Sit-To-Stand Movement Evaluated Using an Inertial Measurement Unit Embedded in Smart Glasses—A Validation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
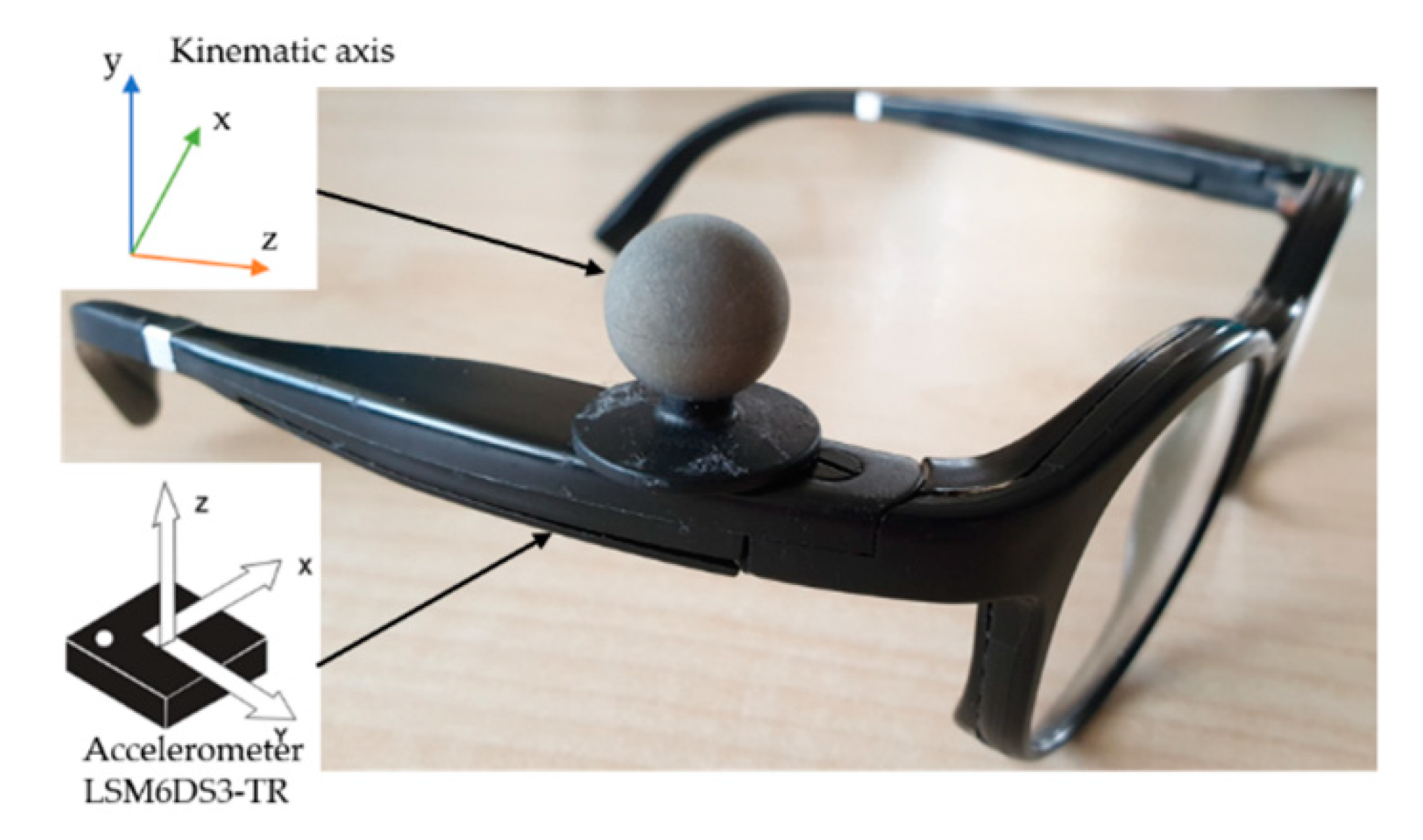
2.3. Apparatus, Data Collection and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reproducibility Intra- and Inter-Session of the Glasses and the Optoelectronic System
3.2. Reliability Intra- and Inter-Session of the Glasses and the Optoelectronic System
3.3. Concurrent Validity of the Glasses against the Optoelectronic System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohannon, R.W. Daily Sit-to-Stands Performed by Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrito, A.; Bichsel, L.; Radlinger, L.; Schmid, S. Reliability and Validity of a Smartphone-Based Application for the Quantification of the Sit-to-Stand Movement in Healthy Seniors. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, W.G.M.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Horemans, H.L.D.; Stam, H.J. Analysis and Decomposition of Accelerometric Signals of Trunk and Thigh Obtained during the Sit-to-Stand Movement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2005, 43, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A Short Physical Performance Battery Assessing Lower Extremity Function: Association with Self-Reported Disability and Prediction of Mortality and Nursing Home Admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csuka, M.; McCarty, D.J. Simple Method for Measurement of Lower Extremity Muscle Strength. Am. J. Med. 1985, 78, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.; Rikli, R.E.; Beam, W.C. A 30-s Chair-Stand Test as a Measure of Lower Body Strength in Community-Residing Older Adults. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1999, 70, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufaki, P.; Mercer, T.H.; Naish, P.F. Effects of Exercise Training on Aerobic and Functional Capacity of End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2002, 22, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, A.; Mancini, M.; Lindemann, U.; Chiari, L.; Zijlstra, W. Sit-Stand and Stand-Sit Transitions in Older Adults and Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: Event Detection Based on Motion Sensors versus Force Plates. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington, P.J.; Myklebust, B.M.; Shambes, G.M. Biomechanical Analysis of the Sit-to-Stand Motion in Elderly Persons. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1992, 73, 609–617. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, W.G.; Bussmann, H.B.; Stam, H.J. Determinants of the Sit-to-Stand Movement: A Review. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, A.; Jaeger, R.J.; Munih, M. Analysis of Standing up and Sitting down in Humans: Definitions and Normative Data Presentation. J. Biomech. 1990, 23, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, Y.-C.; Rogers, M.W. Speed Variation and Resultant Joint Torques during Sit-to-Stand. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1991, 72, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, F.; Cornu, C.; Beaune, B.; Frère, J.; Rahmani, A. Sit to Stand in Elderly Fallers vs Non-Fallers: New Insights from Force Platform and Electromyography Data. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 28, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regterschot, G.R.H.; Zhang, W.; Baldus, H.; Stevens, M.; Zijlstra, W. Accuracy and Concurrent Validity of a Sensor-Based Analysis of Sit-to-Stand Movements in Older Adults. Gait Posture 2016, 45, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmers, S.; Fudickar, S.; Lau, S.; Elgert, L.; Diekmann, R.; Bauer, J.; Hein, A. Measurement of the Chair Rise Performance of Older People Based on Force Plates and IMUs. Sensors 2019, 19, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, B.K.; Jain, H.; Vijay, V.; Yadav, S.K.; Mathur, A.; Hewson, D.J. A Comparison of Four Approaches to Evaluate the Sit-to-Stand Movement. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, R.B.; Gentile, A.M. Sit-to-Stand: Functional Relationship between Upper Body and Lower Limb Segments. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1994, 13, 817–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahmadi, M.R.; Ebrahimi Takamjani, I.; Jaberzadeh, S.; Sarrafzadeh, J.; Sanjari, M.A.; Bagheri, R.; Jannati, E. Test-Retest Reliability of Sit-to-Stand and Stand-to-Sit Analysis in People with and without Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2018, 35, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millor, N.; Lecumberri, P.; Gómez, M.; Martínez-Ramírez, A.; Izquierdo, M. An Evaluation of the 30-s Chair Stand Test in Older Adults: Frailty Detection Based on Kinematic Parameters from a Single Inertial Unit. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, W.; Bisseling, R.W.; Schlumbohm, S.; Baldus, H. A Body-Fixed-Sensor-Based Analysis of Power during Sit-to-Stand Movements. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regterschot, G.R.H.; Zhang, W.; Baldus, H.; Stevens, M.; Zijlstra, W. Test–Retest Reliability of Sensor-Based Sit-to-Stand Measures in Young and Older Adults. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giansanti, D.; Maccioni, G. Physiological Motion Monitoring: A Wearable Device and Adaptative Algorithm for Sit-to-Stand Timing Detection. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, W.G.M.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Horemans, H.L.D.; Stam, H.J. Validity of Accelerometry in Assessing the Duration of the Sit-to-Stand Movement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regterschot, G.R.H.; Folkersma, M.; Zhang, W.; Baldus, H.; Stevens, M.; Zijlstra, W. Sensitivity of Sensor-Based Sit-to-Stand Peak Power to the Effects of Training Leg Strength, Leg Power and Balance in Older Adults. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Hsu, Y.-L. A Review of Accelerometry-Based Wearable Motion Detectors for Physical Activity Monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 7772–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, U.; Hock, A.; Stuber, M.; Keck, W.; Becker, C. Evaluation of a Fall Detector Based on Accelerometers: A Pilot Study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2005, 43, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdalga, E.; Ozdalga, A.; Ahuja, N. The Smartphone in Medicine: A Review of Current and Potential Use Among Physicians and Students. J. Med. Internet Res. 2012, 14, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cárdenas, J.D.; Rodríguez-Juan, J.J.; Smart, R.R.; Jakobi, J.M.; Jones, G.R. Validity and Reliability of an IPhone App to Assess Time, Velocity and Leg Power during a Sit-to-Stand Functional Performance Test. Gait Posture 2018, 59, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán Jiménez, C.; Bennett, P.; Ortiz García, A.; Cuesta Vargas, A.I. Fatigue Detection during Sit-To-Stand Test Based on Surface Electromyography and Acceleration: A Case Study. Sensors 2019, 19, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Mercant, A.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Differences in Trunk Accelerometry Between Frail and Nonfrail Elderly Persons in Sit-to-Stand and Stand-to-Sit Transitions Based on a Mobile Inertial Sensor. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2013, 1, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, S.T.; Metcalfe, J.W.; Liefeith, A.; Jordan, A.R. Validity of Various Portable Devices to Measure Sit-to-Stand Velocity and Power in Older Adults. Gait Posture 2020, 76, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganea, R.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; Büla, C.; Rochat, S.; Aminian, K. Multi-Parametric Evaluation of Sit-to-Stand and Stand-to-Sit Transitions in Elderly People. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabuffetti, M.; Scalera, G.; Ferrarin, M. Effects of Gait Strategy and Speed on Regularity of Locomotion Assessed in Healthy Subjects Using a Multi-Sensor Method. Sensors 2019, 19, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, A. An Analysis on Sensor Locations of the Human Body for Wearable Fall Detection Devices: Principles and Practice. Sensors 2016, 16, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GlassesCrafter.com. Available online: http://www.glassescrafter.com/information/percentage-population-wears-glasses.html (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- Epsilon. Available online: https://www.epsilon.insee.fr/jspui/bitstream/1/23534/1/er881.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying Test-Retest Reliability Using the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, L.M.; Soderberg, G.L.; Ballantyne, B.T.; Clarke, W.R. A Study of Various Normalization Procedures for within Day Electromyographic Data. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1994, 4, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, G.; Nevill, A.M. Statistical Methods for Assessing Measurement Error (Reliability) in Variables Relevant to Sports Medicine. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamako, G.; Chosa, E.; Totoribe, K.; Fukao, Y.; Deng, G. Quantification of the Sit-to-Stand Movement for Monitoring Age-Related Motor Deterioration Using the Nintendo Wii Balance Board. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mean Acceleration Value (Standard Error) in m·s−2 | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (95% Confidence Interval) | Standard Error of the Measurement | Minimum Detectable Change | Coefficient of Variation (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Session 1 | Session 2 | Session 1 | Session 2 | Test-Retest | Session 1 | Session 2 | Test-Retest | Session 1 | Session 2 | Test-Retest | Session 1 | Session 2 | |
| Glasses | |||||||||||||
| VA | |||||||||||||
| Comfort WCC | 14.65 (1.65) | 14.63 (1.19) | 0.88 (0.79–0.94) | 0.86 (0.76–0.93) | 0.87 (0.69–0.95) | 0.60 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 1.65 | 1.46 | 1.44 | 5.17 | 5.33 |
| Comfort CC | 13.29 (1.70) | 13.49 (1.04) | 0.90 (0.82–0.95) | 0.78 (0.66–0.89) | 0.83 (0.61–0.93) | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 1.63 | 1.70 | 1.66 | 6.12 | 5.79 |
| Slow WCC | 13.13 (1.74) | 12.57 (1.72) | 0.89 (0.81–0.95) | 0.91 (0.85–0.96) | 0.75 (0.46–0.90) | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.87 | 1.68 | 1.49 | 2.41 | 4.71 | 4.63 |
| Slow CC | 11.94 (1.68) | 11.71 (1.35) | 0.91 (0.84–0.96) | 0.90 (0.83–0.95) | 0.63 (0.25–0.84) | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.92 | 1.47 | 1.27 | 2.56 | 4.84 | 4.65 |
| APA | |||||||||||||
| Comfort WCC | 2.50 (0.99) | 2.65 (0.94) | 0.72 (0.58–0.85) | 0.70 (0.55–0.84) | 0.45 (0.01–0.74) | 0.47 | 0.55 | 0.73 | 1.24 | 1.51 | 2.01 | 37.61 | 53.32 |
| Comfort CC | 1.76 (0.85) | 2.12 (1.21) | 0.79 (0.66–0.89) | 0.88 (0.79–0.94) | 0.51 (0.08–0.78) | 0.36 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 1.01 | 2.08 | 2.11 | 59.84 | 33.06 |
| Slow WCC | 2.01 (0.99) | 1.80 (1.19) | 0.80 (0.69–0.90) | 0.82 (0.71–0.91) | 0.60 (0.21–0.82) | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.70 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.93 | 53.45 | 56.88 |
| Slow CC | 1.24 (1.12) | 1.20 (1.28) | 0.78 (0.66–0.89) | 0.89 (0.81–0.95) | 0.67 (0.32–0.86) | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 1.11 | 1.32 | 1.94 | 33.32 | 64.35 |
| OptiTrack | |||||||||||||
| VA | |||||||||||||
| Comfort WCC | 4.85 (1.46) | 4.95 (1.04) | 0.90 (0.83–0.95) | 0.84 (0.74–0.92) | 0.92 (0.81–0.97) | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 1.38 | 1.30 | 1.00 | 13.77 | 11.99 |
| Comfort CC | 4.95 (1.64) | 5.31 (1.42) | 0.92 (0.86–0.96) | 0.87 (0.79–0.94) | 0.72 (0.40–0.88) | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 1.37 | 1.55 | 2.26 | 18.53 | 17.67 |
| Slow WCC | 3.27 (1.34) | 2.74 (1.47) | 0.87 (0.78–0.94) | 0.94 (0.89–0.97) | 0.72 (0.40–0.88) | 0.51 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 1.42 | 1.03 | 2.10 | 19.31 | 19.18 |
| Slow CC | 3.14 (1.31) | 2.88 (1.61) | 0.84 (0.74–0.92) | 0.92 (0.86–0.96) | 0.59 (0.21–0.82) | 0.57 | 0.47 | 0.93 | 1.57 | 1.31 | 2.57 | 19.11 | 21.91 |
| APA | |||||||||||||
| Comfort WCC | 2.77 (0.80) | 2.93 (0.77) | 0.79 (0.68–0.90) | 0.80 (0.68–0.90) | 0.94 (0.85–0.98) | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.20 | 1.18 | 1.14 | 0.55 | 17.67 | 16.26 |
| Comfort CC | 2.85 (0.68) | 3.01 (0.61) | 0.79 (0.66–0.89) | 0.78 (0.66–0.89) | 0.70 (0.37–0.87) | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 1.02 | 17.88 | 18.05 |
| Slow WCC | 1.93 (0.75) | 1.73 (0.76) | 0.83 (0.73–0.92) | 0.90 (0.82–0.95) | 0.74 (0.45–0.89) | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.99 | 0.74 | 1.09 | 23.54 | 22.72 |
| Slow CC | 1.93 (0.78) | 1.79 (0.78) | 0.82 (0.71–0.92) | 0.82 (0.71–0.91) | 0.86 (0.68–0.95) | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 0.82 | 21.55 | 24.14 |
| Pearson Correlation (r) | Bland-Altman | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Session 1 | Session 2 | Global | Bias (Mean Difference) | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |
| VA | ||||||
| Comfort WCC | 0.78 *** | 0.60 *** | 0.72 *** | −9.73 | −12.10 | −7.35 |
| Comfort CC | 0.62 *** | 0.37 *** | 0.52 *** | −8.29 | −11.30 | −5.29 |
| Slow WCC | 0.94 *** | 0.94 *** | 0.94 *** | −9.84 | −11.12 | −8.56 |
| Slow CC | 0.76 *** | 0.80 *** | 0.76 *** | −8.84 | −10.89 | −6.79 |
| APA | ||||||
| Comfort WCC | 0.41 *** | 0.36 *** | 0.38 *** | 0.28 | −2.33 | 2.88 |
| Comfort CC | 0.43 *** | 0.61 *** | 0.53 *** | 0.97 | −1.24 | 3.18 |
| Slow WCC | 0.42 *** | 0.48 *** | 0.46 *** | −0.07 | −2.46 | 2.31 |
| Slow CC | 0.54 *** | 0.43 *** | 0.48 *** | 0.64 | −1.84 | 3.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hellec, J.; Chorin, F.; Castagnetti, A.; Colson, S.S. Sit-To-Stand Movement Evaluated Using an Inertial Measurement Unit Embedded in Smart Glasses—A Validation Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185019
Hellec J, Chorin F, Castagnetti A, Colson SS. Sit-To-Stand Movement Evaluated Using an Inertial Measurement Unit Embedded in Smart Glasses—A Validation Study. Sensors. 2020; 20(18):5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185019
Chicago/Turabian StyleHellec, Justine, Frédéric Chorin, Andrea Castagnetti, and Serge S. Colson. 2020. "Sit-To-Stand Movement Evaluated Using an Inertial Measurement Unit Embedded in Smart Glasses—A Validation Study" Sensors 20, no. 18: 5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185019
APA StyleHellec, J., Chorin, F., Castagnetti, A., & Colson, S. S. (2020). Sit-To-Stand Movement Evaluated Using an Inertial Measurement Unit Embedded in Smart Glasses—A Validation Study. Sensors, 20(18), 5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185019





