Measurements of Rotational Events Generated by Artificial Explosions and External Excitations Using the Optical Fiber Sensors Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
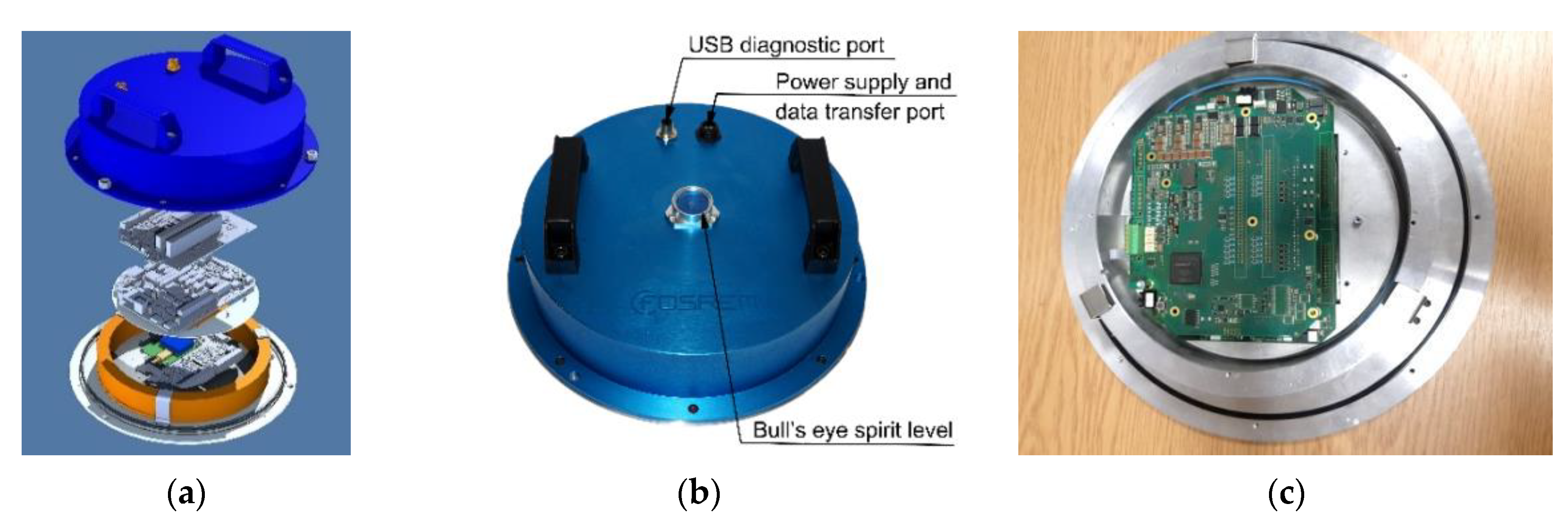
2. Construction of the Applied FOSREM Type FOS5
3. Experiment Description
4. Results of Recorded Rotational Events Generated by Artificial Explosions and External Excitations Generated by the VibroSeis Truck
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, W.H.K. Seismology, Rotation. In Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics; Gupta, H.K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.G. Strong-motion seismology. In The International Handbook of Earthquake and Engineering Seismology, Part B, 1st ed.; Lee, W.H.K., Kanamori, H., Jennings, P.C., Kisslinger, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Chapter 57; pp. 937–965. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A. Earthquake Engineering—From Engineering Seismology to Optimal Seismic Design of Engineering Structures, 1st ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zembaty, Z.; Mutke, G.; Nawrocki, D.; Bobra, P. Rotational Ground-Motion Records from Induced Seismic Events. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presentation on Seismotectonics from the Department of Geophysics, University of Munich. Available online: http://www.geophysik.uni-muenchen.de/~igel/Lectures/Sedi/sedi_tectonics.ppt (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Venkateswara, K.; Hagedorn, C.A.; Turner, M.D.; Arp, T.; Gundlach, J.H. A high-precision mechanical absolute-rotation sensor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trifunac, M.D. A note on rotational components of earthquake motions on ground surface for incident body waves. Int. J. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1982, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunac, M.D. Effects of Torsional and Rocking Excitations on the Response of Structures. In Earthquake Source Asymmetry, Structural Media and Rotation Effects; Teisseyre, R., Majewski, E., Takeo, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 569–582. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzych, A.T.; Jaroszewicz, L.R.; Krajewski, Z.; Dudek, M.; Teisseyre, K.P.; Kowalski, J.K. Two Correlated Interferometric Optical Fiber Systems Applied to the Mining Activity Recordings. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 4851–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewicz, L.R.; Kurzych, A.; Krajewski, Z.; Marć, P.; Kowalski, J.; Bobra, P.; Zembaty, Z.; Sakowicz, B.; Jankowski, R. Review of the Usefulness of Various Rotational Seismometers with Laboratory Results of Fibre-Optic Ones Tested for Engineering Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, K.U.; Stedman, G.E.; Igel, H.; Flaws, A. Ring Laser Gyroscopes as Rotation Sensors for Seismic Wave Studies. In Earthquake Source Asymmetry, Structural Media and Rotation Effects; Teisseyre, R., Majewski, E., Takeo, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 377–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bernauer, F.; Wassermann, J.; Igel, H. Rotational sensors—A comparison of different sensor types. J. Seismol. 2012, 16, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkowski, P.A.; Zembaty, Z.; Minch, M.Y. Time history response analysis of a slender tower under translational-rocking seismic excitations. Eng. Struct. 2018, 155, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havskov, J.; Alguacil, G. Instrumentation in Earthquake Seismology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, S. Tilt measurement using broadband velocity seismograms. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2008, 98, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiszniowski, J. Rotation and twist motion recording—Couple pendulum and rigid seismometer system. In Earthquake Source Asymmetry, Structural Media and Rotation Effects, 1st ed.; Teisseyre, R., Takeo, M., Majewski, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Chapter 33; pp. 451–470. [Google Scholar]
- Brokešová, J. Short-Period Seismic Rotations and Translations Recorded by Rotaphone. Habilitation Thesis, Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brokešová, J.; Málek, J. Six-degree-of-freedom near-source seismic motions II: Examples of real seismogram analysis and S-wave velocity retrieval. J. Seismol. 2015, 19, 511–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horizon User’s Guide. Available online: http://www.systron.com/sites/default/files/964013-rev.d_horizon_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- ARS-14/16 MHD Angular Rate Sensors. Available online: http://atacorp.com/angular_rate_sensors.html (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- High Resolution Rotational Seismometer Model R-1. Available online: http://www.eentec.com/R-1_data_new.htm (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Nighor, R.L.; Evans, J.R.; Hutt, C.R. Laboratory and field testing of commercial rotational seismometers. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Post, E.J. Sagnac effect. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1967, 39, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Simonelli, A.; Lin, C.-J.; Bernauer, F.; Donner, S.; Braun, T.; Wassermann, J.; Igel, H. Six Degree-of-Freedom Broadband Ground-Motion Observations with Portable Sensors: Validation, Local Earthquakes, and Signal Processing. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2020, 110, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFevre, H.C. The Fiber Optic Gyroscope, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sagnac, G. L’éther Lumineux Démontré Par l’effet Du Vent Relatif d’éther Dans Un Interféromètre En Rotation Uniforme. Compte-Renduz À L’Académie Sci. 1913, 95, 708–710. [Google Scholar]
- Jaroszewicz, L.R.; Kurzych, A.; Krajewski, Z.; Dudek, M.; Kowalski, J.K.; Teisseyre, K.P. The Fiber-Optic Rotational Seismograph—Laboratory Tests and Field Application. Sensors 2019, 19, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korkishko, Y.N.; Fedorov, V.A.; Feoktistova, O.Y. LiNbO3 optical waveguide fabrication by high-temperature proton exchange. J. Light. Technol. 2000, 18, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzych, A.; Jaroszewicz, L.R.; Kowalski, J.K.; Sakowicz, B. Investigation of rotational motion in a reinforced concrete frame construction by a fiber optic gyroscope. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2020, 28, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard Specification Format Guide and Test Procedure for Single-Axis Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyros, IEEE-SA Standards Board 952. 1997. Available online: 10.1109/IEEESTD.1998.86153 (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Allan Variance: Noise Analysis for Gyroscopes; Application Note AN5087 Rev. 0.2/2015; Freescale Semiconductor Inc.: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2015.
- Gebauer, A.; Tercjak, M.; Schreiber, U.; Igel, H.; Kodet, J.; Hugentobler, U.; Wassermann, J.; Bernauer, F.; Lin, C.; Donner, S.; et al. Reconstruction of the Instantaneous Earth Rotation Vector with Sub-Arcsecond Resolution Using a Large Scale Ring Laser Array. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 033605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igel, H.; Schreiber, U.; Flaws, A.; Schuberth, B.; Velikoseltsev, A.; Cochard, A. Rotational motions induced by the M8.1 Tokachi-oki earthquake, 25 September 2003. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L08309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igel, H.; Cochard, A.; Wassermann, J.; Flaws, A.; Schreiber, U.; Veikoseltsev, A.; Dinh, N.P. Broad-band observations of earthquake-induced rotational ground motions. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 168, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





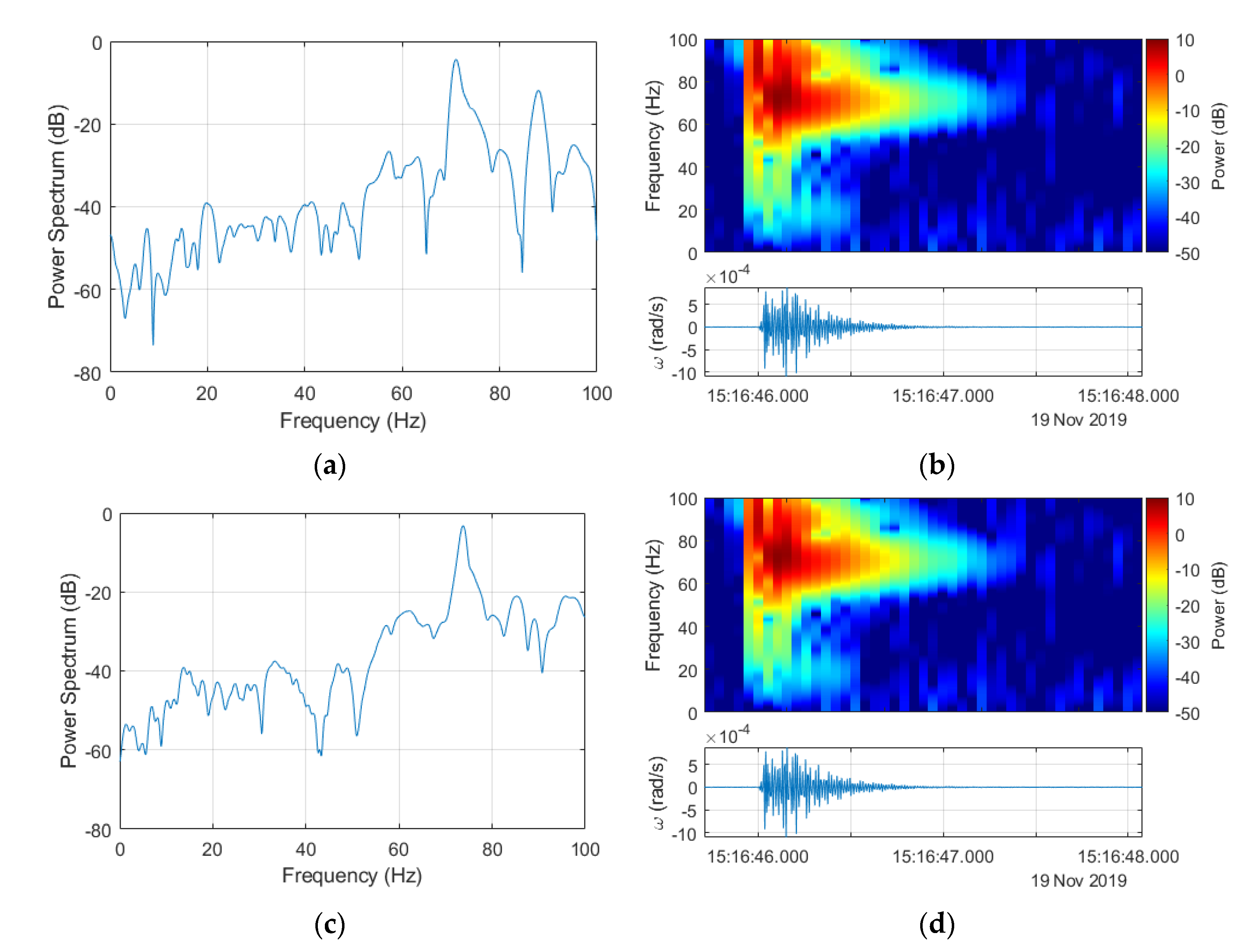



| Number of Explosions | Date | Time (UTC) | Amount of Explosive (g) | Distance from FOS5s (m) | Maximum Signal Amplitude (rad/s) for FOS5-01/02 | Signal Energy Coefficient (rad) FOS5-01/02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 November 2019 | 10:26 | 150 | 220 | 5.86 × 10−5/3.04 × 10−5 | 1.71 × 10−5/1.9 × 10−5 |
| 2 | 19 November 2019 | 15:16 | 500 | 52 | 135.78 × 10−5/86.28 × 10−5 | 18.72 × 10−5/13.71 × 10−5 |
| Data | Number of Series | Time (UTC) | Distance from FOS5s (m) | Signal Maximum Amplitude (rad/s) FOS5-01/02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 November 2019 | 1 | 13:44 | 96 | 1.77 × 10−5/1.66 × 10−5 |
| 2 | 13:45 | 105 | 2.52 × 10−5/1.54 × 10−5 | |
| 3 | 13:48 | 113 | 3.86 × 10−5/2.20 × 10−5 | |
| 4 | 13:49 | 121 | 1.58 × 10−5/1.32 × 10−5 | |
| 5 | 13:52 | 130 | 1.56 × 10−5/1.44 × 10−5 | |
| 6 | 13:54 | 138 | 1.41 × 10−5/1.25 × 10−5 | |
| Average: 2.15 × 10−5 ± 0.86 × 10−5/1.57 × 10−5 ± 0.31 × 10−5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurzych, A.T.; Jaroszewicz, L.R.; Dudek, M.; Kowalski, J.K.; Bernauer, F.; Wassermann, J.; Igel, H. Measurements of Rotational Events Generated by Artificial Explosions and External Excitations Using the Optical Fiber Sensors Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216107
Kurzych AT, Jaroszewicz LR, Dudek M, Kowalski JK, Bernauer F, Wassermann J, Igel H. Measurements of Rotational Events Generated by Artificial Explosions and External Excitations Using the Optical Fiber Sensors Network. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216107
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurzych, Anna T., Leszek R. Jaroszewicz, Michał Dudek, Jerzy K. Kowalski, Felix Bernauer, Joachim Wassermann, and Heiner Igel. 2020. "Measurements of Rotational Events Generated by Artificial Explosions and External Excitations Using the Optical Fiber Sensors Network" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216107
APA StyleKurzych, A. T., Jaroszewicz, L. R., Dudek, M., Kowalski, J. K., Bernauer, F., Wassermann, J., & Igel, H. (2020). Measurements of Rotational Events Generated by Artificial Explosions and External Excitations Using the Optical Fiber Sensors Network. Sensors, 20(21), 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216107









