Recent Advances in the Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 and Its Pertinent Metabolite Aflatoxin M1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Aptamers
3. Electrochemical Techniques for AFs Detection
4. Electrochemical Aptasensors for AFs Detection
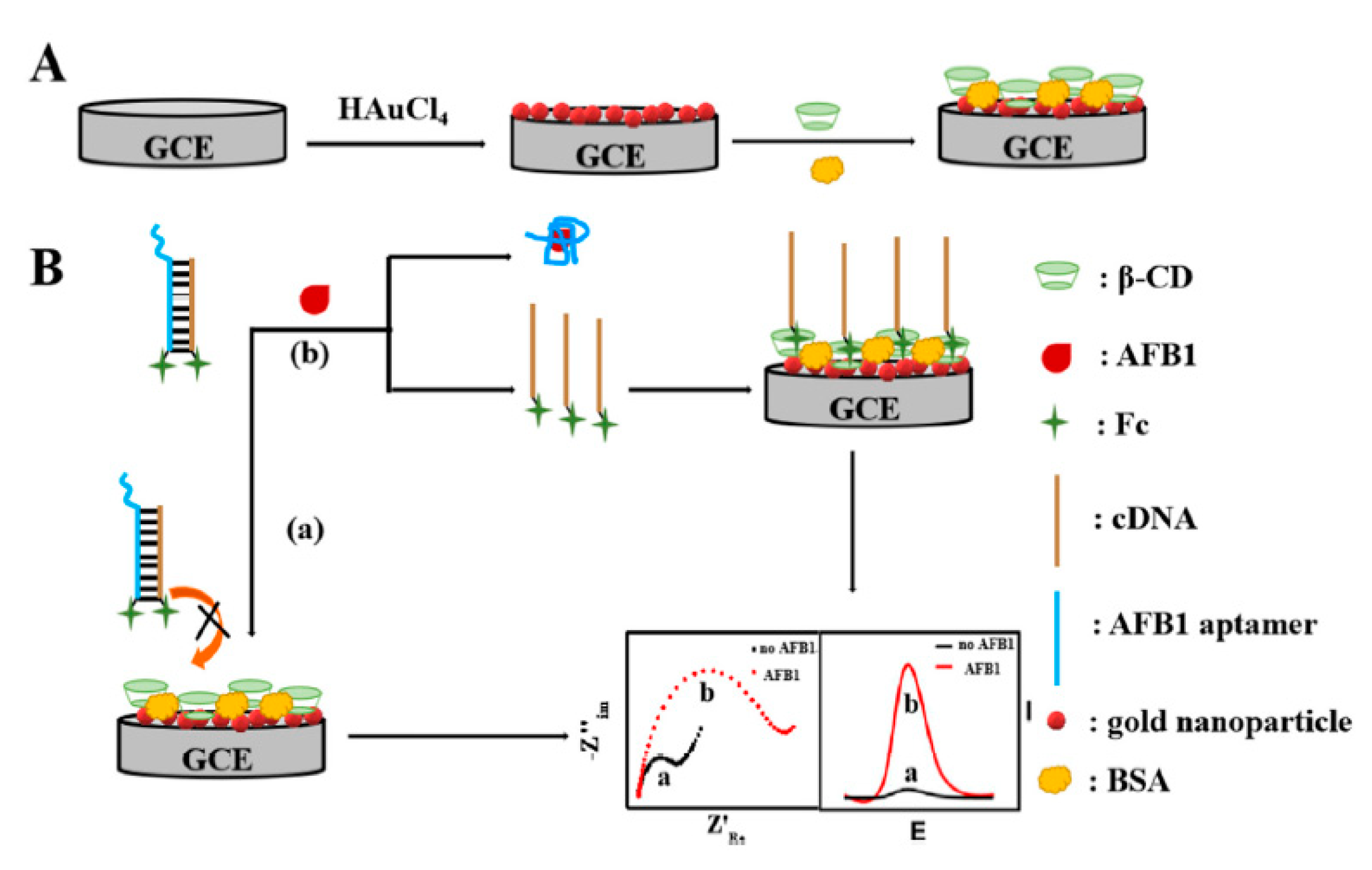
4.1. GCE-Based Aptasensors
4.2. SPE-Based Aptasensors
4.3. Gold Electrode-Based Aptasensors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evtugyn, G.; Porfireva, A.; Stepanova, V.; Sitdikov, R.; Stoikov, I.; Nikolelis, D.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical aptasensor based on polycarboxylic macrocycle modified with neutral red for aflatoxin B1 detection. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Pan, M.; Hu, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Quartz crystal microbalance sensor based on covalent organic framework composite and molecularly imprinted polymer of poly (o-aminothiophenol) with gold nanoparticles for the determination of aflatoxin B1. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtugyn, G.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical Immuno-and Aptasensors for Mycotoxin Determination. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abnous, K.; Danesh, N.M.; Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Emrani, A.S.; Zolfaghari, R.; Taghdisi, S.M. A new amplified π-shape electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Calderón, A.; Contreras-Medina, L.M.; Muñoz-Huerta, R.F.; Millán-Almaraz, J.R.; González, R.G.G.; Torres-Pacheco, I. Methods for Detection and Quantification of Aflatoxins; Intech Open: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Dors, G.C.; Caldas, S.S.; Feddern, V.; Bemvenuti, R.H.; Hackbart, H.C.S.; Souza, M.M.; Furlong, E. Aflatoxins: Contamination, Analysis and Control; Intech Open: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 416–438. [Google Scholar]
- Zejli, H.; Goud, K.Y.; Marty, J.L. An electrochemical aptasensor based on polythiophene-3-carboxylic acid assisted methylene blue for aflatoxin B1 detection. Sens. Biosensing Res. 2019, 25, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh, P.; Hejazi, M.; de la Guardia, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Recent advances in nanomaterial-mediated bio and immune sensors for detection of aflatoxin in food products. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2017, 87, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E.; Zentek, J.; Razzazi, E. Review on sample preparation strategies and methods used for the analysis of aflatoxins in food and feed. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 508–524. [Google Scholar]
- Stroka, J.; Van Otterdijk, R.; Anklam, E. Immunoaffinity column clean-up prior to thin-layer chromatography for the determination of aflatoxins in various food matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 904, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, Y.; Saito, K.; Hanioka, N.; Narimatsu, S.; Kataoka, H. Determination of aflatoxins in food samples by automated on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4416–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.D.; Da Silva, J.L.G.; Caldas, E.D. Simultaneous analysis of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, M1 and ochratoxin A in breast milk by high-performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence after liquid–liquid extraction with low temperature purification (LLE–LTP). J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinckaya, E.; Kınık, Ö.; Sezgintürk, M.K.; Altuğ, Ç.; Akkoca, A. Development of an impedimetric aflatoxin M1 biosensor based on a DNA probe and gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3806–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.S.; Wei, M.; Wei, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Electrochemical aptasensor for aflatoxin B1 based on smart host-guest recognition of β-cyclodextrin polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Peng, X.; Fu, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Recent advances in the development of electrochemical aptasensors for detection of heavy metals in food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 147, 111777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdian, A.; Fooladi, E.; Rouhbakhsh, Z. Recent progress in the development of recognition bioelements for polychlorinated biphenyls detection: Antibodies and aptamers. Talanta 2019, 202, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patris, S.; Vandeput, M.; Kauffmann, J.M. Antibodies as target for affinity biosensors. TrAC Trends. Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.S.; Kumar, V.; Aggarwal, N.K. Aptamers: Biotechnological Applications of a Next Generation Tool, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Yang, S. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Teng, J.; Cheng, L.; Ye, Y.; Pan, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, W. Hetero-enzyme-based two-round signal amplification strategy for trace detection of aflatoxin B1 using an electrochemical aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yu, Z.; Han, X.; Lai, R.Y. Electrochemical aptamer-based sensors for food and water analysis: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1051, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Jia, N. Highly sensitive electrochemical impedance spectroscopy immunosensor for the detection of AFB1 in olive oil. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, G.; Shi, H.; Liu, M.; Li, Z. A highly selective electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based aptasensor for sensitive detection of acetamiprid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Upadhyay, S.S.; Rawool, C.R.; Punde, N.S.; Rajpurohit, A.S. Voltammetric techniques for the analysis of drugs using nanomaterials based chemically modified electrodes. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 15, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meronard, K.; Josowicz, M.; Saheb, A. Voltammetric Label-free Detection of DNA Hypermethylation Using Polypyrrole-modified Microelectrode Array. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, R.; Radhapyari, K.; Jadon, N.; Agarwal, S. Voltammetric techniques for the assay of pharmaceuticals—A review. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 408, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, P.F.P.; Vieira, E.G.; Cumba, L.R.; Paim, L.L.; Nakamura, A.P.R.; Andrade, R.D.A.; Ribeiro, D. Voltammetric techniques for pesticides and herbicides detection-an overview. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 3418–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, M.; McCreery, R.L. In situ laser activation of glassy carbon electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 2745–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, G.S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z. A novel reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide/polyaniline nanocomposite-based electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B1. Analyst 2018, 143, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolko, V.; Shurpik, D.; Porfireva, A.; Evtugyn, G.; Stoikov, I.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical aptasensor based on poly (neutral red) and carboxylated pillar [5] arene for sensitive determination of aflatoxin M1. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, V.; Smolko, V.; Gorbatchuk, V.; Stoikov, I.; Evtugyn, G.; Hianik, T. DNA-Polylactide Modified Biosensor for Electrochemical Determination of the DNA-Drugs and Aptamer-Aflatoxin M1 Interactions. Sensors 2019, 19, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goud, K.Y.; Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Satyanarayana, M.; Gobi, K.V.; Marty, J.L. An electrochemical aptasensor based on functionalized graphene oxide assisted electrocatalytic signal amplification of methylene blue for aflatoxin B1 detection. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istamboulié, G.; Paniel, N.; Zara, L.; Granados, L.R.; Barthelmebs, L.; Noguer, T. Development of an impedimetric aptasensor for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, K.Y.; Catanante, G.; Hayat, A.; Satyanarayana, M.; Gobi, K.V.; Marty, J.L. Disposable and portable electrochemical aptasensor for label free detection of aflatoxin B1 in alcoholic beverages. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sharma, R.; Singh, D. Immobilized aptamer on gold electrode senses trace amount of aflatoxin M1. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalalian, S.H.; Ramezani, M.; Danesh, N.M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin M1 based on target-induced immobilization of gold nanoparticles on the surface of electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Qian, J.; An, K.; Ren, C.; Lu, X.; Hao, N.; Wang, K. Fabrication of magnetically assembled aptasensing device for label-free determination of aflatoxin B1 based on EIS. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 108, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aissa, S.B.; Mars, A.; Catanante, G.; Marty, J.L.; Raouafi, N. Design of a redox-active surface for ultrasensitive redox capacitive aptasensing of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Talanta 2019, 195, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvolini, G.; Lettieri, M.; Tassoni, L.; Gastaldello, S.; Grillo, M.; Maran, C.; Marrazza, G. Electrochemical enzyme-linked oligonucleotide array for aflatoxin B1 detection. Talanta 2019, 203, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, G.; Spinella, K.; Poturnayová, A.; Šnejdárková, M.; Mosiello, L.; Hianik, T. Detection of aflatoxin B1 by aptamer-based biosensor using PAMAM dendrimers as immobilization platform. Food Control 2015, 52, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetis, S.; Nikolelis, D.; Hianik, T. Label-free and redox markers-based electrochemical aptasensors for aflatoxin M1 detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, G.; Li, X.; Cui, F.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, H. Aflatoxin B1 electrochemical aptasensor based on tetrahedral DNA nanostructures functionalized three dimensionally ordered macroporous MoS2–AuNPs film. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 17551–17559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleat, Z.; Khoshroo, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M. Screen-printed electrodes for biosensing: A review (2008–2013). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorga, S.E.; Hu, L.X.; Marsili, E.; Huang, Y. Ordered micropillar array gold electrode increases electrochemical signature of early biofilm attachment. Mater. Des. 2020, 185, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hong, K.; Suh, J.M.; Lee, T.H.; Kwon, O.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Jang, H.W. Facile synthesis of monodispersed Pd nanocatalysts decorated on graphene oxide for reduction of nitroaromatics in aqueous solution. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2019, 45, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Suh, J.M.; Lee, T.H.; Cha, J.H.; Choi, J.-W.; Jang, H.W.; Varma, R.S.; Shokouhimehr, M. Copper oxide–graphene oxide nanocomposite: Efficient catalyst for hydrogenation of nitroaromatics in water. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shokouhimehr, M.; Yu, S.H.; Lee, D.C.; Ling, D.; Hyeon, T.; Sung, Y.E. Metal hexacyanoferrate nanoparticles as electrode materials for lithium ion batteries. Nanosci. Nanotech. Lett. 2013, 5, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Aflatoonian, M.R.; Mohtate, B.; Aflatoonian, B.; Shoaie, I.S.; Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Ziasistani, M.; Zhang, K.; Jang, H.W.; et al. Fabrication of magnetic iron oxide-supported copper oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4/CuO): Modified screen-printed electrode for electrochemical studies and detection of desipramine. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15171–15178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Electrode Materials | Analyte | Analytical Methods | LOD | Linear Range | Real Samples | Aptamer Length | Sequences | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral red-thiacalix [4] arene A-DNA aptamer | AFB1 | CV | 0.1 nM | 0.1–100 nM | peanuts, cashew nuts, white wine and soy sauce samples | 50 | 5′-GTT GGG CAC GTG TTG TCT CTC TGT GTC TCG TGC CCT TCG CTA GGC CCA CA-3′ | [1] |
| RGO/MoS2/PANI@AuNPs | AFB1 | DPV | 0.002 fg/mL | 0.01 fg/mL–1.0 fg/mL | Wine samples | 50 | 5′-GTT GGG CAC GTG TTG TCT CTC TGT GTC TCG TGC CCT TCG CTA GGC CCA CA-3′ | [29] |
| poly NR–P [5] A COOH layer modified with the aptamer | AFM1 | EIS | 0.5 ng/L | 5–120 ng/L | sheep and cow milk samples | 21 | 5′-ACT GCT AGA GAT TTT CC CAT-3′ | [30] |
| Thiacalix [4] arenes bearing oligolactic fragments, poly(ethylene imine) and DNA | AFM1 | EIS | 5.0 ng/L | 20.0–200.0 ng/L | Milk samples | 21 | 50-NH2-ACT GCT AGA GAT TTT CCA CAT-30 | [31] |
| Electrode Materials | Analyte | Analytical Methods | LOD | Linear Range | Real Samples | Aptamer Length | Sequences | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apt-complementary strands complex | AFB1 | DPV | 2.0 pg/mL | 7.0–500.0 pg/mL | human serum and grape juice samples | – | – | [4] |
| Graphene/methylene blue tagged aptamer | AFB1 | DPV | 0.05 ng mL−1 | 0.05–6.0 ng mL−1 | Alcoholic beverage samples (beer and wine) | 35 | 50-TGGGGTTTGGTGGGTGGTGTACGGGCAGG-30 | [32] |
| AFM1-Aptamer | AFM1 | Impedimetric | 1.15 ng/L | 2.0–150.0 ng/L | Milk samples (raw milk, micro-filtered full-fat milk, pasteurized full-fat milk and pasteurized skimmed milk) | 21 | 5′-ACT-GCT- AGA-GAT-TTT-CCA-CAT-3′ | [33] |
| diazonium/Aptamer (two aptamers sequences A and B) | AFB | EIS | 0.12 ng/mL | 0.125–16.0 ng/mL | Wine and beer samples | 35 | 5′TGGGGTTTTGGTGGCGGGTGGTGTACGGGCAGGG-3′ | [34] |
| biotinylated-TEG-aptamer | AFM1 | SWV | – | 1.0–105 ppt | – | 72 | 5′ATCCGTCAACCTGCTCTGACGCTGGGGTCGACCCGGAGAAATGCATTCCCTGTGGTGTTGGCTCCCGAT-TEG Biotin3′ | [35] |
| CS-modified AuNPs/Apt | AFM1 | DPV | 0.9 ng/L | 2.0–600.0 ng/L | Serum and milk samples | – | – | [36] |
| Fe3O4@Au-Apt | AFB1 | EIS | 15.0 pg/mL | 20.0 pg/mL−50.0 ng/mL | Peanut samples | 50 | 5′-GTT GGG CAC GTG TTG TCT CTC TGT GTC TCG TGC CCT TCG CTA GGC CCA CA-SH-3′ | [37] |
| anti-AFM1/Fc/SiNPs-PpPD | AFM1 | Electrochemical capacitance spectroscopy (ECS) | 4.53 fM | 10.0–500.0 fmol/L | Commercial pasteurized milk sample | 21 | 5′-ACT GCT AGA GAT TTT CCA CAT-3′ | [38] |
| apt-BIO/AFB1-BSA/PANI-PAA | AFB1 | DPV | 0.086 ng/mL | 0.1–10.0 ng/mL | Maize flour samples | 50 | 5′-(biotin)-TEG(triethylene glycol)- GTT GGG CAC GTG TTG TCT CTC TGT GTC TCG TGC CCT TCG CTA GGC CCA CA-3′ | [39] |
| Electrode Materials | Analyte | Analytical Methods | LOD | Linear Range | Real Samples | Aptamer Length | Aptamer Length | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21-mer ss-HSDNA | AFM1 | EIS | – | 1.0–14.0 ng/mL | Milk sample | 21 | ss-HSDNA (5_-thiol-(CH2)6 ACT GCTAGA GATTTT CCA CAT-3_) | [13] |
| telomerase primer—AuNPs-c-DNA/MB | AFB1 | SWV | 0.6 × 10−4 ppt | 0.0001–100.0 ppt | Corn samples | 50 | 5′- GTTGGGC AC GTGTT GTCTCTC TGTGTCT CGTGCCC TTCGCTA GGCCCA CA-(CH2)6-SH-3′ | [20] |
| Aptamers on dendrimers | AFB1 | EIS, CV | 0.4 nM | 0.1–10.0 nM | Peanut samples | 50 | NH2-5′-GTTGGG CACGTG TTGTCTC TC TGTGTC TCGTGCCCTTCG CTAGGCC CA CA-3′ | [40] |
| Biotinylated aptamers immobilized at neutravidin layer modified by ferrocene | AFM1 | DPV | 8.47 ng/L | 15–120 ng/L | Milk samples | 21 | 50-ACT GCT AGA GAT TTT CCA CAT-30 (APT1) | [41] |
| 8.52 ng/L | 35 | 50-TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT ACT GCT AGA GATTTT CCACAT-30 (APT2 | ||||||
| 8.64 ng/L | 50 | 50-GTT GGG CAC GTG TTG TCT CTC TGT GTC TCG TGC CCT TCG CTA GGCCC CA-30 (APT3) | ||||||
| 3DOM MoS2-AuNPs,HRP/AuNPs-SiO2@Fe3O4 | AFB1 | DPV | 0.01 fg/mL | 0.1 fg/mL–0.1 μg/mL | Rice and wheat powder samples | – | – | [42] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Dourandish, Z.; Zhang, K.; Le, Q.V.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Shokouhimehr, M. Recent Advances in the Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 and Its Pertinent Metabolite Aflatoxin M1. Sensors 2020, 20, 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113256
Beitollahi H, Tajik S, Dourandish Z, Zhang K, Le QV, Jang HW, Kim SY, Shokouhimehr M. Recent Advances in the Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 and Its Pertinent Metabolite Aflatoxin M1. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113256
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeitollahi, Hadi, Somayeh Tajik, Zahra Dourandish, Kaiqiang Zhang, Quyet Van Le, Ho Won Jang, Soo Young Kim, and Mohammadreza Shokouhimehr. 2020. "Recent Advances in the Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 and Its Pertinent Metabolite Aflatoxin M1" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113256
APA StyleBeitollahi, H., Tajik, S., Dourandish, Z., Zhang, K., Le, Q. V., Jang, H. W., Kim, S. Y., & Shokouhimehr, M. (2020). Recent Advances in the Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 and Its Pertinent Metabolite Aflatoxin M1. Sensors, 20(11), 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113256










