Experimental Demonstration of MmWave Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communications Using IEEE 802.11ad
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We conducted mmWave V2V communications using commercial IEEE 802.11ad modules.
- We analyzed inter-vehicle connectivity by mmWave of short-range radio.
- We compared the mmWave V2V communications in different driving environments.
2. Related Works
3. GiV2V Communication Architecture
3.1. GiV2V Communication Antenna
3.2. GiV2V Communication Radio Range
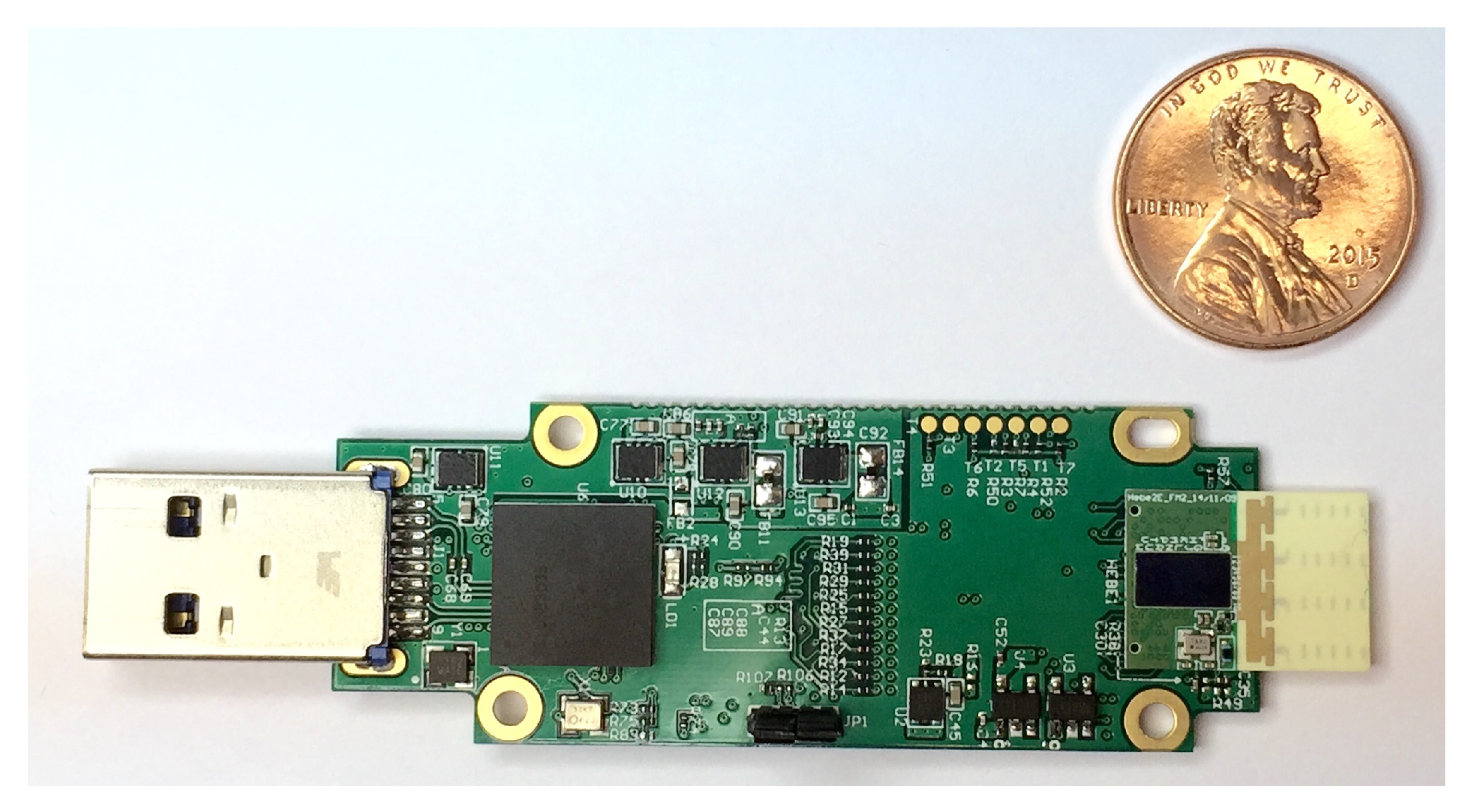
4. Experimental Configuration
4.1. IEEE 802.11ad
4.2. On-Board Unit Installation
4.3. Directional Antenna
4.4. Driving Test Environment
5. Experimental Result
5.1. Coverage and Beam Measurement
5.2. Campus Experiment
5.3. City Experiment
6. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, S.; Mayzus, R.; Zhao, H.; Azar, Y.; Wang, K.; Wong, G.N.; Schulz, J.K.; Samimi, M.; Gutierrez, F. Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: It will work! IEEE Access 2013, 1, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; MacCartney, G.R.; Samimi, M.K.; Nie, S.; Rappaport, T.S. Millimeter wave multi-beam antenna combining for 5G cellular link improvement in New York City. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–27 May 2014; pp. 5468–5473. [Google Scholar]
- Maccartney, G.R.; Rappaport, T.S. 73 GHz millimeter wave propagation measurements for outdoor urban mobile and backhaul communications in New York City. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–27 May 2014; pp. 4862–4867. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, T.S.; MacCartney, G.R.; Samimi, M.K.; Sun, S. Wideband millimeter-wave propagation measurements and channel models for future wireless communication system design. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 3029–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, S.; Shafi, M. 5G channel model with improved accuracy and efficiency in mmWave bands. IEEE 5G Tech Focus 2017, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Samimi, M.K.; Rappaport, T.S. Statistical channel model with multi-frequency and arbitrary antenna beamwidth for millimeter-wave outdoor communications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Samimi, M.K.; Rappaport, T.S. 3-D millimeter-wave statistical channel model for 5G wireless system design. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W. MC-GiV2V: Multichannel Allocation in mmWave-Based Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Available online: http://www.3gpp.org/ (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Loch, A.; Asadi, A.; Sim, G.H.; Widmer, J.; Hollick, M. mm-Wave on wheels: Practical 60 GHz vehicular communication without beam training. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bengaluru, India, 4–8 January 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.J.; Lee, J.; Liang, J.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.C.; Kim, M.D. Millimeter wave vehicular blockage characteristics based on 28 GHz measurements. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 86th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–27 September 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- VVa, V.; Shimizu, T.; Bansal, G.; Heath, R.W., Jr. Millimeter wave vehicular communications: A survey. Found. Trends Netw. 2016, 10, 1–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, B.; Moayyed, M.T.; Basagni, S. mmWave channel propagation modeling for V2X communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Matolak, D.W.; Ai, B. Shadowing Characterization for 5 GHz Vehicle-to-Vehicle Channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ai, B.; Stüber, G.L.; Wang, G.; Zhong, Z. Geometrical-based modeling for millimeter-wave MIMO mobile-to-mobile channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 2848–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Va, V.; Gonzalez-Prelcic, N.; Daniels, R.; Bhat, C.R.; Heath, R.W. Millimeter-wave vehicular communication to support massive automotive sensing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatis, I.; Tassi, A.; Piechocki, R.J.; Nix, A. Beam Alignment for Millimetre Wave Links with Motion Prediction of Autonomous Vehicles. 2017. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.04264.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2019).
- Kumari, P.; Choi, J.; Prelcic, N.G.; Heath, R.W. IEEE 802.11 ad-based Radar: An Approach to Joint Vehicular Communication-Radar System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 3012–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Prelcic, N.; Méndez-Rial, R.; Heath, R.W. Radar aided beam alignment in mmwave V2I communications supporting antenna diversity. In Proceedings of the 2016 Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), La Jolla, CA, USA, 31 January–5 February 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Perfecto, C.; Del Ser, J.; Bennis, M. On the interplay between scheduling interval and beamwidth selection for low-latency and reliable V2V mmWave communications. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th Conference on Innovations in Clouds, Internet and Networks (ICIN), Paris, France, 7–9 March 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Perfecto, C.; Del Ser, J.; Bennis, M. Millimeter-wave V2V communications: Distributed association and beam alignment. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2148–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Va, V.; Choi, J.; Heath, R.W. The impact of beamwidth on temporal channel variation in vehicular channels and its implications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 5014–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samimi, M.K.; MacCartney, G.R.; Sun, S.; Rappaport, T.S. 28 GHz millimeter-wave ultrawideband small-scale fading models in wireless channels. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, S.; Baek, S.; Kim, B.; Chang, Y.; Molisch, A.F.; Rappaport, T.S.; Haneda, K.; Park, J. Proposal on millimeter-wave channel modeling for 5G cellular system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 10, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Rappaport, T.S.; Thomas, T.A.; Ghosh, A. A preliminary 3D mm wave indoor office channel model. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Garden Grove, CA, USA, 16–19 February 2015; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Weiler, R.J.; Peter, M.; Keusgen, W.; Maltsev, A.; Karls, I.; Pudeyev, A.; Bolotin, I.; Siaud, I.; Ulmer-Moll, A.M. Quasi-deterministic millimeter-wave channel models in MiWEBA. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2016, 2016, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, A.; Pudeyev, A.; Karls, I.; Bolotin, I.; Morozov, G.; Weiler, R.; Peter, M.; Keusgen, W. Quasi-deterministic approach to mmwave channel modeling in a non-stationary environment. In Proceedings of the Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 966–971. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.G.; Bai, T.; Kulkarni, M.N.; Alkhateeb, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Heath, R.W. Modeling and analyzing millimeter wave cellular systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 65, 403–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Andrews, J.G.; Baccelli, F.; Novlan, T.D.; Zhang, C.J. Design and analysis of initial access in millimeter wave cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 6409–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Rappaport, T.S.; Qiao, Y.; Lauffenburger, S.J. Millimeter-wave 60 GHz outdoor and vehicle AOA propagation measurements using a broadband channel sounder. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference-GLOBECOM 2011, Houston, TX, USA, 5–9 December 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, R.; Didascalou, D.; Wiesbeck, W. Impact of road surfaces on millimeter-wave propagation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2000, 49, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, Y. Multipath fading due to road surface reflection and fading reduction by means of space diversity in ITS vehicle-to-vehicle communications at 60 Ghz. Electron. Commun. Jpn. Part I Commun. 2002, 85, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ai, B.; Stuber, G.L.; Wang, G.; Zhong, Z. A cluster based geometrical model for millimeter wave mobile-to-mobile channels. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Qingdao, China, 22–24 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tassi, A.; Egan, M.; Piechocki, R.J.; Nix, A. Modeling and Design of Millimeter-Wave Networks for Highway Vehicular Communication. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 10676–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorca, J.; Hunukumbure, M.; Wang, Y. On overcoming the impact of Doppler spectrum in millimeter-wave V2I communications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Venugopal, K.; Molisch, A.F.; Heath, R.W. MmWave vehicle-to-infrastructure communication: Analysis of urban microcellular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 7086–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Va, V.; Zhang, X.; Heath, R.W. Beam switching for millimeter wave communication to support high speed trains. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 82nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2015-Fall), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Va, V.; Shimizu, T.; Bansal, G.; Heath, R.W. Beam design for beam switching based millimeter wave vehicle-to-infrastructure communications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–27 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, N.; Wymeersch, H.; Ström, E.G.; Slock, D. Location-aided mm-wave channel estimation for vehicular communication. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 17th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Edinburgh, UK, 3–6 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Maschietti, F.; Gesbert, D.; de Kerret, P.; Wymeersch, H. Robust location-aided beam alignment in millimeter wave massive MIMO. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017–2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Va, V.; Shimizu, T.; Bansal, G.; Heath, R.W. Position-aided millimeter wave V2I beam alignment: A learning-to-rank approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Va, V.; Choi, J.; Shimizu, T.; Bansal, G.; Heath, R.W. Inverse multipath fingerprinting for millimeter wave V2I beam alignment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 4042–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Klautau, A.; Ribero, M.; Narasimha, M.; Heath, R.W. MmWave Vehicular Beam Training with Situational Awareness by Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Abu Dhabi, UAE, 9–13 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Eltayeb, M.E.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Heath, R.W. Compressive sensing for blockage detection in vehicular millimeter wave antenna arrays. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Mao, S.; Kompella, S.; Swami, A. On Link Scheduling in Dual-Hop 60-GHz mmWave Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 11180–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taya, A.; Nishio, T.; Morikura, M.; Yamamoto, K. Coverage Expansion through Dynamic Relay Vehicle Deployment in mmWave V2I Communications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 87th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Porto, Portugal, 3–6 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, V.; Kokkoniemi, J.; Moltchanov, D.; Lehtomäki, J.; Juntti, M.; Koucheryavy, Y. The impact of interference from the side lanes on mmWave/THz band V2V communication systems with directional antennas. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5028–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, M.; Mezzavilla, M.; Rangan, S.; Zorzi, M. Multi-connectivity in 5G mmWave cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Mediterranean Ad Hoc Networking Workshop (Med-Hoc-Net), Vilanova i la Geltru, Spain, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Giordani, M.; Mezzavilla, M.; Rangan, S.; Zorzi, M. An Efficient Uplink Multi-Connectivity Scheme for 5G Millimeter-Wave Control Plane Applications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 6806–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayeb, M.E.; Choi, J.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Heath, R.W. Enhancing secrecy with multiantenna transmission in millimeter wave vehicular communication systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 8139–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.; Mbianke, C.; Kürner, T. A dynamic 60 GHz radio channel model for system level simulations with MAC protocols for IEEE 802.11 ad. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE 2010), Braunschweig, Germany, 7–10 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Coll-Perales, B.; Gruteser, M.; Gozalvez, J. Evaluation of IEEE 802.11 ad for mmWave V2V Communications. In Proceedings of the Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW), Barcelona, Spain, 15–18 April 2018; pp. 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Venugopal, K.; Molisch, A.F.; Heath, R.W. Blockage and coverage analysis with mmwave cross street BSs near urban intersections. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, A.; Maslennikov, R.; Sevastyanov, A.; Khoryaev, A.; Lomayev, A. Experimental investigations of 60 GHz WLAN systems in office environment. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2009, 27, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE 802.15.3 Working Group, Part 15.3: Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs), IEEE Unapproved Draft Std P802.15.3c/D10; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; bibtex:ieee80215c. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. Part11: Wireless LAN Medium Acess Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications C Amendment 5: Enhancements for Very High Throughput in the 60 GHz Band. IEEE P802.11ad/D1.0; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tensorcom. Available online: http://tensorcom.com/ (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Hyundai Motor. Available online: https://www.hyundai.com/worldwide/en (accessed on 23 April 2019).












| References | Contents of the Studies on mmWave V2X Communications |
|---|---|
| [12,13,14,15,31,32,33] | Vehicular channel models with link blockage, scattering, shadowing and multipath fading are established. Furthermore, reflection and diffraction of mmWave at realistic road surfaces and geometries are explored for the model. |
| [34,35,36,53] | A stochastic model for V2X communications with blockage probability from RSU and throughput is presented. |
| [44,45,46] | Blockage detection and relay/multi-hop routing in V2X communications to avoid obstacles or extend network coverage is demonstrated. |
| [37,38,39,40,41,42,43] | Location or situation-based channel estimation, beam direction steering and training are achieved when prior channel information or past measurement is given for each location or situation. Machine learning techniques can be applied. |
| [18,19] | A mmWave link is configured using Long-Range Radar (LRR) mounted on the road infrastructures and on the vehicles for V2I and V2V communications. |
| [16,17] | The mmWave link configuration is assisted by motion and posture information of vehicles estimated from vehicular sensors. DSRC beacons carry the sensor information periodically. |
| [8,47] | Effect of inter-beam interference in V2V networks is analyzed and beam alignment and multi-channel assignment are considered. |
| [20,21,22] | Distributed beam alignment and width decision are achieved by channel and queue state information. V2V association and scheduling problem are solved in a decentralized manner. |
| [48,49] | Multi-connectivity with use of microwave frequencies (e.g., DSRC, LTE) is considered to increase the robustness connectivity (e.g., handover or relay) and reduce the beam tracking overhead. |
| [10,11,30] | Testbeds for mmWave V2I or V2V communications and experiment results are introduced. |
| [52] | The IEEE 802.11ad standard (WiGig) is investigated for mmWave V2X communications using simulation. |
| [50] | Security techniques of physical layer in mmWave and MIMO systems are proposed. |
| EIRP | 12.5 dBm |
| IL | 7.5 dB |
| G | 7.5 dBi |
| MIMO | 2 × 2 |
| BW | 1.76 GHz |
| MCS | 0–7 |
| Pathloss exponent () | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| Distance (m) | 10.01 | 9.96 | 8.11 | 7.41 | 6.81 | 6.31 | 5.88 | 5.50 | 5.18 | 4.89 |
| MCS | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| SNR (dB) | −10 | −1 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 9.5 |
| SNR (dB) | −1 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 9.5 |
| Distance (m) | 10 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3.5 | 2.5 |
| Pathloss exponent () | 2.1 | 2.07 | 2.09 | 2.0 | 2.08 | 2.1 | 2.2 |
| Campus | City | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean throughput (Mbps) | 177 | 194 |
| Mean disconnection (s) | 1.16 | 1.54 |
| Mean connection (s) | 1.45 | 2.38 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W. Experimental Demonstration of MmWave Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communications Using IEEE 802.11ad. Sensors 2019, 19, 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092057
Kim W. Experimental Demonstration of MmWave Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communications Using IEEE 802.11ad. Sensors. 2019; 19(9):2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Wooseong. 2019. "Experimental Demonstration of MmWave Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communications Using IEEE 802.11ad" Sensors 19, no. 9: 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092057
APA StyleKim, W. (2019). Experimental Demonstration of MmWave Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communications Using IEEE 802.11ad. Sensors, 19(9), 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092057





