A Low-Cost, Disposable and Portable Inkjet-Printed Biochip for the Developing World
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Platform Characterization
3.2. Platform Characterization for Clinically Relevant Reagents
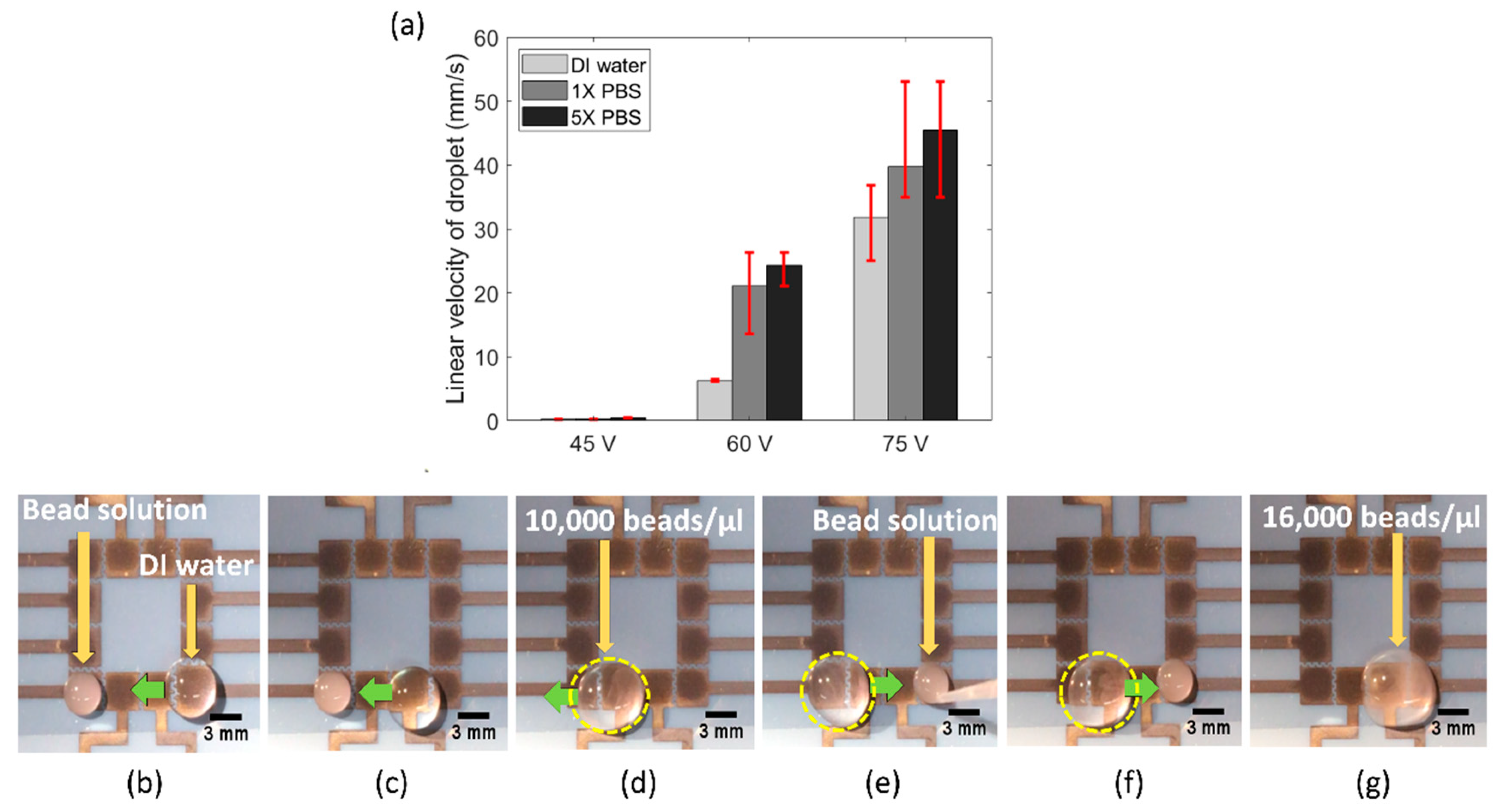
3.3. Portable FINP-DMF Platform
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figeys, D.; Pinto, D. Lab-on-a-chip: A revolution in biological and medical sciences. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franke, T.A.; Wixforth, A. Microfluidics for miniaturized laboratories on a chip. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2008, 9, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, R.S.; Ng, R.; Nuffer, M.; Basmajian, M.; Coyne, J.; Elderbroom, J.; Hull, D.; Kay, K.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Roberts, C.; et al. Digital microfluidic platform to maximize diagnostic tests with low sample volumes from newborns and pediatric patients. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vyawahare, S.; Griffiths, A.D.; Merten, C.A. Miniaturization and parallelization of biological and chemical assays in microfluidic devices. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Hejazian, M.; Ooi, C.H.; Kashaninejad, N. Recent advances and future perspectives on microfluidic liquid handling. Micromachines 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samiei, E.; Tabrizian, M.; Hoorfar, M. A review of digital microfluidics as portable platforms for lab-on a-chip applications. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2376–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Davis, R.W.; Javanmard, M. Digital microfluidic assay for protein detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogojevic, D.; Chamberlain, M.D.; Barbulovic-Nad, I.; Wheeler, A.R. A digital microfluidic method for multiplexed cell-based apoptosis assays. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, N.; McDonnell, M.B.; Munro, I.; McCluskey, D.K.; Johnston, I.D.; Tan, C.K.L.; Coudron, L. Electrowetting-based digital microfluidics platform for automated enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 2020, e60489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, I.; Lee, T.M. Design and fabrication of printed electrowetting-on-dielectric device. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.H.; Fan, S.K.; Kim, C.J.; Yao, D.J. EWOD microfluidic systems for biomedical applications. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 16, 965–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.C.; Kim, C.J.C. Droplet actuation by electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD): A review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Fair, R.B. An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Rouse, J.L.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Schell, W.A.; Benton, J.L.; Mitchell, T.G.; Pollack, M.G. Multiplexed real-time polymerase chain reaction on a digital microfluidic platform. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sista, R.; Hua, Z.; Thwar, P.; Sudarsan, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Eckhardt, A.; Pollack, M.; Pamula, V. Development of a digital microfluidic platform for point of care testing. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2091–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Kang, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Rapid and sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I for point-of-care tests based on red fluorescent microspheres. Molecules 2018, 23, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, C.; Ng, A.H.C.; Fobel, R.; Miltenburg, M.B.; Wheeler, A.R. An inkjet printed, roll-coated digital microfluidic device for inexpensive, miniaturized diagnostic assays. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4560–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNerney, R. Diagnostics for developing countries. Diagnostics 2015, 5, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Moon, H.; Kim, C.J. Creating, Transporting, Cutting, and Merging Liquid Droplets by Electrowetting-Based Actuation for Digital Microfluidic Circuits. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karuwan, C.; Sukthang, K.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Patthanasettakul, V.; Wechsatol, W.; Tuantranont, A. Electrochemical detection on electrowetting-on-dielectric digital microfluidic chip. Talanta 2011, 84, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthier, J. Electrowetting Theory; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781455725502. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, L.S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chen, C.H. Effect of electrode geometry on performance of EWOD device driven by battery-based system. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.H.C.; Lee, M.; Choi, K.; Fischer, A.T.; Robinson, J.M.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital Microfluidic Platform for the Detection of Rubella Infection and Immunity: A Proof of Concept. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salman, W.M.; Abdelsalam, M.S.; El-Dosoky, M.F.F.; Abdelgawad, M. Effect of electrical conductivity and permittivity of liquids and the frequency of the applied voltage on droplets actuation on digital microfluidic devices. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences (microTAS 2014), San Antonio, TX, USA, 26–30 October 2014; Volume 1302, pp. 1302–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Hazra, K.; Dasgupta, S.S.; Chakraborty, S. Analysis of Electrowetting Phenomenon Using Image Processing Tool. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 10622–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.C.C.; Yang, H.; Jebrail, M.J.; Fobel, R.; McIntosh, N.; Al-Dirbashi, O.Y.; Chakraborty, P.; Wheeler, A.R. Dried blood spot analysis by digital microfluidics coupled to nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3731–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witters, D.; Knez, K.; Ceyssens, F.; Puers, R.; Lammertyn, J. Digital microfluidics-enabled single-molecule detection by printing and sealing single magnetic beads in femtoliter droplets. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandyarpour, R.; Esfandyarpour, H.; Javanmard, M.; Harris, J.S.; Davis, R.W. Microneedle biosensor: A method for direct label-free real time protein detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esfandyarpour, R.; Javanmard, M.; Koochak, Z.; Esfandyarpour, H.; Harris, J.S.; Davis, R.W. Label-free electronic probing of nucleic acids and proteins at the nanoscale using the nanoneedle biosensor. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 044114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandyarpour, R.; Esfandyarpour, H.; Harris, J.S.; Davis, R.W. Simulation and fabrication of a new novel 3D injectable biosensor for high throughput genomics and proteomics in a lab-on-a-chip device. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 465301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, K.; Esfandyarpour, R. An Inkjet-Printed and Reusable Platform for Single Cell Impedance Cytometry. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/11235/112350Y/An-inkjet-printed-and-reusable-platform-for-single-cell-impedance/10.1117/12.2543160.short (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Esfandyarpour, R.; DiDonato, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Durmus, N.G.; Harris, J.S.; Davis, R.W. Multifunctional, inexpensive, and reusable nanoparticle-printed biochip for cell manipulation and diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1306–E1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, H.; Cho, S.K. Low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joshi, K.; Velasco, V.; Esfandyarpour, R. A Low-Cost, Disposable and Portable Inkjet-Printed Biochip for the Developing World. Sensors 2020, 20, 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123593
Joshi K, Velasco V, Esfandyarpour R. A Low-Cost, Disposable and Portable Inkjet-Printed Biochip for the Developing World. Sensors. 2020; 20(12):3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123593
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoshi, Kushal, Vanessa Velasco, and Rahim Esfandyarpour. 2020. "A Low-Cost, Disposable and Portable Inkjet-Printed Biochip for the Developing World" Sensors 20, no. 12: 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123593
APA StyleJoshi, K., Velasco, V., & Esfandyarpour, R. (2020). A Low-Cost, Disposable and Portable Inkjet-Printed Biochip for the Developing World. Sensors, 20(12), 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123593



