Bovine Serum Albumin Protein-Based Liquid Crystal Biosensors for Optical Detection of Toxic Heavy Metals in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of N,N-Dimethyl-N-octadecyl-3-Aminopropyltrimethoxyysilychloride (DMOAP) Modified Surface
2.2. Immobilization of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) with Heavy Metal Ions
2.3. Fabrication of Optical Cell
3. Results and Discussion
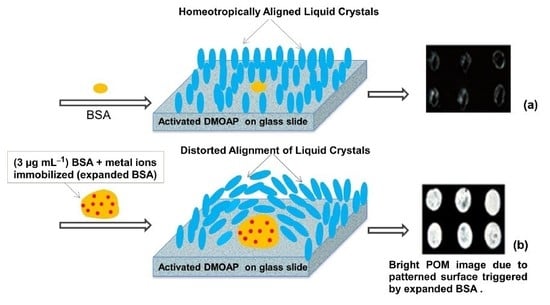
3.1. The Effect of Modified and Unmodified DMOAP Surfaces on Immobilization of BSA
3.2. Optimization of BSA Concentrations
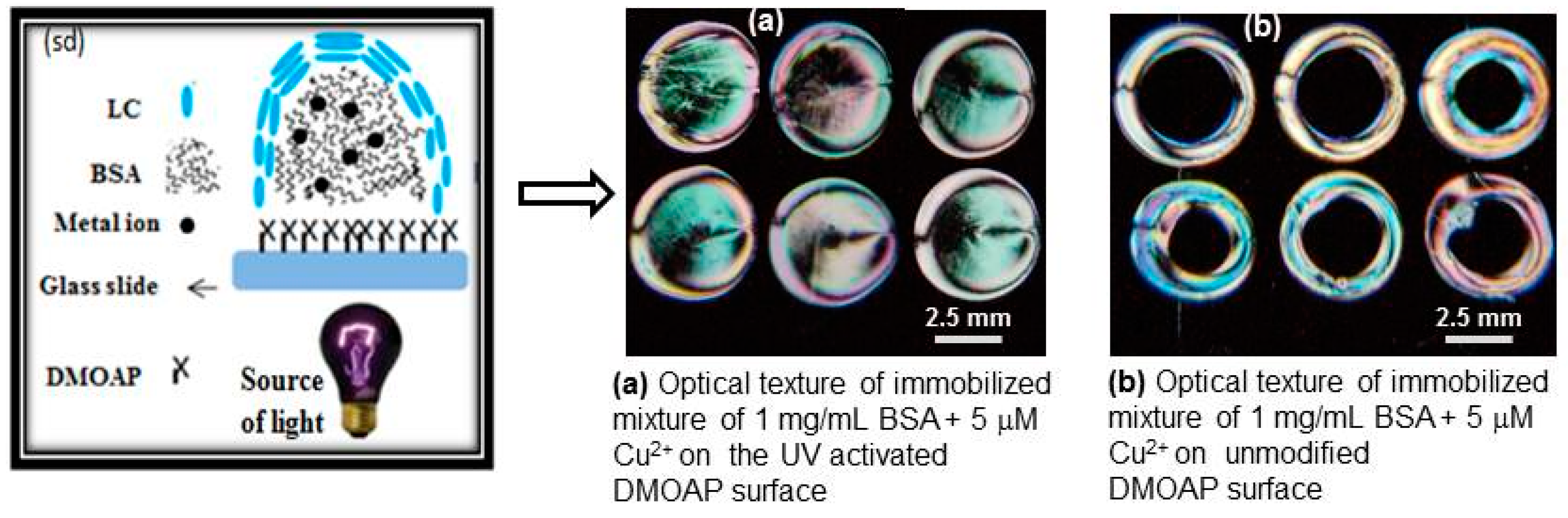
3.3. Detection Mechanism of the Liquid Crystal (LC)/BSA Based Sensor
3.4. The Selectivity and Limit of Detection of BSA Based LC Sensor
3.5. Effect of Anions on Sensing Response of LC Sensor
3.6. Reproducability of BSA Based LC Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Cuero, R.; Ouellet, T.; Yu, J.; Mogongwa, N. Metal ion enhancement of fungal growth, gene expression and aflatoxin synthesis in Aspergillus flavus: RT-PCR characterization. J. Appl. Microbial. 2003, 94, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnham, K.J.; Bush, A.I. Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demayo, A.; Taylor, M.C.; Taylor, K.W.; Hodson, P.V.; Hammond, P.B. Toxic effects of lead and lead compounds on human health, aquatic life, wildlife plants, and livestock. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. 1982, 12, 257–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Chang, C.M.; Wang, J.Y.; Hou, M.F.; Wang, J.M.; Shiurba, R.; Chang, W.C.; Chang, W.C. Function of DNA methyltransferase 3a in lead (Pb2+)-Induced Cyclooxygenase-2 gene. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiyan, W.; Stuanes, A.O. Heavy metal pollution in air-water-soil-plant system of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, China. Water Air Soil Poll. 2003, 147, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Yoo, S.M.; Kang, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B. Single-step multiplex detection of toxic metal ions by Au nanowires-on-chip sensor using reporter elimination. Lab. Chip 2012, 12, 3077–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Goloubinoff, P.; Christen, P. Heavy metal ions are potent inhibitors of protein folding. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Johnson, R.C.; Hupp, J.T. Gold nanoparticle-based sensing of “spectroscopically silent” heavy metal ions. Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, G.; Uzun, L.; Denizli, A. Lysine-promoted colorimetric response of gold nanoparticles: A simple assay for ultrasensitive mercury2+ detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 86, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Blue-to-red colorimetric sensing strategy for Hg2+ and Ag+ via redox-regulated surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2011, 3, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.; Palmero, S. Determination of heavy metals in milk by potentiometric stripping analysis using a home-made flow cell. Food Control. 2004, 15, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragay, G.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A. Enhanced electrochemical detection of heavy metals at heated graphite nanoparticle-based screen-printed electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4326–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.; García, M.B.G.; Santos, D.H.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Ribotti, A.; McCaul, M.; Diamond, D.; Magni, P. Screen-printed electrodes for environmental monitoring of heavy metal ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Tan, H.; Wu, Y.; Liao, S.; Wu, Z.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Label-free liquid crystal biosensor based on specific oligonucleotide probes for heavy metal ions. Anal. Chem. 2012, 85, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Khan, A.R.; Shin, J.-H.; Park, S.-Y. A liquid-crystal-based DNA biosensor for pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Nandi, R.; Mishra, K.; Singh, H.K.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, B. Liquid crystal based sensor system for the real time detection of mercuric ions in water using amphiphilic dithiocarbamate. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2016, 226, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Lee, A.S.-Y. Ligand-doped liquid crystal sensor system for detecting mercuric ion in aqueous solutions. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4546–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.-Z.; Jang, C.-H. Liquid crystal-based sensors for the detection of heavy metals using surface-immobilized urease. Colloids Surf. B Biointer. 2011, 88, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Zipursky, S.L.; Matsudaira, P.; Baltimore, D.; Darnell, J. Molecular Cell Biology, 4th ed. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21475/ (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Ong, L.H.; Ding, X.; Yang, K.-L. Mechanistic study for immobilization of cysteine-labeled oligopeptides on UV-activated surfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointer 2014, 122, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Sakiyama, T.; Imamura, K. On the adsorption of proteins on solid surfaces, a common but very complicated phenomenon. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Barnett, G.V.; Pathak, J.A.; Roberts, C.J.; Sarangapani, P.S. Protein aggregation, particle formation, characterization & rheology. Curr. Opin. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2014, 19, 438–449. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Huang, M.; Ye, W.; Chen, D.; He, S.; Ding, L.; Yao, Y.; Wan, L.; Xu, J.; Miao, S. Conformational change of bovine serum albumin molecules at neutral pH in ultra-diluted aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 12207–12214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.-Y.; Yang, K.-L. Dark-to-bright optical responses of liquid crystals supported on solid surfaces decorated with proteins. Langmuir 2008, 2, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhazmi, H.A. FT-IR Spectroscopy for the Identification of Binding Sites and Measurements of the Binding Interactions of Important Metal Ions with Bovine Serum Albumin. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belatik, A.; Hotchandani, S.; Carpentier, R.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.-A. Locating the binding sites of Pb2+ ion with human and bovine serum albumins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunyk, L.A.; Rosenzweig, A.C. Cu(I) binding and transfer by the N terminus of the Wilson disease protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8622–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.X.; Pang, X. Electrostatic Interactions in Protein Structure, Folding, Binding, and Condensation. Chem Rev. 2018, 118, 1691–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, R.J.; Ma, C.D.; Gupta, J.K.; Abbott, N.L. Influence of specific anions on the orientational ordering of thermotropic liquid crystals at aqueous interfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Rodenhausen, K.B.; Schubert, M.; Bartz, J.C. Investigation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) attachment onto self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) using combinatorial quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) and spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Transducer | Probe | Detection Limit | Metal Ions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC | Thiodiacarbamate | 0.5 µM | Hg2+ | [17] |
| LC | 5-(pyridine-4-yl)-2(5-(pyridine-4-yl)thiophen-yl)diazole | 10 µM | Hg2+ | [18] |
| LC | Urease | 10 µM | Cu2+ | [19] |
| LC | DNA | 5 nM | Hg2+ | [15] |
| LC | BSA | 1 nM | Cu2+ | This work |
| LC | BSA | 10 nM | Pb2+ | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, N.u.; Siddiqi, H.M.; Kun Lin, Y.; Hussain, Z.; Majeed, N. Bovine Serum Albumin Protein-Based Liquid Crystal Biosensors for Optical Detection of Toxic Heavy Metals in Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010298
Amin Nu, Siddiqi HM, Kun Lin Y, Hussain Z, Majeed N. Bovine Serum Albumin Protein-Based Liquid Crystal Biosensors for Optical Detection of Toxic Heavy Metals in Water. Sensors. 2020; 20(1):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010298
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Noor ul, Humaira Masood Siddiqi, Yang Kun Lin, Zakir Hussain, and Nasir Majeed. 2020. "Bovine Serum Albumin Protein-Based Liquid Crystal Biosensors for Optical Detection of Toxic Heavy Metals in Water" Sensors 20, no. 1: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010298
APA StyleAmin, N. u., Siddiqi, H. M., Kun Lin, Y., Hussain, Z., & Majeed, N. (2020). Bovine Serum Albumin Protein-Based Liquid Crystal Biosensors for Optical Detection of Toxic Heavy Metals in Water. Sensors, 20(1), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010298