Analysis of Accuracy and Reliability of Different Types of GPS Receivers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
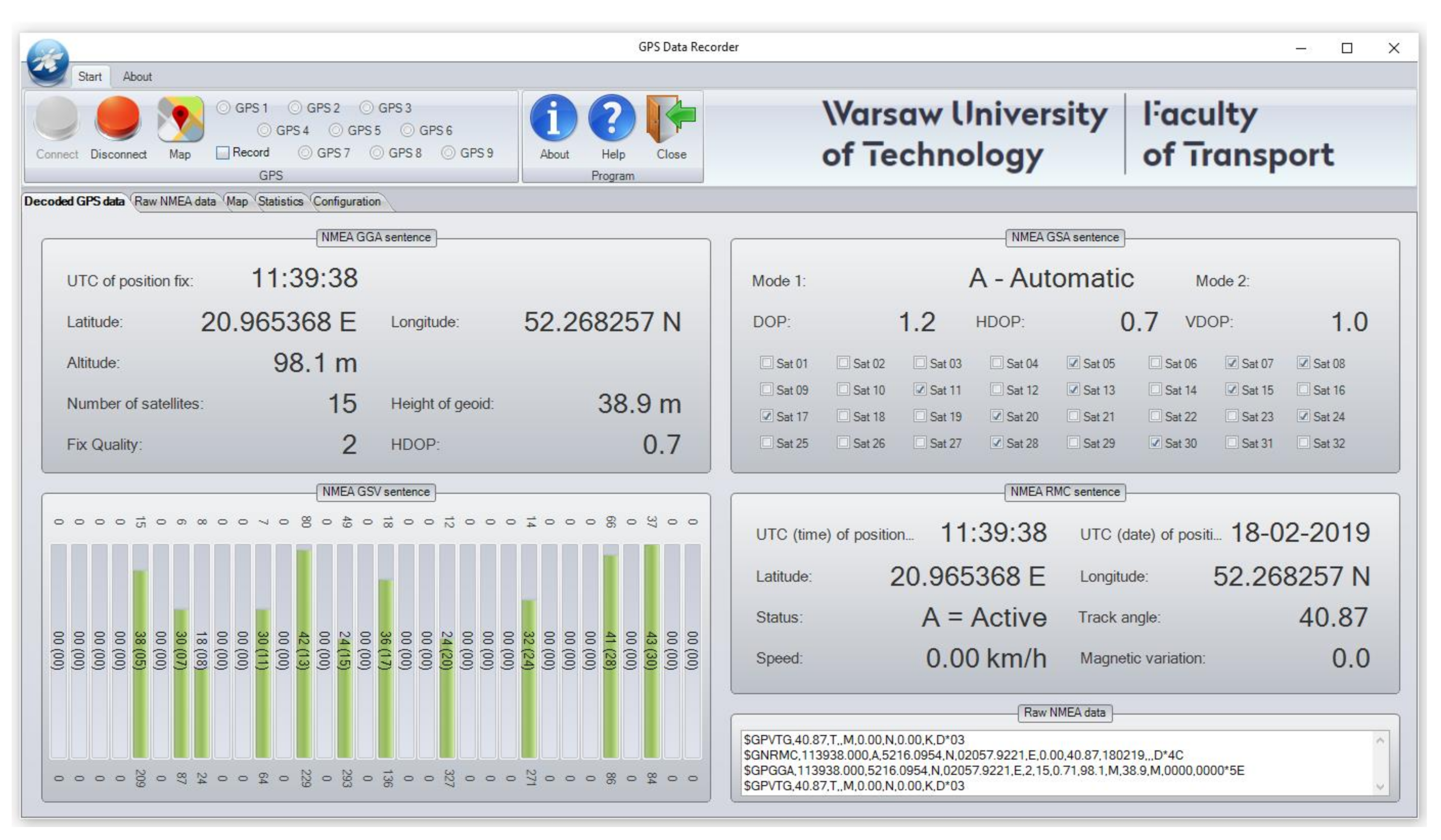
2. Materials and Methods
- static (standalone) in an open area;
- dynamic (real time kinematic—RTK) at minimum speed of 100 km h−1 on a dual carriage way;
- RTK at maximum speed of 50 km h−1 in a built up area;
- static in a built up area.
3. Results and Discussion
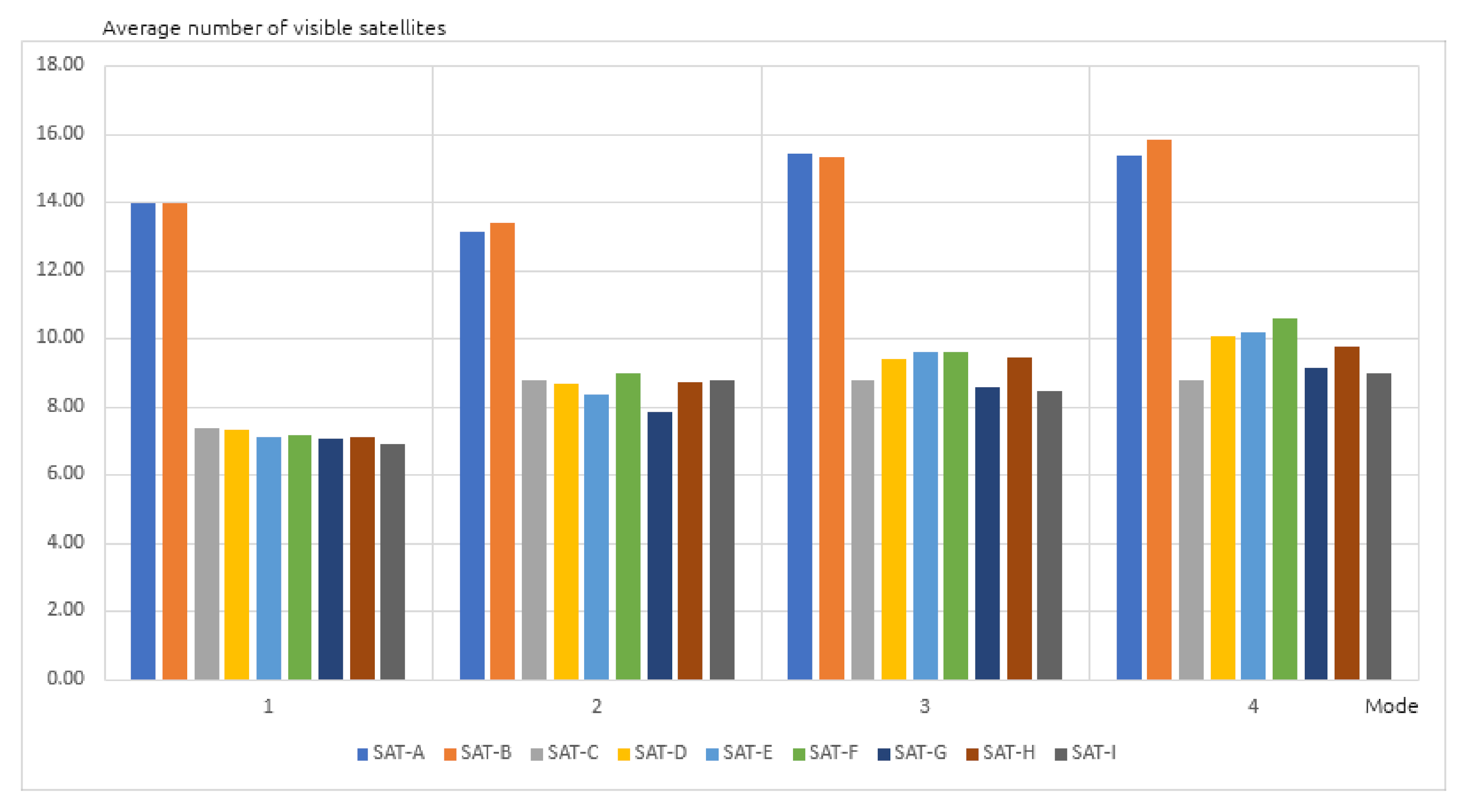
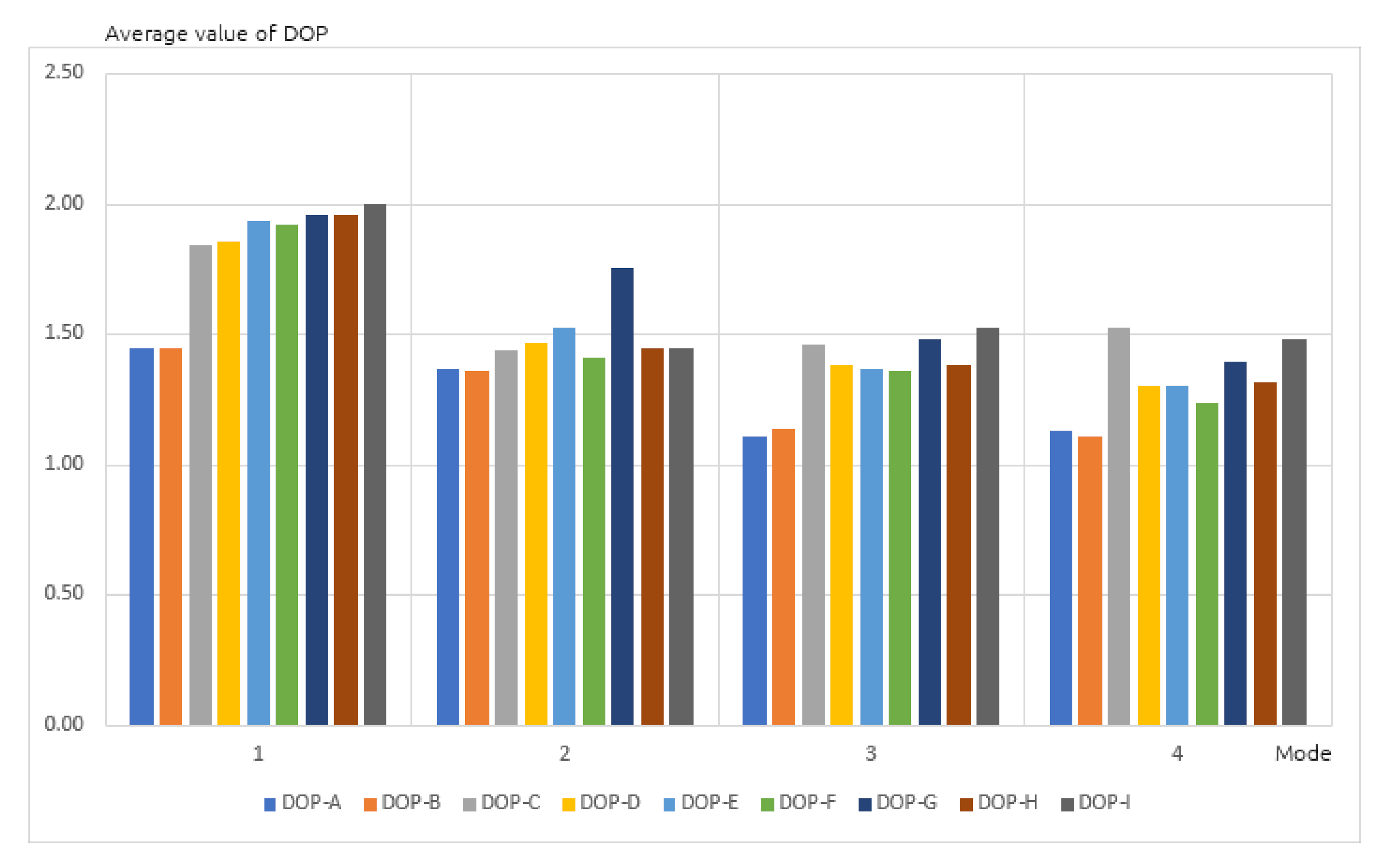
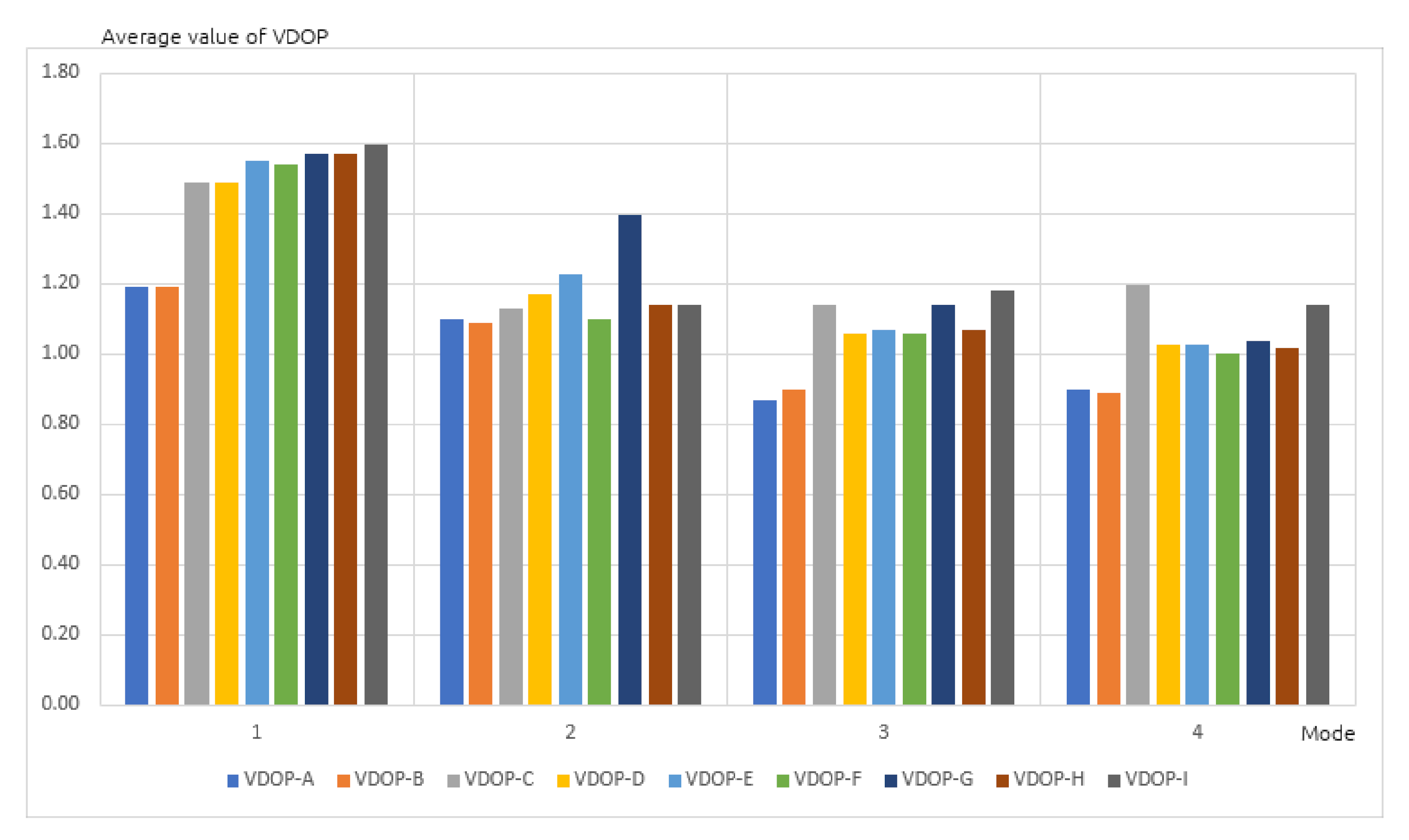
3.1. Accuracy Analysis of GPS Receivers
- Stationary in an open area,
- At minimum speed of 100 km/h on a dual carriageway,
- At maximum speed of 50 km/h in a built-up area,
- Stationary in a built-up area.
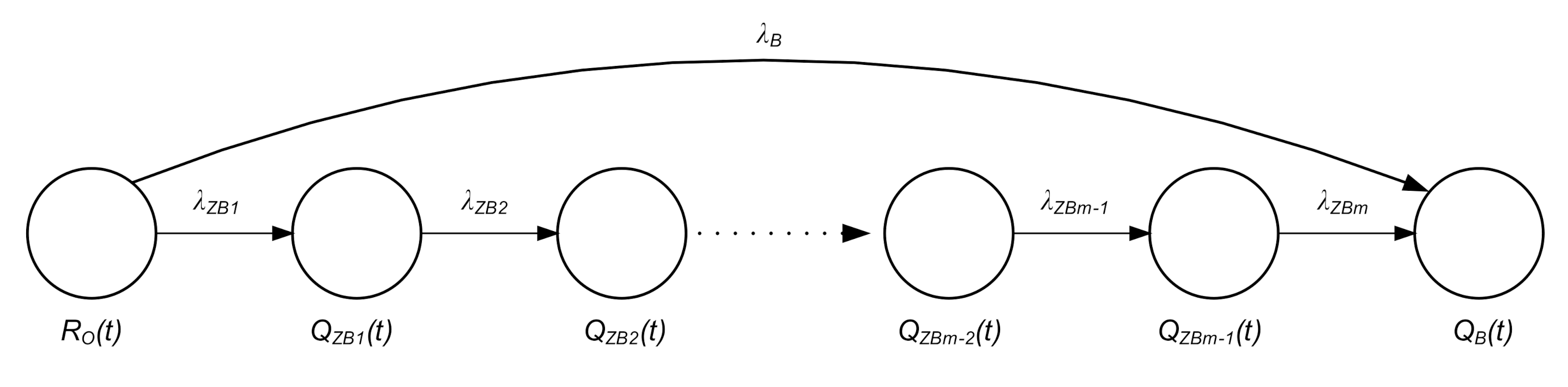
3.2. Reliability Analysis of GPS Receiver
- RO(t)—the probability function of the system in the state of full operational capability,
- QZB(t)—the probability function of the system in the state of safety threat,
- QB(t)—the probability function of the system in the state of safety breach,
- λB—equivalent change rate of serial branch elements,
- λZB—change rate of parallel branch elements.
- Example 1
- -
- research time—1 year (given in hours [h]):
- -
- failure rate of the device using GPS Recorder utility software λB:
- -
- type I GPS receiver failure rate λZB1:
- -
- type II GPS receiver failure rate λZB2:
- -
- type III GPS receiver failure rate λZB3:
- -
- type IV GPS receiver failure rate λZB4:
- -
- type V GPS receiver failure rate λZB5:
- -
- type VI GPS receiver failure rate λZB6:
- -
- type VII GPS receiver failure rate λZB7:
- -
- type VIII GPS receiver failure rate λZB8:
- -
- type IX GPS receiver failure rate λZB9:
- -
- in the state of full operational capability RO(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB1(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB2(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB3(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB4(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB5(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB6(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB7(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZB8(t):
- -
- in the state of safety threat QZ(t):
- -
- The reliability of the whole system is given by:
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catania, P.; Comparetti, A.; Febo, P.; Morello, G.; Orlando, S.; Roma, E.; Vallone, M. Positioning accuracy comparison of GNSS receivers used for mapping and guidance of agricultural machines. Agronomy 2020, 10, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siergiejczyk, M.; Krzykowska, K.; Rosiński, A.; Grieco, L.A. Reliability and Viewpoints of Selected ITS System. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Systems Engineering ICSEng 2017, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–24 August 2017; IEEE, Conference Publishing Services (CPS): Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Losurdo, F.; Dileo, I.; Siergiejczyk, M.; Krzykowska, K.; Krzykowski, M. Innovation in the ICT Infrastructure as a Key Factor in Enhancing Road Safety: A Multi-Sectoral Approach. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Systems Engineering ICSEng 2017, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–24 August 2017; IEEE Computer Society Conference Publishing Services (CPS): Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Fu, C.; Stewart, K.; Zhang, L. Using big GPS trajectory data analytics for vehicle miles traveled estimation. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 103, 298–307. [Google Scholar]
- Jacyna, M.; Żak, J.; Gołębiowski, P. The EMITRANSYS model and the possibilities of its application for the analysis of the development of sustainable transport systems. Combust. Engines 2019, 179, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hadavi, S.; Verlinde, S.; Verbeke, W.; Macharis, C.; Guns, T. Monitoring Urban-Freight Transport Based on GPS Trajectories of Heavy-Goods Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 3747–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, D.; Łubkowski, P.; Pawlak, E.; Stańczyk, P. Anthropotechnical Systems Reliability. In Safety and Reliability: Methodology and Applications, Proceedings of the European Safety and Reliability Conference ESREL, Zurich, Switzerland, 7–10 September 2015; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2015; pp. 399–407. [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski, T. Problems of reliability modelling of multiple-phased systems. Eksploat. I Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2011, 4, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Duer, S.; Duer, R.; Mazuru, S. Determination of the expert knowledge base on the basis of a functional and diagnostic analysis of a technical object. Rom. Assoc. Nonconv. Technol. 2016, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Duer, S.; Zajkowski, K.; Duer, R.; Paś, J. Designing of an effective structure of system for the maintenance of a technical object with the using information from an artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2012, 23, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlicki, M.; Kasprzyk, Z. Increasing Performance of SMS Based Information Systems. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Dependability and Complex Systems DepCoS-RELCOMEX, Brunów, Poland, 30 June–4 July 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Cybulski, R.; Wilczewski, G.; Perlicki, K. Theoretical and experimental verification of polarization pulling for G.652 fiber. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siergiejczyk, M.; Krzykowska, K.; Rosiński, A. Reliability Assessment of Integrated Airport Surface Surveillance System. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Dependability and Complex Systems DepCoS-RELCOMEX, Brunów, Poland, 29 June–3 July 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Siergiejczyk, M.; Rosiński, A.; Krzykowska, K. Reliability Assessment of Supporting Satellite System EGNOS. In New Results in Dependability and Computer Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kozuba, J.; Jafernik, H.; Krasuski, K. Utilization of the PPP Method for the Aircraft Position Determination Using Code Observations in GPS System. In Proceedings of the 16th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June–6 July 2016; SGEM: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2016; pp. 945–956. [Google Scholar]
- Kozuba, J.; Krasuski, K.; Ćwiklak, J.; Jafernik, H. Aircraft position determination in SBAS System in air transport. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 23–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzyk, Z.; Rychlicki, M. Analysis of Physical Layer Model of WLAN 802.11g Data Transmission Protocol in Wireless Networks used by Telematic Systems. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference Dependability and Complex Systems DepCoS-RELCOMEX, Brunów, Poland, 30 June–4 July 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Rychlicki, M.; Kasprzyk, Z.; Jaśkiewicz, K. Optimisation of the Municipal Waste Collection Process in a Small Size and Scarcely Populated Municipality. J. Konbin 2018, 45, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zalewski, P. Integrity Concept for Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships’ Position Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Park, M.; Bae, Y.; Kim, O.-J.; Kim, D.; Kim, B.; Kee, C. A Low-Cost, High-Precision Vehicle Navigation System for Deep Urban Multipath Environment Using TDCP Measurements. Sensors 2020, 20, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banachowicz, A.; Bober, R.; Szewczuk, T.; Wolski, A. Badanie wpływu geometrii systemu na dokładność określania pozycji za pomocą odbiornika GPS. Zesz. Nauk. Akad. Mar. Wojennej 2008, 4, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Maciuk, K. Współczynniki DOP w obserwacjach GNSS. Bud. I Archit. 2015, 14, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuichiro, K.; Toshiyuki, T. Improvements in Accurate GPS Positioning Using Time Series Analysis. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–21 August 2010; Society of Instrument and Control Engineers: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; pp. 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro, H.R.; Cruz, A.M.; Niño, F.; Ferro, R.; Gomez, E.; Cantor, E.L. GPS Data Analysis and Acquisition Software over IP Platform. In Proceedings of the WAMICON 2011 Conference Proceedings, Clearwater Beach, FL, USA, 18–19 April 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, R. A Self-Healing Plug-in Parser for NMEA Streams. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 7–9 April 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1023–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Sun, G. Reliability and Separability Analysis of Integrated GPS/BDS System. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2016 Proceedings, Changsha, China, 18–20 May 2016; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bridgelall, R.; Tolliver, D. Accuracy Enhancement of Anomaly Localization with Participatory Sensing Vehicles. Sensors 2020, 20, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Valle, R.L.; García, J.G.; Roncagliolo, P.A. A Dual-Band RF Front-End Architecture for Accurate and Reliable GPS Receivers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium—2018, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–15 June 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 995–998. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, E.; Milner, C.; Macabiau, C.; Estival, P. Preliminary Integrity Assessment for GPS/GLONASS RAIM with Multiple Faults. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium PLANS 2018, Monterey, CA, USA, 23–26 April 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Jia, C. Integrity monitoring of high-accuracy GNSS-based attitude determination. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.T.; Gu, Y.; Kamijo, S. 3D Building Model-Based Pedestrian Positioning Method Using GPS/GLONASS/QZSS and its Reliability Calculation. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, D.; Nogin, G.; Koch, P.; Racz, D.; Goldszmidt, M.; Horvitz, E. Predicting Travel Time Reliability Using Mobile Phone GPS Data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 75, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzykowska, K.; Krzykowski, M. Forecasting Parameters of Satellite Navigation Signal through Artificial Neural Networks for the Purpose of Civil Aviation. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 2019, 7632958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siergiejczyk, M.; Paś, J.; Rosiński, A. Issue of reliability–exploitation evaluation of electronic transport systems used in the railway environment with consideration of electromagnetic interference. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 10, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caban, D.; Walkowiak, T. Dependability Analysis of Hierarchically Composed System-of-Systems. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Dependability and Complex Systems DepCoS-RELCOMEX, Brunów, Poland, 2–6 June 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- VisualGPS™ Software and Services. Available online: http://www.visualgps.net/#visualgpsview-content (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Lin, J.; Chang, C.; Peng, J.; Tung, M.; Liu, C. Evolving GPS position correction function using genetic programming. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems, and the 13th International Symposium on Advanced Intelligence Systems, Cairo, Egypt, 1–3 September 2012; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Rosinski, A. Design of the Electronic Protection Systems with Utilization of the Method of Analysis of Reliebility Structures. In Proceedings of the 2008 19th International Conference on Systems Engineering, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19–21 August 2008; IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA; pp. 421–426. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Skytraq V6 | Syngio BU353-S4 | Hama | Holux M-215+ | Holux GR-213 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chipset | Venus V6 | SiRF StarIV | SiRF StarIII | MTK MT3333 GPS/GLONASS chipset | SiRF StarIII |
| Receiver Type | L1, C/A code 51-channel acquisition 14-channel tracking | L1, 1575.42 MHZ 48 all-in-view tracking | L1, up to 20 satellites | L1, 1575.42 MHz 66 parallel searching, 22 tracking channels | L1, up to 20 satellites |
| C/A Code | N/A | 1.023 MHz | N/A | 1.023 MHz | N/A |
| Maximum Update Rate | 10 Hz | 1 Hz | 1 Hz | 1 Hz | 1 Hz |
| Accuracy | Position 2.5 m CEP Velocity 0.1 m/s Time 250 ns | < 2.5 m 2D RMS SBAS Enabled | up to 2 m (WAAS) | Non DGPS (Differential GPS): Position: 3.0 m CEP excluding SA Velocity: 0.1m/s. Interval: 0.1 µs to Sync GPS DGPS (EGNOS/WAAS/ MSAS): 2.5 M | Non DGPS (Differential GPS) Position 5–25 m CEP without SA Velocity 0.1 m/s, without SA Time 1 μs sync GPSTime EGNOS/WAAS: Position < 2.2 m, horizontal 95% of time < 5 m, vertical 95% of time |
| Time To First Fix | Hot-Start < 1 s Warm-Start 25 s average Cold-Start 29 s average | Hot-Start 1 s average Warm-Start 35 s average Cold-Start 35 s average | Hot-Start < 1 s Warm-Start 35 s Cold-Start 42 s | Hot-Start 1 s Warm-Start 30 s Cold-Start 31 s | Hot-Start 1 s Warm-Start 38 s Cold-Start 42 s |
| Sensitivity | −161 dBm | −163 dBm | −159 dBm | −165 dBm | −159 dBm |
| Protocol | NMEA-0183 v3.01 Secondary: SkyTraq Binary | NMEA0183 Secondary: SiRFbinary | NMEA-0183 v.3.00 | NMEA-0183 v3.01 | NMEA-0183 v2.2 |
| Interface | USB 2.0 | USB 2.0 | USB 2.0 | USB 2.0 | USB 2.0 |
| Supply Voltage | 1.2 V, 3.3 V | 5.5 V (USB) | 5.5 V (USB) | 5.5 V (USB) | 5.5 V (USB) |
| Current Consumption | Acquisition ~50 mA Tracking ~23 mA | 55 mA Maximum | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Operating Temperature | −40 °C~85 °C | −40 °C~85 °C | −40 °C~85 °C | −10 °C~65 °C | −10 °C~65 °C |
| Dimension | 38.0 × 40.5 × 12.3 mm | 53.0 × 19.2 mm | 45.0 × 37.0 × 20.0 mm | 64.5 × 42 × 17.8 mm | 64.5 × 42 × 17.8 mm |
| Weight | N/A | 62.37 g | 70.0 g | 84.0 g | 84.0 g |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rychlicki, M.; Kasprzyk, Z.; Rosiński, A. Analysis of Accuracy and Reliability of Different Types of GPS Receivers. Sensors 2020, 20, 6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226498
Rychlicki M, Kasprzyk Z, Rosiński A. Analysis of Accuracy and Reliability of Different Types of GPS Receivers. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226498
Chicago/Turabian StyleRychlicki, Mariusz, Zbigniew Kasprzyk, and Adam Rosiński. 2020. "Analysis of Accuracy and Reliability of Different Types of GPS Receivers" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226498
APA StyleRychlicki, M., Kasprzyk, Z., & Rosiński, A. (2020). Analysis of Accuracy and Reliability of Different Types of GPS Receivers. Sensors, 20(22), 6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226498






