Evanescent-Wave Fiber Optic Sensing of the Anionic Dye Uranine Based on Ion Association Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of CATB Concentration
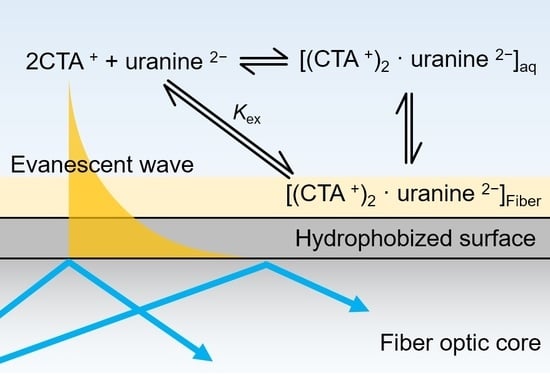
3.2. Distribution Equilibrium Model
Kf = [(CTA+)2 · uranine2−]aq / [CTA+]2 [uranine2−]
{(CTA+)2 · uranine2−}aq ⇌ {(CTA+)2 · uranine2−}fiber ;
3.3. Adsorption Model
3.4. Regeneration of the Fiber Sensor
3.5. Determination of Uranine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3269–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, C.; Burke, C.S.; MacCraith, B.D. Optical Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 400–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-D.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2008–2012). Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2013–2015). Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2015–2019). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 397–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, H.; Mohammad, A.; Akram, M. Recent Progress in Optical Chemical Sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 16522–16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Punjabi, N.; Satija, J.; Mukherji, S. Evanescent Wave Absorption Based Fiber-Optic Sensor—Cascading of Bend and Tapered Geometry for Enhanced Sensitivity. In Smart Sensors, Measurement and Instrumentation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 25–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, T.-S.; Chu, C.-S.; Lo, Y.-L. Highly sensitive optical fiber oxygen sensor using Pt(II) complex embedded in sol–gel matrices. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2006, 119, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Luo, M.; Peng, G.; Cheng, W. Broad range pH sensor based on sol-gel entrapped indicators on fibre optic. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhu, D.Q.; Duan, C.F.; Wang, J.W.; Guan, Y.F. Small-volume fiber-optic evanescent-wave absorption sensor for nitrite determination. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan Pillai, A.; Varghese, B.; Madhusoodanan, K.N. Design and development of novel sensors for the determination of fluoride in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, B.; Gu, C.; He, M. Aptamer-based detection of melamine in milk using an evanescent wave fiber sensor. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4871–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Wu, S.; He, M.; Tong, T.; Shi, H. Ultrasensitive quantum dots-based DNA detection and hybridization kinetics analysis with evanescent wave biosensing platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2390–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, R.; Sai, V.V.R.; Thakare, K.; Dhawangale, A.; Kundu, T.; Titus, S.; Verma, P.K.; Mukherji, S. Evanescent wave absorbance based fiber optic biosensor for label-free detection of E. coli at 280nm wavelength. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3367–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Imai, K.; Tan, S.Y.; Yong, Y.T.; Rahman, F.A.; Hata, N.; Taguchi, S.; Ueda, A.; Kuramitz, H. Fundamental Study on the Development of Fiber Optic Sensor for Real-time Sensing of CaCO3 Scale Formation in Geothermal Water. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, T.; Orii, T.; Ueda, A.; Ozawa, A.; Kuramitz, H. Fiber Optic Sensor for Real-Time Sensing of Silica Scale Formation in Geothermal Water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, K.; Okazaki, T.; Hata, N.; Taguchi, S.; Sugawara, K.; Kuramitz, H. Simultaneous multiselective spectroelectrochemical fiber-optic sensor: Demonstration of the concept using methylene blue and ferrocyanide. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Shiokawa, E.; Orii, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hata, N.; Taguchi, A.; Sugawara, K.; Kuramitz, H. Simultaneous Multiselective Spectroelectrochemical Fiber-Optic Sensor: Sensing with an Optically Transparent Electrode. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2440–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Imai, K.; Sultana, A.; Hata, N.; Taguchi, S.; Kuramitz, H. Development of a Fiber Optic Evanescent Wave Sensor for Anionic Surfactants Using Ethyl Violet. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toei, K. Ion-association reagents. A review. Anal. Sci. 1987, 3, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watarai, H. Fundamentals in Solvent Extraction Processes, Thermodynamic, Kinetic, and Interfacial Aspects. In Solvent Extraction and Liquid Membranes; Aguilar, M., Cortina, J.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 19–57. [Google Scholar]
- Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. Japanese Indutrial Standards K0102; Japanese Industrial Standards Committee: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mushahida-AL-Noor, S.; Murashima, R.; Okazaki, T.; Taguchi, S.; Kuramitz, H.; Hata, N. Micro-organic Ion-associate Phase Extraction/micro-volume Back-extraction for the Preconcentration and GF-AAS Determination of Cadmium, Nickel and Lead in Environmental Water. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 1445–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, N.; Yuwatini, E.; Ando, K.; Yamada, M.; Kasahara, I.; Taguchi, S. Micro-organic Ion-associate Phase Extraction via in situ Fresh Phase Formation for the Preconcentration and Determination of Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in River Water by HPLC. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, N.; Kasahara, I.; Taguchi, S. Micro-phase Sorbent Extraction for Trace Analysis via in situ Sorbent Formation: Application to the Preconcentration and the Spectrophotometric Determination of Trace Ammonia. Anal. Sci. 2002, 18, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, S.; Nakayama, K.; Hata, N.; Kasahara, I.; Goto, K. Membrane filters for concentration of trace elements in water: Distribution of 2-(2-pyridylazo)-5-diethylaminophenol between the membrane filter and the aqueous phases. Analyst 1994, 119, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Fujimoto, N.; Okamoto, T.; Ando, Y.; Watanabe, H. Tumorigenicity study of phloxine (FR 104) in B6C3F1 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara-Licudine, J.P.; Kawate, M.K.; Li, Q.X. Method for the Analysis of Phloxine B, Uranine, and Related Xanthene Dyes in Soil Using Supercritical Fluid Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licudine, J.A.; McQuate, G.T.; Cunningham, R.T.; Liquido, N.J.; Li, Q.X. Efficacy and residues of phloxine B and uranine for the suppression of Mediterranean fruit fly in coffee fields. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, T.L.; Mundie, T.G.; Ross, J.H.; Heitz, J.R. Synergistic Effect of Fluorescein on Rose Bengal-Induced, Light-Dependent Toxicity. Environ. Entomol. 1981, 10, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, I.; Bucher, K. Geothermal Energy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Foguel, M.V.; Ton, X.-A.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. A molecularly imprinted polymer-based evanescent wave fiber optic sensor for the detection of basic red 9 dye. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, S.; Maitz, M.; Hänsel, S.; Renner, L.D.; Werner, C. Analyzing the antiseptic capacity of silver-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol)–heparin hydrogels after human whole blood exposure. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Information. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/docs/Sigma/Product_Information_Sheet/1/sl2pis.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- De Sá, A.; Abreu, A.S.; Moura, I.; Machado, A.V. Polymeric materials for metal sorption from hydric resources. In Water Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 289–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Tang, T.; Jed Harrison, D.; Lee, W.E.; Jemere, A.B. A regenerating self-assembled gold nanoparticle-containing electrochemical impedance sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FT200EMT Spec Sheet. Available online: https://www.thorlabs.co.jp/drawings/ae728e64c3999cfd-3FE1C16E-BAFF-B1B0-9E0155A9277DFD9E/FT200EMT-SpecSheet.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Okazaki, T.; Seto, R.; Watanabe, T.; Ueda, A.; Kuramitz, H. U-Shaped Polymer Cladding and Hetero-Core Fiber Optic Sensors for Monitoring Scale Formation in Geothermal Brine. Anal. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okazaki, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kuramitz, H. Evanescent-Wave Fiber Optic Sensing of the Anionic Dye Uranine Based on Ion Association Extraction. Sensors 2020, 20, 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102796
Okazaki T, Watanabe T, Kuramitz H. Evanescent-Wave Fiber Optic Sensing of the Anionic Dye Uranine Based on Ion Association Extraction. Sensors. 2020; 20(10):2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102796
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkazaki, Takuya, Tomoaki Watanabe, and Hideki Kuramitz. 2020. "Evanescent-Wave Fiber Optic Sensing of the Anionic Dye Uranine Based on Ion Association Extraction" Sensors 20, no. 10: 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102796
APA StyleOkazaki, T., Watanabe, T., & Kuramitz, H. (2020). Evanescent-Wave Fiber Optic Sensing of the Anionic Dye Uranine Based on Ion Association Extraction. Sensors, 20(10), 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102796