Development of a Low-Cost Portable Electronic Nose for Cigarette Brands Identification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
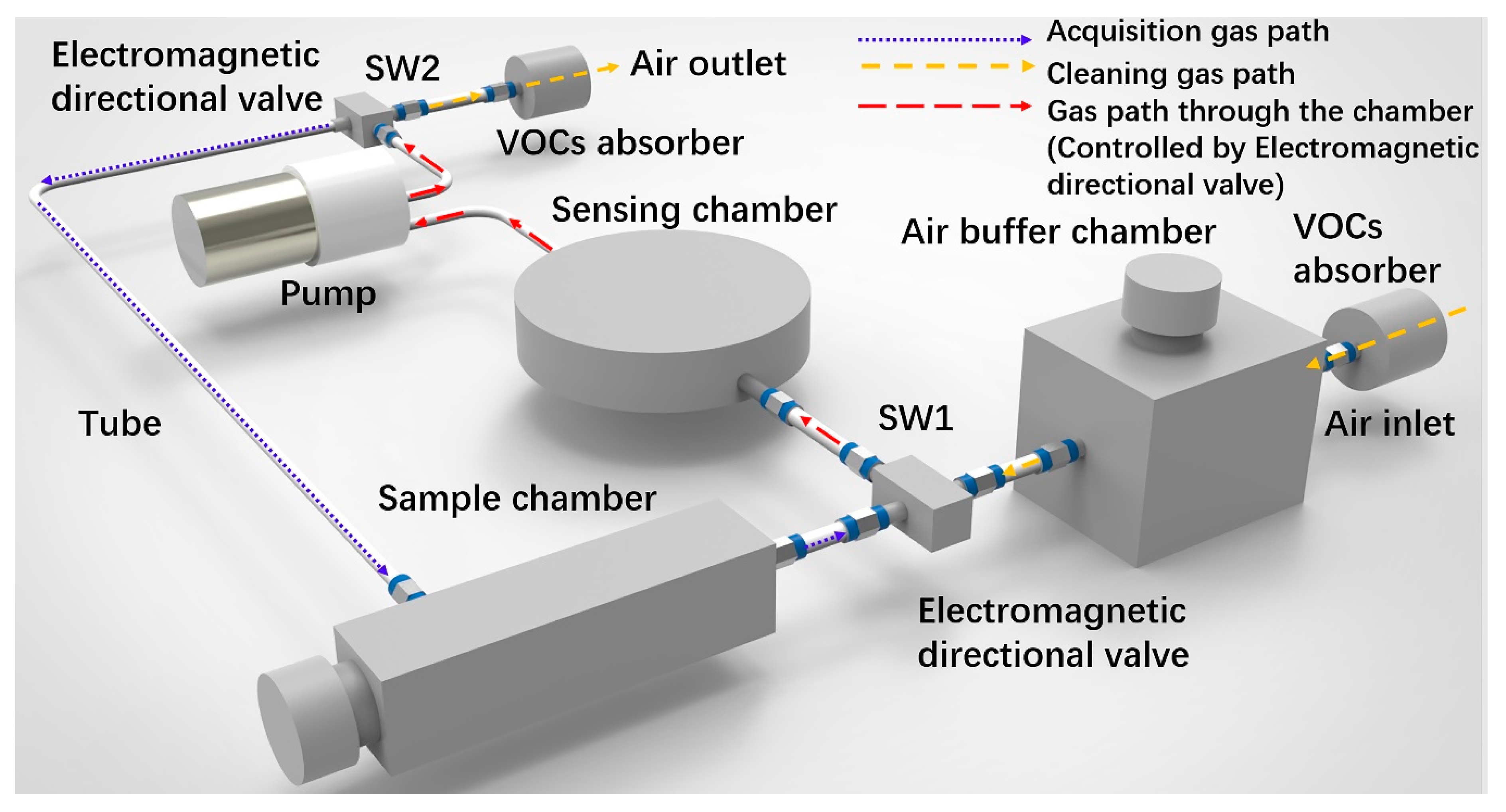
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Chamber Structure on Airflow Distribution
3.2. The Effect of Removing Other Interfering Gases from the Environment
3.3. Analysis of Sensor Response
3.4. Pattern Recognition
3.4.1. Random Forest
3.4.2. K Nearest Neighbors
3.4.3. Effectiveness of Sensors and Features
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Degler, D.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Current Understanding of the Fundamental Mechanisms of Doped and Loaded Semiconducting Metal-Oxide-Based Gas Sensing Materials. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2228–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyodo, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Ueda, T.; Nakagoe, O.; Kamada, K.; Sasahara, T.; Tanabe, S.; Shimizu, Y. Adsorption/combustion-type VOC sensors employing mesoporous γ-alumina co-loaded with noble-metal and oxide. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2015, 220, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, J.; Bonanati, P.; Jaeschke, C.; Hübner, M.; Mädler, L.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Conduction mechanism in undoped and antimony doped SnO2 based FSP gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2013, 188, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polleux, J.; Gurlo, A.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U.; Antonietti, M.; Niederberger, M. Template-Free Synthesis and Assembly of SingleCrystalline Tungsten Oxide Nanowires and Their Gas-Sensing Properties. Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, B.; Shui, H. Investigation on Formaldehyde Gas Sensor with ZnO Thick Film Prepared through Microwave Heating Method. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2009, 142, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, K.; Dodd, G. Analysis of discrimination mechanisms in the mammalian olfactory system using a model nose. Nature 1982, 299, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfi, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Mani, G.K.; Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 2015, 144, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, C.; Ricci, I.; Marone, M.; Derossi, A.; De Pilli, T. Chang-es in the Aromatic Profile of Espresso Coffee as a Function of the Grinding Grade and Extraction Time: A Study by the Electronic Nose System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S.; Godbole, A.; Widdicombe, B.; Unnithan, R.R. Development of a low-cost e-nose to assess aroma profiles: An artificial intelligence application to assess beer quality. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 308, 127688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, H.G.J.; Mendes Junior, J.J.A.; Farinelli, M.E.; Stevan, S.L., Jr. A Prototype to Detect the Alcohol Content of Beers Based on an Electronic Nose. Sensors 2019, 19, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, G.; Lin, B.; Chang, M.; He, W. Quality level identification of West Lake Longjing green tea using electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 301, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, L. Discrimination and characterization of strawberry juice based on electronic nose and tongue: Comparison of different juice processing approaches by LDA, PLSR, RF, and SVM. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6426–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wali, R.P. An Electronic Nose to Differentiate Aromatic Flowers using a Real-Time Information-Rich Piezoelectric Resonance Measurement. Procedia Chem. 2012, 6, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Novoa, O.; Fernández-Caramés, T.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Castedo, L. A cost-effective IoT system for monitoring Indoor radon gas concentration. Sensors 2018, 18, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagula, A.; Zennaro, M.; Inggs, G.; Scott, S.; Gascon, D. Ubiquitous sensor networking for development (usn4d): An application to pollution monitoring. Sensors 2012, 12, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, P.J.; Aujla, A.; Grant, K.H.; Brundle, A.G.; Thompson, M.R.; Vande Hey, J.; Leigh, R.J. Practical use of metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors for measuring nitrogen dioxide and ozone in urban environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Pandey, R.A.; Jana, A. Application of electronic nose for industrial odors and gaseous emissions measurement and monitoring—An overview. Talanta 2015, 144, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laref, R.; Losson, E.; Sava, A.; Siadat, M. Support Vector Machine Regression for Calibration Transfer between Electronic Noses Dedicated to Air Pollution Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, E.R.; Cabete, S.; Ferreira, N.M.F.; Ferreira, F.J.T.E. Electronic Nose; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda, D.M.; Pérez, J.C. SENose: An under U $50 electronic nose for the monitoring of soil gas emissions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 133, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarmaji, A.; Kitagawa, A. Application of temperature modulation-SDP on MOS gas sensors: Capturing soil gaseous profile for discrimination of soil under different nutrient addition. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1035902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHINADAILY China Intensifies Crackdown on Smuggled, Counterfeit Cigarettes. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/business/2017-07/21/content_30201115.htm (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- CHINADAILY Chinese Police Bust Counterfeit Cigarette Gang. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2016-10/20/content_27122177.htm (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Luo, D.; Hosseini, H.G.; Stewart, J.R. Application of ANN with extracted parameters from an electronic nose in cigarette brand identification. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2004, 99, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, C.H.A.; Iglesias, B.A.; Ogawa, T.; Araki, K.; Hoehne, L.; Gruber, J. Identification of Tobacco Types and Cigarette Brands Using an Electronic Nose Based on Conductive Polymer/Porphyrin Composite Sensors. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6476–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudzewski, K.; Osowski, S.; Golembiecka, A. Differential electronic nose and support vector machine for fast recognition of tobacco. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 9886–9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, Z.; Amari, A.; Alami, H.; El Bari, N.; Llobet, E.; Bouchikhi, B. A portable electronic nose system for the identification of cannabis-based drugs. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2011, 155, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzewski, K.; Osowski, S.; Ulaczyk, J. Differential electronic nose of two chemo sensor arrays for odor discrimination. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2010, 145, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.E. K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia 2009, 4, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Gatton, T.M.; Lee, K.-K. A monitoring and advisory system for diabetes patient management using a rule-based method and KNN. Sensors 2010, 10, 3934–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]








| Sensor | Target Analyte | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| TGS2600 | Hydrogen, Carbon mon-oxide | 2.8 |
| TGS2602 | Ammonia, Hydrogen sulfide | 3.1 |
| TGS2620 | Alcohol, Solvent vapors | 3.4 |
| TGS2611 | Methane Natural Gas | 3.0 |
| Label | Price (USD/Box) |
|---|---|
| A | 2.1 |
| B | 2.5 |
| C | 5.6 |
| D1 | 3.1 |
| D2 | 4.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Lu, N.; Yan, M.; Wu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Fan, S. Development of a Low-Cost Portable Electronic Nose for Cigarette Brands Identification. Sensors 2020, 20, 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154239
Wu Z, Zhang H, Sun W, Lu N, Yan M, Wu Y, Hua Z, Fan S. Development of a Low-Cost Portable Electronic Nose for Cigarette Brands Identification. Sensors. 2020; 20(15):4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154239
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhiyuan, Hanying Zhang, Wentao Sun, Ning Lu, Meng Yan, Yi Wu, Zhongqiu Hua, and Shurui Fan. 2020. "Development of a Low-Cost Portable Electronic Nose for Cigarette Brands Identification" Sensors 20, no. 15: 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154239
APA StyleWu, Z., Zhang, H., Sun, W., Lu, N., Yan, M., Wu, Y., Hua, Z., & Fan, S. (2020). Development of a Low-Cost Portable Electronic Nose for Cigarette Brands Identification. Sensors, 20(15), 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154239






