor Stability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Functionalized SPCE
3.2. Detection of Glucose in Aqueous Solution by EIS
3.3. Repeatability and Reproducibility Analysis
3.4. Response Time
3.5. Investigation of the Effect of Dopamine, NaCl and Serum on the Performance of the Glucose Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Su, X. WS2 quantum dots as a sensitive fluorescence probe for the detection of glucose. J. Lumin. 2018, 207, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, Global Report on Diabetes. WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data, ISBN 978 92 4 156525 7 (2016) Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204871 (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Silva, L.M.C.; Santos, V.P.S.; Salgado, A.M.; Pereira, K.S. Biosensors for contaminants monitoring in food and environment for human and environmental health. In State of the Art in Biosensors—General Aspects; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Feng, T.; Dong, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Xie, M. Development of dual-emission ratiometric probe-based on fluorescent silica nanoparticle and CdTe quantum dots for determination of glucose in beverages and human body fluids. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor-Gutiérrez, O.; Rama, E.C.; Costa-García, A.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Paper-based maskless enzymatic sensor for glucose determination combining ink and wire electrodes. Bios. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehezkeli, O.; Tel-Vered, R.; Raichlin, S.; Willner, I. Nano-engineered Flavin-Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase/Gold Nanoparticle-Modified Electrodes for Glucose Sensing and Biofuel Cell Applications. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.; Babaei, Z. Fabrication and characterization of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on ternary NiO/CuO/polyaniline nanocomposite. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 498, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.-L.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, D.-P.; Tang, D. Eggshell membrane-templated synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous Au networks for electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Bios. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, W.V.; Mobashsher, A.T.; Abbosh, A. The progress of glucose monitoring – a review of invasive to minimally and non-invasive techniques, devices and sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hong, Y.J.; Baik, S.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Enzyme-based glucose sensor: from invasive to wearable device. Adv. Healthc. Mat. 2018, 7, 1701150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisdat, F.; Schäfer, D. The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.A.D.; Heneine, L.G.D.; Matencio, T.; Messaddeq, Y. Faradaic and non-faradaic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as transduction techniques for sensing applications. Int. J. Bios. Bioelectron. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randviir, E.P.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: an overview of bioanalytical applications. Anal. Met. 2013, 5, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randviir, E.P.; Metters, J.P.; Stainton, J.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy versus cyclic voltammetry for the electroanalytical sensing of capsaicin utilising screen printed carbon nanotube electrodes. Analyst. 2013, 138, 2970–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark Jr, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, S.K.; Girigoswami, K. Diagnostic biosensors in medicine – a review. Biocatal. Agricult. Biotech. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.-W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, V.; Hashim, U. Advances in biosensors: principle, architecture and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Asgher, M.; Cheng, H.; Yan, Y.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Multi-point enzyme immobilization, surface chemistry, and novel platforms: a paradigm shift in biocatalyst design. Critic. Rev. Biotech. 2018, 39, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Guo, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. State-of-the-art protein engineering approaches using biological macromolecules: a review from immobilization to implementation view point. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, M.; Ebrahim, S.; Soliman, M. Graphene quantum dots prepared from glucose as optical sensor for glucose. J. Lumin. 2017, 184, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatada, M.; Loew, N.; Inose-Takahashi, Y.; Okuda-Shimazaki, J.; Tsugawa, W.; Mulchandani, A.; Sode, K. Development of a glucose sensor employing quick and easy modification method with meadiator for altering eléctron aceptor preference. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 121, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-M.; Moon, J.-M.; Lee, W.-C.; Yoon, J.-H.; Choi, C.S.; Shim, Y.-B. A potentiometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor using a molecularly imprinted layer bonded on a conducting polymer. Bios. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.A.D.; Messaddeq, Y.; Heneine, L.G.D.; Matencio, T. Application of screen-printed carbon electrodes as an electrochemical transducer in biosensors. Int. J. Bios. Bioelectron. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, F.E.; Foster, C.W.; Bonacin, J.A.; Banks, C.E. Exploring the electrical wiring of screen-printed configurations utilised in electroanalysis. Anal. Met. 2015, 7, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.M.; Pemberton, P.; Hart, N.J.P. Fabrication of miniaturized screen-printed glucose biosensors, using a water-based ink, and the evaluation of their electrochemical behaviour. Electroanal. 2018, 30, 1616–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine Research, Screen-printed electrode information. Carbon and ceramic electrode information, pine research2016, document DRP 10036. Available online: https://www.pineresearch.com/shop/products/electrodes/screen-printed-electrodes/carbon-spes/ (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- Faria, R.A.D.; Iden, H.; Bharucha, E.; Lins, V.F.C.; Messaddeq, Y.; Matencio, T.; Heneine, L.G.D. A new tool for the detection of horsemeat adulteration in raw meat. J. Bios. Bioelectron. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.K.; Rout, C.S. High performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on one-step electrodeposited nickel sulfide. Chem. Eur. J. Commun. 2015, 21, 9355–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Arduini, F.; Carbone, M.; Sansone, L.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Screen-printed electrodes modified with carbon nanomaterials: a comparison among carbon black, carbon nanotubes and graphene. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvano, F.; Albanese, D.; Crescitelli, A.; Pilloton, R.; Esposito, E. Impedimetric label-free immunosensor on disposable modified screen-printed electrodes for ochratoxin A. Biosensors 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsley, J.R.; Yu, J.; Wegener, K.L.; Hoppmann, C.; Rück-Braun, K.; Abell, A.D. Photoswitchable peptide-based ‘on-off’ biosensor for electrochemical detection and control of protein-protein interactions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terbouche, A.; Lameche, S.; Ait-Ramdane-Terbouche, C.; Guerniche, D.; Lerari, K.; Bachari, K.; Hauchard, D. A new electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode/Ru(III) complex for determination of nitrite: Electrochemical impedance and cyclic voltammetry measurements. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Conf. 2016, 92, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagati, A.K.; Choi, Y.; Park, J.; Choi, J.-W.; Jun, H.-S.; Cho, S. Silver nanoflower–reduced graphene oxide composite based micro-disk electrode for insulin detection in serum. Bios. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, M.; Sarac, A.S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of poly[carbazole-co-N-p-tolylsulfonyl pyrrole] on carbon fiber microelectrodes, equivalent circuits for modelling. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 65, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Zhou, H.; Chen, B.; Mendes, P.M.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Long, Y.-T. A bis-boronic acid modified electrode for the sensitive and selective determination of glucose concentrations. Analyst 2013, 138, 7146–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suea-Ngam, A.; Rattanarat, P.; Wongravee, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Srisa-Art, M. Droplet-based glucosamine sensor using gold nanoparticles and polyaniline-modified electrode. Talanta 2016, 158, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Kaur, G.; Wang, B. Progress in boronic acid-based fluorescent glucose sensors. J. Fluor. 2004, 14, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, Ö.; Dudak, F.C.; Baş, D.; Tamer, U.; Boyacı, I.H. Thermodynamic analysis of the interaction between 3-aminophenylboronic acid and monosaccharides for development of biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.A.D.; Lins, V.F.C.; Nappi, G.U.; Matencio, T.; Heneine, L.G.D. Development of an impedimetric immunosensor for specific detection of snake venom. BioNanoSci. 2018, 8, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhong, L.; Song, Z.; Guo, L.; Wu, H.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, F.; Chen, G. Visual detection of blood glucose on peroxidase-like activity of WS2 nanosheets. Bios. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichi, M.J.; Ehsani, M. A novel glucose sensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase on the chitosan-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and the luminol–H2O2 –gold nanoparticle chemiluminescence detection system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Li, J.; Chu, X.; Xu, M.; Jin, F.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Fang, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, W. High sensitivity glucose detection at extremely low concentrations using a MoS2-based field-effect transistor. Royal Soc. Chem. 2018, 8, 7942–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassas, I.; Braiek, M.; Bonhomme, A.; Bessuelle, F.; Rafin, G.; Majdoub, H.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Voltammetric glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase encapsulation in a chitosan-kappa-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complex. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 95, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Dong, C. A high performance nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on polyvinylpyrrolidone–graphene nanosheets–nickel nanoparticles–chitosan nanocomposite. Talanta 2015, 137, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, H.; Shirdel, H.; Mohammad-Rezaei, R. NiO nanoparticles electrodeposited on reduced GO-CuO nanocomposite bulk modified CCE as a sensitive glucose sensors. Nano-Mic Lett. 2017, 12, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghayeri, M.; Amiri, A.; Farhadi, S. Development of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on efficient loading Ag nanoparticles on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranji, S.N.; Nozaki, S.; Sahu, S.N. ZnO nanorod-based non-enzymatic optical glucose sensor. J. Biomed. Nanotech. 2015, 11, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Al-Dossary, O.; Kumar, G.; Umar, A. Zinc oxide nanostructures for NO2 gas-sensor applications: A review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.L.; Carballo, R. Impedimetric non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel hydroxide thin film onto gold electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xu, C.; Deng, D.; Xing, Y.; Liu, L.; Pang, H.; Zhang, D. Graphene oxide/nickel oxide modified glassy carbon electrode for supercapacitor and nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; Rama, E.C.; García, A.C. Electrochemical study and determination of electroactive species with screen-printed electrodes. J. Chem. Edu. 2016, 93, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Use of Enzyme | Transducer Substrate/Unit of Recognition | LOD [µM] | Technique of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | SPCE containing 3-aminophenylboronic acid | 0.0085 | EIS | Present work |
| Yes | WS2 nanosheets | 2.9 | Spectrophotometry | [42] |
| Yes | chitosan-coated Fe3O4 NPs | 0.43 | Chemiluminescence | [43] |
| Yes | MoS2-based field-effect transistor | 0.3 | Measurement of the source-drain current | [44] |
| Yes | chitosan/-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complex | 5 | Square wave voltammetry | [45] |
| Yes | WS2 quantum dots | 0.3 | Fluorescence measurement | [1] |
| No | Ni NPs polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) stabilized graphene nanosheets (GNs) with chitosan (CS) | 0.03 | Chronoamperometry | [46] |
| No | NiO NPs electrodeposited on reduced graphene oxide–copper oxide nanocomposite bulk modified carbon ceramic electrode | 2.63 | Cyclic Voltammetry | [47] |
| No | Ag NPs on multiwall carbon nanotubes | 0.0003 | Amperometry | [48] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorledo de Faria, R.A.; Iden, H.; Heneine, L.G.D.; Matencio, T.; Messaddeq, Y. Non-Enzymatic Impedimetric Sensor Based on 3-Aminophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Glucose Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071686
Dorledo de Faria RA, Iden H, Heneine LGD, Matencio T, Messaddeq Y. Non-Enzymatic Impedimetric Sensor Based on 3-Aminophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Glucose Detection. Sensors. 2019; 19(7):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071686
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorledo de Faria, Ricardo Adriano, Hassan Iden, Luiz Guilherme Dias Heneine, Tulio Matencio, and Younès Messaddeq. 2019. "Non-Enzymatic Impedimetric Sensor Based on 3-Aminophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Glucose Detection" Sensors 19, no. 7: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071686
APA StyleDorledo de Faria, R. A., Iden, H., Heneine, L. G. D., Matencio, T., & Messaddeq, Y. (2019). Non-Enzymatic Impedimetric Sensor Based on 3-Aminophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Glucose Detection. Sensors, 19(7), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071686