Development of an Electrical Resistance Sensor from High Strength Steel for Automotive Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Metal Sheet
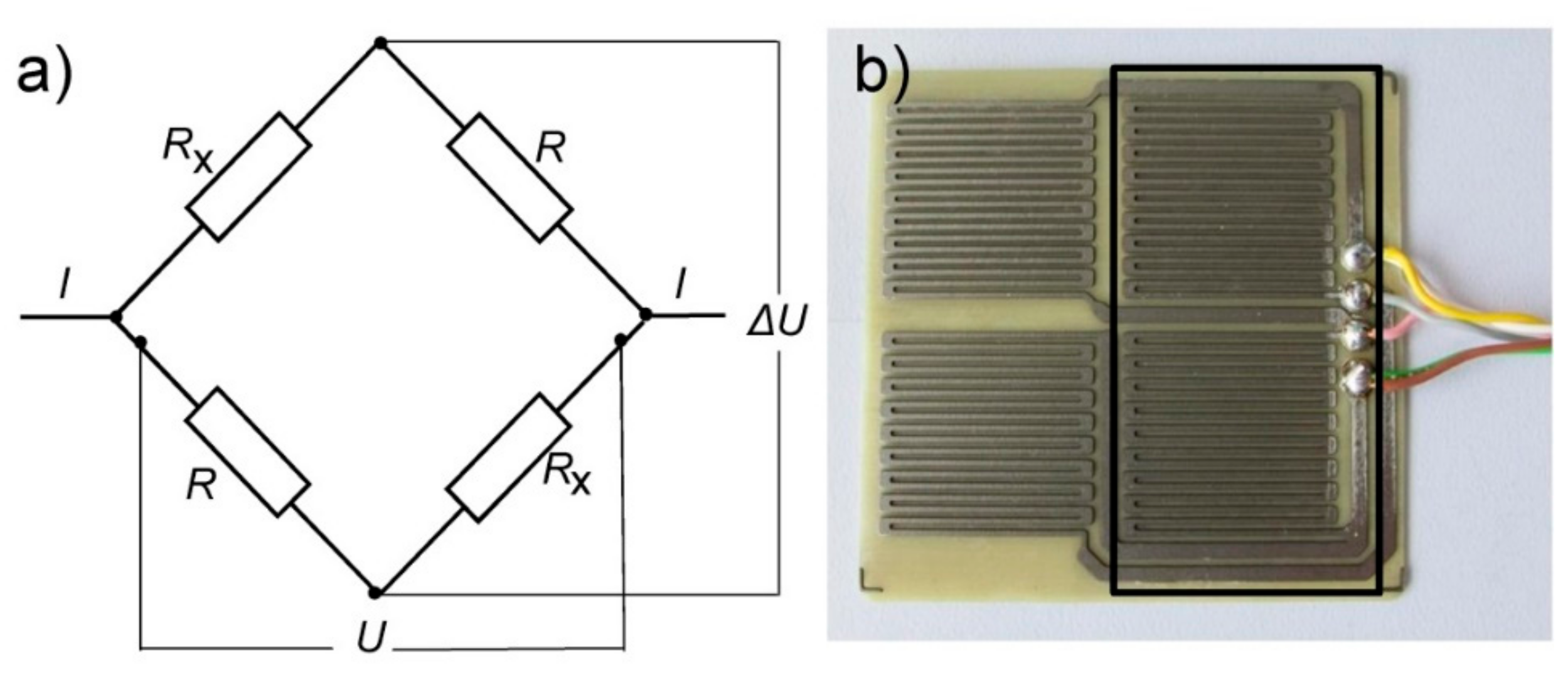
2.2. Design of ER Sensor
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Electrochemical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metallographic Investigation
3.2. ER corrosion Monitoring Measurements
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The sensor system for automotive application by using ER sensors enabled continuous monitoring of the installed sensors into a vehicle.
- (2)
- The sensors were designed and made from high strength steel used in the automotive industry with dimensions that can fit into the inner parts of a vehicle’s carrosserie.
- (3)
- The thinning of the high strength steel sheet was performed by double-sided chemical etching with the aim of keeping the microstructural properties unchanged.
- (4)
- The corrosion rates estimated from continuous monitoring by ER sensors correlated well with the electrochemical measurements obtained by potentiodynamic tests in a 0.5 M NaCl solution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, G.E.C.; Moore, C.G. Low-profile electrical resistance corrosion sensor. U.S. Patent 7,915,901, 29 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lankinen, E.; Pohjakallio, M.; Sundholm, G.; Talonen, P.; Saario, T. Application of in situ UV-vis spectroscopy and an in situ dc resistance measurement technique to the study of a poly(thiophene-3-methanol) film. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1997, 437, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.-P.; Lyon, S.B. A mechanistic study of initial atmospheric corrosion kinetics using electrical resistance sensors. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2956–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouril, M.; Prosek, T.; Scheffel, B.; Degres, Y. Corrosion monitoring in archives by the electrical resistance technique. J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Zhang, X.-X.; Dong, Z.-H. Monitoring of atmospheric corrosion and dewing process by interlacing copper electrode sensor. Corros. Sci. 2019, 150, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, A. Monitoring of steel corrosion in concrete by electrode arrays and electrical resistance probes. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7590–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šajna, A.; Legat, A.; Bjegović, D.; Kosec, T.; Stipanović, I.; Serdar, M.; Kuhar, V.; Gartner, N.; Pardi, L.; Augustynski, L. Recommendations for the Use of Corrosion Resistant Reinforcement; FEHRL: Brussels, Belgium, 2009; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- SMARTRAIL. Available online: http://smartrail.fehrl.org/?m=3&id_directory=7607 (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- DESTination Rail. Available online: http://www.destinationrail.eu/documents (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Zajec, B.; Bajt Leban, M.; Kosec, T.; Kuhar, V.; Legat, A.; Lenart, S.; Fifer Bizjak, K.; Kenneth, G. Corrosion monitoring of steel structure coating degradation. Tehnički Vjesnik 2018, 25, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Rosborg, B.; Pan, J. An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of copper in a bentonite/saline groundwater environment. Electrochim. Acta. 2008, 53, 7556–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosborg, B.; Kranjc, A.; Kuhar, V.; Legat, A. Corrosion rate of pure copper in an oxic bentonite/saline groundwater environment. Corros. Eng. Sci. Techn. 2011, 46, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosec, T.; Kranjc, A.; Rosborg, B.; Legat, A. Post examination of copper ER sensors exposed to bentonite. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 459, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoulil, J.; Kaňok, J.; Kouřil, M.; Parschová, H.; Novák, P. Influence of temperature on corrosion rate and porosity of corrosion products of carbon steel in anoxic bentonite environment. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 443, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outokompu-Forta –range-datasheet.pdf. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=2ahUKEwjmrbeMo-jhAhVTAogKHQbZAegQFjAAegQIAhAC&url=https%3A%2F%2Fotk-sitecore-prod-v2-cdn.azureedge.net%2F-%2Fmedia%2Ffiles%2Fproducts%2Fforta%2Foutokumpu-forta-range-datasheet.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0CZj37YqNqf-DkG0Lbx8Y4 (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- TATA STEEL Hot-rolled CP800-UC. Available online: https://www.tatasteeleurope.com/static_files/Downloads/Automotive/Data%20Sheets/Tata%20Steel%20AM%20-%20HR%20CP800-UC%20-%20data%20sheet%20EN.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Tait, S.W. An Introduction to Electrochemical Corrosion Testing for Practicing Engineers and Scientists; PairODocs Publications: Racine, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G102-89(2015)e1, Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements. Available online: http://www.cosasco.com/documents/ASTM_G102_Standard_Practice.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2019).






| H800-1 mm | CP800 | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | ||
| Fe [%] | 68.0 | 97.5 |
| Mn [%] | 16.1 | 1.41 |
| Cr [%] | 13.5 | 0.272 |
| Al [%] | 0.0097 | 0.0444 |
| C [%] | 0.257 | 0.0713 |
| Si [%] | 0.375 | 0.242 |
| P [%] | 0.0454 | 0.0174 |
| S [%] | 0.0019 | 0.0022 |
| Mo [%] | 0.0347 | 0.161 |
| Ni [%] | 0.216 | 0.0122 |
| N [%] | 0.347 | 0.0097 |
| Cu [%] | 0.485 | 0.0095 |
| Nb [%] | 0.023 | 0.033 |
| Ti [%] | 0.0198 | 0.087 |
| Mechanical Properties [15,16] | ||
| Rp 0,2 [MPa] | 800 | 680 |
| Rm [MPa] | 1000 | 780 |
| A80 [%] | 31 | 12 |
| Sample | Ecorr (mV) | jcorr (µA/cm2) | Eb(mV) | CR (µm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H800-as-received | −220 | 0.0175 | 203 | 0.21 |
| H800-etched | −262 | 0.181 | −105 | 2.1 |
| CP800 | −672 | 4.71 | - | 55 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosec, T.; Kuhar, V.; Kranjc, A.; Malnarič, V.; Belingar, B.; Legat, A. Development of an Electrical Resistance Sensor from High Strength Steel for Automotive Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19081956
Kosec T, Kuhar V, Kranjc A, Malnarič V, Belingar B, Legat A. Development of an Electrical Resistance Sensor from High Strength Steel for Automotive Applications. Sensors. 2019; 19(8):1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19081956
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosec, Tadeja, Viljem Kuhar, Andrej Kranjc, Vili Malnarič, Branko Belingar, and Andraž Legat. 2019. "Development of an Electrical Resistance Sensor from High Strength Steel for Automotive Applications" Sensors 19, no. 8: 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19081956
APA StyleKosec, T., Kuhar, V., Kranjc, A., Malnarič, V., Belingar, B., & Legat, A. (2019). Development of an Electrical Resistance Sensor from High Strength Steel for Automotive Applications. Sensors, 19(8), 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19081956






