Magnetic Cell Centrifuge Platform Performance Study with Different Microsieve Pore Geometries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
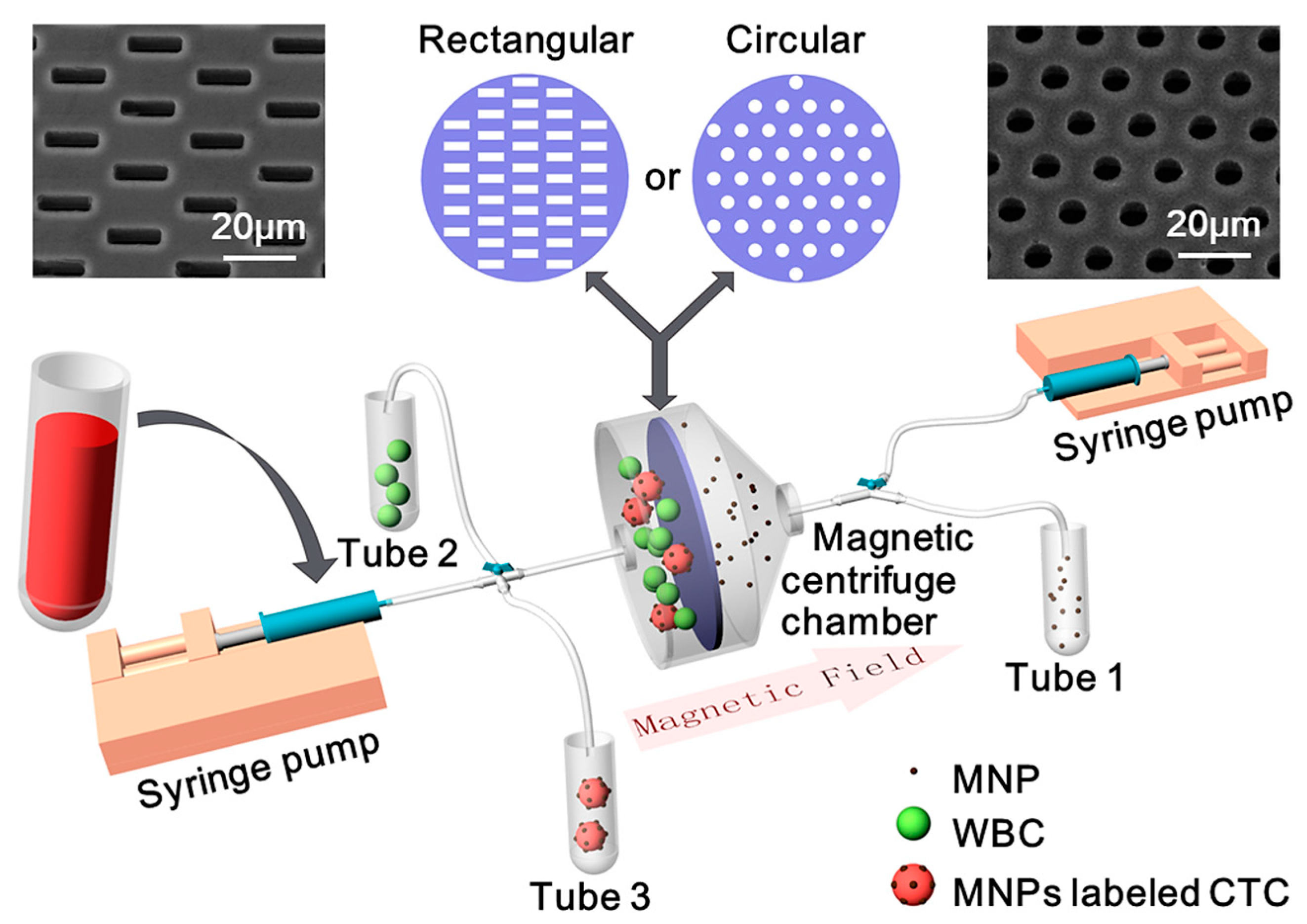
2.1. System Design and Fabrication
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Operation Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Device Modeling and Simulation
3.2. Microsieve Performance and Comparison
3.3. Magnetically Labeled Target Cell Separation Performance and Comparison
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weigelt, B.; Peterse, J.L.; Van’t Veer, L.J. Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massagué, J. Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steeg, P.S. Tumor metastasis: Mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhana, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Nanotechnology for enrichment and detection of circulating tumor cells. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1973–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alixpanabières, C.; Pantel, K. Circulating Tumor Cells: Liquid Biopsy of Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiltermann, T.J.; Pore, M.M.; van den Berg, A.; Timens, W.; Boezen, H.M.; Liesker, J.J.; Schouwink, J.H.; Wijnands, W.J.; Kerner, G.S.; Kruyt, F.A.; et al. Circulating tumor cells in small-cell lung cancer: A predictive and prognostic factor. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Hayes, D.F.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: A novel prognostic factor for newly diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 33, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Speicher, M.R. The biology of circulating tumor cells. Oncogene 2015, 35, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebotaru, C.L.; Olteanu, E.D.; Antone, N.Z.; Buiga, R.; Nagy, V. Circulating tumor cells in germ cell tumors: Are those biomarkers of real prognostic value? A review. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann.Oncol. 2009, 20, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoecklein, N.H.; Klein, C.A. Genetic disparity between primary tumours, disseminated tumour cells, and manifest metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulfoni, M.; Turetta, M.; Del Ben, F.; Di Loreto, C.; Beltrami, A.P.; Cesselli, D. Dissecting the heterogeneity of circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer: Going far beyond the needle in the haystack. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, S.J.; Rosenfeld, N.; Caldas, C. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Winer, E.P.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Srkalovic, G.; Tejwani, S.; Schott, A.F.; O’Rourke, M.A.; Lew, D.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells and Response to Chemotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer: SWOG S0500. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleijfer, S.; Gratama, J.W.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Kraan, J.; Martens, J.W.; Foekens, J.A. Circulating tumour cell detection on its way to routine diagnostic implementation? Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Pantel, K.; Kang, Y. Tumor metastasis: Moving new biological insights into the clinic. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W. Tumor Cells Circulate in the Peripheral Blood of All Major Carcinomas but not in Healthy Subjects or Patients with Nonmalignant Diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sollier, E.; Go, D.E.; Che, J.; Gossett, D.R.; O’Byrne, S.; Weaver, W.M.; Kummer, N.; Rettig, M.; Goldman, J.; Nickols, N.; et al. Size-selective collection of circulating tumor cells using Vortex technology. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.K.; Zheng, S.; Williams, A.J.; Balic, M.; Groshen, S.; Scher, H.I.; Fleisher, M.; Stadler, W.; Datar, R.H.; Tai, Y.C.; et al. Portable filter-based microdevice for detection and characterization of circulating tumor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5011–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, R.; Gertler, R.; Friederichs, J.; Fuehrer, K.; Dahm, M.; Phelps, R.; Thorban, S.; Nekarda, H.; Siewert, J.R. Comparison of two density gradient centrifugation systems for the enrichment of disseminated tumor cells in blood. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2002, 49, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.J.; Yobas, L.; Lee, G.Y.H.; Ong, C.N.; Lim, C.T. Microdevice for the isolation and enumeration of cancer cells from blood. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmerbach, T.W.; Wottawah, F.; Dietrich, J.; Lincoln, B.; Wittekind, C.; Guck, J. Oral cancer diagnosis by mechanical phenotyping. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shim, S.; Gascoyne, P.; Noshari, J.; Hale, K.S. Dynamic physical properties of dissociated tumor cells revealed by dielectrophoretic field-flow fractionation. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Dielectrophoretic platforms for bio-microfluidic systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.I.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial Focusing for Tumor Antigen–Dependent and –Independent Sorting of Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earhart, C.M.; Hughes, C.E.; Gaster, R.S.; Ooi, C.C.; Wilson, R.J.; Zhou, L.Y.; Humke, E.W.; Xu, L.; Wong, D.J.; Willingham, S.B.; et al. Isolation and mutational analysis of circulating tumor cells from lung cancer patients with magnetic sifters and biochips. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Jia, C.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Mao, H.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. A microfluidic chip integrated with a high-density PDMS-based microfiltration membrane for rapid isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Fusi, A.; Klopocki, E.; Schmittel, A.; Tinhofer, I.; Nonnenmacher, A.; Keilholz, U. Negative enrichment by immunomagnetic nanobeads for unbiased characterization of circulating tumor cells from peripheral blood of cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, G.; Herrler, M.; Burgess, D.; Manna, E.; Krag, D.; Burke, J.F. Enrichment with anti-cytokeratin alone or combined with anti-EpCAM antibodies significantly increases the sensitivity for circulating tumor cell detection in metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Z.; Wu, X.; Cui, G.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Leng, Q.; Ye, J.; Ma, B.; et al. Circulating tumor cell capture and single cell detection based on magnetic cell centrifuge platform. 2019; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lin, H.K.; Lu, B.; Williams, A.; Datar, R.; Cote, R.J.; Tai, Y.C. 3D microfilter device for viable circulating tumor cell (CTC) enrichment from blood. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.D.; Hao, S.; Williams, A.J.; Harouaka, R.A.; Schrand, B.; Rawal, S.; Ao, Z.; Brenneman, R.; Gilboa, E.; Lu, B.; et al. Separable bilayer microfiltration device for viable label-free enrichment of circulating tumour cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Lu, B.; Tai, Y.C.; Goldkorn, A. A cancer detection platform which measures telomerase activity from live circulating tumor cells captured on a microfilter. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6420–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Hong, B.; Chen, X. The effects of 3D channel geometry on CTC passing pressure–towards deformability-based cancer cell separation. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdich, R.; Kosvintsev, S.; Cumming, I.; Zhdanov, S. Pore design and engineering for filters and membranes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2005, 364, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Pei, R. High-purity capture of CTCs based on micro-beads enhanced isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells (ISET) method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J. Circulating tumor microemboli: Progress in molecular understanding and enrichment technologies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1367–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rostami, P.; Kashaninejad, N.; Moshksayan, K.; Saidi, M.S.; Firoozabadi, B.; Nguyenc, N.-T. Novel approaches in cancer management with circulating tumor cell clusters. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, R.; Tsang, C.M.; Tsao, S.W.; Sun, D.; Lam, R.H.W. Revealing elasticity of largely deformed cells flowing along confining microchannels. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boccaccio, A.; Uva, A.E.; Papi, M.; Fiorentino, M.; De Spirito, M.; Monno, G. Nanoindentation characterisation of human colorectal cancer cells considering cell geometry, surface roughness and hyperelastic constitutive behaviour. Nanotechnology 2016, 28, 045703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, S.; Brink, R.; Nijdam, W.; Krijnen, G.J.; Elwenspoek, M.C. Ceramic microsieves: Influence of perforation shape and distribution on flow resistance and membrane strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 196, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xu, T.; Zheng, S.; Goldkorn, A.; Tai, Y.-C. Parylene membrane rectangular filter for the capture, analysis and culture of viable circulating tumor cells. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Hong Kong, China, 24–28 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.M.; Ramani, V.C.; Jeffrey, S.S. Circulating tumor cell technologies. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 374–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Bai, Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, G.; Yang, M.; Yang, Q.; Ma, B.; Song, Q.; Tian, D.; Ceyssens, F.; et al. Magnetic Cell Centrifuge Platform Performance Study with Different Microsieve Pore Geometries. Sensors 2020, 20, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010048
Wu X, Bai Z, Wang L, Cui G, Yang M, Yang Q, Ma B, Song Q, Tian D, Ceyssens F, et al. Magnetic Cell Centrifuge Platform Performance Study with Different Microsieve Pore Geometries. Sensors. 2020; 20(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xinyu, Zhongyang Bai, Lin Wang, Guangchao Cui, Mengzheng Yang, Qing Yang, Bo Ma, Qinglin Song, Dewen Tian, Frederik Ceyssens, and et al. 2020. "Magnetic Cell Centrifuge Platform Performance Study with Different Microsieve Pore Geometries" Sensors 20, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010048
APA StyleWu, X., Bai, Z., Wang, L., Cui, G., Yang, M., Yang, Q., Ma, B., Song, Q., Tian, D., Ceyssens, F., Puers, R., Kraft, M., Zhao, W., & Wen, L. (2020). Magnetic Cell Centrifuge Platform Performance Study with Different Microsieve Pore Geometries. Sensors, 20(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010048




