All-Fiber Measurement of Surface Tension Using a Two-Hole Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
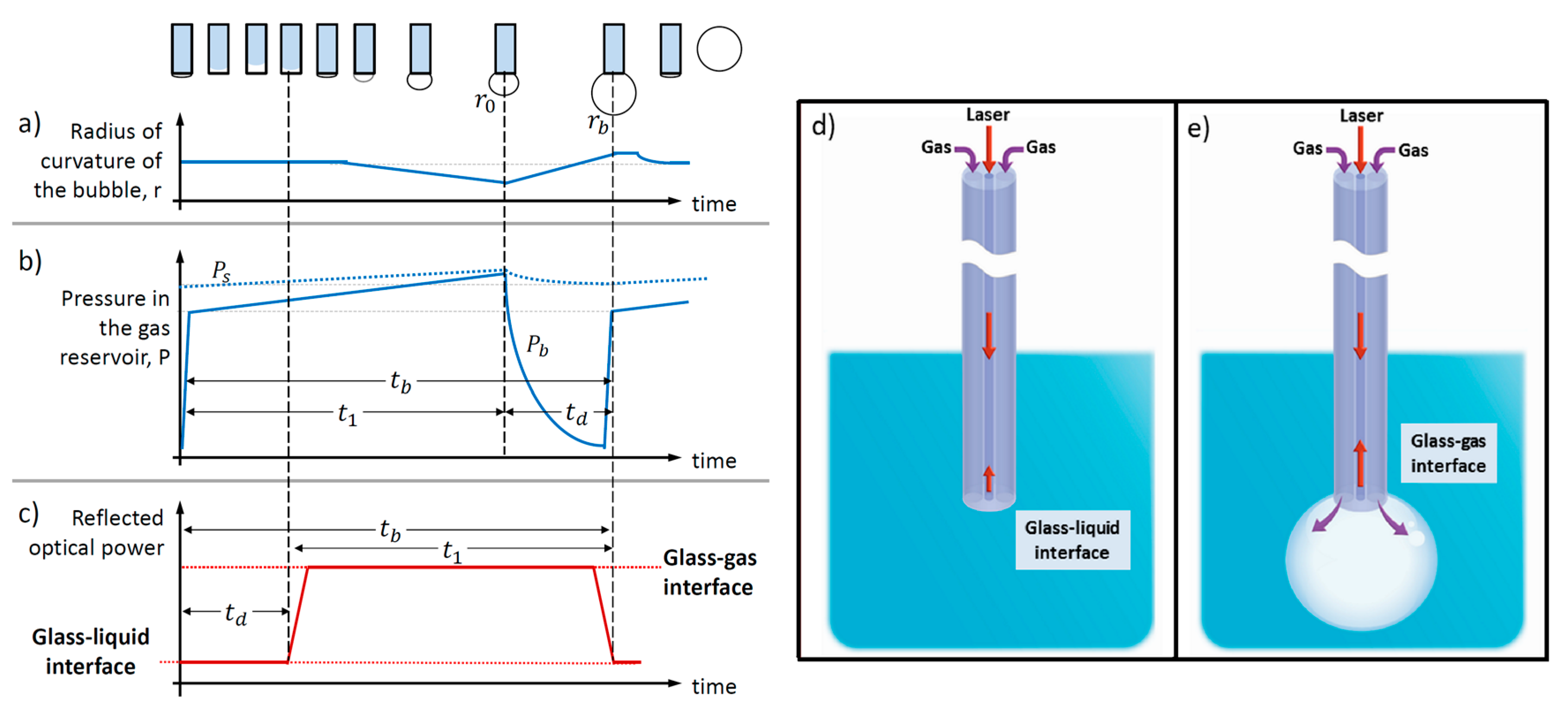
2. Principle of Operation: An Analogy with the Maximum Bubble Pressure Method
3. Materials and Methods
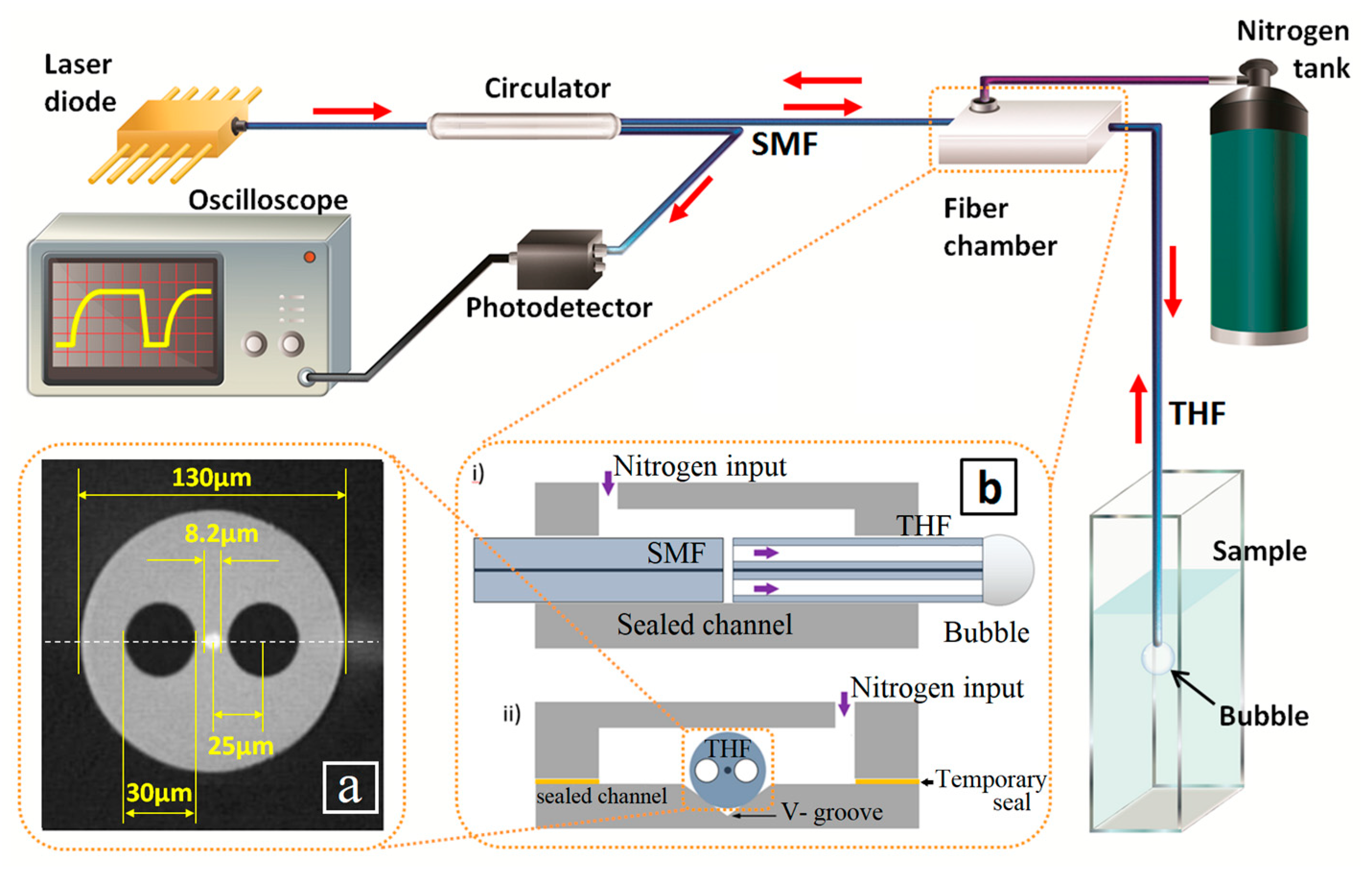
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Fabrication of the Device
3.3. Sample Preparation
4. Results
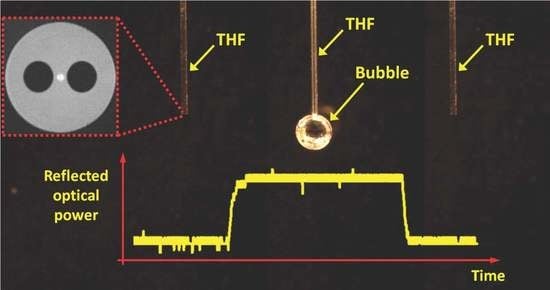
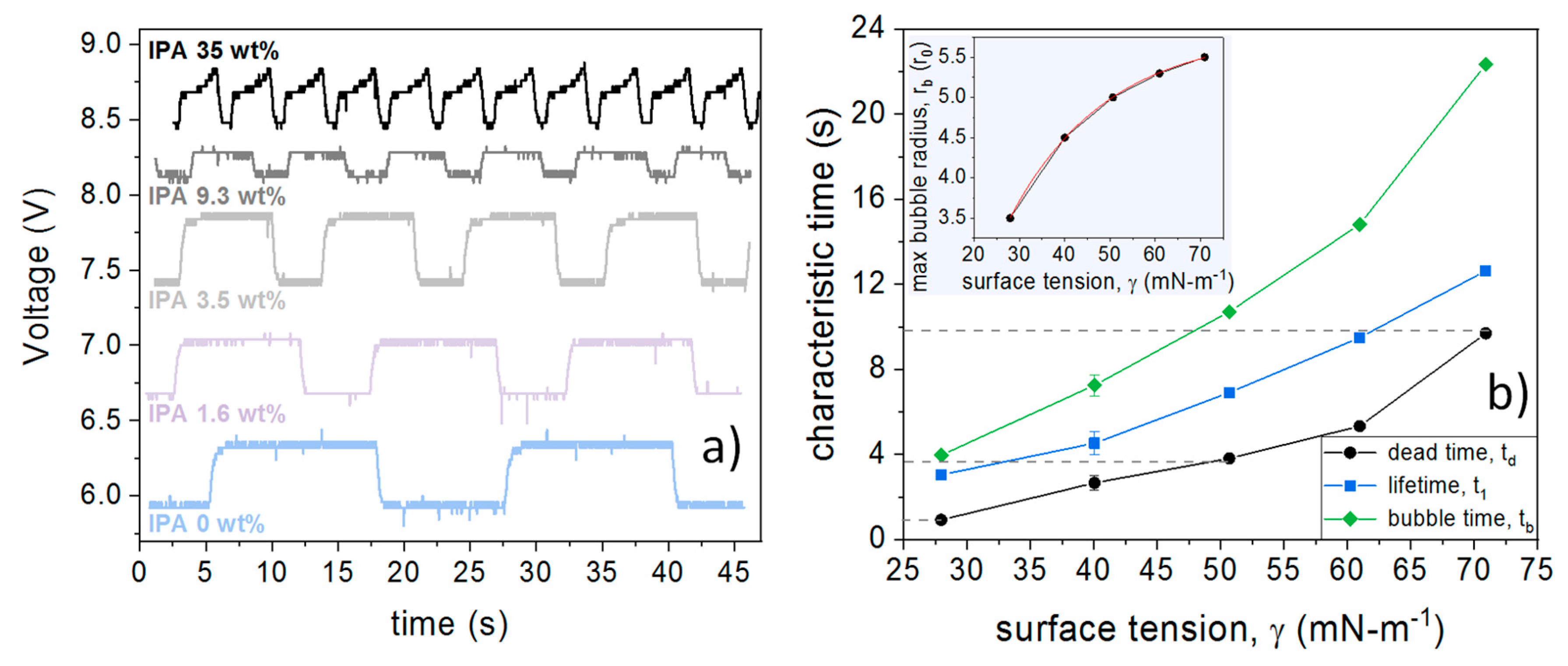
4.1. Observation of the Bubbles
4.2. Determination of the Dead Time
4.3. Estimations of the Dead Time in our Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Thermal Effects Due to Radiation Absorption
| Water | IPA | |
|---|---|---|
| Density, (kg-m-3) | 1000 | 786 |
| Specific heat capacity, (J-kg-1-K-1) | 4179.6 | 2680 |
| Imaginary part of the complex RI (refractive index), k @ 1.55 µm | 1.475 × 10−4 | 4.389 × 10−5 |
| Duration of the stimulus (s) | 5 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−4 |
| Bubble radius (r0), where | 5.5 | 3.5 |
| EM delivering volume, (m3) | 1.70 × 10−10 (170 nL) | 0.44 × 10−10 (44 nL) |
| Temperature increase when (°C) | 0.138 | 0.021 |
Appendix B. The Validity of the Approximations of (1) the Spherical Bubble Growth and (2) the Inertia-Less Regime
Appendix B.1. Spherical Approximation of the Bubble’s Meniscus
Appendix B.1.1. Estimation 1
Appendix B.1.2. Estimation 2
Appendix B.2. Inertia-Less Approximation
Appendix B.2.1. Estimation 1
Appendix B.2.2. Estimation 2
References
- Hartland, S. Surface and Interfacial Tension: Measurement, Theory, and Applications; CRC Press: Zürich, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ebnesajjad, S.; Landrock, A.H. Adhesives Technology Handbook; William Andrew: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzi, A.; Mittal, K.L. Handbook of Adhesive Technology; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Lassemono, S.; Chollet, F.A.; Yang, C. Interfacial tension measurement with an optofluidic sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, H.; Duits, M.H.; Mugele, F. Interfacial tension measurements with microfluidic tapered channels. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 389, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steegmans, M.L.; Warmerdam, A.; Schroen, K.G.; Boom, R.M. Dynamic interfacial tension measurements with microfluidic Y-junctions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9751–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glawdel, T.; Ren, C.L. Droplet formation in microfluidic T-junction generators operating in the transitional regime. III. Dynamic surfactant effects. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 026308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.S.; Wexler, J.S.; Wan, J.; Stone, H.A. Microfluidic ultralow interfacial tensiometry with magnetic particles. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Apolito, R.; Perazzo, A.; D’Antuono, M.; Preziosi, V.; Tomaiuolo, G.; Miller, R.; Guido, S. Measuring interfacial tension of emulsions in situ by microfluidics. Langmuir 2018, 34, 4991–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerken, M.J.; Lammertink, R.G.; Wessling, M. Interfacial aspects of water drop formation at micro-engineered orifices. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 312, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. A new interfacial tension measurement method through a pore array micro-structured device. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2009, 331, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Mukataka, S.; Nakajima, M. Novel asymmetric through-hole array microfabricated on a silicon plate for formulating monodisperse emulsions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7629–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Cruz, V.A.; Hernández-Cordero, J.A. Fiber optic Fabry-Perot sensor for surface tension analysis. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 3028–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kang, J.; Sang, T.; Dong, X.; Zhao, C. Hollow fiber-based Fabry–Perot cavity for liquid surface tension measurement. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 7814–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukhin, S.; Fainerman, V.; Miller, R. Hydrodynamic processes in dynamic bubble pressure experiments 1. A general analysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 114, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.; Miller, R. The Maximum Bubble Pressure Tensiometry. In Studies in Interface Science; Elsevier: Lyon, France, 1998; Volume 6, pp. 279–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalchuk, V.; Dukhin, S. Dynamic effects in maximum bubble pressure experiments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 192, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhin, S.; Mishchuk, N.; Fainerman, V.; Miller, R. Hydrodynamic processes in dynamic bubble pressure experiments: 2. slow meniscus oscillations. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 138, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval’chuk, V.; Dukhin, S.; Makievski, A.; Fainerman, V.; Miller, R. Simultaneous calculation of lifetime and deadtime in maximum bubble pressure measurements. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1998, 198, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval’chuk, V.; Dukhin, S.; Fainerman, V.; Miller, R. Lifetime calculations relative to maximum bubble pressure measurements. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1998, 197, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.; Miller, R. Maximum bubble pressure tensiometry: Theory, analysis of experimental constrains and applications. Bubble Drop Interf. 2011, 2, 75–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fainerman, V.; Miller, R.; Joos, P. The measurement of dynamic surface tension by the maximum bubble pressure method. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1994, 272, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.R.; Gupta, K.; Wasilik, M. Etch rates for micromachining processing-Part II. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 761–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazquez, G.; Alvarez, E.; Navaza, J.M. Surface tension of alcohol water+ water from 20 to 50. degree. C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1995, 40, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.H.; Green, D.W.; Maloney, J.O. Manual del Ingeniero Químico; McGraw-Hill: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, A.W.; Gast, A.P. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Brutin, D. Droplet Wetting and Evaporation: From Pure to Complex Fluids; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Neimz, M.H. Laser-Tissue Interactions: Fundamentals and Applications; “Interaction Mechanisms”; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 45–76, Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.; Wade, S.; Brown, W.; Sttoddart, P. Modeling of light absorption in tissue during infrared neural stimulation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 075002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugden, S. XCVII.—The determination of surface tension from the maximum pressure in bubbles. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1922, 121, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, S.V. The determination of surface tension from the maximum pressure in bubbles. Part II. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1924, 125, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholkovskij, E.; Kovalchuk, V.; Fainerman, V.; Loglio, G.; Krägel, J.; Miller, R.; Zholob, S.; Dukhin, S. Resonance behavior of oscillating bubbles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2000, 224, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Concentration of Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA) (wt %) | Weight of Water (g) | Weight of IPA (g) | Surface Tension, γ (mN-m−1) @ 25C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 0 | 70.91 |
| 1.64 | 19.678 | 0.32 | 60.96 |
| 3.5 | 19.3 | 0.7 | 50.67 |
| 9.3 | 18.14 | 1.86 | 40.04 |
| 35 | 13.0086 | 6.99 | 27.95 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzman-Sepulveda, J.R.; May-Arrioja, D.A.; Fuentes-Fuentes, M.A.; Cuando-Espitia, N.; Torres-Cisneros, M.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, K.; LiKamWa, P. All-Fiber Measurement of Surface Tension Using a Two-Hole Fiber. Sensors 2020, 20, 4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154219
Guzman-Sepulveda JR, May-Arrioja DA, Fuentes-Fuentes MA, Cuando-Espitia N, Torres-Cisneros M, Gonzalez-Gutierrez K, LiKamWa P. All-Fiber Measurement of Surface Tension Using a Two-Hole Fiber. Sensors. 2020; 20(15):4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154219
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzman-Sepulveda, Jose R., Daniel A. May-Arrioja, Miguel A. Fuentes-Fuentes, Natanael Cuando-Espitia, Miguel Torres-Cisneros, Karina Gonzalez-Gutierrez, and Patrick LiKamWa. 2020. "All-Fiber Measurement of Surface Tension Using a Two-Hole Fiber" Sensors 20, no. 15: 4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154219
APA StyleGuzman-Sepulveda, J. R., May-Arrioja, D. A., Fuentes-Fuentes, M. A., Cuando-Espitia, N., Torres-Cisneros, M., Gonzalez-Gutierrez, K., & LiKamWa, P. (2020). All-Fiber Measurement of Surface Tension Using a Two-Hole Fiber. Sensors, 20(15), 4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154219