Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Rational
1.2. Review Questions
1.3. Identification of the Need for a Review
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection
2.3.1. Study Selection Criteria
2.3.2. Study Selection Process
2.4. Study Quality Assessment
2.4.1. Study Selection Criteria
Eligibility Criteria
Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
- Study design. Articles that demonstrate the objective and the process of the DT that was carried out inside the HEI.
- Are all research questions answered adequately?
- Are the main goals of the DT at HEIs stated?
- Does the paper outline the methods used to address DT in HEIs?
- System design. Articles that show the dimensions, participants, and/or their relationships in processes of DT of HEIs.
- Does the proposed DT apply to the whole HEI?
- Are the business model, dimensions, technology, actors, and relationship involved in DT at HEIs clearly described and defined?
- Were all model construction methods to apply DT in HEIs fully defined?
2.5. Data Extraction
2.5.1. Design of Data Extraction Forms
2.5.2. Data Extraction Procedures
2.6. Data Syntesis
3. Results
3.1. Included and Excluded Studies
Search Strategy
3.2. Definitions of DT that Are Stated in the Literature and Are Applied to HEIs
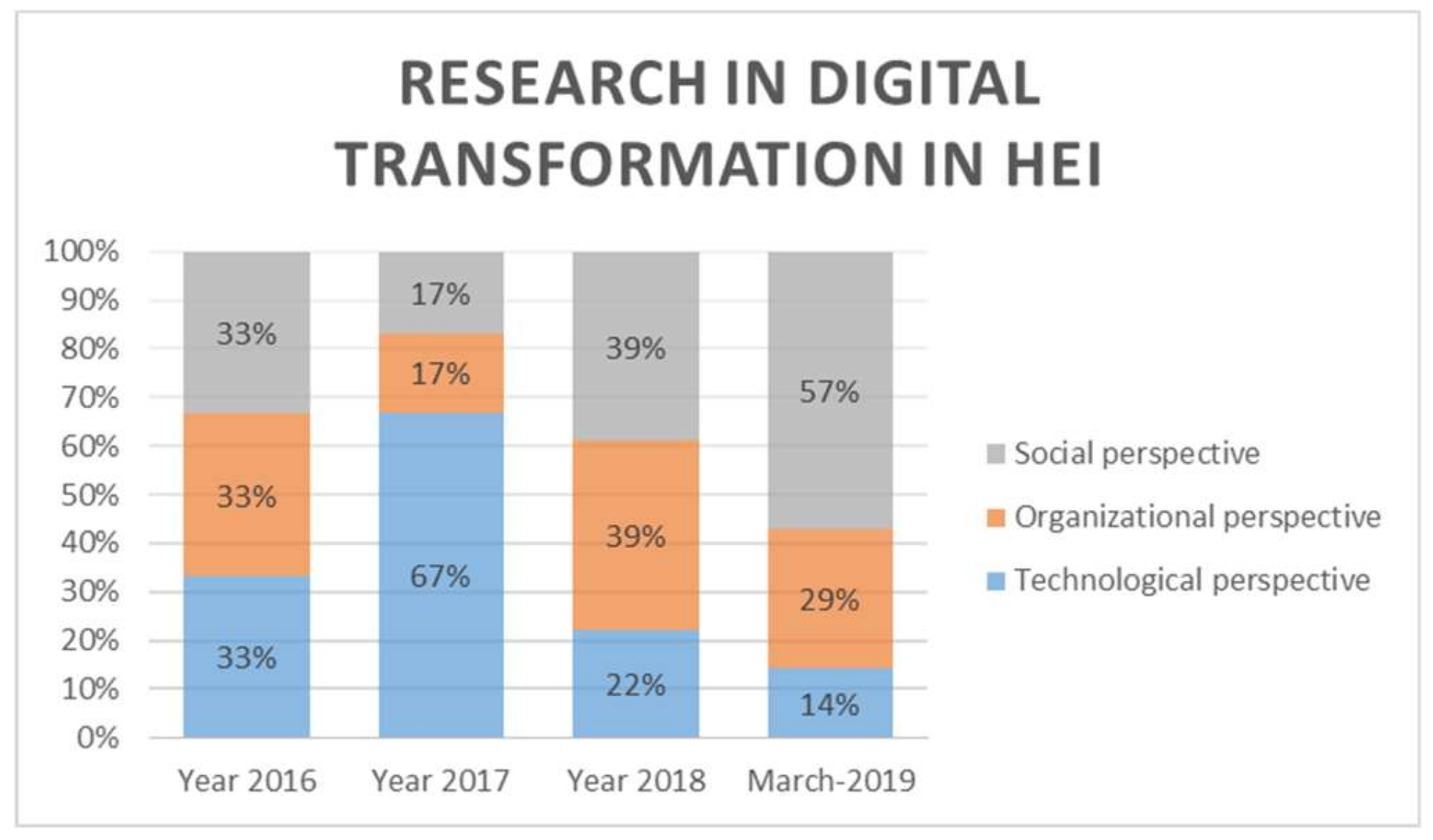
3.3. How Has the DT of HEIs Been Addressed?
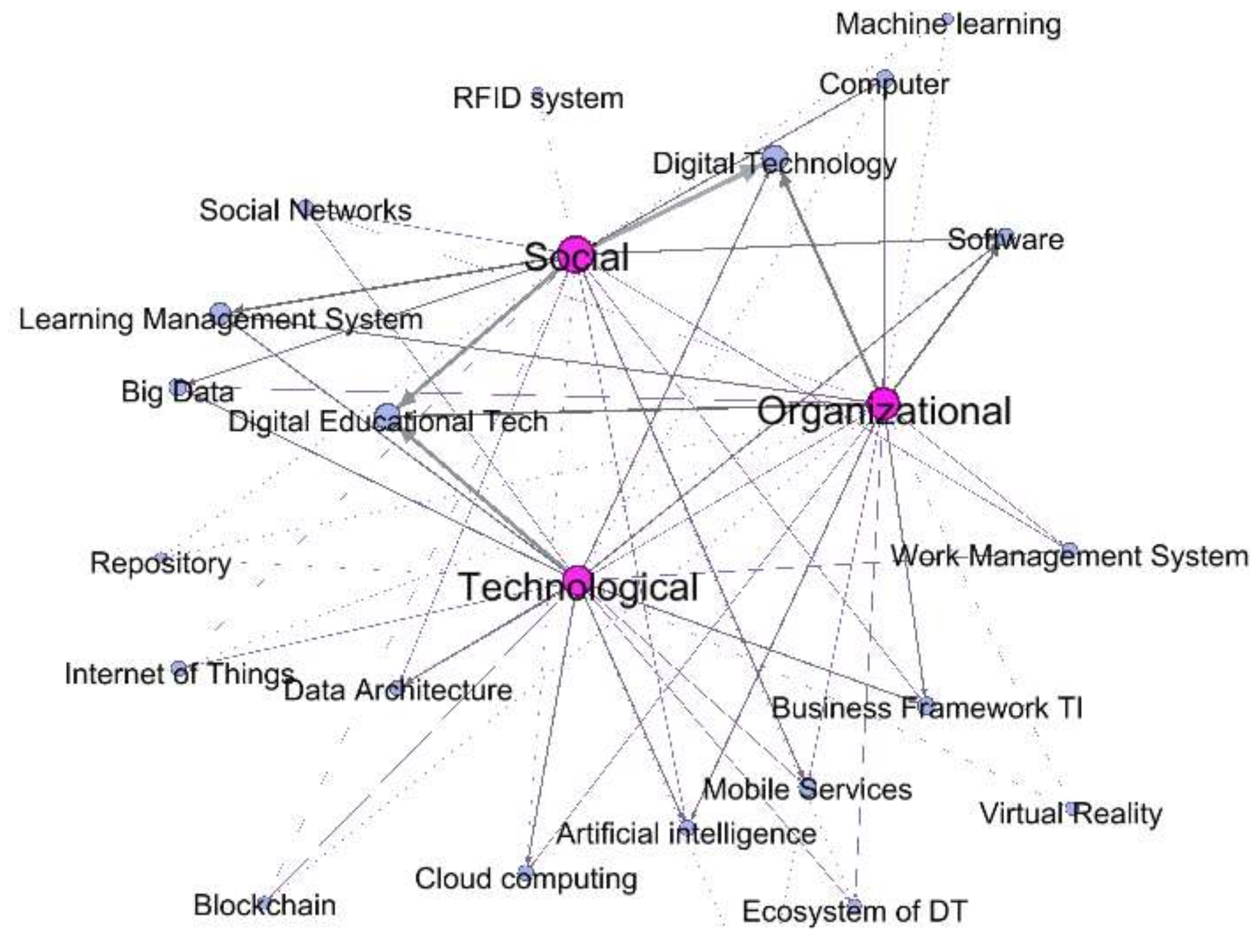
3.4. Interrelationships inside DT of HEIs
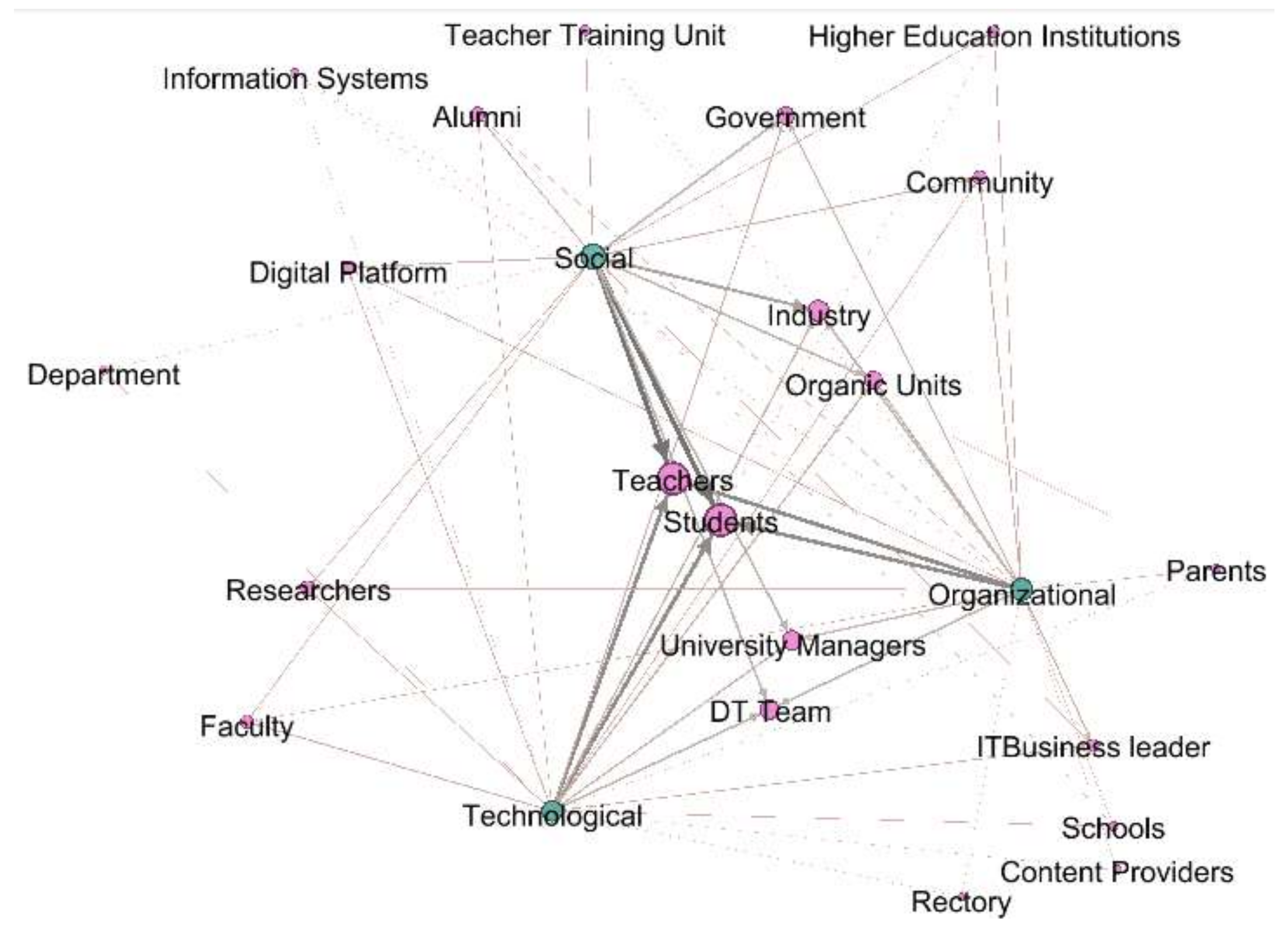
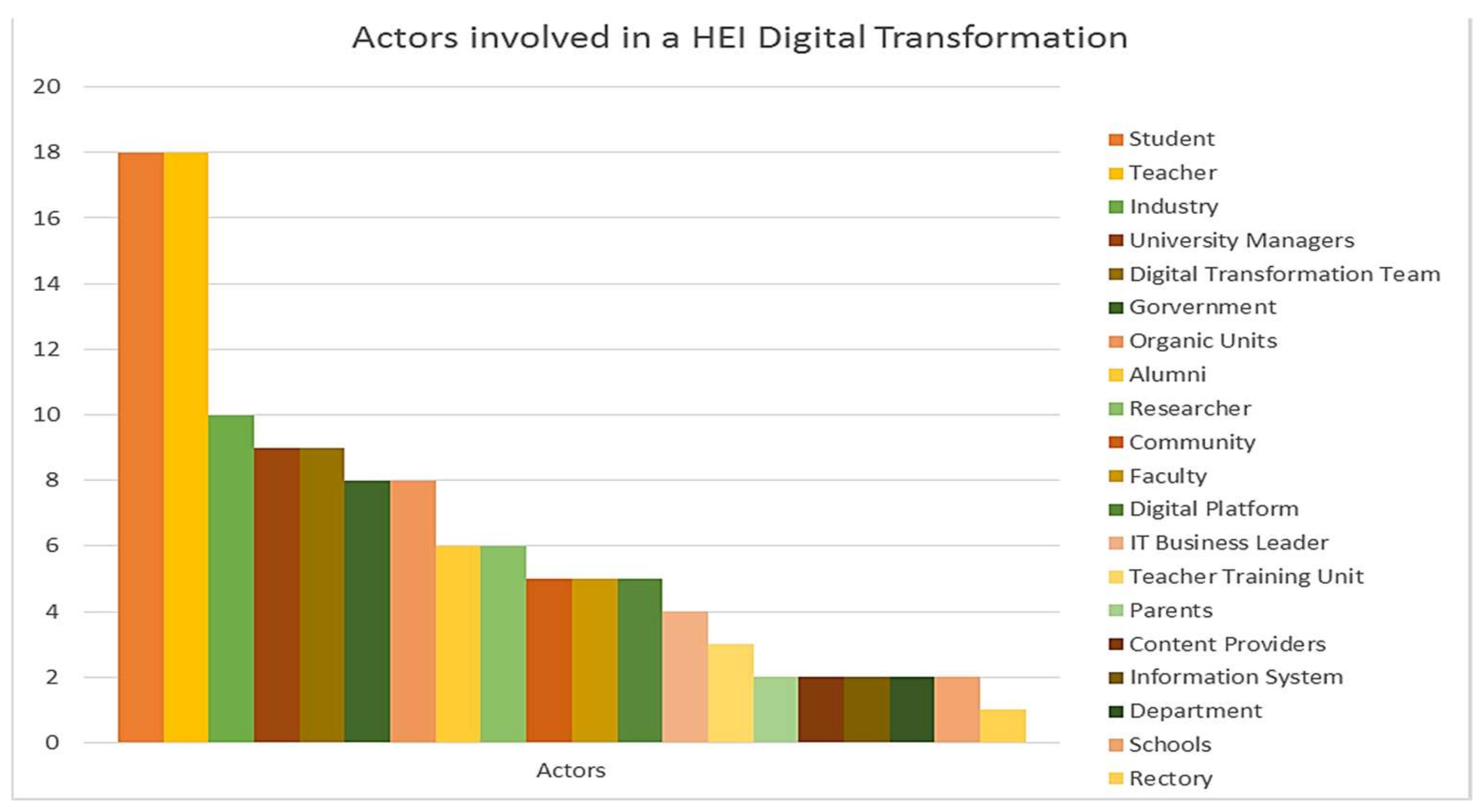
3.5. DT of HEIs Addressed by Actors
3.6. Route Established by HEIs to Carry Out their DT
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Distinctive Characteristics of DT in HEIs
DT at HEIs Reflected in the Literature
4.2. How Has the DT in HEIs Been Addressed?
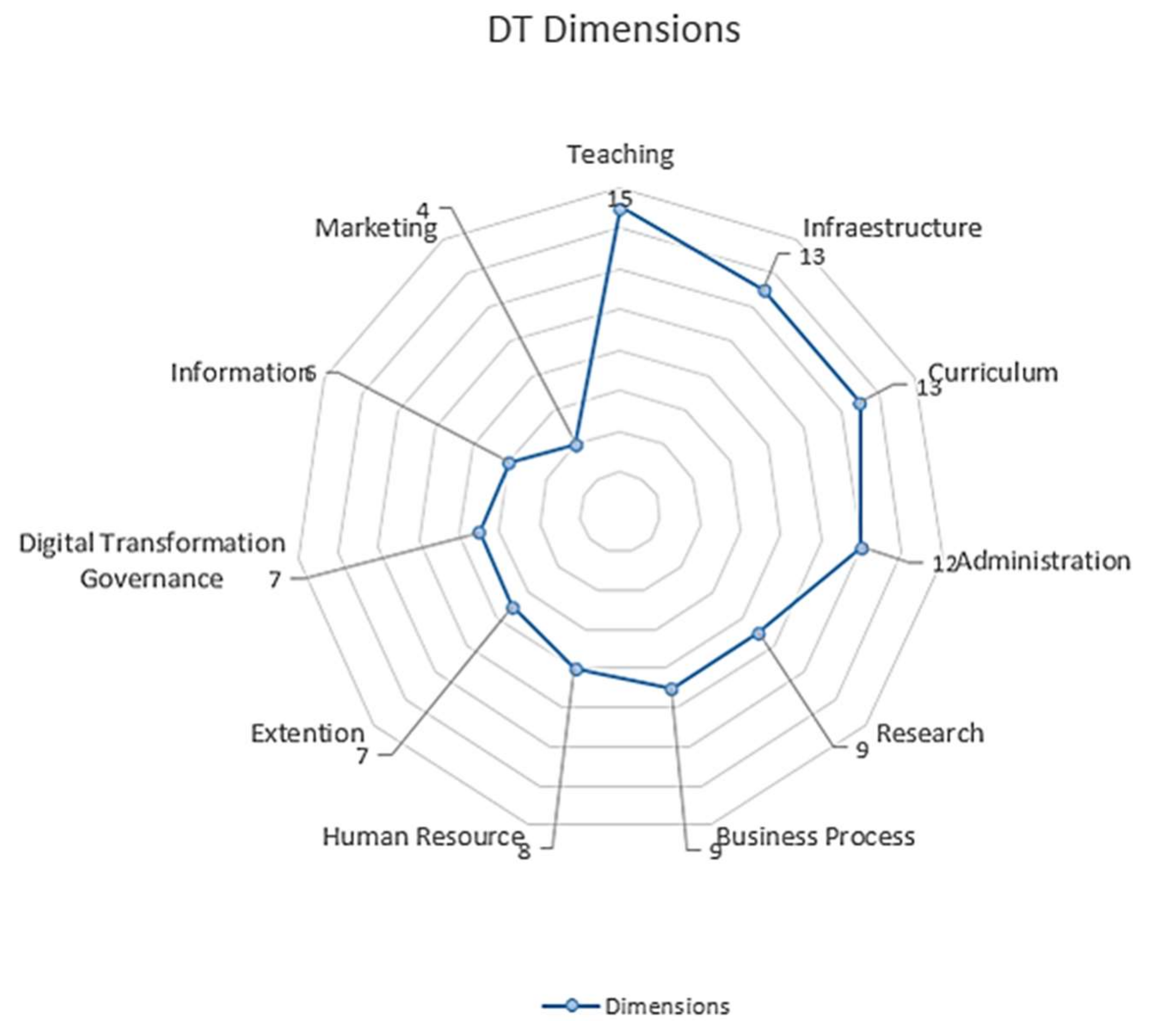
4.2.1. DT in HEIs Dimensions
4.2.2. Remarkable Relationships of DT of HEIs
4.2.3. Addressing of the DT in HEIs by the Different Actors
4.2.4. Route Established by HEIs to Carry Out Their DT
4.3. Risks to Validity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hess, T.; Matt, C.; Benlian, A.; Wiesböck, F. Options for formulating a digital transformation strategy. MIS Quart. Execut. 2016, 15, 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Gobble, M.M. Digital strategy and digital transformation. Res. Manag. 2018, 61, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.; Nóvoa, H. Digital transformation at the University of Porto. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Global Innovation and Knowledge Academy, Valencia, Spain, 14–16 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, M.D.A.; Branch, J.W.; Benavides, L.M.C.; Burgos, D. Un modelo conceptual de transformación digital. Openergy y el caso de la Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Educ. Knowl. Soc. 2019, 19, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The 2018 Digital University: Staying Relevant in the Digital Age; PwC: Leeds, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.pwc.co.uk/assets/pdf/the-2018-digital-university-staying-relevant-in-the-digital-age.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2018).
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 349, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Software Engineering, Shanghai, China, 20–28 May 2006; Available online: http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1134285.1134500 (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Kitchenham, B.A.; Brereton, O.P.; Budgen, D.; Turner, M.; Bailey, J.; Linkman, S. Systematic literature reviews in software engineering—A systematic literature review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2009, 51, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advances in information systems and technologies. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2013, 206. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.S. Challenges of digital transformation in higher education institutions: A brief discussion. In Proceedings of the 30th International Business Information Management Association Conference, IBIMA 2017—Vision 2020: Sustainable Economic Development, Innovation Management, and Global Growth, Madrid, Spain, 8–9 November 2017; Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85048618825&partnerID=40&md5=65525232d18dbc0ae37a733eb45b100d (accessed on 4 April 2019).
- Wade, M. Digital Business Transformation a Conceptual Framework. Glob Cent Digit Bus Transform. Available online: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/vala-afshar/accenture-digital-7-digital-business-transformation-lessons_b_6622648.html (accessed on 9 August 2019).
- Sullivan, C.; Staib, A. Digital disruption ‘syndromes’ in a hospital: Important considerations for the quality and safety of patient care during rapid digital transformation. Aust. Health Rev. 2018, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemer, K.; Uri, G.; Hamann, J.; Gilchriest, B.; Teixeira, M. Digital Disruptive Intermediaries. Available online: https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/bitstream/handle/2123/12761/ADTL_Digital%20Disruptive%20Intermediaries-final.pdf?sequence=7&isAllowed=y (accessed on 13 August 2019).
- Betchoo, N.K. Digital transformation and its impact on human resource management: A case analysis of two unrelated businesses in the Mauritian public service. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Innovative Business Practices for the Transformation of Societies (EmergiTech), Balaclava, Mauritius, 3–6 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Liao, H.-T.; Sun, S.-P. An Education literature review on digitization, digitalization, datafication, and digital transformation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Humanities and Social Science Research (ICHSSR 2020), Hangzhou, China, 10–12 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, J.A.; Nóvoa, H. Digital Transformation at the University of Porto. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Exploring Services Science, Porto, Portugal, 5–7 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminskyi, O.Y.; Yereshko, J.; Kyrychenko, S.O. Digital transformation of University Education in Ukraine: Trajectories of Development in the conditions of new technological and economic order. Inf. Technol. Learn. Tools. 2018, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleaca, E. Embedding digital teaching and learning practices in the modernization of higher education institutions. In Proceedings of the SGEM2017 International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 20–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, J.A.P. Intelligent educational dual architecture for University digital transformation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), San Jose, CA, USA, 3–6 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, G. The role of academic libraries in the digital transformation of the universities. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Symposium on Emerging Trends and Technologies in Libraries and Information Services (ETTLIS), Noida, India, 21–23 February 2018; pp. 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Grab, B.; Olaru., M.; Gavril., R. Self-managed as a key to unlocking digital transformation in business management. Qual Success. 2019, 20, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bresinsky, M.; Von Reusner, F. GLOBE—Learn and innovate digitization by a virtual collaboration exercise and living lab. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference, ArtsIT 2017, and Second International Conference, DLI 2017, Heraklion, Greece, 30–31 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Henriette, E.; Feki, M.; Boughzala, I. The shape of digital transformation: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the 9th Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems, Samos, Greece, 3–5 October 2015; Available online: http://aisel.aisnet.org/mcis2015/10 (accessed on 17 October 2018).
- Thoring, A.; Rudolph, D.; Vogl, R. The digital transformation of teaching in higher education from an academic’s point of view: An explorative study. In Proceedings of the applications of evolutionary computation, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–20 July 2018; Volume 10924, pp. 294–309. [Google Scholar]
- Bozhko, Y.V.; Maksimkin, A.I.; Baryshev, G.K.; Voronin, A.I.; Kondratyeva, A.S. Digital transformation as the key to synthesis of educational and innovation process in the research university. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Digital Transformation and Global Society, DTGS, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 22–24 June 2016; pp. 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Marín, V.I.; Dolch, C.; Bedenlier, S.; Zawacki-Richter, O. Digital transformation in German higher education: Student and teacher perceptions and usage of digital media. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2018, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarenko, N.Y.; Mikheenko, O.V.; Chepikova, E.M.; Kazakov, O.D. Formation of innovative mechanism of staff training in the conditions of digital transformation of economy. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference “Quality Management, Transport and Information Security, Information Technologies” (IT&QM&IS), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 764–768. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, H.L.; Low, S.W.K. Digitalization of learning resources in a HEI—A lean management perspective. Int. J. Prod. Perform. Manag. 2017, 66, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfikar, M.W.; Bin Hashim, A.I.; Umri, H.U.B.A.; Dahlan, A.R.A. A business case for digital transformation of a Malaysian-Based University. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for the Muslim World (ICT4M), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–25 July 2018; pp. 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hulla, M.; Karre, H.; Hammer, M.; Ramsauer, C. A teaching concept towards digitalization at the LEAD factory of Graz University of Technology. In 21st International Conference on Interactive Collaborative Learning, ICL; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 917, pp. 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolze, A.; Sailer, K.; Gillig, H. Entrepreneurial mindset as a driver for digital transformation—A novel educational approach from university-industry interactions. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship, ECIE, Aveiro, Portugal, 20–21 September 2018; pp. 806–813. [Google Scholar]
- Panichkina, M.V.; Sinyavskaya, I.A.; Shestova, E. Challenges of professional adaptation of university graduates in response to the economics’ digital transformation. In Proceedings of the 2018 XVII Russian Scientific and Practical Conference on Planning and Teaching Engineering Staff for the Industrial and Economic Complex of the Region (PTES), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 14–15 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, M.; Chesbrough, H.; Moedas, C. Open innovation: Research, practices, and policies. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2018, 60, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, D.H.; Trelsgård, K. Enterprise architecture adoption challenges: An exploratory case study of the Norwegian higher education sector. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Level | Description | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | Information is explicitly defined/evaluated | 1 |
| Partially | information is implicit/stated | 0.5 |
| No | information is not inferable | 0 |
| Source | Acronym |
|---|---|
| DT description | Technological (TC) Organizational (OR) Social (S). We use the classification proposed by [9] |
| DT Goals and services | Use (US) Access (AC) Innovation (IN) Jobs (JO) Society (SO) Trust (TR) Market Openness (MO) Growth and Wellbeing (GW) |
| DT dimensions and characteristics | Research (RE) Teaching (TE) Social (SO) Business Process (BP) Human Resource (HC) Curricula (CU) Infrastructure (IN) DT Government (DG) Administration (AD) Marketing (MK) Information (INF) |
| Actors or Stakeholders involved in DT | Students (S) Alumni (A)- Teachers (T) -Researchers (R) University Managers (M) Community (C) Faculty (F) Department (D) Government (G) IT Business leader (ITB) Rectory (Ry) Organic Units (OU) Schools (Sc) DT Team (Te) Teacher Training Unit (TT) Industry (I) Parents (P) Content Providers (CP) HEIs (HEI) Digital Platform (DP) Information Systems (IS) Library (L) |
| DT implementing methods | Guidelines DT (G) DT Center (DC) Reengineering Process (RE) Build and Running System (BS) IT Architecture Management (ITAM) Competences Center (CC) Digitalization (DI) Change Management (CM) Enterprise Architecture (EA) |
| Technologies used | Work Management System (WMS) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Business Framework TI (BF) Information Communication Technology (ICT) Software (SW) Learning Management System (LMS) Digital Educational Tech (DE) Computer (PC) Cloud computing (CL) Blockchain (B) Internet of Things (IoT) Mobile Services (MS) Big Data (BD) Social Networks (SN) Data Architecture (DA) Digital Technology (DT) Ecosystem of DT (ECO) Computer Power 5G Networks, Artificial intelligence (AI) Virtual Reality (VR) Augmented Reality (AR) RFID system Machine learning (ML) Repository (Re) |
| Governance | Public Politics (PP) Governability for DT (GDT) |
| Criteria | Filters | Scopus | Web of Science (WoS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restriction | Topic (title, abstract, author keywords) | 129 | 31 |
| Period | 2001–2019. The first article published in WoS was in 2001 1980–2019 Scopus | 128 | 30 |
| Document type | Articles and conference proceedings | 107 | 30 |
| Language | English | 100 | 19 |
| Total | 119 |
| Criteria | Papers |
|---|---|
| Articles Elected | 40 |
| Excluded articles | 21 |
| Criteria | Papers |
|---|---|
| Full reading papers | 19 |
| Excluded articles | 21 |
| Paper | Digital Transformation |
|---|---|
| [10] | DT is fundamentally about change and it involves people, processes, strategies, structures, and competitive dynamics [11]. |
| [12] | Digital disruption is defined as the changes facilitated by digital technologies that occur at a pace and magnitude that disrupt established ways of value creation, social interactions, doing business and more generally our thinking [13]. |
| [14] | The realignment of, or new investment in, technology and business models to more effectively engage digital customers at every touch point in the customer experience lifecycle. Companies needed to think of DT as a “formal effort to renovate business vision, models, and investments for a new digital economy [15].” |
| [16] | DT goes well beyond de-materialization of processes, encompassing an innovative use of new technologies (cloud, social, mobile, and analytics) to promote new services, re-define business models, and innovative interactions with its users. |
| [17] | DT of the university education system should have a broader focus and must include the modernization of corporate IT architecture management, which could provide an important contribution to structuring the efforts of innovation in education. |
| [18] | The modern developments in the area of modernizing educational system with the aid of ITC technology and applied process thinking principles in the attempt to capture and model interrelated activities required to integrate digital technologies in teaching, learning, and organizational practices. |
| [19] | DT is an accelerated evolution. It is also revolution because of its radical and structural implications for people as for infrastructure that also requires new educational and business models. |
| [20] | Digital business transformation can be defined as the modification of business processes, procedures, capabilities and policies to take advantage of the changes and opportunities presented by new digital technologies, as well as the impact they have on society, while always thinking about current and future trends. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benavides, L.M.C.; Tamayo Arias, J.A.; Arango Serna, M.D.; Branch Bedoya, J.W.; Burgos, D. Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113291
Benavides LMC, Tamayo Arias JA, Arango Serna MD, Branch Bedoya JW, Burgos D. Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113291
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenavides, Lina María Castro, Johnny Alexander Tamayo Arias, Martín Darío Arango Serna, John William Branch Bedoya, and Daniel Burgos. 2020. "Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: A Systematic Literature Review" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113291
APA StyleBenavides, L. M. C., Tamayo Arias, J. A., Arango Serna, M. D., Branch Bedoya, J. W., & Burgos, D. (2020). Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors, 20(11), 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113291






