A New Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Image Registration Using Phase Congruency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
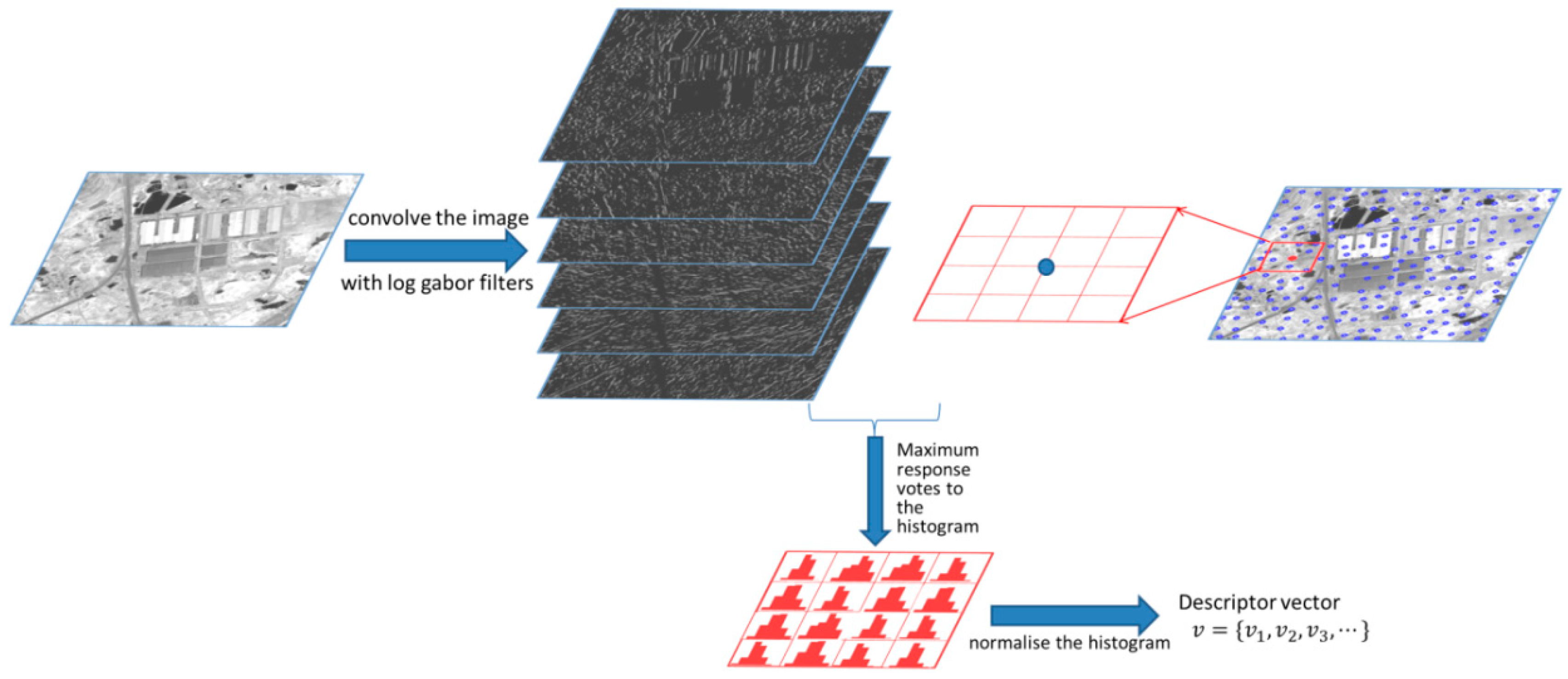
2.1. Feature Extraction
2.2. Feature Description
2.2.1. Phase Congruency
2.2.2. Descriptor Generation
- A window with fixed size is selected around each extracted keypoint, and the voting bin of each pixel in the selected window is calculated according to Equation (6).
- The local window around each keypoint is divided into 4 × 4 blocks, and every pixel in the block makes a contribution to a certain bin in the histogram in the corresponding block. As mentioned above, here, ‘certain bin’ is determined by Equation (6) for each pixel. Furthermore, the contribution to each bin by every pixel is set to 1.
- After obtaining all the histograms in each block, we concatenate the histograms and normalize the feature vector by its L2 norm.
- (1)
- Similar to the first part of descriptor generation, a window of identical size is extracted along each keypoint.
- (2)
- We calculate the angle for each pixel in the local window and constrain this angle within [0, π]. Then, the local window is divided into 4 × 4 blocks, and each block contains a six-bin histogram. Next, we divide into six identical angle domains: [0, 30], [30, 60], [60, 90], [90, 120], [120, 150] and [150, 180], which correspond to the six bins in each histogram in each block. The contribution of each bin is weighted by the overall amplitudes of each pixel.
- (3)
- After obtaining the four histogram vectors, we concatenate the vectors and normalize them by using the L2 norm. At this step, the generation of the second part of the proposed descriptor is complete.
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Description of Datasets
3.2. Evaluation Criteria
3.3. Parameter Settings
3.4. Description of Compared Methods
- (1)
- (2)
- LGHD [31]: LGHD is a descriptor that directly utilizes the log-Gabor filter response as the constituent in the descriptor. In this study, a bank of 24 log-Gabor filters was utilized to represent filters of four scales and six orientations.
- (3)
- EOH [16]: EOH is a descriptor that utilizes the results of the edge detector; this descriptor consists of the maximum response of the orientation filter on the results of the edge detector.
- (4)
- PIIFD [13]: PIIFD is a partially intensity invariant feature descriptor that utilizes the image outlines within local windows to generate orientation histograms. We utilized the suggested parameters in this study.
- (5)
- GDISIFT [14]: It constrains the range of the main orientation of each keypoint within instead of under the assumption that the non-linear intensity change causes the gradient orientation inverse in the opposite direction.
- (6)
- HOG [9]: HOG is a feature descriptor used in computer vision; it counts occurrences of gradient orientation in localized portions of an image. HOG is computed on a dense grid of uniformly spaced cells and uses overlapping local contrast normalization for improved accuracy.
- (7)
- SURF [6]: SURF is a fast and robust algorithm for tasks such as object recognition and image registration. Its descriptor is based on the sum of the Haar wavelet response around the keypoint.
- (8)
- PCEHD [33]: PCEHD is a descriptor proposed for solving the correspondence problem between multimodal images. This descriptor is based on the combination of responses of log-Gabor filters and spatial information on the shape of the neighboring region around keypoints.
3.5. Performance Tests on Three Datasets and Analysis
3.5.1. Performance on Dataset 1
3.5.2. Performance on Dataset 2
3.5.3. Performance on Dataset 3
3.6. Computational Time Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, L.G. A survey of image registration techniques. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 1992, 24, 325–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitová, B.; Flusser, J. Image registration methods: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference on Computer vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Sukthankar, R. PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasby, A.A. Image Registration: Principles, Tools and Methods; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, J.-M.; Yu, G. ASIFT: A New Framework for Fully Affine Invariant Image Comparison. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2009, 2, 438–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Calonder, M.; Lepetit, V.; Strecha, C.; Fua, P. BRIEF: Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features. In Computer Vision-Eccv 2010, Pt Iv; Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 6314, pp. 778–792. [Google Scholar]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Alahi, A.; Ortiz, R.; Vandergheynst, P. Freak: Fast retina keypoint. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tian, J.; Lee, N.; Zheng, J.; Smith, R.T.; Laine, A.F. A Partial Intensity Invariant Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Retinal Image Registration. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firmenichy, D.; Brown, M.; Süsstrunk, S. Multispectral interest points for RGB-NIR image registration. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, S.; Sablatnig, R. A Robust SIFT Descriptor for Multispectral Images. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, C.; Barrera, F.; Lumbreras, F.; Sappa, A.D.; Toledo, R. Multispectral Image Feature Points. Sensors 2012, 12, 12661–12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarfraz, M.S.; Hellwich, O. Head Pose Estimation in Face Recognition across Pose Scenarios. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, Funchal, Portugal, 22–25 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shechtman, E.; Irani, M. Matching local self-similarities across images and videos. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, K.; Philbin, J.; Zisserman, A. Efficient retrieval of deformable shape classes using local self-similarities. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Shan, J. A local descriptor based registration method for multispectral remote sensing images with non-linear intensity differences. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 90, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shen, L.; Hao, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Robust Optical-to-SAR Image Matching Based on Shape Properties. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Li, X.R.; Yang, H.; Zhao, L.Y. Robust local feature descriptor for multisource remote sensing image registration. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Ebadi, H. Distinctive Order Based Self-Similarity descriptor for multi-sensor remote sensing image matching. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maver, J. Self-Similarity and Points of Interest. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ryu, S.; Ham, B.; Kim, J.; Sohn, K. Local self-similarity frequency descriptor for multispectral feature matching. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 5746–5750. [Google Scholar]
- Torabi, A.; Bilodeau, G.-A. Local self-similarity-based registration of human ROIs in pairs of stereo thermal-visible videos. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodensteiner, C.; Huebner, W.; Juengling, K.; Mueller, J.; Arens, M. Local multi-modal image matching based on self-similarity. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 937–940. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Zeng, G.H.; Fan, J.P. Fast Local Self-Similarity for describing interest regions. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Wan, W.B.; Zhao, Q.F.; Zhang, X.M. Local self-similarity descriptor for point-of-interest reconstruction of real-world scenes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerroui, D.; Noble, J.A.; Brady, M. On the selection of band-pass quadrature filters. In Frontiers in Robotics Research; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 69–112. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, C.A.; Sappa, A.D.; Toledo, R. LGHD: A feature descriptor for matching across non-linear intensity variations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kovesi, P. Image features from phase congruency. Videre J. Comput. Vis. Res. 1999, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mouats, T.; Aouf, N. Multimodal stereo correspondence based on phase congruency and edge histogram descriptor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Fusion, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 July 2013; pp. 1981–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Shan, J.; Bruzzone, L.; Shen, L. Robust Registration of Multimodal Remote Sensing Images Based on Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2941–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shen, L. Hopc: A novel similarity metric based on geometric structural properties for multi-modal remote sensing image matching. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, G.; Kruger, U.; Yan, P. Deep learning in medical image registration: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2020, 31, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, C.A.; Sappa, A.D.; Aguilera, C.; Toledo, R. Cross-spectral local descriptors via quadruplet network. Sensors 2017, 17, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y. Deep similarity learning for multimodal medical images. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2018, 6, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovsky, M.; Gutiérrez-Becker, B.; Mateus, D.; Navab, N.; Komodakis, N. A deep metric for multimodal registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Wells, W.M. Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 24, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hel-Or, Y.; Hel-Or, H.; David, E. Matching by Tone Mapping: Photometric Invariant Template Matching. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesto-Diaz, M.; Tombari, F.; Gonzalez-Aguilera, D.; Lopez-Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez-Gonzalvez, P. Feature matching evaluation for multimodal correspondence. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 129, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesi, P. Phase Congruency Detects Corners and Edges. In Proceedings of the Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, Sydney, Australia, 10–12 December 2003; pp. 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.-L.; Ngo, C.-W. Scale-rotation invariant pattern entropy for keypoint-based near-duplicate detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Threshold | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 0.822 | 0.844 | 0.867 | 0.889 | 0.911 | 0.933 | 0.956 | 0.978 | 1 | ||
| SIFT | Precision | 0.149 | 0.13 | 0.112 | 0.094 | 0.076 | 0.062 | 0.049 | 0.038 | 0.03 | 0.024 |
| Recall | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.02 | 0.022 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.025 | 0.027 | |
| F-Measure | 0.029 | 0.03 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.031 | 0.029 | 0.027 | 0.025 | |
| LGHD | Precision | 0.341 | 0.321 | 0.31 | 0.292 | 0.29 | 0.278 | 0.258 | 0.257 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| Recall | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.022 | 0.03 | 0.041 | 0.055 | 0.079 | 0.111 | 0.22 | |
| F-Measure | 0.02 | 0.026 | 0.033 | 0.042 | 0.054 | 0.071 | 0.09 | 0.121 | 0.152 | 0.204 | |
| EOH | Precision | 0.252 | 0.145 | 0.134 | 0.127 | 0.109 | 0.096 | 0.08 | 0.065 | 0.054 | 0.046 |
| Recall | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.027 | 0.054 | |
| F-Measure | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.02 | 0.024 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.05 | |
| GDISIFT | Precision | 0.352 | 0.29 | 0.251 | 0.211 | 0.162 | 0.124 | 0.097 | 0.075 | 0.059 | 0.047 |
| Recall | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.031 | 0.036 | 0.054 | |
| F-Measure | 0.027 | 0.031 | 0.035 | 0.038 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.05 | |
| PIIFD | Precision | 0.138 | 0.112 | 0.091 | 0.075 | 0.059 | 0.047 | 0.038 | 0.03 | 0.024 | 0.018 |
| Recall | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.02 | |
| F-Measure | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.023 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.023 | 0.021 | 0.019 | |
| Proposed | Precision | 0.407 | 0.387 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.309 | 0.307 | 0.289 | 0.281 | 0.251 | 0.201 |
| Recall | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.037 | 0.046 | 0.06 | 0.076 | 0.099 | 0.127 | 0.237 | |
| F-Measure | 0.039 | 0.047 | 0.054 | 0.067 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.147 | 0.169 | 0.218 | |
| PCEHD | Precision | 0.274 | 0.251 | 0.222 | 0.202 | 0.176 | 0.15 | 0.127 | 0.106 | 0.093 | 0.085 |
| Recall | 0.023 | 0.026 | 0.029 | 0.033 | 0.038 | 0.043 | 0.047 | 0.053 | 0.06 | 0.096 | |
| F-Measure | 0.043 | 0.047 | 0.051 | 0.057 | 0.063 | 0.067 | 0.068 | 0.071 | 0.073 | 0.09 | |
| HOG | Precision | 0.079 | 0.072 | 0.07 | 0.062 | 0.055 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.038 | 0.034 | 0.034 |
| Recall | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.039 | |
| F-Measure | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.02 | 0.022 | 0.024 | 0.025 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.037 | |
| SURF | Precision | 0.252 | 0.251 | 0.209 | 0.179 | 0.164 | 0.145 | 0.132 | 0.108 | 0.088 | 0.071 |
| Recall | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | |
| F-Measure | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.012 | |
| Threshold | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 0.822 | 0.844 | 0.867 | 0.889 | 0.911 | 0.933 | 0.956 | 0.978 | 1 | ||
| SIFT | Precision | 0.508 | 0.454 | 0.397 | 0.341 | 0.285 | 0.232 | 0.185 | 0.145 | 0.111 | 0.084 |
| Recall | 0.089 | 0.09 | 0.091 | 0.092 | 0.093 | 0.094 | 0.096 | 0.097 | 0.098 | 0.099 | |
| F-Measure | 0.151 | 0.15 | 0.148 | 0.145 | 0.141 | 0.134 | 0.126 | 0.116 | 0.104 | 0.091 | |
| LGHD | Precision | 0.546 | 0.533 | 0.517 | 0.501 | 0.483 | 0.462 | 0.439 | 0.409 | 0.367 | 0.307 |
| Recall | 0.152 | 0.164 | 0.176 | 0.189 | 0.203 | 0.217 | 0.233 | 0.251 | 0.269 | 0.357 | |
| F-Measure | 0.238 | 0.251 | 0.263 | 0.274 | 0.286 | 0.296 | 0.305 | 0.311 | 0.311 | 0.33 | |
| EOH | Precision | 0.33 | 0.316 | 0.305 | 0.292 | 0.277 | 0.261 | 0.242 | 0.22 | 0.193 | 0.164 |
| Recall | 0.055 | 0.061 | 0.068 | 0.076 | 0.085 | 0.095 | 0.107 | 0.121 | 0.137 | 0.193 | |
| F-Measure | 0.095 | 0.103 | 0.112 | 0.121 | 0.13 | 0.139 | 0.148 | 0.156 | 0.16 | 0.177 | |
| GDISIFT | Precision | 0.561 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.414 | 0.358 | 0.301 | 0.246 | 0.195 | 0.15 | 0.116 |
| Recall | 0.079 | 0.082 | 0.086 | 0.089 | 0.092 | 0.095 | 0.099 | 0.102 | 0.105 | 0.136 | |
| F-Measure | 0.139 | 0.142 | 0.145 | 0.146 | 0.147 | 0.145 | 0.141 | 0.134 | 0.124 | 0.125 | |
| PIIFD | Precision | 0.494 | 0.438 | 0.38 | 0.321 | 0.266 | 0.213 | 0.166 | 0.128 | 0.096 | 0.072 |
| Recall | 0.075 | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.079 | 0.08 | 0.081 | 0.081 | 0.082 | 0.083 | 0.084 | |
| F-Measure | 0.131 | 0.13 | 0.129 | 0.126 | 0.123 | 0.117 | 0.109 | 0.1 | 0.089 | 0.077 | |
| Proposed | Precision | 0.584 | 0.569 | 0.554 | 0.536 | 0.517 | 0.495 | 0.47 | 0.439 | 0.396 | 0.341 |
| Recall | 0.183 | 0.196 | 0.209 | 0.223 | 0.237 | 0.252 | 0.267 | 0.284 | 0.302 | 0.397 | |
| F-Measure | 0.279 | 0.292 | 0.304 | 0.315 | 0.325 | 0.334 | 0.341 | 0.345 | 0.343 | 0.367 | |
| PCEHD | Precision | 0.602 | 0.553 | 0.503 | 0.448 | 0.393 | 0.338 | 0.286 | 0.237 | 0.194 | 0.163 |
| Recall | 0.113 | 0.117 | 0.121 | 0.124 | 0.128 | 0.132 | 0.136 | 0.14 | 0.144 | 0.189 | |
| F-Measure | 0.19 | 0.193 | 0.194 | 0.195 | 0.193 | 0.19 | 0.184 | 0.176 | 0.165 | 0.175 | |
| HOG | Precision | 0.368 | 0.329 | 0.289 | 0.253 | 0.218 | 0.187 | 0.159 | 0.134 | 0.112 | 0.099 |
| Recall | 0.062 | 0.065 | 0.068 | 0.071 | 0.074 | 0.077 | 0.081 | 0.084 | 0.087 | 0.116 | |
| F-Measure | 0.106 | 0.108 | 0.11 | 0.111 | 0.111 | 0.109 | 0.107 | 0.103 | 0.098 | 0.106 | |
| SURF | Precision | 0.514 | 0.474 | 0.435 | 0.398 | 0.361 | 0.325 | 0.292 | 0.261 | 0.234 | 0.207 |
| Recall | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | |
| F-Measure | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | |
| Threshold | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 0.822 | 0.844 | 0.867 | 0.889 | 0.911 | 0.933 | 0.956 | 0.978 | 1 | ||
| SIFT | Precision | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Recall | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| F-Measure | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| LGHD | Precision | 0.215 | 0.204 | 0.192 | 0.175 | 0.164 | 0.15 | 0.137 | 0.125 | 0.107 | 0.086 |
| Recall | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.023 | 0.029 | 0.038 | 0.052 | 0.072 | 0.121 | |
| F-Measure | 0.016 | 0.02 | 0.026 | 0.031 | 0.04 | 0.049 | 0.06 | 0.074 | 0.086 | 0.1 | |
| EOH | Precision | 0.142 | 0.131 | 0.118 | 0.111 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.078 | 0.068 | 0.059 | 0.048 |
| Recall | 0.008 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.021 | 0.026 | 0.033 | 0.043 | 0.069 | |
| F-Measure | 0.015 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.034 | 0.039 | 0.044 | 0.05 | 0.057 | |
| GDISIFT | Precision | 0.095 | 0.084 | 0.074 | 0.063 | 0.053 | 0.044 | 0.036 | 0.029 | 0.023 | 0.019 |
| Recall | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.02 | 0.028 | |
| F-Measure | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.02 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.021 | 0.023 | |
| PIIFD | Precision | 0.011 | 0.01 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Recall | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| F-Measure | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| Proposed | Precision | 0.259 | 0.244 | 0.222 | 0.207 | 0.193 | 0.176 | 0.158 | 0.14 | 0.122 | 0.1 |
| Recall | 0.018 | 0.022 | 0.027 | 0.032 | 0.039 | 0.047 | 0.058 | 0.073 | 0.093 | 0.142 | |
| F-Measure | 0.033 | 0.04 | 0.047 | 0.055 | 0.064 | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.096 | 0.106 | 0.118 | |
| PCEHD | Precision | 0.129 | 0.108 | 0.098 | 0.082 | 0.068 | 0.057 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.035 | 0.028 |
| Recall | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.01 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.02 | 0.026 | 0.039 | |
| F-Measure | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.03 | 0.033 | |
| HOG | Precision | 0.043 | 0.038 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.025 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.011 |
| Recall | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.012 | 0.016 | |
| F-Measure | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.013 | |
| SURF | Precision | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| Recall | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.018 | |
| F-Measure | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.004 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, G.; Zhao, S. A New Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Image Registration Using Phase Congruency. Sensors 2020, 20, 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185105
Yu G, Zhao S. A New Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Image Registration Using Phase Congruency. Sensors. 2020; 20(18):5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185105
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Guorong, and Shuangming Zhao. 2020. "A New Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Image Registration Using Phase Congruency" Sensors 20, no. 18: 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185105
APA StyleYu, G., & Zhao, S. (2020). A New Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Image Registration Using Phase Congruency. Sensors, 20(18), 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185105




