Temperature and Torque Measurements of Switched Reluctance Actuator with Composite or Laminated Magnetic Cores
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
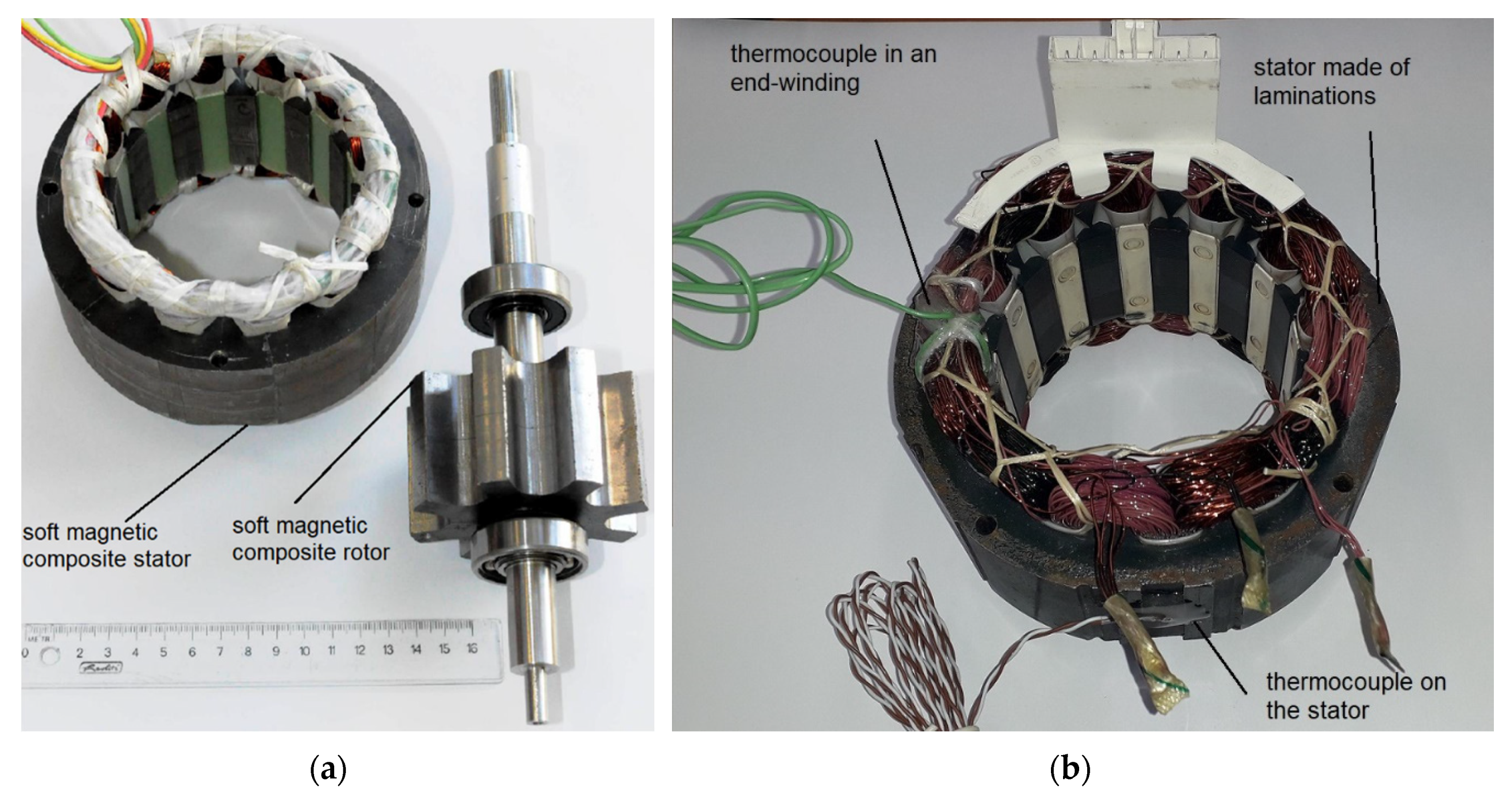
2.1. Soft Magnetic Composites for SRM
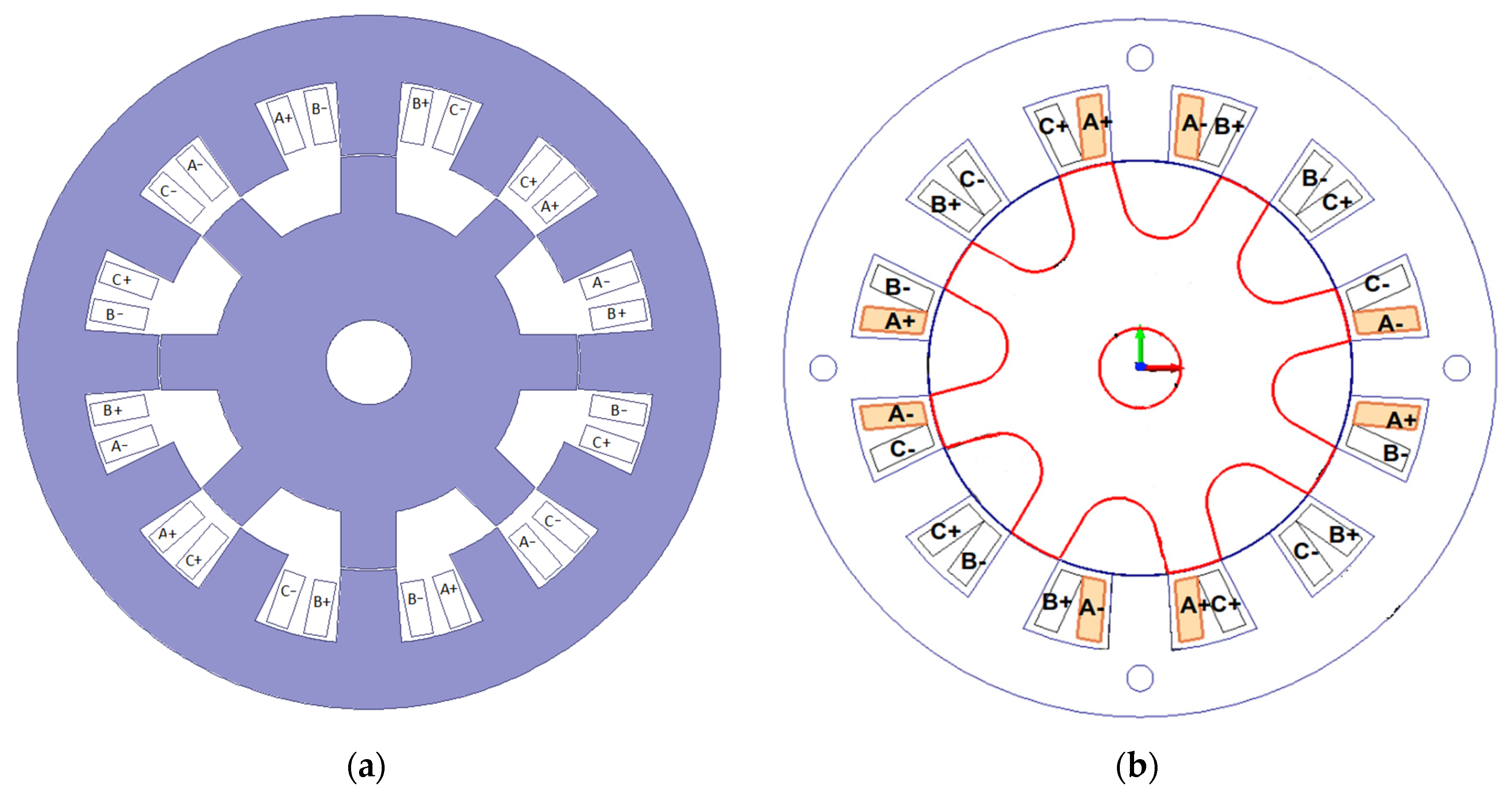
2.2. SRM Motor Design
2.3. Methodology of SRM Measurements
3. Results
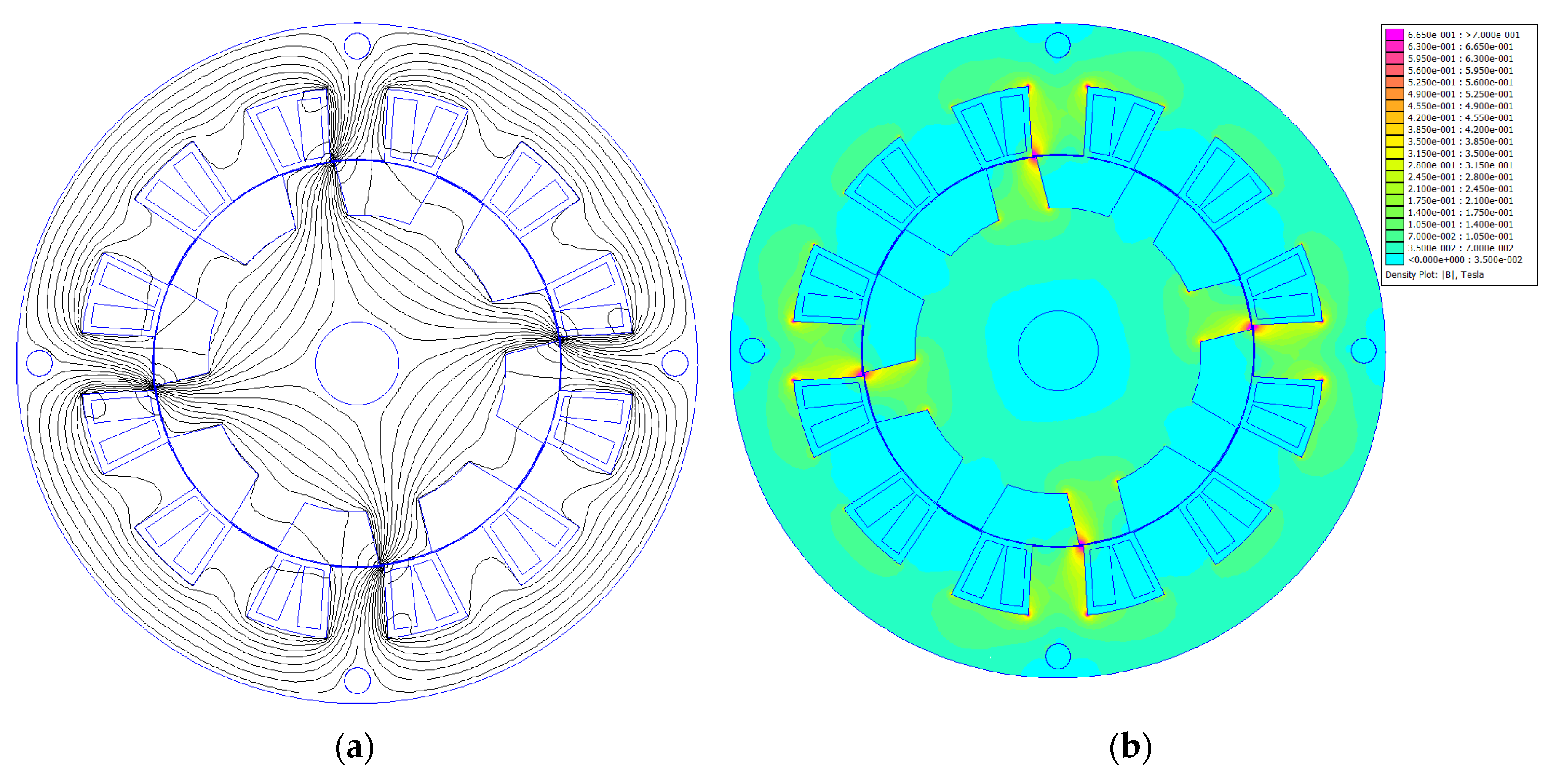
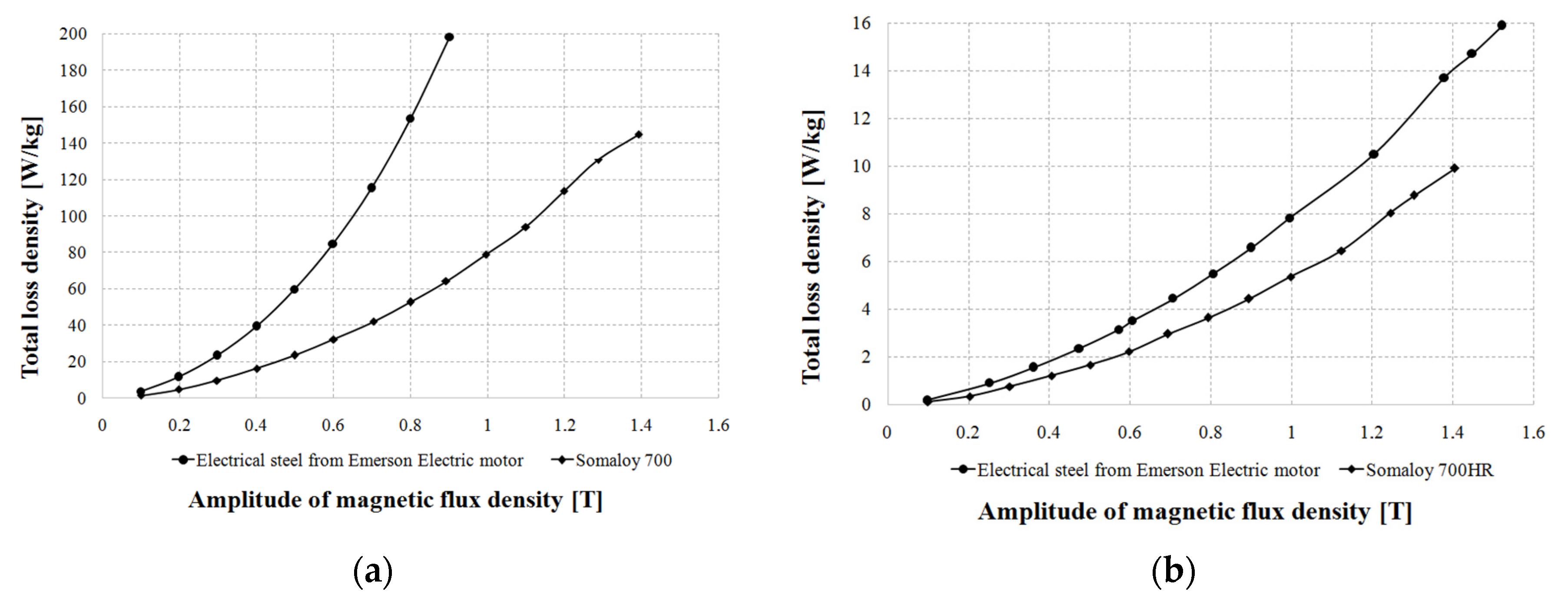
3.1. Measurement of Magnetization and Iron Loss Characteristics
3.2. Measurements of Drive Performance
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, T.J.E. Brushless Permanent-Magnet and Reluctance Motor Drives; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; pp. 149–189. [Google Scholar]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Rezaei, N.; Lowther, D.A.; Rahman, T. Many-objective shape optimisation of IPM motors for electric vehicle traction. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2019, 60, S149–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Palka, R.; Paplicki, P.; Szkolny, S. Design optimization of a permanent-magnet excited synchronous machine for electrical automobiles. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2012, 39, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Przybylski, M.; Rezaei, N.; Slusarek, B.; Wiak, S. Field-based analysis and optimal shape synthesis of switched reluctance motors. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2018, 452, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Riba, J.-R.; López-Torres, C.; Romeral, L.; Garcia, A. Rare-earth-free propulsion motors for electric vehicles: A technology review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widmer, J.D.; Martin, R.; Kimiabeigi, M. Electric vehicle traction motors without rare earth magnets. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2015, 3, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Uniquely Designed and Technologically Advanced Washing Machine Drive. Available online: http://www.srdrives.com/washing-machine.shtml (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Randall, S.P.; Sudgen, D.M.; Vail, W.; Brown, G.T. Rotor Position Encoder Having Features in Decodable Angular Positions. U.S. Patent 5,539,293, 23 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrollahi, H.; Janghorban, K. Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 189, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Périgo, E.A.; Weidenfeller, B.; Kollár, P.; Füzer, J. Past, present and future of soft magnetic composites. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 1–142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lei, G.; Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. Development of a new low-cost 3-D flux transverse flux FSPMM with soft magnetic composite cores and ferrite magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lei, G.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Comparative study of small electrical machines with soft magnetic composite cores. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Jang, G.; Kim, J.; Ahn, J.; Baek, C.; Choi, J. Comparison of axial flux permanent magnet synchronous machines with electrical steel core and soft magnetic composite core. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Kim, W. Electromagnetic analysis and steady-state performance of double-sided flat linear motor using soft magnetic composite. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y. Design considerations of PM transverse flux machines with soft magnetic composite cores. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Lei, G.; Zhu, J.; Guo, Y. Design optimization of a permanent magnet claw pole motor with soft magnetic composite cores. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenin, N.C. Experimentation of three phase outer rotating switched reluctance motor with soft magnetic composite materials. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 12, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Nikam, S.P.; Fernandes, B.G. Design of soft magnetic composite based modular four phase SRM for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines, Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, K.; Karthikeyen, R.; Arumugam, R. Analysis and characterization of a switched reluctance machine using soft magnetic composite material. J. Electr. Eng. 2011, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyen, R.; Vijayakumar, K.; Arumugam, R. Soft magnetic composite switched reluctance generator—Fabrication and analysis. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 383–390, 5516–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrenson, P.J.; Stephenson, J.M.; Blenkinsop, P.T.; Corda, J.; Fulton, N.N. Variable-speed switched reluctance motors. IEE Proc. 1980, 127, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- Materu, P.N.; Krishnan, R. Estimation of switched reluctance motor losses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 668–679. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, Y.; Miller, T.J.E. A new approach to calculating core losses in the SRM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Raulin, V.; Radun, A.; Husain, I. Modeling of losses in switched reluctance machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Charton, J.T.; Corda, J.; Hughes, A.; Stephenson, J.M.; McClelland, M.L. Modelling and prediction of iron loss with complex flux waveforms. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2005, 152, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Ganji, B.; Carstensen, C.E.; De Doncker, R.W. Loss prediction in switched reluctance motors using finite element method. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2009, 19, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, M.; Andrada, P.; Blanqué, B.; Martinez, E.; Perat, J.I.; Sanchez, J.A. Method for estimating core losses in switched reluctance motors. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 2010, 21, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, L.; Burkhart, B.; De Doncker, R.W. Fast iron loss and thermal prediction method for power density and efficiency improvement in switched reluctance machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4463–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabianski, B.; Zawirski, K. Switched reluctance motor drive embedded control system. In Mechatronics—Recent Technological and Scientific Advances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Fabianski, B. Energetic properties of a new, iron powder based switched reluctance motor drive. In Mechatronics—Recent Technological and Scientific Advances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Höganäs Web Page. Available online: https://www.hoganas.com/en/powder-technologies/soft-magnetic-composites/products/coated-powders-for-electromagnetic-applications/ (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- Przybylski, M.; Ślusarek, B.; Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Wiak, S. Thermal measurements of the drive with a switched reluctance motor with a magnetic circuit made of soft magnetic composite. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nancy, France, 29–31 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FEMM 4.2. Software. Available online: www.femm.info (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- Przybylski, M. Modelling and analysis of the low-power 3-phase switched reluctance motor. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2019, 68, 443–454. [Google Scholar]
- Di Barba, P.; Wiak, S. MEMS: Field Models and Optimal Design; Springer: Basel Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–185. [Google Scholar]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Przybylski, M.; Rezaei, N.; Ślusarek, B.; Wiak, S. Geometry optimization for a class of switched-reluctance motors: A bi-objective approach. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2018, 57, S107–S122. [Google Scholar]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Wiak, S.; Przybylski, M.; Slusarek, B. Optimization and measurements of switched reluctance motors exploiting soft magnetic composite. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2018, 57, S83–S93. [Google Scholar]


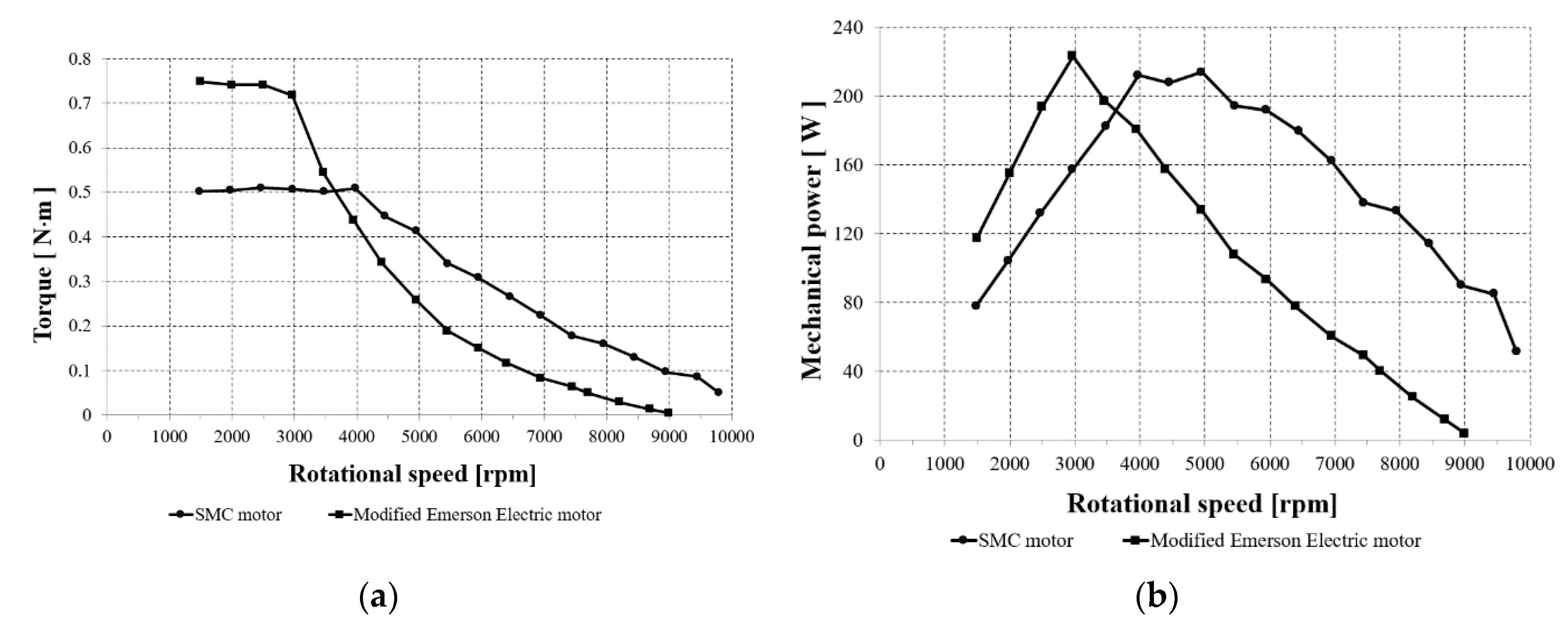
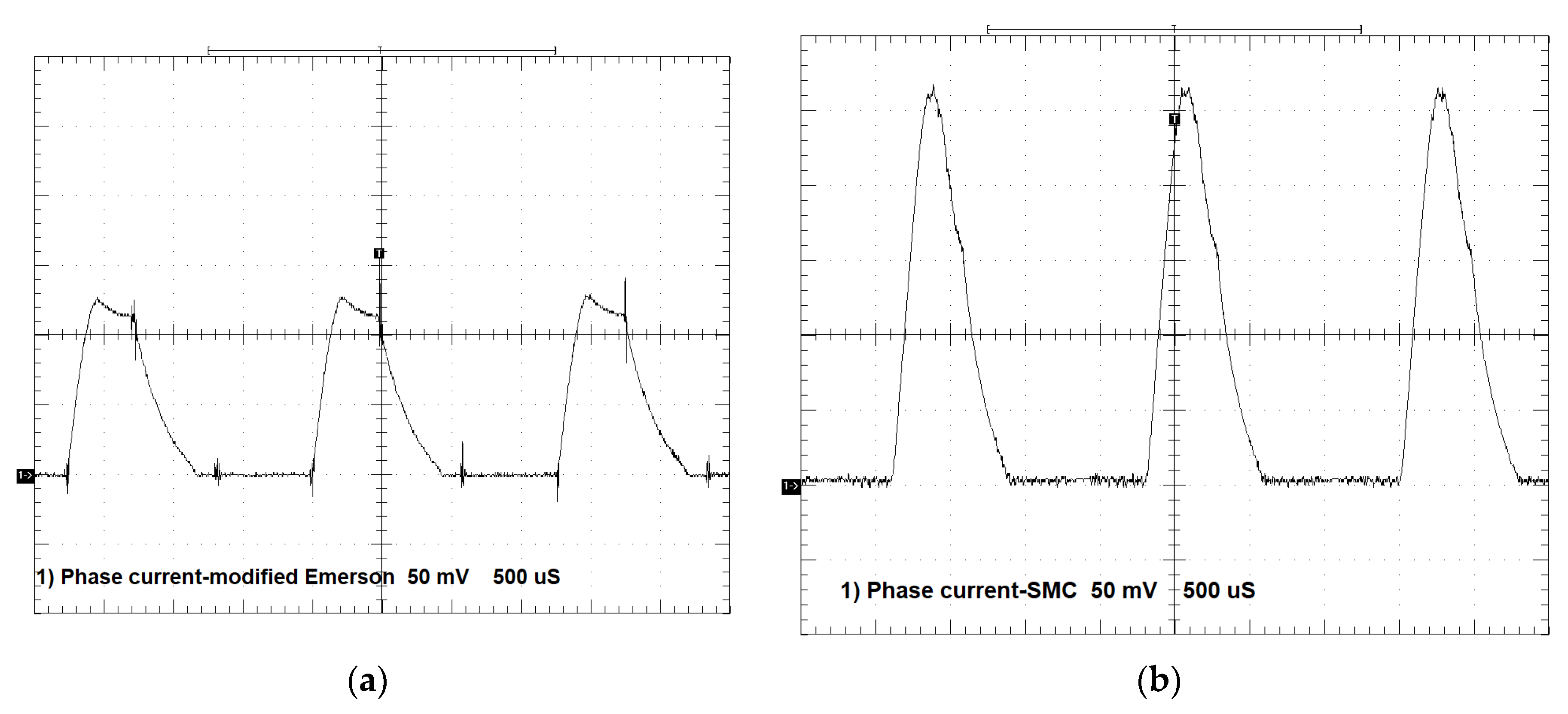
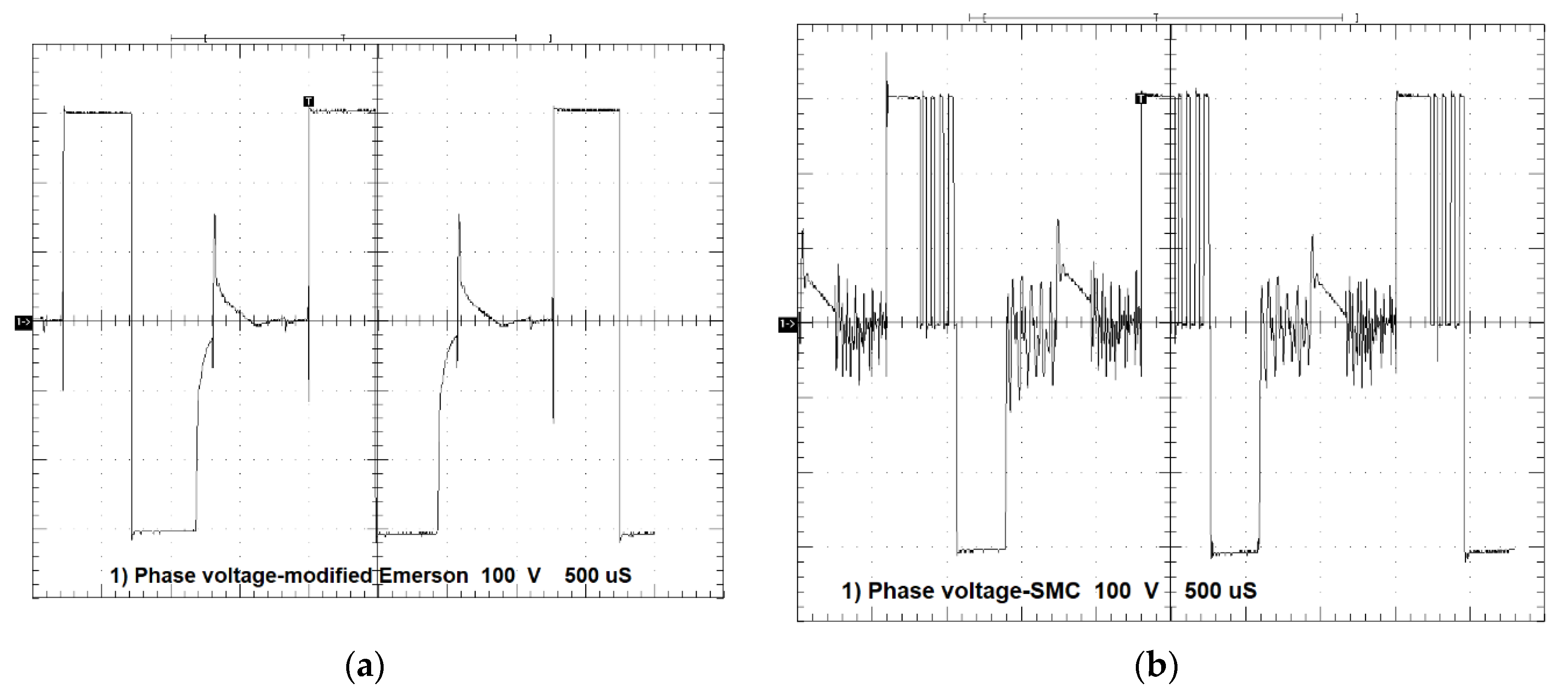
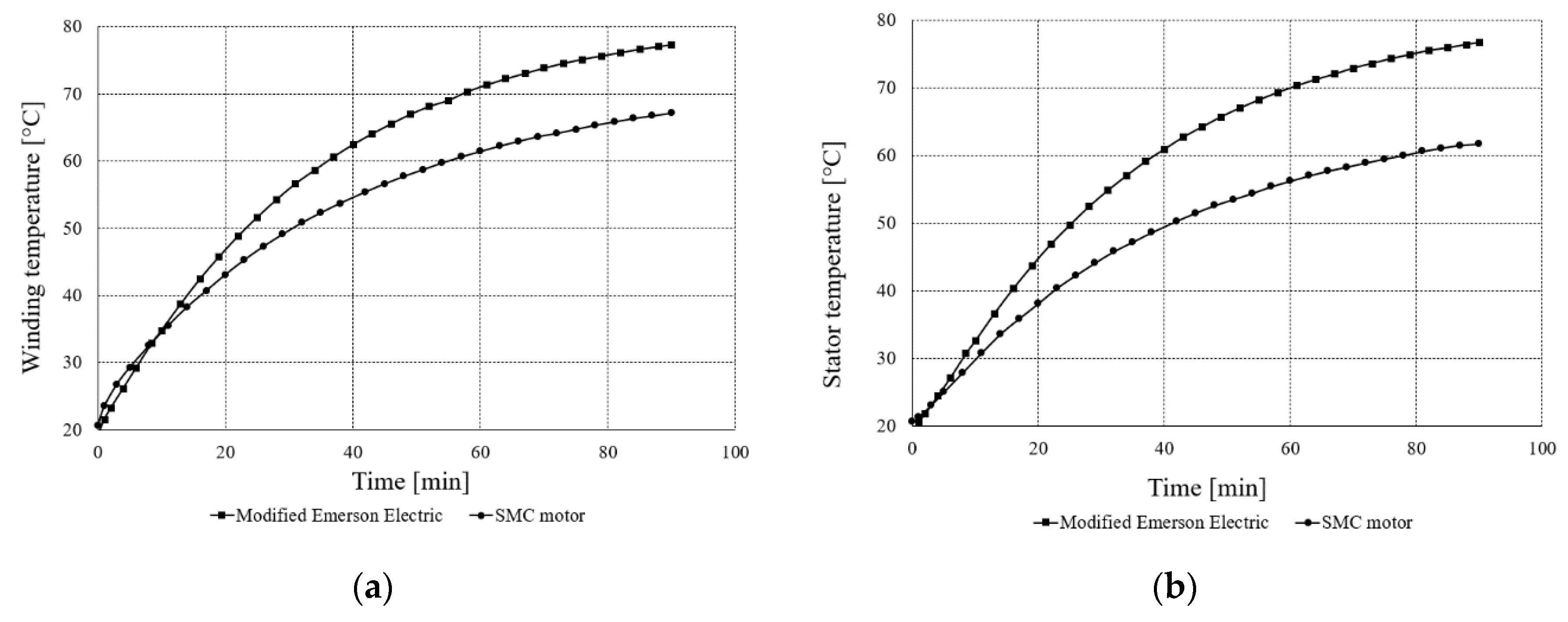
| Parameter | Modified Emerson Electric Motor | Prototype Made of SMCs |
|---|---|---|
| DC supply voltage | 310 V | 310 V |
| Max. rotational speed | 9000 rpm | 9800 rpm |
| External stator diameter | 139.5 | 139.5 |
| External rotor diameter | 83 mm | 83 mm |
| Axial length of magnetic core | 47.3 mm | 46.6 mm |
| Air gap length | 0.4 mm | 0.25 mm |
| Number of phases | 3 | 3 |
| Number of stator poles | 12 | 12 |
| Number of rotor poles | 8 | 8 |
| Material of stator core | Steel lamination | Somaloy 700 |
| Material of rotor core | Steel lamination | Somaloy 700HR |
| Phase resistance | 8.4 ± 0.3 Ω | 5.7 ± 0.3 Ω |
| Coil turns | 172 | 134 |
| Wire diameter | 0.56 mm | 0.60 mm |
| Phase inductance—aligned | 242 mH | 139 mH |
| Phase inductance—unaligned | 36 mH | 24 mH |
| Stator pole angle | 15.5° | 15.5° |
| Rotor pole angle | 16° | 16° |
| Type of Motor | DC Phase Voltage [V] | RMS Current [A] | Average Current [A] | Peak Current [A] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Emerson Electric | 310 ± 4 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.09 |
| SMC | 310 ± 4 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 2.75 ± 0.14 |
| Type of Motor | AC Supply Voltage [V] | AC IRMS [A] | Input Power [W] | Output Power [W] | Efficiency [%] | Current THD [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Emerson Electric | 230 ± 1 | 1.83 ± 0.01 | 256 ± 1 | 161 ± 8 | 63 ± 4 | 126 |
| SMC | 230 ± 1 | 1.71 ± 0.01 | 229 ± 1 | 161 ± 8 | 71 ± 4 | 134 |
| Type of Motor | Input Power [W] | Output Power [W] | Copper Loss [W] | Iron Loss [W] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Emerson Electric | 256 ± 1 | 161 ± 8 | 11.3 ± 0.8 | 83.7 ± 8.2 |
| SMC | 229 ± 1 | 161 ± 8 | 15.8 ± 1.1 | 52.2 ± 8.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Przybylski, M.; Ślusarek, B.; Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Wiak, S. Temperature and Torque Measurements of Switched Reluctance Actuator with Composite or Laminated Magnetic Cores. Sensors 2020, 20, 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113065
Przybylski M, Ślusarek B, Di Barba P, Mognaschi ME, Wiak S. Temperature and Torque Measurements of Switched Reluctance Actuator with Composite or Laminated Magnetic Cores. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113065
Chicago/Turabian StylePrzybylski, Marek, Barbara Ślusarek, Paolo Di Barba, Maria Evelina Mognaschi, and Sławomir Wiak. 2020. "Temperature and Torque Measurements of Switched Reluctance Actuator with Composite or Laminated Magnetic Cores" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113065
APA StylePrzybylski, M., Ślusarek, B., Di Barba, P., Mognaschi, M. E., & Wiak, S. (2020). Temperature and Torque Measurements of Switched Reluctance Actuator with Composite or Laminated Magnetic Cores. Sensors, 20(11), 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113065







