Estimation of Stresses in Concrete by Using Coda Wave Interferometry to Establish an Acoustoelastic Modulus Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Concrete Samples
2.2. Measurement Procedure
3. Methodology and Data Processing
3.1. Velocity Variations Determination
3.2. Acoustoelastic Modulus Calculation
4. Stress Estimation and Results
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardini, A.; DeWolf, J. Long-term structural health monitoring of a multi-girder steel composite bridge using strain data. Struct Health Monit. 2009, 8, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdardottir, D.; Glisic, B. Neutral axis as damage sensitive feature. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, D.; Forde, M. Review of NDT methods in the assessment of concrete and masonry structures. NDT E Int. 2001, 34, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, V.; Piwakowski, B.; Abraham, O.; Villain, G.; Payan, C.; Chaix, J.F. Acoustic techniques for concrete evaluation: Improvements, comparisons and consistency. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugonda, P.; Wiehn, J.; Tuner, J. Diffusion of ultrasound in concrete. Ultrasonics 2001, 39, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frojd, P.; Ulriksen, P. Continuous wave measurements in a network of transducers for structural health monitoring of a large concrete floor slab. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 15, 403412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, R. Diffusion Coefficient Estimation and Its Application in Interior Change Evaluation of Full-size Reinforced Concrete Structures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04018398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Kane, Y.; Turner, J. Ultrasound diffusion for crack depth determination in concrete. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, E.; Planes, T.; Rossetto, V.; Margerin, L. Locating a small change in multiple scattering environment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 204101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, T.; Larose, E.; Rossetto, V.; Margerin, L. Imaging multiple local changes in heterogeneous media with diffuse waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frojd, P.; Ulriksen, P. Detecting damage events in concrete using diffuse ultrasound structural health monitoring during strong environment variations. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 17, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Larose, E.; Moreau, L.; Ozouville, G. Three-dimensional in-situ imaging of cracks in concrete using diffuse ultrasound. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 17, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, R. Three-Dimensional Images Generated from Diffuse Ultrasound Wave: Detections of Multiple Cracks in Concrete Structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 19, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, R. Stress Evaluation for Rocks and Structural Concrete Members through Ultrasonic Wave Analysis: Review. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snieder, R.; Grêt, A.; Douma, H.; Scales, J. Coda wave interferometry for estimating nonlinear behavior in seismic velocity. Science 2002, 295, 2253–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, T.; Larose, E. A review of ultrasonic Coda Wave Interferometry in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 53, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, E.; Hall, S. Monitoring stress related velocity variation in concrete with a 2 × 10−5 relative resolution using diffuse ultrasound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhi, P.; Zoga, A.; Wiggenhauser, H. Nondestructive investigation of stress-induced damage in concrete. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2010, 2010, 740189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stähler, S.; Sens-Schönfelder, C.; Niederleithinger, E. Monitoring stress changes in a concrete bridge with coda wave interferometry. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Abraham, O.; Grondin, F.; Loukili, A.; Tournat, V.; Le Duff, A.; Lascoup, B.; Durand, O. Study of stress-induced velocity variation in concrete under direct tensile force and monitoring of the damage level by using thermally-compensated Coda Wave Interferometry. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederleithinger, E.; Wang, X.; Herbrand, M.; Muller, M. Processing Ultrasonic Data by Coda Wave Interferometry to Monitor Load Tests of Concrete Beams. Sensors 2018, 18, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.; Kelly, J. Second-order elastic deformation of solids. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupin, R.; Bernstein, B. Sound waves in deformed perfectly elastic materials. Acoustoelastic effect. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1961, 33, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Garnier, V.; Moysan, J.; Johnson, P. Determination of third order elastic constants in a complex solid applying coda wave interferometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 011904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Hirose, S. Nonlinear Ultrasonic Investigation of Concrete Damaged under Uniaxial Compression Step Loading. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, N.; Larose, E.; Rossetto, V. Probing slow dynamics of consolidated granular multicomposite materials by diffuse acoustic wave spectroscopy. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
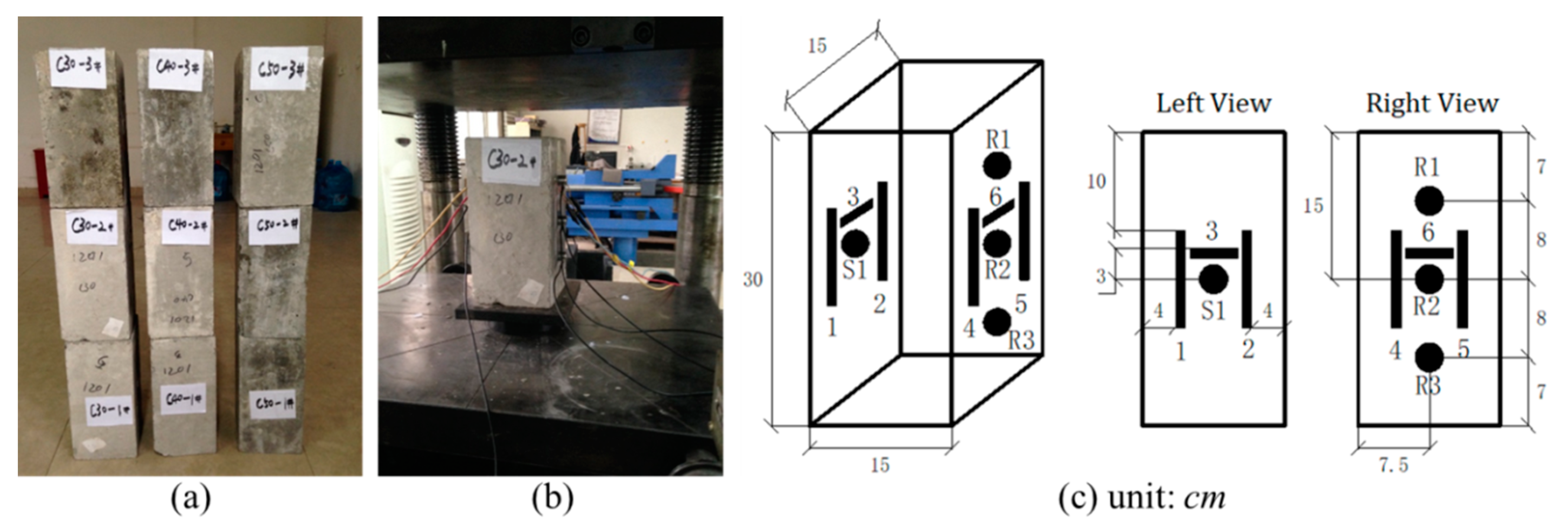
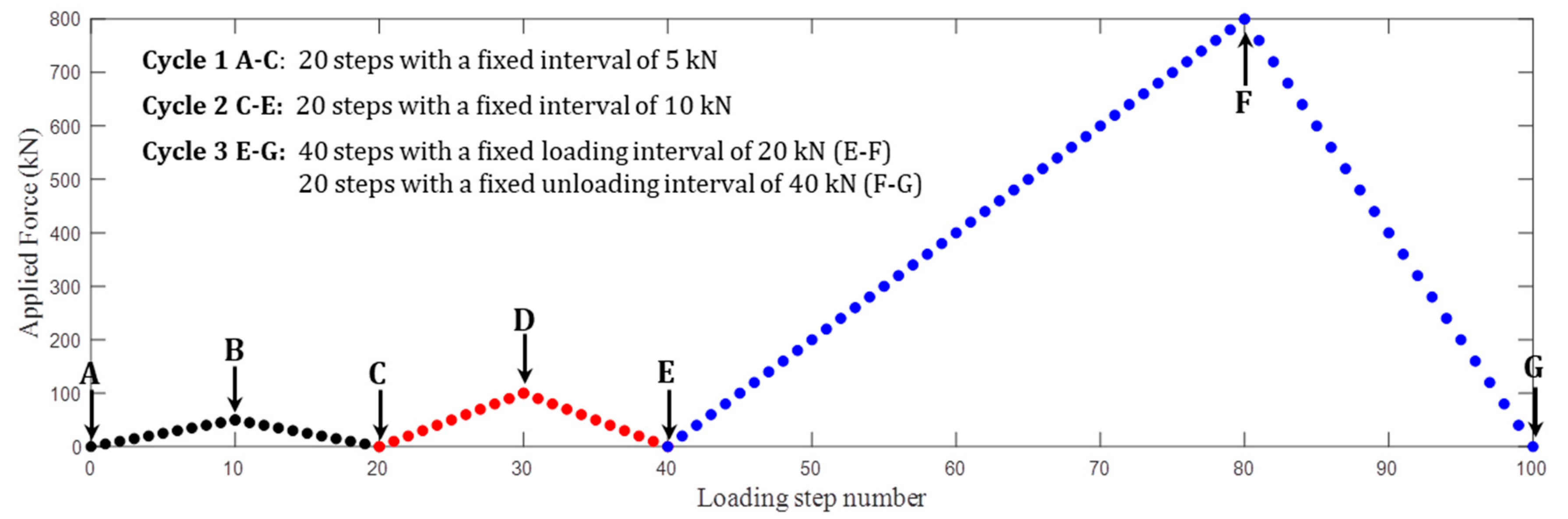
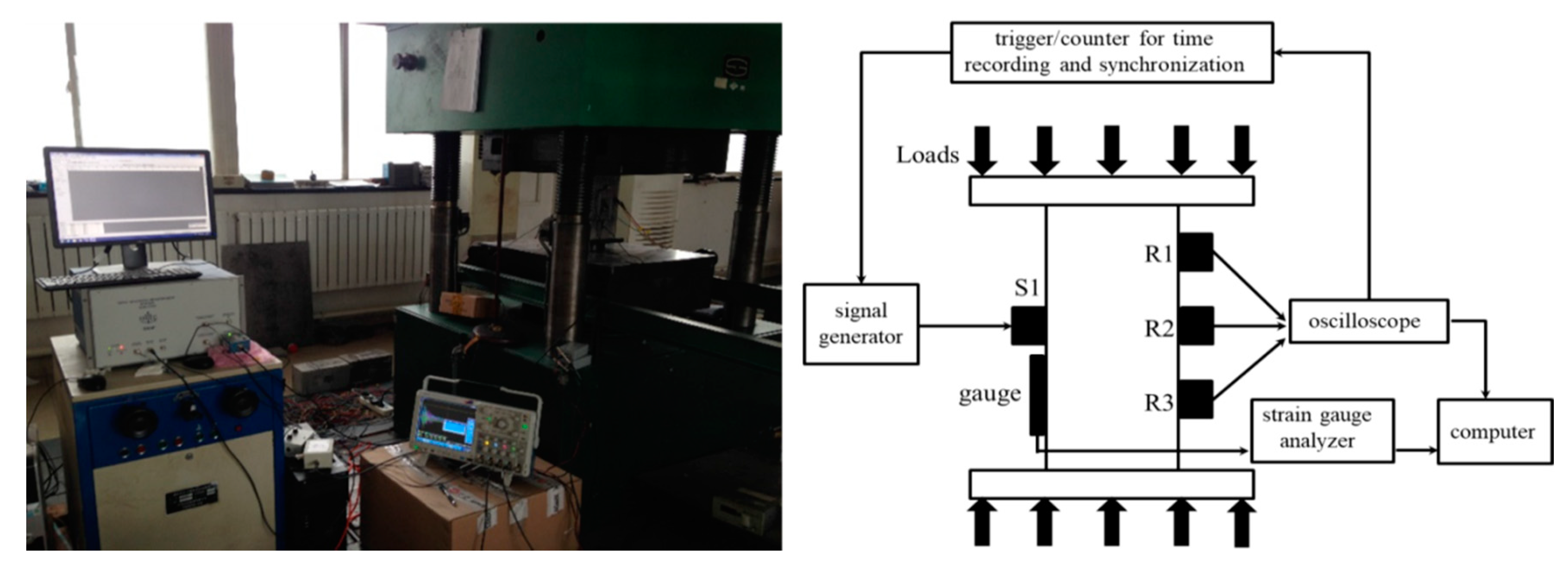



| Cement (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | Sand (kg/m3) | Gravel (kg/m3) | Superplasticizer (kg/m3) | Break-Down Force (kN) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C30 | 360 | 148 | 789 | 1090 | 3.6 | 1000 |
| C40 | 400 | 139 | 706 | 1154 | 4.3 | 1200 |
| C50 | 400 | 131 | 700 | 1136 | 4.8 | 1300 |
| Type | Receiver | A–B | B–D | AHML (A–B–D) | C–B | E–D | BHML (CB, ED) | Q (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C30 | R1 | 5.623 | 6.073 | 5.852 | 10.685 | 11.365 | 11.030 | 460 |
| R2 | 5.175 | 5.848 | 5.522 | 10.350 | 10.348 | 10.350 | 460 | |
| R3 | 5.573 | 5.852 | 5.681 | 11.700 | 11.246 | 11.475 | 460 | |
| C40 | R1 | 4.563 | 4.619 | 4.592 | 9.520 | 8.917 | 9.223 | 540 |
| R2 | 4.502 | 4.280 | 4.392 | 8.780 | 9.446 | 9.119 | 540 | |
| R3 | 4.725 | 4.277 | 4.507 | 9.225 | 9.560 | 9.394 | 540 | |
| C50 | R1 | 3.823 | 3.821 | 3.823 | 7.313 | 7.142 | 7.227 | 600 |
| R2 | 3.600 | 3.602 | 3.601 | 6.975 | 7.533 | 7.259 | 600 | |
| R3 | 3.602 | 3.827 | 3.717 | 7.425 | 6.975 | 7.205 | 600 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhuang, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, R. Estimation of Stresses in Concrete by Using Coda Wave Interferometry to Establish an Acoustoelastic Modulus Database. Sensors 2020, 20, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20144031
Zhan H, Jiang H, Zhuang C, Zhang J, Jiang R. Estimation of Stresses in Concrete by Using Coda Wave Interferometry to Establish an Acoustoelastic Modulus Database. Sensors. 2020; 20(14):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20144031
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Hanyu, Hanwan Jiang, Chenxu Zhuang, Jinquan Zhang, and Ruinian Jiang. 2020. "Estimation of Stresses in Concrete by Using Coda Wave Interferometry to Establish an Acoustoelastic Modulus Database" Sensors 20, no. 14: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20144031
APA StyleZhan, H., Jiang, H., Zhuang, C., Zhang, J., & Jiang, R. (2020). Estimation of Stresses in Concrete by Using Coda Wave Interferometry to Establish an Acoustoelastic Modulus Database. Sensors, 20(14), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20144031





