Convolution Kernel Operations on a Two-Dimensional Spin Memristor Cross Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Logic Switch Based on Spin Memristor
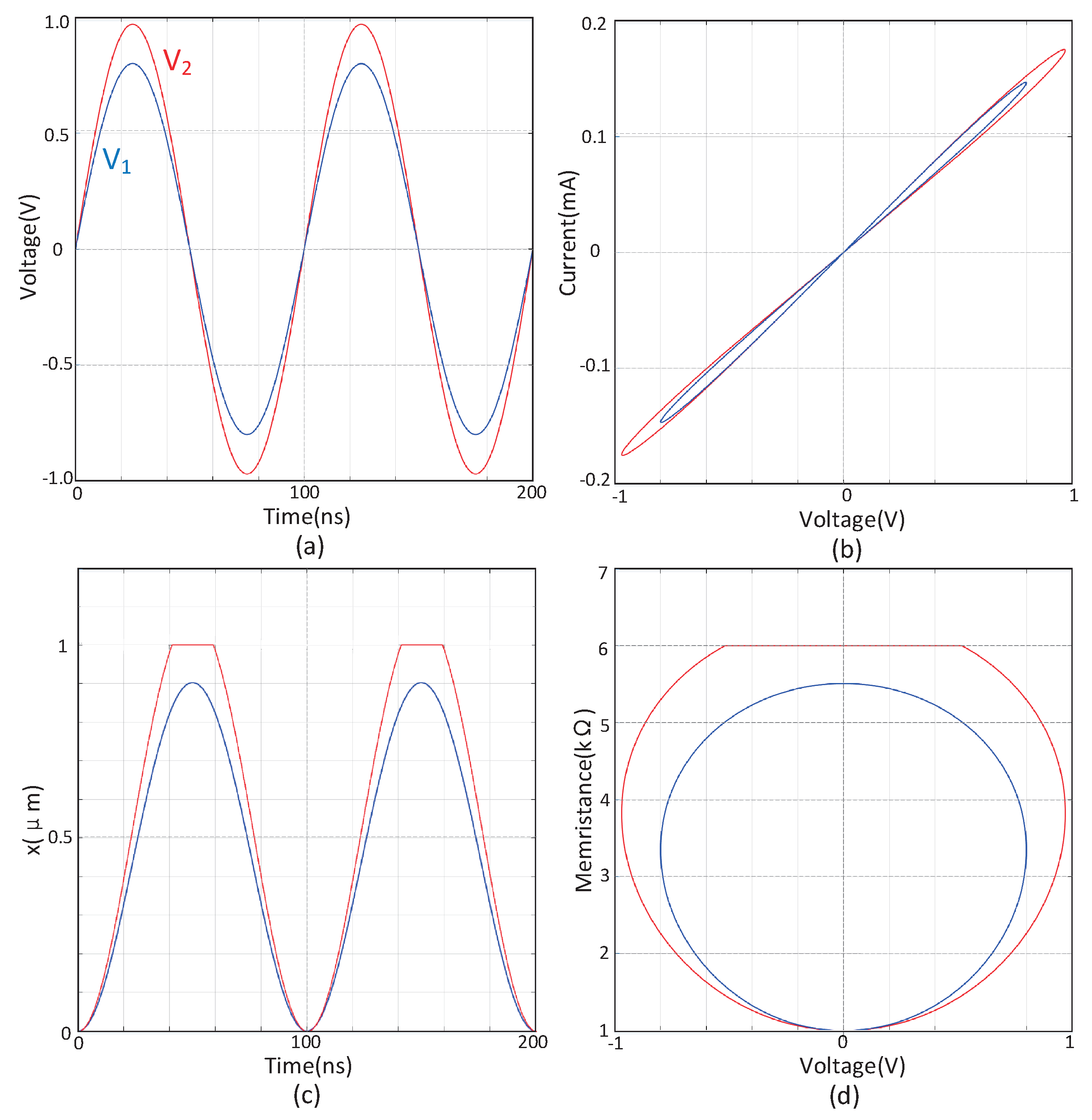
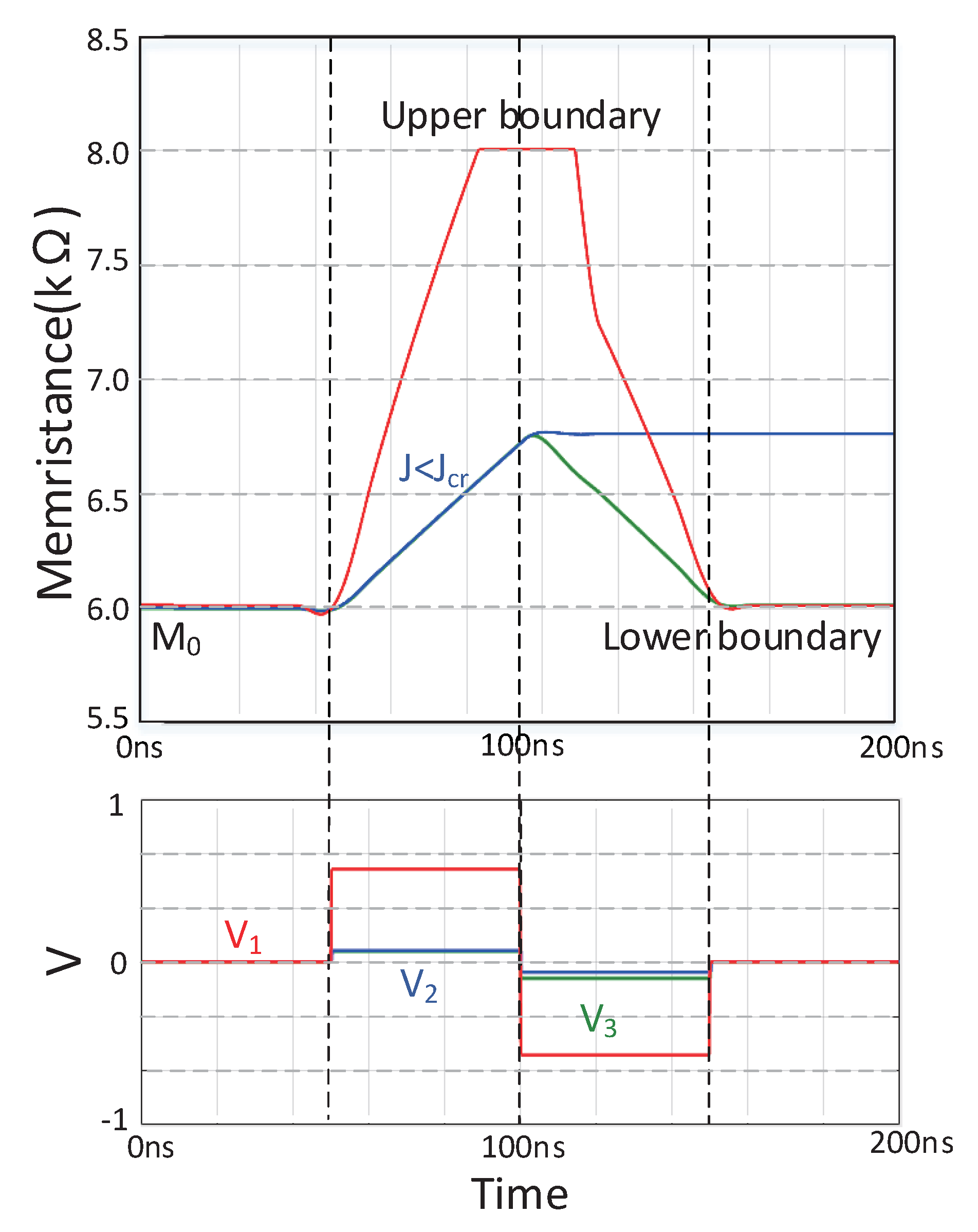
2.1. Introduction to Spin Memristors
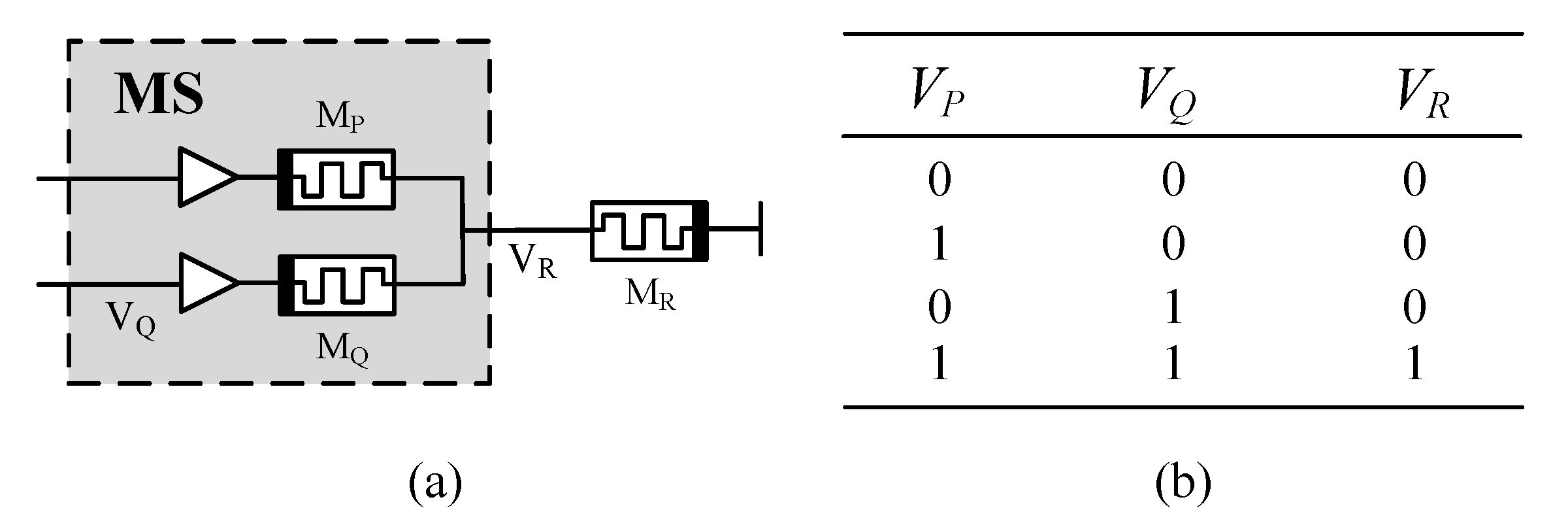
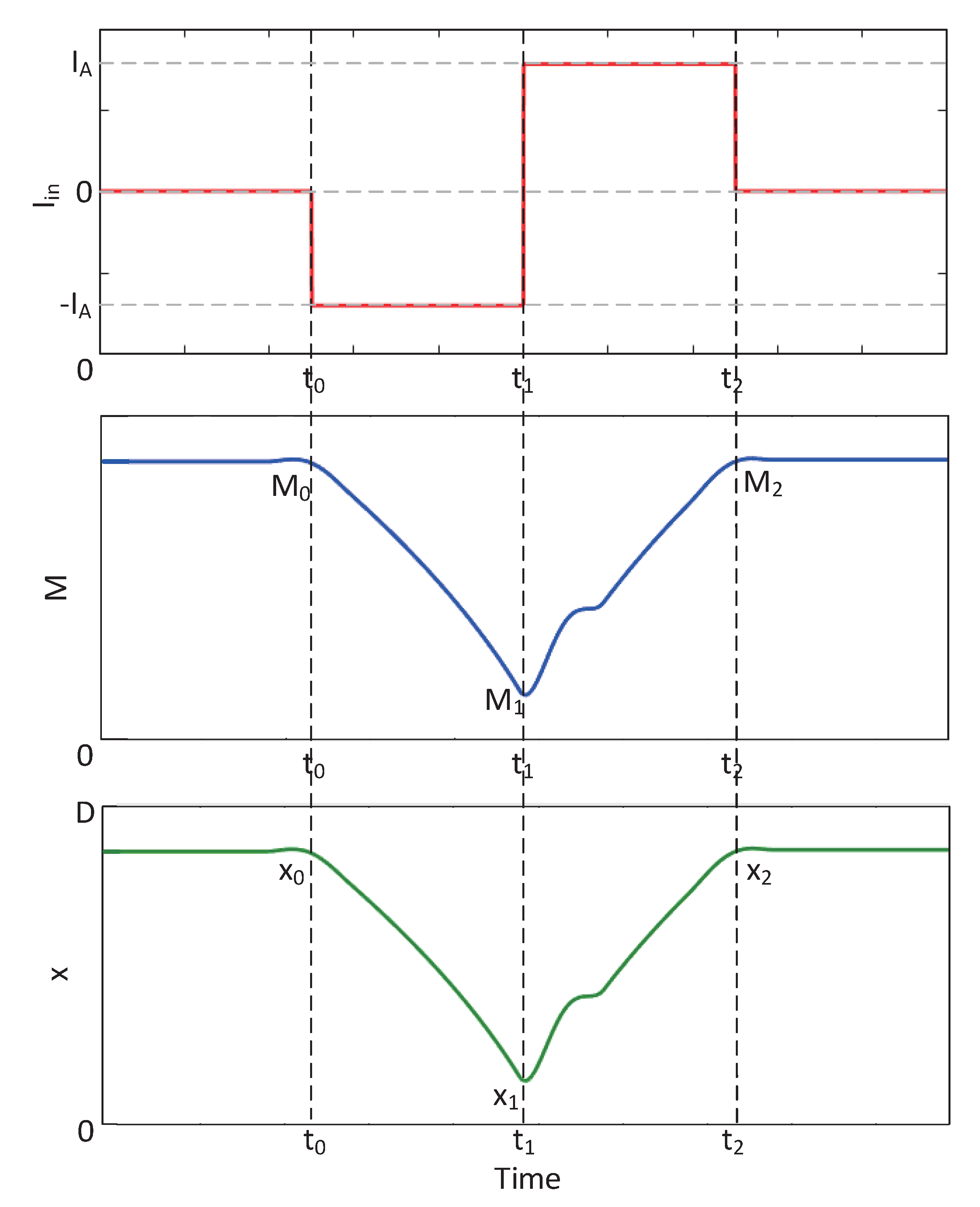
2.2. Memristor Switch (MS) Based on Magnetic Flux Control Spin Memristor
- VP = VQ = VH = “1” (“1” stands for logic 1, VH stands for high-level voltage; “0” stands for logic 0, VL stands for low-level voltage, and VL = 0), the output voltage VR isSince there is a positive voltage across MR, its memristive is reduced. After time T2, RR = Ron, the logic value stored in MR changes to logic 1.
- VP = VH = “1”, VQ = VL = “0”, the voltage across MP is negative, and the voltage across MQ is positive. After time T1, RP = rH, RP = rL(Ron ≪ rH), the output voltage VR isThe logical value is stored in MR to retain logic 0.
- VP = VL = “0”, VQ = VH = “1”, the voltage across MP is positive, and the voltage across MQ is negative. After time T1, RP = rL, RQ = rH, the output voltage VR isThe logical value is stored in MR to retain logic 0.
- VP = VQ = VL = “0”. The output voltage VR = 0, so the logic value is stored in MR to retain logic 0. Therefore, the total time required for a complete logic switch operation is
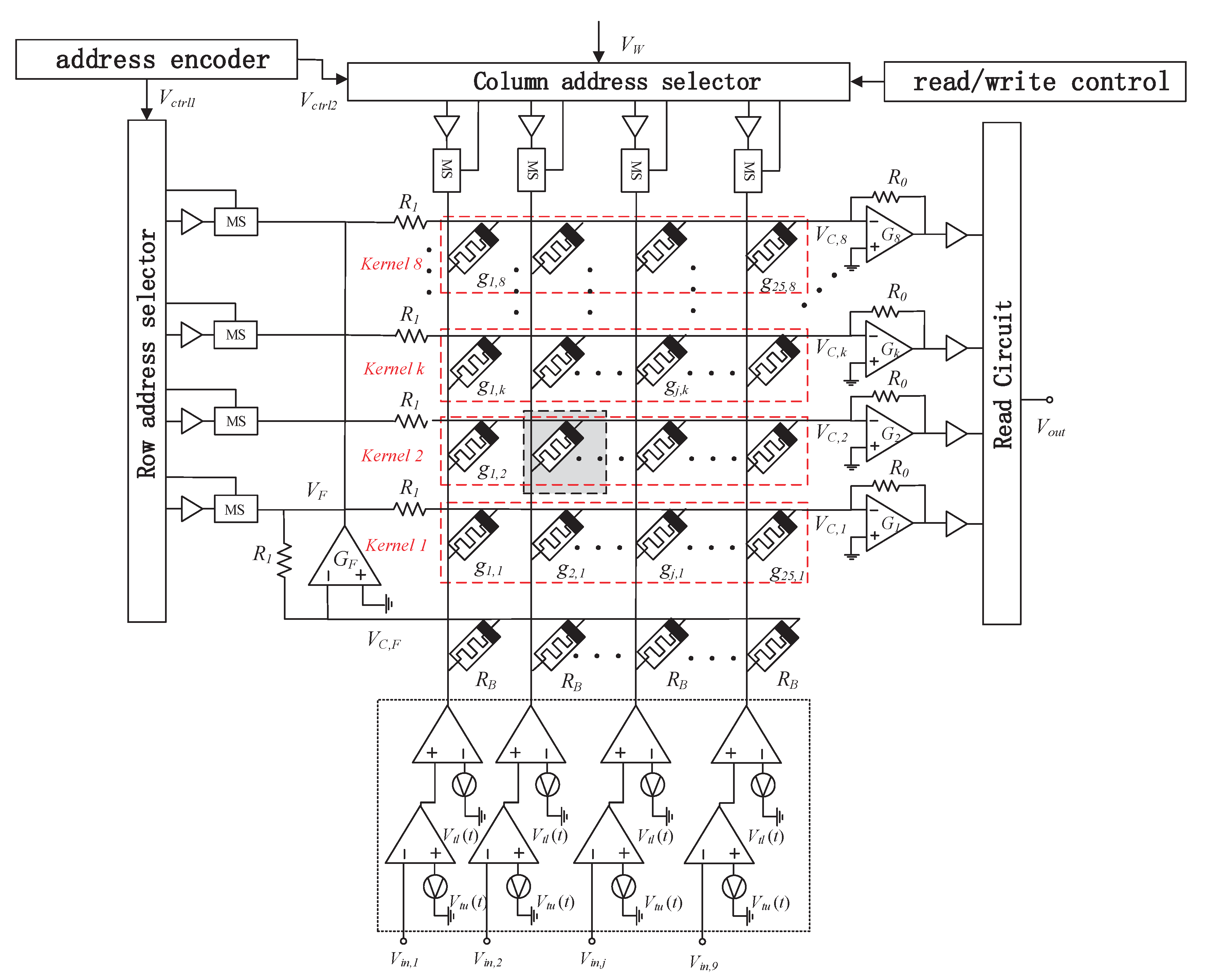
3. Spin Memristor Cross-Array Circuit for Realizing Convolution Operation
3.1. Cross Array Circuit Based on Spin Memristor
3.2. Convolution Operation on Memristor Cross-Array Circuit
4. Application of Convolution Circuit in Color Image Denoising and Color Image Edge Extraction
4.1. Color Image Denoising Based on Different Filter Operators
4.2. Color Image Edge Detection Based on Different Convolution Operators
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Chen, B.; Polatkan, G.; Sapiro, G.; Blei, D.; Dunson, D.; Carin, L. Deep leaming with hierarchical convolutional factor analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1887–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaxiras, S. Architecture at the End of Moore; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilzadeh, H.; Blem, E.; Amant, R.S.; Sankaralingam, K.; Burger, D. Dark silicon and the end of multicore scaling. In Proceedings of the 2011 38th Annual international symposium on computer architecture (ISCA), San Jose, CA, USA, 4–8 June 2011; pp. 365–376. [Google Scholar]
- Taur, Y. CMOS design near the limit of scaling. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2002, 46, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.F.; Ahmad, I.; Fan, D. An evolutionary technique for performance-energy-temperature optimized scheduling of parallel tasks on multicore processors. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2016, 27, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmahini-Farahani, A.; Ahn, J.H.; Morrow, K.; Kim, N.S. DRAMA: An architecture for accelerated processing near memory. IEEE Comput. Archit. Lett. 2015, 14, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarkhish, E.; Pfister, C.; Rossi, D.; Loi, I.; Benini, L. Logic-base interconnect design for near memory computing in the smart memory cube. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2017, 25, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Yang, C.; Fu, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gan, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, X. Enabling and scaling a global shallow-water atmospheric model on Tianhe-2. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 28th International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Optimizing and scaling HPCG on Tianhe-2: Early experience. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing (ICA3PP), Dalian, China, 24–27 August 2014; pp. 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, G.; Gray, J. What’s next in high-performance computing? Commun. ACM 2002, 45, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. Memristor—The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 5, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Ramadan, M.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Williams, R.S. VTEAM: A general model for voltage-controlled memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.Y.; Wang, X.W.X. Compact modeling and corner analysis of spintronic memristor. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures, San Francisco, CA, USA, 30–31 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ge, N.; Montgomery, E.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Dávila, N.; Graves, C.E.; et al. Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat. Electron. 2017, 1, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.J.; Qian, H. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature 2020, 577, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Correll, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Bothra, V.; Zhang, Z.; Flynn, M.P.; Lu, W.D. A fully integrated reprogrammable memristor-CMOS system for efficient multiply-accumulate operations. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Qi, D.; He, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hu, X.; Duan, S. Easily Cascaded Memristor-CMOS Hybrid Circuit for High-Efficiency Boolean Logic Implementation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2018, 27, 1850149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; He, Y.; Hu, X.; Qi, D.; Duan, S. Flexible memristor-based LUC and its network integration for Boolean logic implementation. IET Nanodielectr. 2019, 2, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Lai, C.S.; Qi, D.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Duan, S. A general memristor-based pulse coupled neural network with variable linking coefficient for multi-focus image fusion. Neurocomputing 2018, 308, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ma, B.; Qi, D.; Luo, L.; Zhou, M. A Hybrid Multi-Frame Super-Resolution Algorithm Using Multi-Channel Memristive Pulse Coupled Neural Network and Sparse Coding. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Information, Communication and Networks (ICICN), Macao, China, 24–26 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Mazumder, P. Memristor-based RRAM with applications. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2012, 55, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Duan, S.; Huang, T.; Wang, H. Pavlov associative memory in a memristive neural network and its circuit implementation. Neurocomputing 2016, 171, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, T.; Li, C. Impulsive Effects and Stability Analysis on Memristive Neural Networks With Variable Delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Hu, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, L.; Mazumder, P. Memristor-Based Cellular Nonlinear/Neural Network: Design, Analysis, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Drakakis, E.; Duan, S.; He, P.; Liao, X. Memristor Model and Its Application for Chaos Generation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2012, 22, 1250205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Duan, S. A Chaotic Attractor in Delayed Memristive System. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2012, 2012, 726927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershin, Y.V.; Ventra, M.D. Practical approach to programmable analog circuits with memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2010, 57, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershin, Y.V.; Ventra, M.D. Spin memristive systems: Spin memory effects in semiconductor spintronics. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 2008, 78, 113309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidl, V.; Němec, P.; Wadley, P.; Hills, V.; Campion, R.P.; Novák, V.; Edmonds, K.W.; Maccherozzi, F.; Dhesi, S.S.; Gallagher, L.B.; et al. Optical determination of the Néel vector in a CuMnAs thin-film antiferromagnet. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ravelosona, D.; Klein, J.O.; Chappert, C. Domain Wall Shift Register-Based Reconfigurable Logic. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2966–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, S.N.; Min, K.S.T. New Memristor-Based Crossbar Array Architecture with 50-% Area Reduction and 48-% Power Saving for Matrix-Vector Multiplication of Analog Neuromorphic Computing. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 2014, 14, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Duan, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, T. SRMC: A multibit memristor crossbar for self-renewing image mask. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2018, 26, 2830–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, P.Y.; Yu, S. Demonstration of Convolution Kernel Operation on Resistive Cross-Point Array. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2016, 37, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, L. A novel design for memristor based logic switch and crossbar circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2015, 62, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Huang, G.M.; Li, P. Dynamical Properties and Design Analysis for Nonvolatile Memristor Memories. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. IEEE Trans. 2011, 58, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, G.J.T.G.Y.; Tang, G. A fast two-dimensional median filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1979, 27, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.A.; Akansu, A.N. A class of fast Gaussian binomial filters for speech and image processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1991, 39, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prewitt, J.M. Object enhancement and extraction. Pict. Process. Psychopictorics 1970, 10, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, H.; Simoncelli, E.P. Optimally rotation-equivariant directional derivative kernels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Kiel, Germany, 10–12 September 1997; pp. 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, R.A. Computer determination of the constituent structure of biological images. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1971, 4, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, J.T.; Borkowitz, D.A.; Clapp, L.C.; Koester, C.J.; Vanderburgh, A., Jr. Optical and Electro-Optical Information Processing; Massachusetts Inst of Tech Cambridge: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]





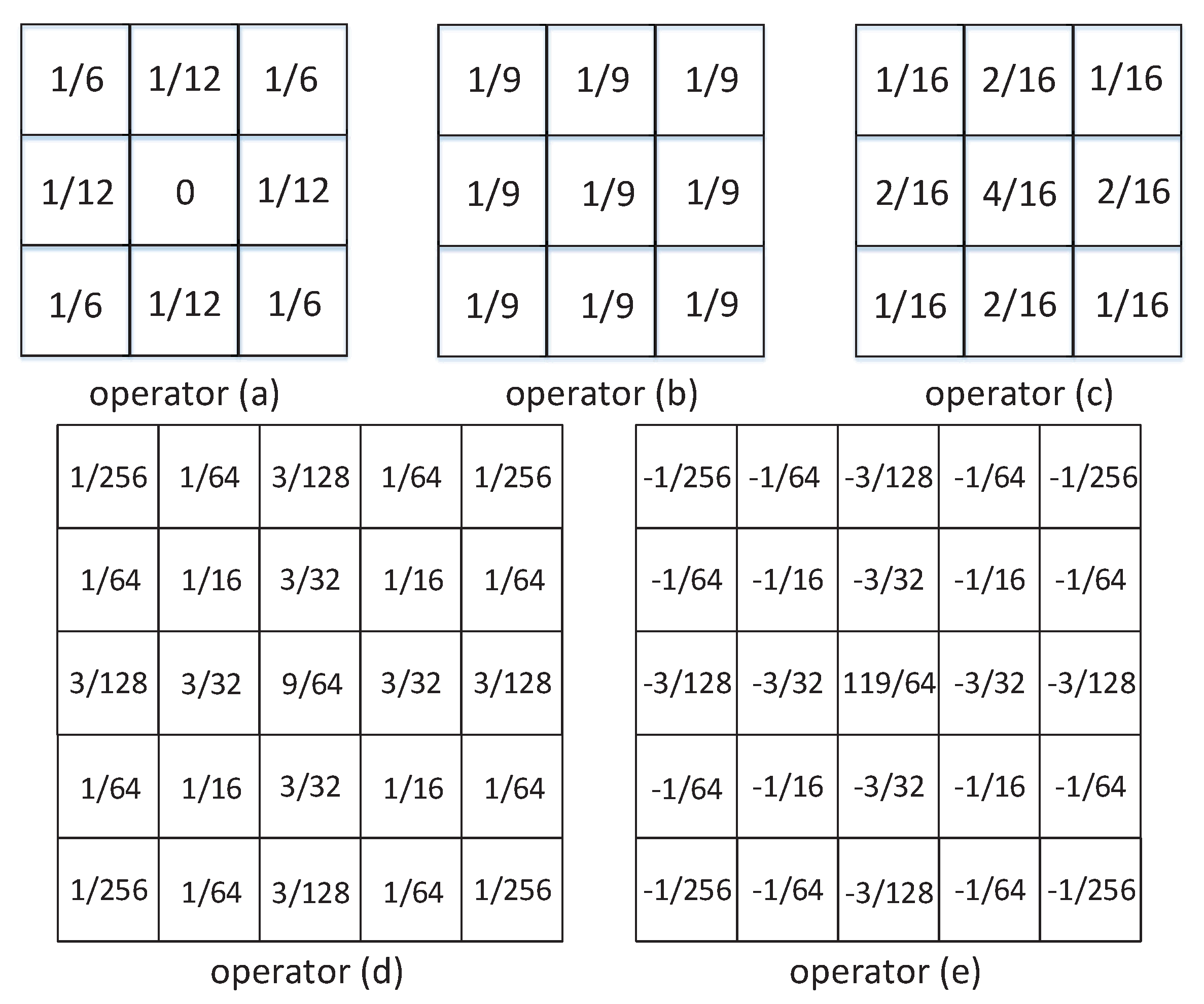

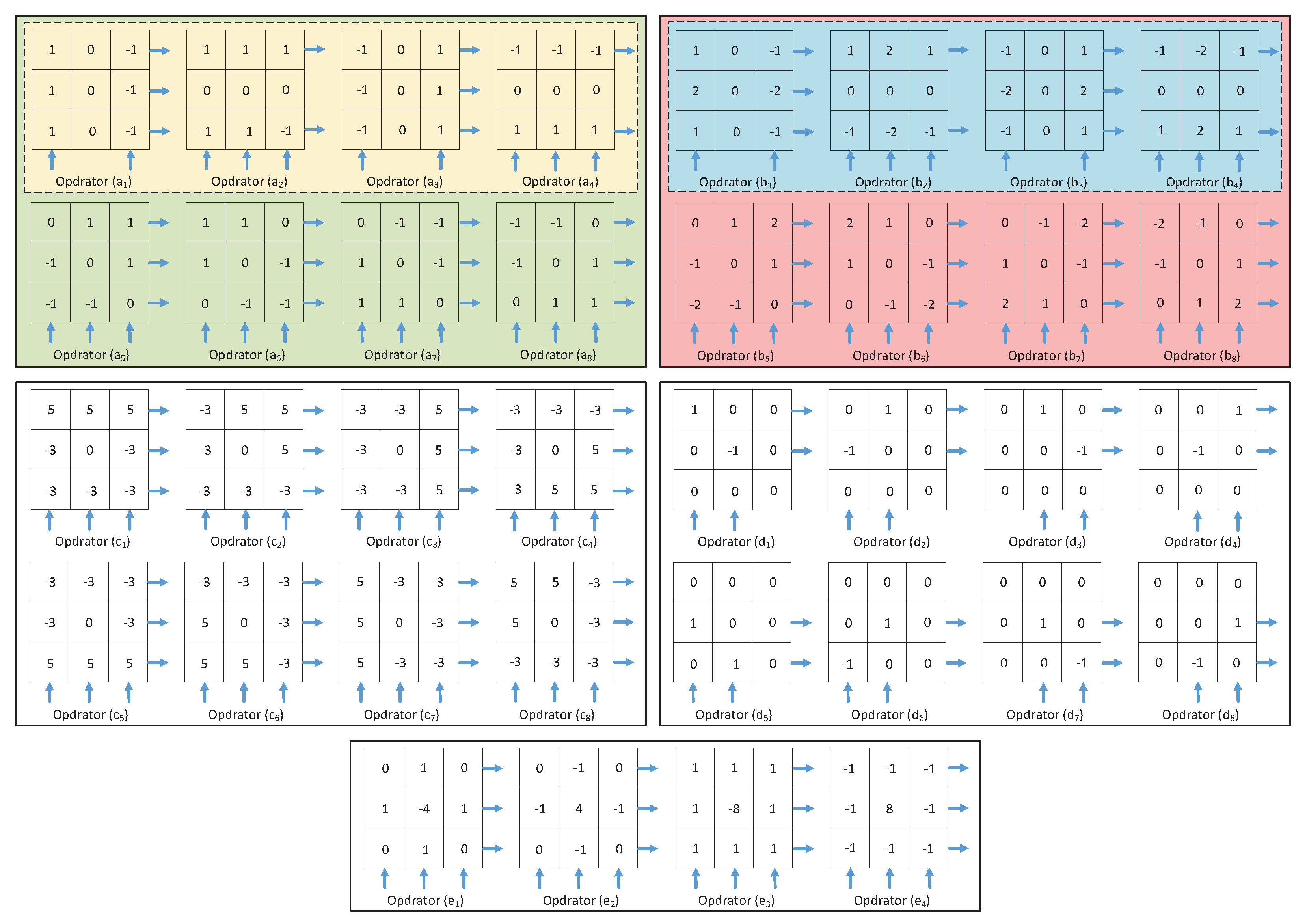
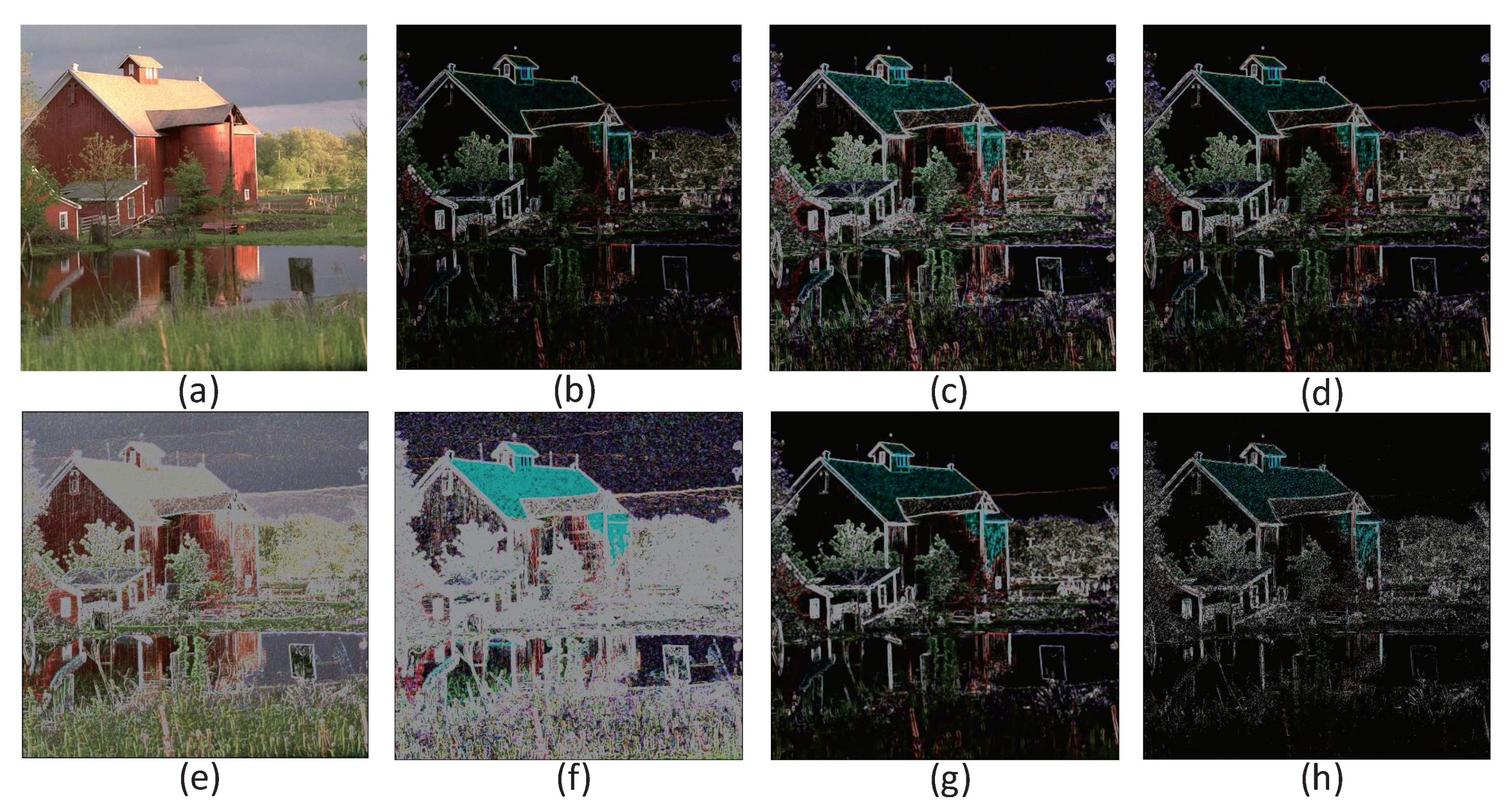
| Test Items | Operator(a) | Operator(b) | Operator(c) | Operator(d) | Operator(e) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR(dB) | 14.8294 | 15.8517 | 17.2997 | 16.8694 | 8.3064 |
| SSIM | 0.2569 | 0.4135 | 0.5943 | 0.5793 | 0.0481 |
| Test Items | Prewitt | Proposed Prewitt | Soble | Proposed Soble | Kirsch | Robert | Laplacian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR(dB) | 7.7960 | 8.8183 | 8.2401 | 15.5461 | 11.2648 | 8.4652 | 8.0827 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Dong, Z.; Duan, S. Convolution Kernel Operations on a Two-Dimensional Spin Memristor Cross Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 6229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216229
Zhu S, Wang L, Dong Z, Duan S. Convolution Kernel Operations on a Two-Dimensional Spin Memristor Cross Array. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216229
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Saike, Lidan Wang, Zhekang Dong, and Shukai Duan. 2020. "Convolution Kernel Operations on a Two-Dimensional Spin Memristor Cross Array" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216229
APA StyleZhu, S., Wang, L., Dong, Z., & Duan, S. (2020). Convolution Kernel Operations on a Two-Dimensional Spin Memristor Cross Array. Sensors, 20(21), 6229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216229






