New Uses for the Personal Glucose Meter: Detection of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Screening †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
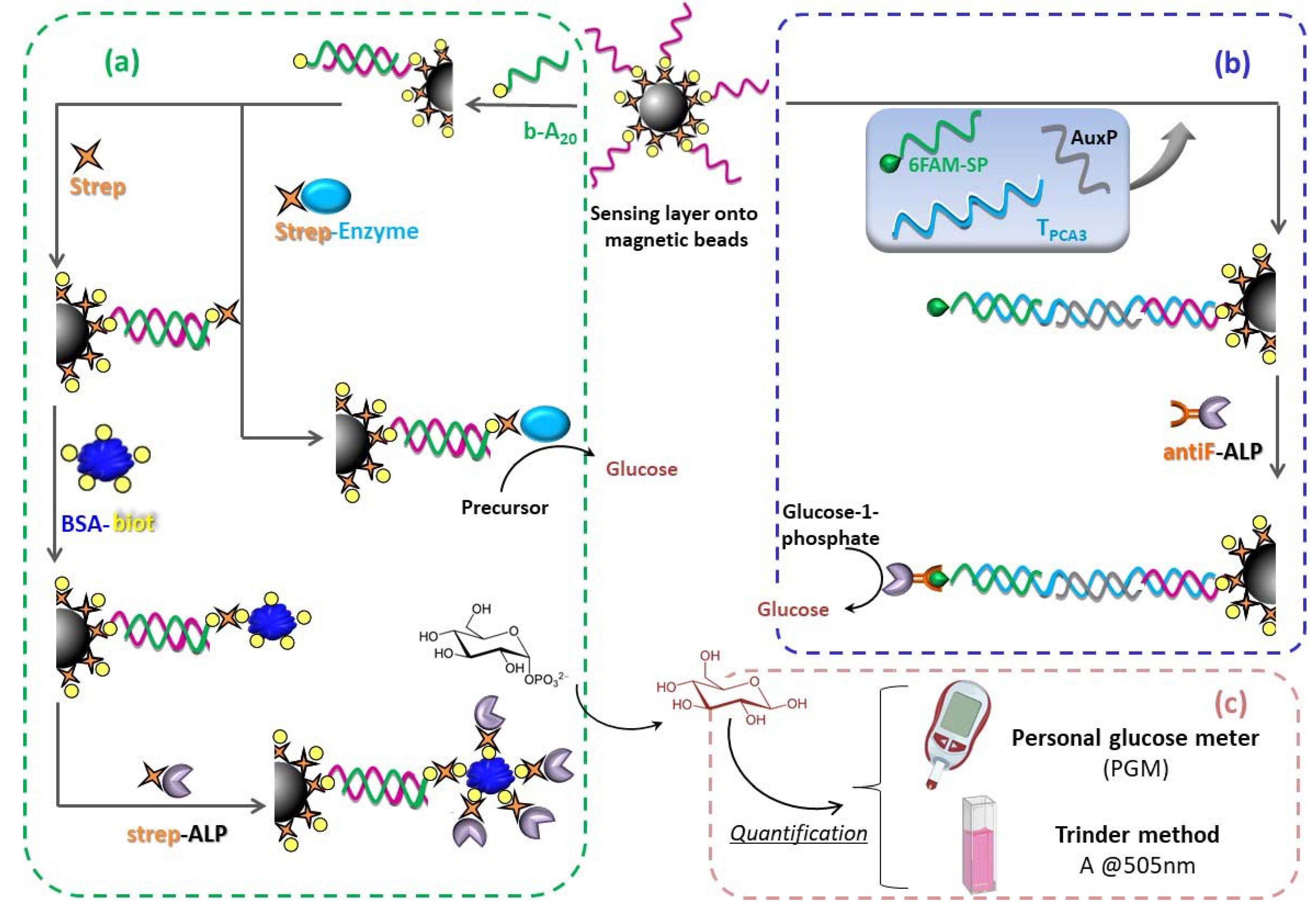
2.3. Sensing Layer Preparation of Magnetic Microbeads
2.4. Hybridization-Based Assay on Magnetic Microbeads
2.5. Trinder Method
2.6. Amplification Based on the Biotin-Streptavidin Recognition Event
3. Results
3.1. β-Galactosidase
3.2. Streptavidin-Alkaline Phosphatase
3.3. Antifluorescein-Fab Fragment-Alkaline Phosphatase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Point-of-Care Testing (POCT)–Requirements for Quality and Competence; ISO 22870; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, T.; Liu, D.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Ruan, Q.; Song, Y.; Tian, T.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lin, H.; et al. A pressure-based bioassay for the rapid, portable and quantitative detection of C-reactive protein. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8452–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Sanjay, S.T.; Dou, M.; Li, X.J. Nanoparticle-mediated photothermal effect enables a new method for quantitative biochemical analysis using a thermometer. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5422–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Yang, J.; Gao, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Enhanced ELISA using a handheld pH meter and enzyme-coated microparticles for the portable sensitive detection of proteins. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3474–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Trends in miniaturized biosensors for point-of-care testing. TrAC 2020, 122, 115701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Pothukuchy, A.; Gollihar, J.D.; Nourani, A.; Li, B.; Ellington, A.D. Coupling sensitive nucleic acid amplification with commercial pregnancy test strips. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.F.; Foster, J.R. A history of blood glucose meters and their role in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 69, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems-Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus; ISO 15197; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Transforming the blood glucose meter into a general healthcare meter for in vitro diagnostics in mobile health. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, C.; Ma, H.; Zhu, L.; Wen, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Li, L. Portable glucose meter: Trends in techniques and its potential application in analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, F.; Peterson, J.R.; Gooding, J.J. The application of personal glucose meters as universal point-of-care diagnostic tools. Biosens. Bioelectrons 2020, 148, 111835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Glucose encapsulating liposome for signal amplification for quantitative detection of biomarkers with glucometer readout. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 72, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhu, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. Bioresponsive controlled release from mesoporous silica nanocontainers with glucometer readout. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Using commercially available personal glucose meters for portable quantification of DNA. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalona, W.J. Prostate cancer screening. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J. Biomarkers for prostate cancer: Prostate-specific antigen and beyond. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussemakers, M.J.; van Bokhoven, A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Smit, F.P.; Karthaus, H.F.; Schalken, J.A.; Debruyne, F.M.J.; Ru, N.; Isaacs, W.B. DD3: A new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5975–5979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Progensa PCA3 Assay. Available online: https://www.hologic.com/package-inserts/diagnostic-products/progensa-pca3-assay (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Barham, D.; Trinder, P. An improved color reagent for the determination of blood glucose by the oxidase system. Analyst 1972, 97, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, D.A.; Chan, D.W. Biomarkers in prostate cancer: what’s new? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Lan, T.; Lu, Y. Using the widely available blood glucose meter to monitor insulin and HbAIc. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helianti, I.; Okubo, T.; Morita, Y. Characterization of thermostable native alkaline phosphatase from an aerobic hyperthermophilic archaeon, Aeropyrum pernix K1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, E.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Monovalent labeling system improves the sensitivity of aptamer-based inhibition assays for small molecule detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.W.; Wang, B.Y.; Lin, H.-S.; Lin, T.-Y.; Hung, Y.-J.; Engebretson, D.A.; Lee, W.; Carey, J.R. Layer by layer assembly of biotinylated protein networks for signal amplification. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Novak, D.E.; Hoganson, G.E.; Zhu, J.; Lu, Y. Using a personal glucose meter and alkaline phosphatase for point-of-care quantification of galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase in clinical galactosemia diagnosis. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, T.-T.; Huang, Z.-F.; Hu, S.-W.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. An exploration of nucleic acid liquid biopsy using a glucose meter. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, W.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, F. Quantitative and selective DNA detection with portable personal glucose meter using loop-based DNA competitive hybridization strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.-P.; Zhang, X. A three-dimensional DNA walking machine for the ultrasensitive dual-modal detection of miRNA using a fluorometer and personal glucose meter. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11279–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue-tao, X.; Kai-yi, L.; Jia-ying, Z. Portable and sensitive quantitative detection of DNA using personal glucose meters and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Analyst 2014, 139, 4982–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; Tao, Y.; Dai, T.; Yuan, C.; Xie, G. Portable and sensitive detection of DNA based on personal glucose meters and nanogold-funcionalized PAMAM dendrimer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, N.; Zheng, J.; Yang, R.; Li, J. Oligonucleotide cross-linked hydrogel for recognition and quantitation of microRNAs based on a portable glucometer readout. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7792–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Sun, F.; Na, N.; Ouyang, J. Detection of p53 DNA using commercially available personal glucose meters based on rolling circle amplification coupled with nicking enzyme signal amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1060, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, S.; Cánovas, R.; Neumann, F.; Paulraj, T.; Nilsson, M.; Crespo, G.A.; Madaboosi, N. The sweet detection of rolling circle amplification: Glucose-based electrochemical genosensor for the detection of viral nucleic acid. Biosens. Bioelectrons 2020, 151, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.-H.; Yu, B.-Y.; Tian, J. Dual signal amplification for microRNA-21 detection based on duplex-specific nuclease and invertase. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11257–11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zaman, M.H. Low-cost tools for diagnosing and monitoring HIV infection in low-resource settings. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Dou, Y.; He, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ye, A.; Liu, W.; Kong, L. Improved sensitivity and specificity for prostate cancer diagnosis based on the urine PCA3/PSA ratio acquired by sequence-specific RNA capture. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Name | Role | Sequence (from 5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| b-T20 | Biotinylated capture probe | Biotin-TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTT |
| b-A20 | Model target | Biotin-AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA |
| b-CP | Biotinylated PCA3 capture probe | Biotin-(T)6-AATTCTGGCTTCTGCTGAGAAT |
| SP-6FAM | 6FAM-Signaling probe | AGACCTAATGCAAGT-6FAM |
| AuxP | Auxiliary probe | ACCGCCTGATGCACAG |
| AuxP6FAM | 6FAM-Auxiliary probe | ACCGCCTGATGCACAG-6FAM |
| TPCA3 | Target PCA3 | AAGCAAAATACTTGCATTAGGTCTCAGCTGGGGCTGTGCATCA GGCGGTTTGAGAAATATTCAATTCTCAGCAGAAGCCAGAATT |
| IPSA | Interference PSA | GGTCTTCCTTTGGCATGGGATGGGGATGAAGTAAGGAGAGGGACTGGACCCCCTGGAAGCTGATTC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abardía-Serrano, C.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. New Uses for the Personal Glucose Meter: Detection of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Screening. Sensors 2020, 20, 5514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195514
Abardía-Serrano C, Miranda-Castro R, de-los-Santos-Álvarez N, Lobo-Castañón MJ. New Uses for the Personal Glucose Meter: Detection of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Screening. Sensors. 2020; 20(19):5514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195514
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbardía-Serrano, Clara, Rebeca Miranda-Castro, Noemí de-los-Santos-Álvarez, and María Jesús Lobo-Castañón. 2020. "New Uses for the Personal Glucose Meter: Detection of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Screening" Sensors 20, no. 19: 5514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195514
APA StyleAbardía-Serrano, C., Miranda-Castro, R., de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N., & Lobo-Castañón, M. J. (2020). New Uses for the Personal Glucose Meter: Detection of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Screening. Sensors, 20(19), 5514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195514








