Smartphone-Based Electrochemical Potentiostat Detection System Using PEDOT: PSS/Chitosan/Graphene Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Dopamine Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Instruments and Apparatus
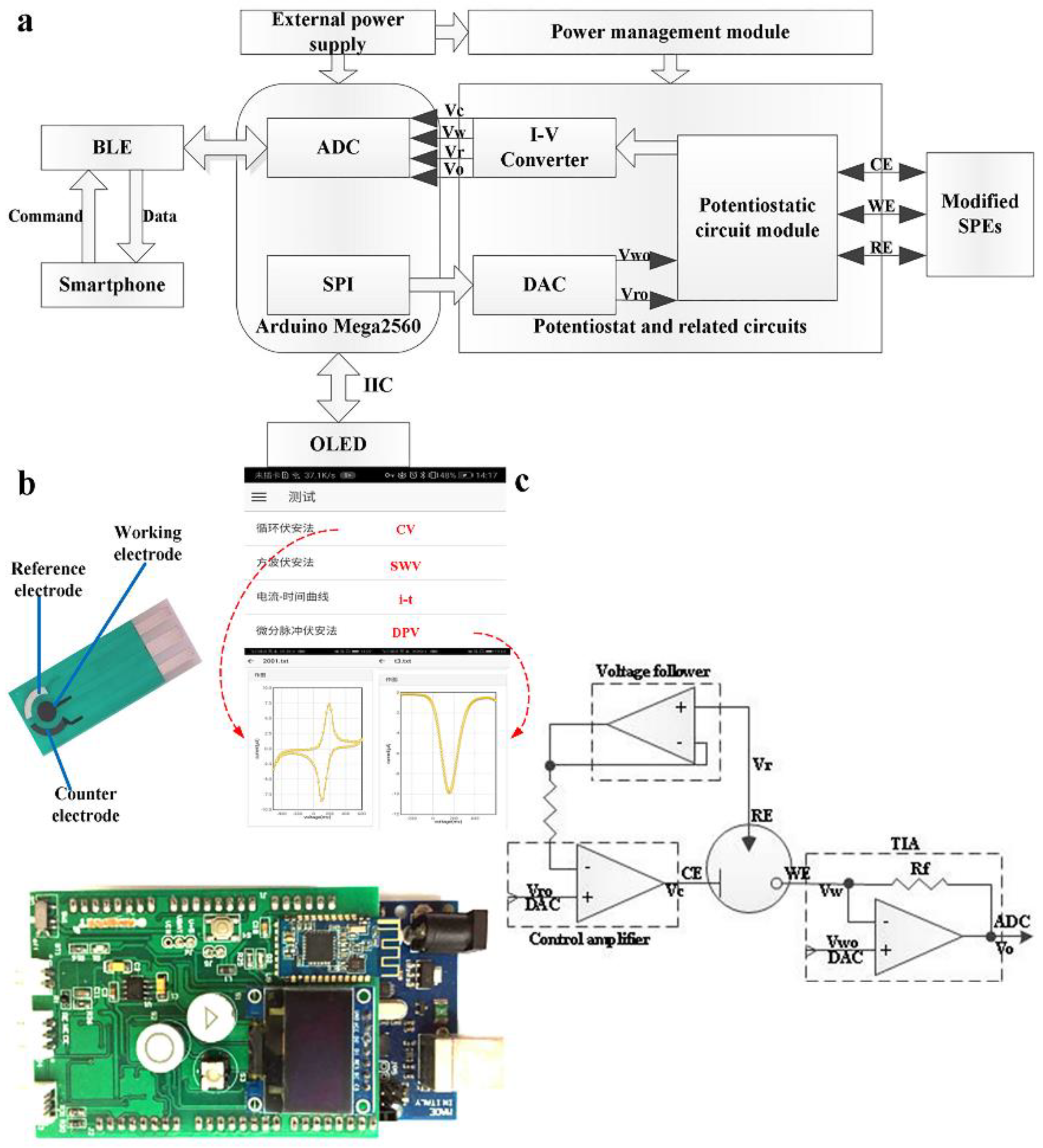
2.3. Design of Detection Circuit and App
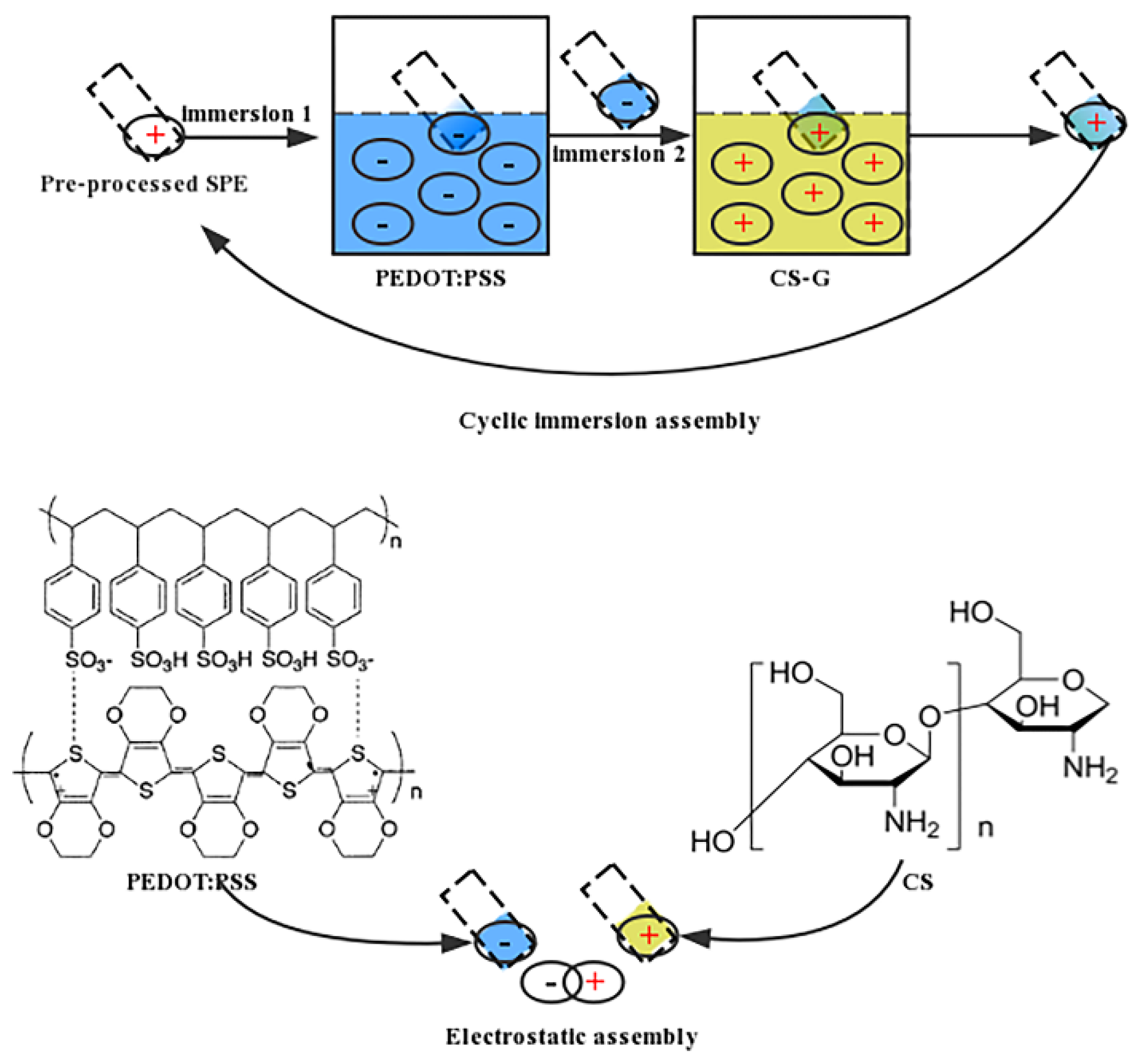
2.4. Modification of SPEs
2.5. Electrochemical Characterization of Modified SPEs
2.6. Dopamine Detection
3. Results and Discussion
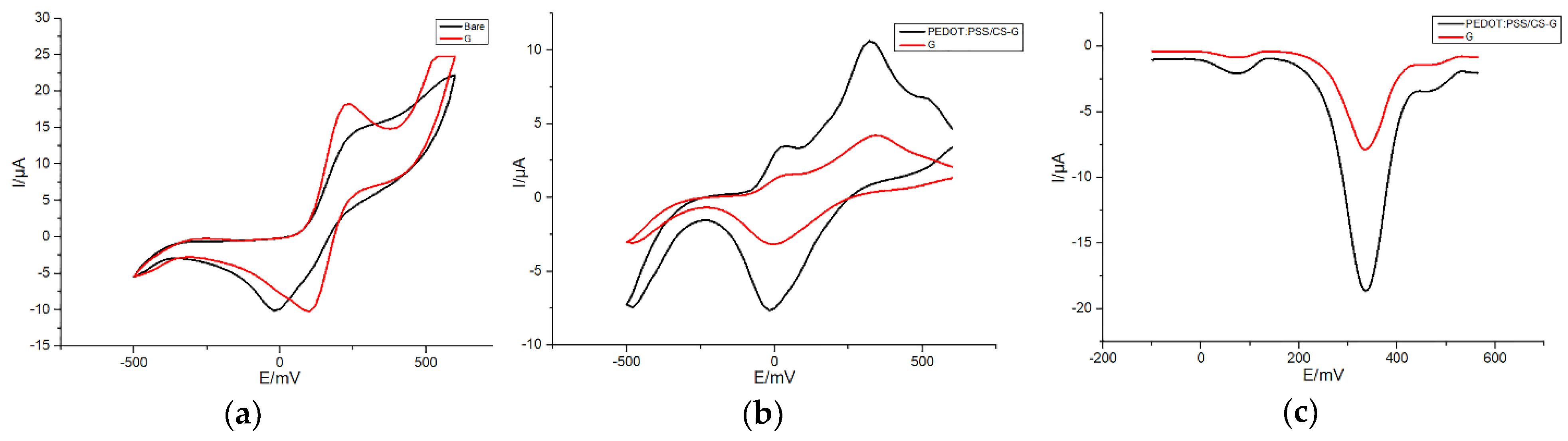
3.1. Electrochemical Characterization of SPEs Modified with Different Materials
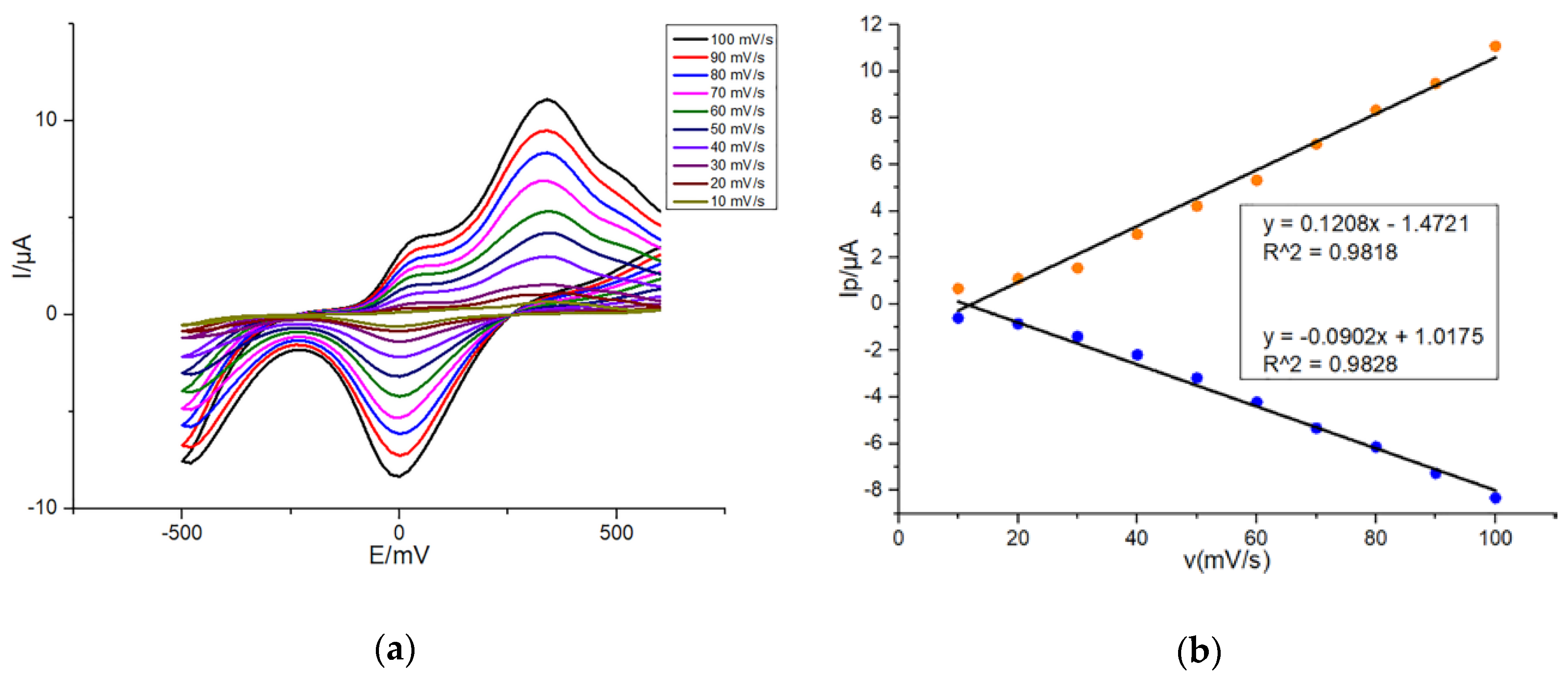
3.2. Scan Rate Dependence of Peak Current on Modified SPEs
3.3. Dopamine Calibration Curve
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Graiti, W.; Yue, Z.; Foroughi, J.; Huang, X.-F.; Wallace, G.; Baughman, R.; Chen, J. Probe sensor using nanostructured multi-walled carbon nanotube yarn for selective and sensitive detection of dopamine. Sensors 2017, 17, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, G.; Cui, X.T.; Sheng, G.; Luo, X. Enhanced catalytic and dopamine sensing properties of electrochemically reduced conducting polymer nanocomposite doped with pure graphene oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackowska, K.; Krysinski, P. New trends in the electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3753–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasta, R.; Nicoletti, A.; Mostile, G.; Dibilio, V.; Sciacca, G.; Contrafatto, D.; Cicero, C.E.; Raciti, L.; Luca, A.; Zappia, M. Side effects induced by the acute levodopa challenge in Parkinson’s Disease and atypical parkinsonisms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, J.; Haumesser, J.; Beck, M.; Altschüler, J.; Kühn, A.; Nikulin, V.; Van Riesen, C. Differential effects of levodopa and apomorphine on neuronal population oscillations in the cortico-basal ganglia loop circuit in vivo in experimental parkinsonism. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 298, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janků, S.; Komendová, M.; Urban, J. Development of an online solid-phase extraction with liquid chromatography method based on polymer monoliths for the determination of dopamine. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4107–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rithesh Raj, D.; Prasanth, S.; Vineeshkumar, T.V.; Sudarsanakumar, C. Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic dopamine sensor using green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Weng, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.M. Synthesis of nitrogen and ironcontaining carbon dots, and their application to colorimetric and fluorometric determination of dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Qi, L.; Liu, Z.; Majeed, S.; Kitte, S.A.; Xu, G. Efficient lucigenin/thiourea dioxide chemiluminescence system and its application for selective and sensitive dopamine detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, F.; Ibrahim, F.; Sheribah, Z.; Alaa, H. Micellar HPLC-UV method for the simultaneous determination of levodopa, carbidopa and entacapone in pharmaceuticals and human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1091, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Pajooheshpour, N.; Jamali, B.; Amidi, S.; Hajian, A.; Khoshsafar, H. A novel electrochemical platform for sensitive and simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid based on Fe3O4SnO2Gr ternary nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2017, 131, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Taleat, Z.; Khoshroo, A.; Beitollahi, H.; Dehghani, H. Electrocatalytic oxidation and voltammetric determination of levodopa in the presence of carbidopa at the surface of a nanostructure based electrochemical sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ding, L.; Wang, Q.; Su, B. Differential pulse voltammetry detection of dopamine and ascorbic acid by permselective silica mesochannels vertically attached to the electrode surface. Analyst 2014, 139, 3926–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, Q. Protein detecting with smartphone-controlled electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for point-of-care applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Gao, F.; Wu, Q.-A.; Xu, P.-Y.; Wang, S.-S.; Gao, N.-N.; Wang, Q.-X. A highly sensitive dopamine sensor based on a polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide/Nafion nanocomposite. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, A.; Sohrabi, M. Selective simultaneous determination of levodopa and acetaminophen in the presence of ascorbic acid using a novel TiO2 hollow sphere/multi-walled carbon nanotube/poly-aspartic acid composite modified carbon paste electrode. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulia, S.; Cinzia, L.; Giovanna, M. Electrochemical Nanocomposite Single-Use Sensor for Dopamine Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3097. [Google Scholar]
- Uge, A.; Zeybek, D.K.; Zeybek, B. An electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of dopamine based on MWCNTs/CeO2 -PEDOT composite. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 813, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, H.; Li, M. Electrodeposition synthesis of a NiO/CNT/PEDOT composite for simultaneous detection of dopamine, serotonin, and tryptophan. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, C. Efficient and stable planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells based on WO_x/PEDOT:PSS composite hole transport layer. Electrochemistry 2016, 22, 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, N.; Ahmadiannamini, P.; Hoogenboom, R. Layer-by-layer preparation of polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for separation. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1817–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Liu, L.; Lee, P.S. Layer-by-layer assembly of PEDOT:PSS and WO3 nanoparticles: Enhanced electrochromic coloration efficiency and mechanism studies by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 174, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.; Rusa, M.; Hinestroza, J. Layer-by-layer deposition of polyelectrolyte nanolayers on natural fibres:cotton. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, S422–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J. Smartphone-Powered Electrochemical Dongle for Point-of-Care Monitoring of Blood β-Ketone. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8609–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Low, S.S.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based integrated voltammetry system for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid with graphene and gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, G.; Cui, G.; Zhou, X.; Liu, G.L. White blood cell counting on smartphone paper electrochemical sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, D.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based cyclic voltammetry system with graphene modified screen printed electrodes for glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, W.; Kricka, L.-J. Current and Emerging Trends in Point-of-Care Technology and Strategies for Clinical Validation and Implementation. Clin. Chem. 2020, 10, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ju, F.; Tao, C.L.; Shen, X.Y. Portable, low cost smartphone-based potentiostat system for the salivary α-amylase detection in stress paradigm. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1334–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Beitollahia, H.; Garkani-Nejadb, F.; Tajikc, S.; Ganjalid, M.-R. Voltammetric determination of acetaminophen and tryptophan using a graphite screen printed electrode modified with functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets within a Fe3O4@SiO2 nanocomposite. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.-W.; Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. A miniaturized electrochemical system for high sensitive determination of chromium(VI) by screen-printed carbon electrode with gold nanoparticles modification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeshin, L.; Pan, Y.-X.; Ji, D.-Z.; Li, Y.-R.; Lu, Y.-L.; He, Y.; Chen, Q.-M.; Liu, Q.-J. Smartphone-based portable electrochemical biosensing system for detection of circulating microRNA-21 in saliva as a proof-of-concept. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 308, 127718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.M.; Zeng, M.; Chen, Z.H. Synthesis and the Effect of Secondary Doping on Its Electrical Conductivity of PEDOT: PSS. Eng. Plast. Appl. 2019, 9, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, F.-F.; Cai, Y.-K.; Geng, X. Microstructure Change and Properties in Process of Synthesis for PEDOT-PSS Film. J. Funct. Polym. 2013, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Gao, Q.; Song, Y.-H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.-R. Layer-by-layer assembled multilayer films of redox polymers for electrocatalytic oxidation of ascorbic acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Y. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using high-performance screen-printed graphene electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.R. An electrochemical sensor for dopamine based on poly(o-phenylenediamine) functionalized with electrochemically reduced graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3706–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-M.; Yang, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lien, C.-H.; Tien, H.-W.; Hsiao, S.-T.; Liao, W.-H.; Tsai, H.-P.; Chang, C.-L.; Ma, C.-C.M. Controllable synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene and its effect on the simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Carbon 2013, 59, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, A.; Chen, S.-M. Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene-co-(5-amino-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid)) (PEDOT-PANS) film modified glassy carbon electrode for selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 596, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghill, K.E.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: A perspective and an evaluation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 5, 1246–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, L.-R.; Chen, W.; Yang, X.-J.; Jin, B.; Zheng, L.-M.; Xia, X.-H. 3-mercaptopropylphosphonic acid modified gold electrode for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 75, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanarat, P.; Dungchai, W.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-modified electrochemical paper-based analytical device for determination of dopamine levels in biological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 744, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Q.; Lai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; Yao, S. A double signal amplification platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen based on a nanocomposite of ferrocene thiolate stabilized Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles with graphene sheet. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Du, J.; Wang, H.W.; Zou, C.E.; Jiang, F.X.; Yang, P.; Du, Y.K. A facile electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and Au nanoplates modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-F.; Guo, C.-R.; Zhou, J.-J.; Zhu, P.-P.; Mou, Q. Study on dopamine electrochemical biosensor based on RuO2/graphene. Liaoning Chem. Ind. 2017, 45, 846–848. [Google Scholar]



| Modified Electrodes | Linear Range (μM) | Detection Limit (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS/CS–G/SPE (Our work) | 0.05–70 | 0.29 |
| SDS/SPCE [43] | 1–100 | 0.37 |
| Fe3O4@Au-Gr/GCE [44] | 0.05–50 | 0.65 |
| Au/RGO/GCE [45] | 6.8–41 | 1.4 |
| RuO2/RGO/GCE [46] | 3–200 | 875 |
| AuNPs@PANI/GSPE [17] | 1–100 | 0.86 |
| PANI-rGO-NF [15] | 0.05–180 | 0.024 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Ju, F.; Li, G.; Ma, L. Smartphone-Based Electrochemical Potentiostat Detection System Using PEDOT: PSS/Chitosan/Graphene Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Dopamine Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102781
Shen X, Ju F, Li G, Ma L. Smartphone-Based Electrochemical Potentiostat Detection System Using PEDOT: PSS/Chitosan/Graphene Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Dopamine Detection. Sensors. 2020; 20(10):2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102781
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xiaoyan, Feng Ju, Guicai Li, and Lei Ma. 2020. "Smartphone-Based Electrochemical Potentiostat Detection System Using PEDOT: PSS/Chitosan/Graphene Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Dopamine Detection" Sensors 20, no. 10: 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102781
APA StyleShen, X., Ju, F., Li, G., & Ma, L. (2020). Smartphone-Based Electrochemical Potentiostat Detection System Using PEDOT: PSS/Chitosan/Graphene Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Dopamine Detection. Sensors, 20(10), 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102781





