Sensor Fusion of Motion-Based Sign Language Interpretation with Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Sensing Module
3.3. Data Preprocessing
- : QTR
- : ELA
- : AGR
- : ACC
- : QTR + ELA + AGR + ACC
- : QTR + ELA + AGR (ACC excluded)
- : QTR + ELA + ACC (AGR excluded)
- : QTR + AGR + ACC (ELA excluded)
- : ELA + AGR + ACC (QTR excluded)
- : QTR + ELA (AGR and ACC excluded)
- : QTR + AGR (ELA and ACC excluded)
- : QTR + ACC (ELA and AGR excluded)
- : ELA + AGR (QTR and ACC excluded)
- : ELA + ACC (QTR and AGR excluded)
- : AGR + ACC (QTR and ELA excluded)
3.4. Classification Model
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheok, M.J.; Omar, Z. A review of hand gesture and sign language recognition techniques. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2017, 10, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Zaidan, B.B.; Zaidan, A.A.; Salih, M.M.; Lakulu, M.M. A review on systems-based sensory gloves for sign language recognition state of the art between 2007 and 2017. Sensors 2018, 18, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bheda, V.; Radpour, D. Using deep convolutional networks for gesture recognition in american sign language. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.06836v3. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, T.W.; Lee, B.G. American sign language recognition using leap motion controller with machine learning approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Infantino, I.; Rizzo, R.; Gaglio, S. A framework for sign language sentence recognition by commonsense context. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Part C 2007, 37, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Martinez, A.M. Modelling and recognition of the linguistic components in american sign language. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 1826–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lane, H.; Grosjean, F. Recent Perspectives on American Sign Language, 1st ed.; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/e/9780203762974 (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Appenrodt, J.; Al-hamadi, A.; Elmezain, M.; Michaelis, B. Data gathering for gesture recognition systems based on single color-, stereo color- and thermal cameras. Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 3, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.G.; Lee, S.M. Smart wearable hand device for sign language interpretation system with sensors fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinect for Windows. Available online: https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/kinect (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Leap Motion Controller. Available online: https://www.leapmotion.com (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Elmezain, M.; Al-Hamadi, A. A hidden markov model-based isolated and meaningful hand gesture recognition. Int. J. Elec. Comp. Syst. Eng. 2008, 3, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Molchanov, P.; Gupta, S.; Kim, K.; Pulli, K. Multi-sensor system for driver’s hand-gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sykora, P.; Kamencay, P.; Hudec, R.M. Comparison of SIFT and SURF methods for use on hand gesture recognition based on depth map. AASRI Procedia 2014, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Li, G.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M. Sign language recognition and translation with kinect. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Auto. Face Gesture Recog. 2013, 655, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Sign language recognition with the kinect sensor based on conditional random fields. Sensors 2015, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia, B.; Viesca, S.A. Real-time american sign language recognition with convolutional neural networks. Convolutional Neural Net. Vis. Recog. 2016, 2, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Sana, U.; Higgins, H.; Braem, B.; Latre, B.; Blondia, C.; Moerman, I.; Saleem, S.; Rahman, Z.; Kwak, K.S. A comprehensive survey of wireless body area networks. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 1065–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Preetham, C.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Kumar, S.; Tamse, A.; Krishnapura, N. Hand talk-implementation of a gesture recognizing glove. In Proceedings of the 2013 Texas Instruments India Educators’ Conference (TIIEC), Bangalore, India, 4–6 April 2013; pp. 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, K.; Pendharkar, G.; Gaikwad, G.N. American sign language detection. Int. J. Scien. R. Pub. 2014, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Yadav, L.; Singhal, M.; Sachan, R.; Goyal, H.; Taparia, K. Smart glove for sign language communications. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Accessibility to Digital World (ICADW), Guwahati, India, 16–18 December 2016; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xia, M.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y.; Cattani, C. Hidden-markov-models-based dynamic hand gesture recognition. Math. Probl. Eng. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummadi, C.K.; Leo, F.P.P.; Verma, K.D.; Kasireddy, S.; Scholl, P.M.; Kempfle, J.; Laerhoven, K.V. Real-time and embedded detection of hand gestures with an imu-based glove. Informatics 2018, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.G.; Tran, V.C.; Chong, T.W. Smart hand device gesture recognition with dynamic time-warping method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data and Internet of Thing, London, UK, 20–22 December 2017; pp. 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, C.; Lime, I.; Lu, J.; Ng, C.; Ong, T. Sign-language recognition through gesture & movement analysis (SIGMA). Mechatron. Mach. Vis. Pract. 3 2018, 3, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M. A study of notation and sign writing systems for the deaf. Intercultural Communication Studies XVII 2008, 4, 97–114. Available online: https://web.uri.edu/iaics/files/08-Mihoko-Kato.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Lapiak, J. Guess What the ASL Word Mean? Handspeak. Available online: https://www.handspeak.com/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Intelligent 9-Axis Absolute Orientation Sensor. Available online: https://cdn-learn.adafruit.com/assets/assets/000/036/832/original/BST/BNO055/DS000/14.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Adafruit BNO055 Absolute Orientation Sensor. Available online: https://cdn-learn.adafruit.com/downloads/pdf/adafruit-bno055-absolute-orientation-sensor.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Teensyduino. Available online: https://www.pjrc.com/teensy/teensyduino.html (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Arduino 1.8.9, Arduino. Available online: https://www.arduino.cc/en/main/software (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- TCA9548A Low-Voltage 8-Channel I2C Switch with Reset, Texas Instruments Incorporated. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/tca9548a.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Bluetooth Module HC-06. Available online: https://www.olimex.com/Products/Components/RF/BLUETOOTH-SERIAL-HC-06/resources/hc06.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Hemingway, E.G.; O’Reilly, O.M. Perspective on Euler angle singularities, gimbal lock, and the orthogonality of applied forces and applied moments. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2018, 44, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numpy Developers, Scipy. Available online: https://www.numpy.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Olah, C. Understanding LSTM Networks; Google Research. Available online: https://research.google/pubs/pub45500/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Geron, A. Hands-On Machine Learning with Sciki-Learn and Tensor Flow; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. R. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Refaeilzadeh, P.; Tang, L.; Liu, H. Cross-Validation, 2009th ed.; Encyclopedia Database Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; Available online: https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-0-387-39940-9_565 (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Sheela, K.G.; Deepa, S.N. Review on methods to fix number of hidden neurons in neural networks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
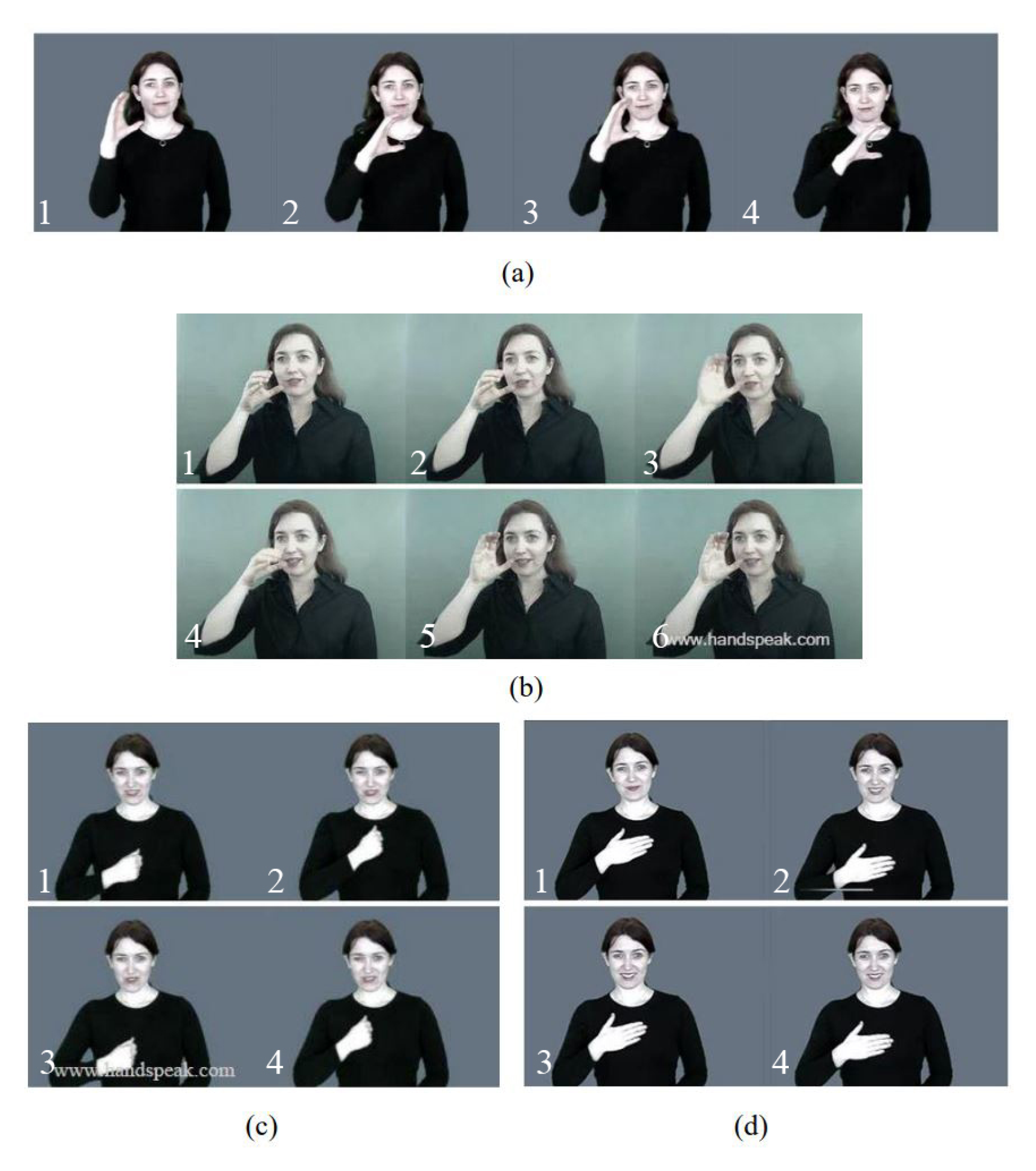









| Words | SIG | DEZ | ORI | TAB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ”Good”-“Happy” | X | |||
| ”Happy”-“Smell” | X | X | X | |
| ”Sorry”-“Please” | X | X | X | |
| ”Hungry”-“Drink”-“Search” | X | |||
| ”Pretty”-“Sleep” | X | X | X | |
| ”There”-“Me/I”-“You”-“Hearing” | X | |||
| ”Hello”-“Bye” | X | X | ||
| ”Thank You”-“Good” | X | X | X | |
| ”Yes”-“Sorry” | X | |||
| ”Eat”-“Water” | X | X | ||
| ”Look”-“Vegetable” | X | |||
| ”Onion”-“Apple” | X | X | X |
| Components | Specification |
|---|---|
| Tri-axial 16 bits gyroscope | |
| IMU | Tri-axial 16 bits accelerometer |
| Geomagnetic sensor | |
| Operating voltage: 2.4V to 3.6V | |
| Operating voltage: 3.3V to 5V | |
| Teensy 3.2 MCU | Processor: Cortex-M4 72 MHz (96 MHz) |
| Flash memory: 256 KB | |
| RAM: 64 KB | |
| I2C: 2 ports | |
| Operating voltage: 1.65V to 5.5V | |
| TCA29548A multiplexer | Clock frequency: 0 to 400 kHz |
| I2C: 3 ADDR pins, 8 buses (4 SDA/SCL) | |
| Operating voltage: 3.3V to 5V | |
| BLE 4.0 HC-06 | Frequency: 2.4 GHz ISM |
| Transmission range: 10 m |
| Category | Features | AR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| QTR | 98.51 | |
| ELA | 98.44 | |
| AGR | 97.89 | |
| ACC | 98.45 | |
| QTR + ELA + AGR + ACC | 99.83 | |
| QTR + ELA + AGR | 99.48 | |
| QTR + ELA + ACC | 99.64 | |
| QTR + AGR + ACC | 99.68 | |
| ELA + AGR + ACC | 99.73 | |
| QTR + ELA | 99.46 | |
| QTR + AGR | 99.29 | |
| QTR + ACC | 99.66 | |
| ELA + AGR | 99.39 | |
| ELA + ACC | 99.59 | |
| AGR + ACC | 99.56 | |
| Average | 99.67 |
| Category | Features | AR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| QTR | 99.65 | |
| ELA | 99.70 | |
| AGR | 99.56 | |
| ACC | 99.66 | |
| QTR + ELA + AGR + ACC | 99.85 | |
| QTR + ELA + AGR | 99.84 | |
| QTR + ELA + ACC | 99.84 | |
| QTR + AGR + ACC | 99.82 | |
| ELA + AGR + ACC | 99.82 | |
| QTR + ELA | 99.83 | |
| QTR + AGR | 99.83 | |
| QTR + ACC | 99.82 | |
| ELA + AGR | 99.78 | |
| ELA + ACC | 99.82 | |
| AGR + ACC | 99.79 | |
| Average | 99.67 |
| Class | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Class | Se (%) | Sp (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None/Invalid | 100 | 100 | “Thank You” | 99.21 | 100 |
| ”Good” | 100 | 99.97 | “Yes” | 100 | 99.97 |
| ”Happy” | 99.13 | 100 | “Please” | 100 | 99.97 |
| ”Sorry” | 100 | 100 | “Drink” | 99.02 | 100 |
| ”Hungry” | 100 | 100 | “Eat” | 100 | 100 |
| ”Understand” | 100 | 99.97 | “Look” | 100 | 100 |
| ”Pretty” | 99.10 | 100 | “Sleep” | 100 | 100 |
| ”Smell” | 100 | 100 | “Hearing” | 100 | 100 |
| ”There” | 100 | 100 | “Water” | 100 | 100 |
| ”You” | 100 | 100 | “Rice” | 100 | 100 |
| ”Me/I” | 100 | 100 | “Search” | 100 | 100 |
| ”OK” | 100 | 100 | “Onion” | 100 | 100 |
| ”Hello” | 100 | 100 | “Apple” | 100 | 100 |
| ”Bye” | 100 | 100 | “Vegetable” | 100 | 100 |
| Reference | Sign Language | Sensor | Algorithm | AR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [22] | 50 CSL | 3-axis ACC | HMM | 91.00 |
| 5 flex sensors | ||||
| Lee et al. [9] | 26 fingerspelling ASL | 1 IMU and 5 flex sensors | SVM | 98.20 |
| Mummadi et al. [23] | 24 static ASL | 5 IMU | RF | 92.95 |
| Lee et al. [24] | 6 hand gestures | 3 IMU sensors | DTW | 93.19 |
| Proposed | 27 word-based ASL | 6 IMU sensors | RNN-LSTM | 99.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.G.; Chong, T.-W.; Chung, W.-Y. Sensor Fusion of Motion-Based Sign Language Interpretation with Deep Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 6256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216256
Lee BG, Chong T-W, Chung W-Y. Sensor Fusion of Motion-Based Sign Language Interpretation with Deep Learning. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216256
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Boon Giin, Teak-Wei Chong, and Wan-Young Chung. 2020. "Sensor Fusion of Motion-Based Sign Language Interpretation with Deep Learning" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216256
APA StyleLee, B. G., Chong, T.-W., & Chung, W.-Y. (2020). Sensor Fusion of Motion-Based Sign Language Interpretation with Deep Learning. Sensors, 20(21), 6256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216256







