A Study of the Radiation Tolerance of CVD Diamond to 70 MeV Protons, Fast Neutrons and 200 MeV Pions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation
3. Sample Description
4. Sample Irradiations
4.1. Proton Irradiations
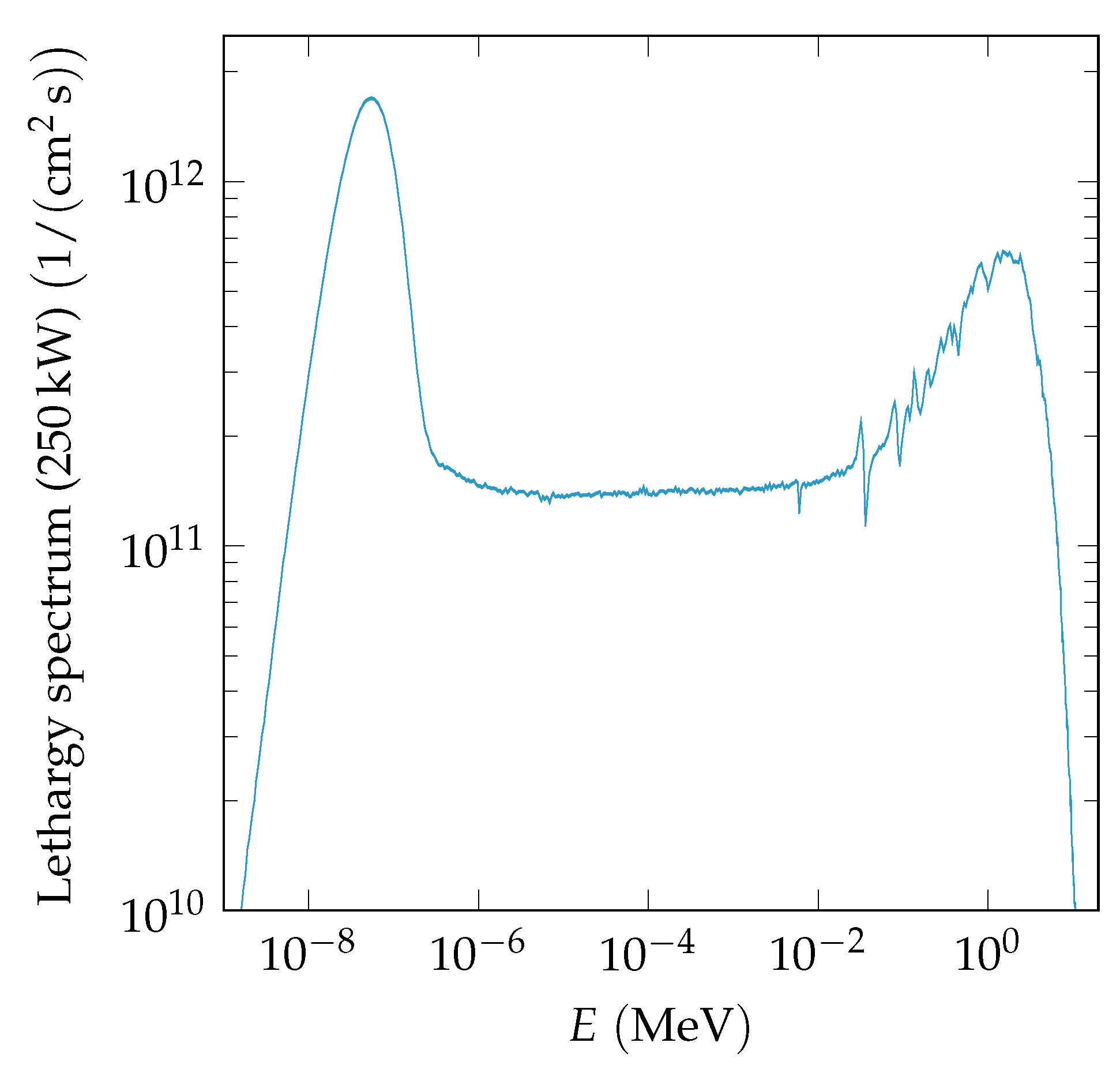
4.2. Neutron Irradiations
4.3. Pion Irradiations
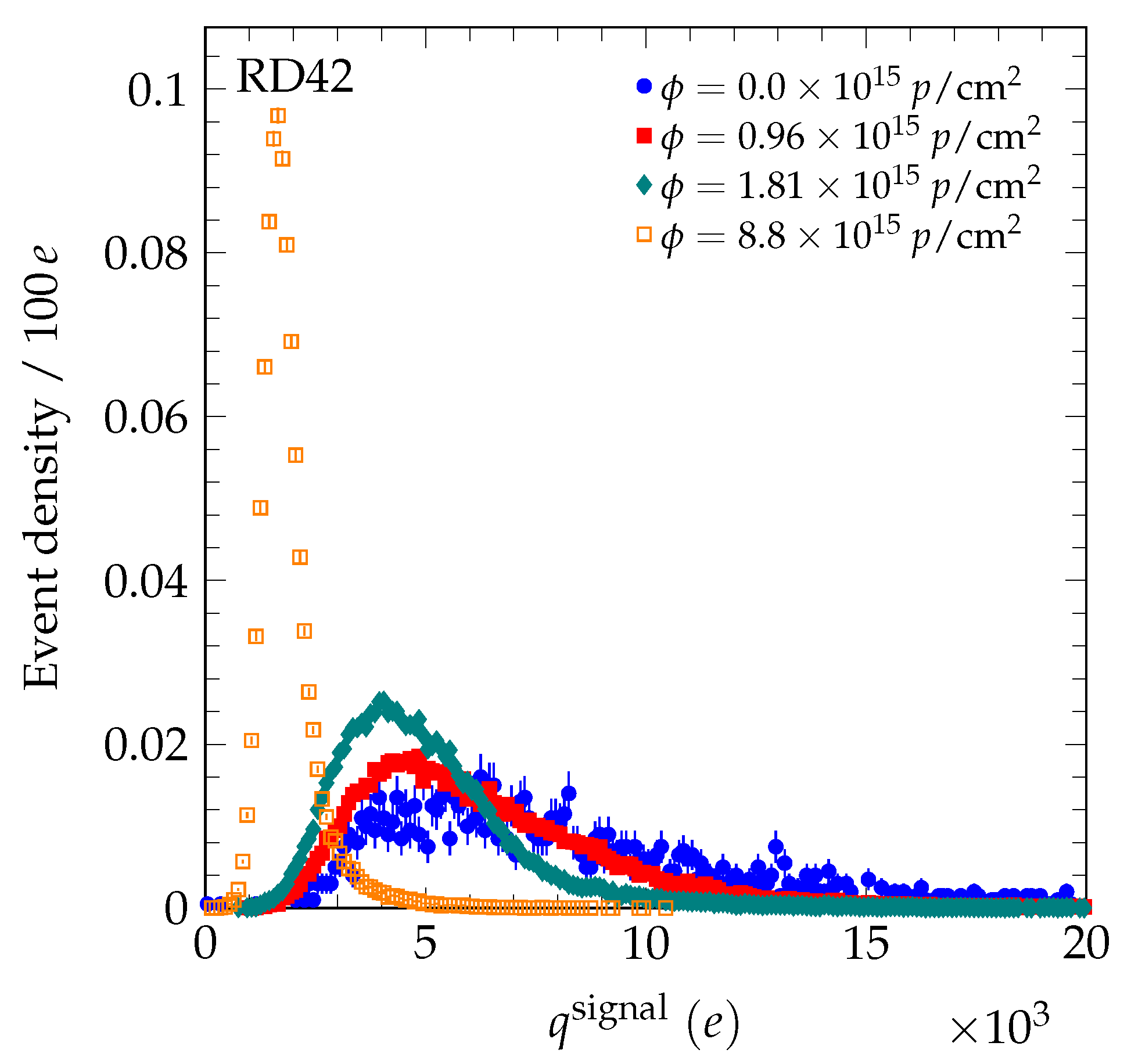
5. Test Beam Analysis
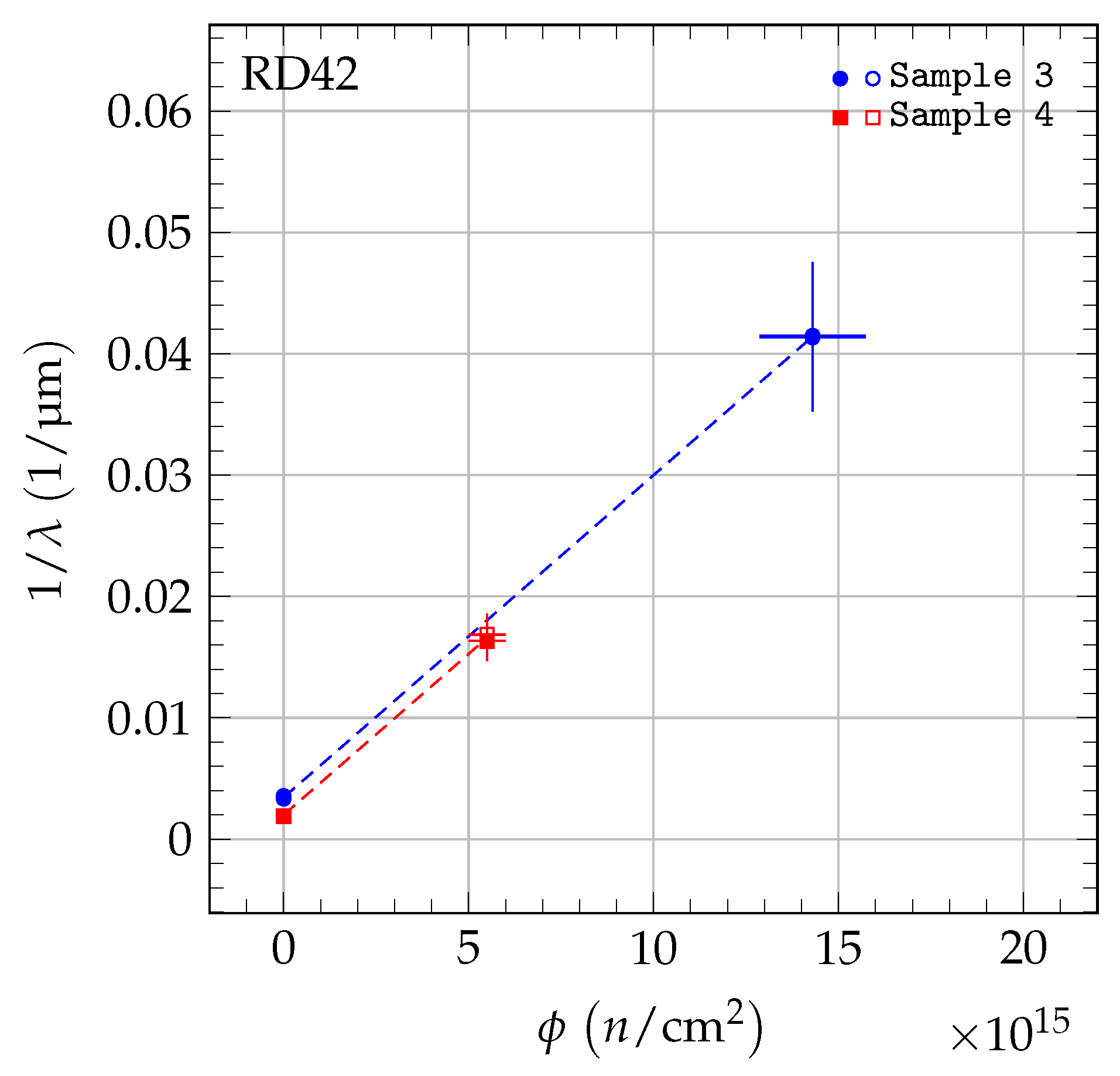
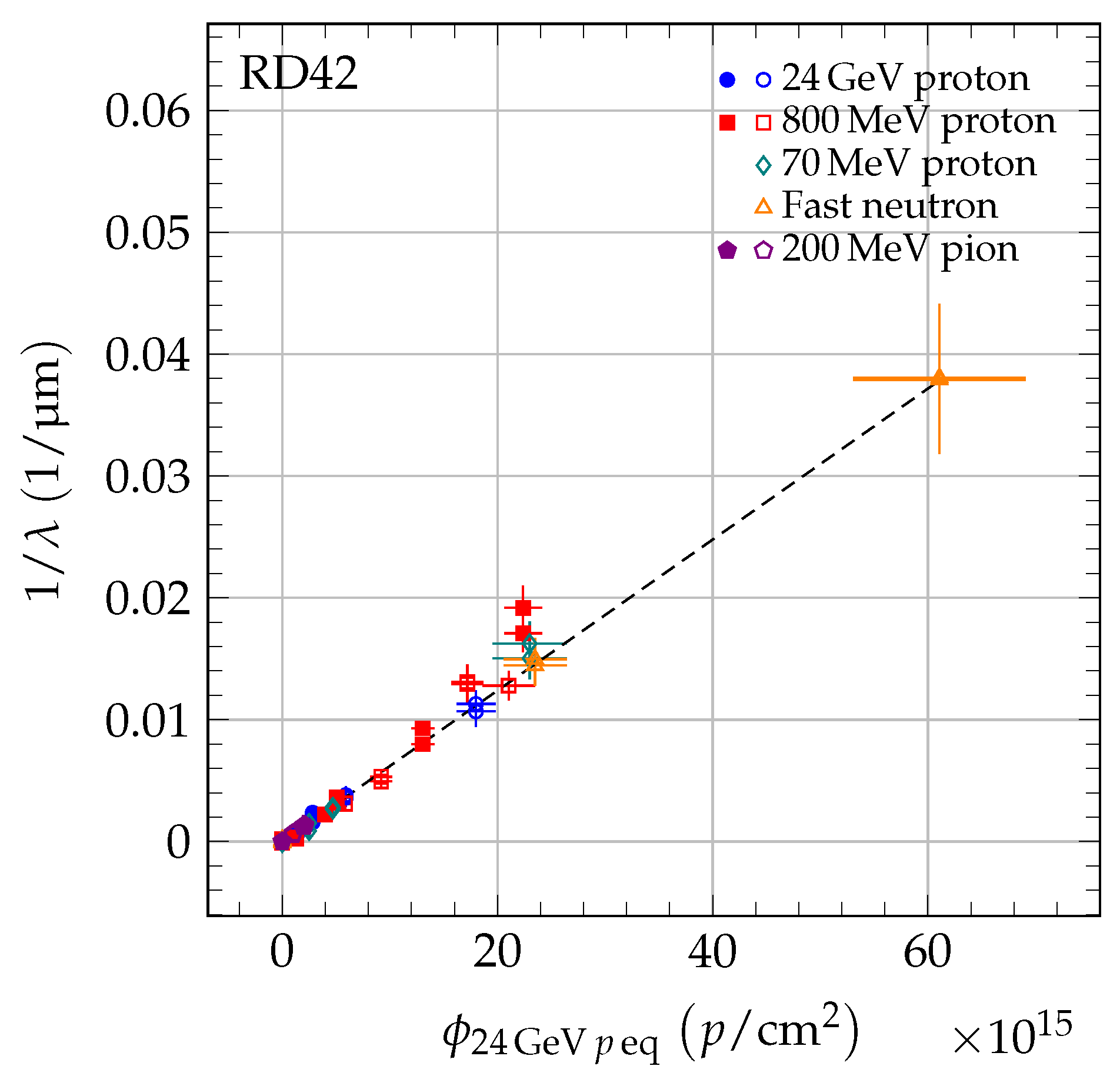
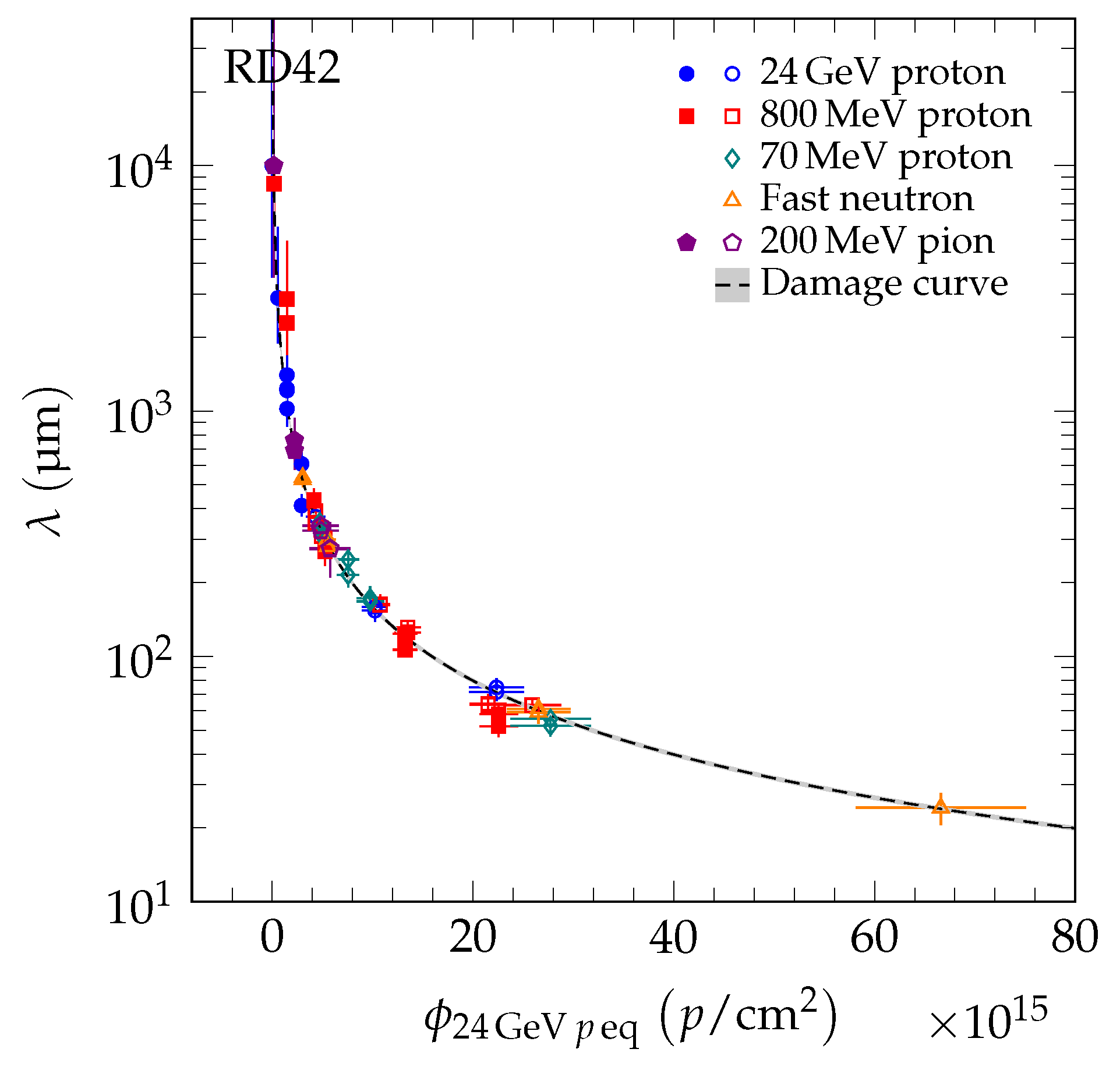
6. Measurement of Damage Constants
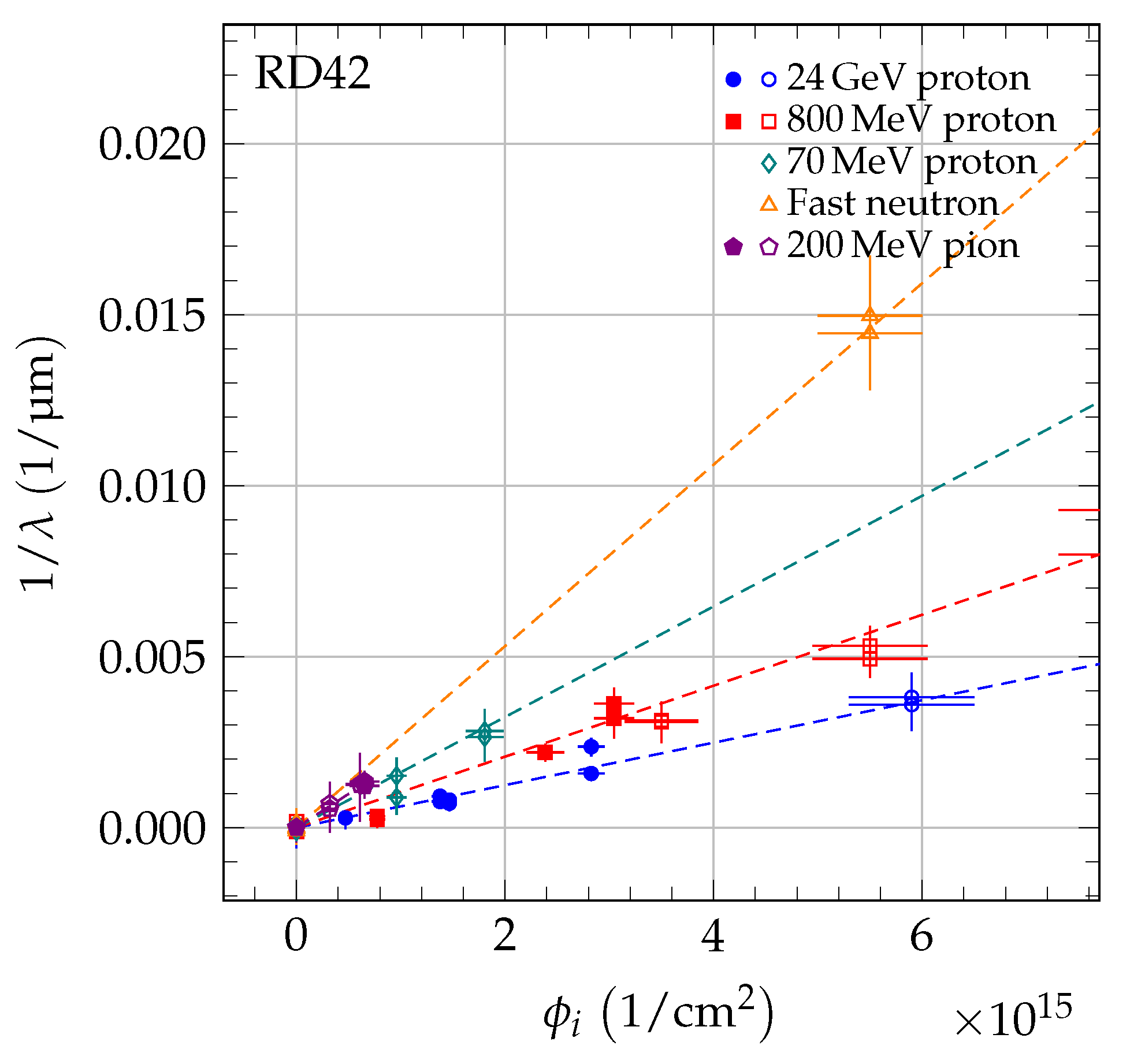
7. Universal Damage Curve
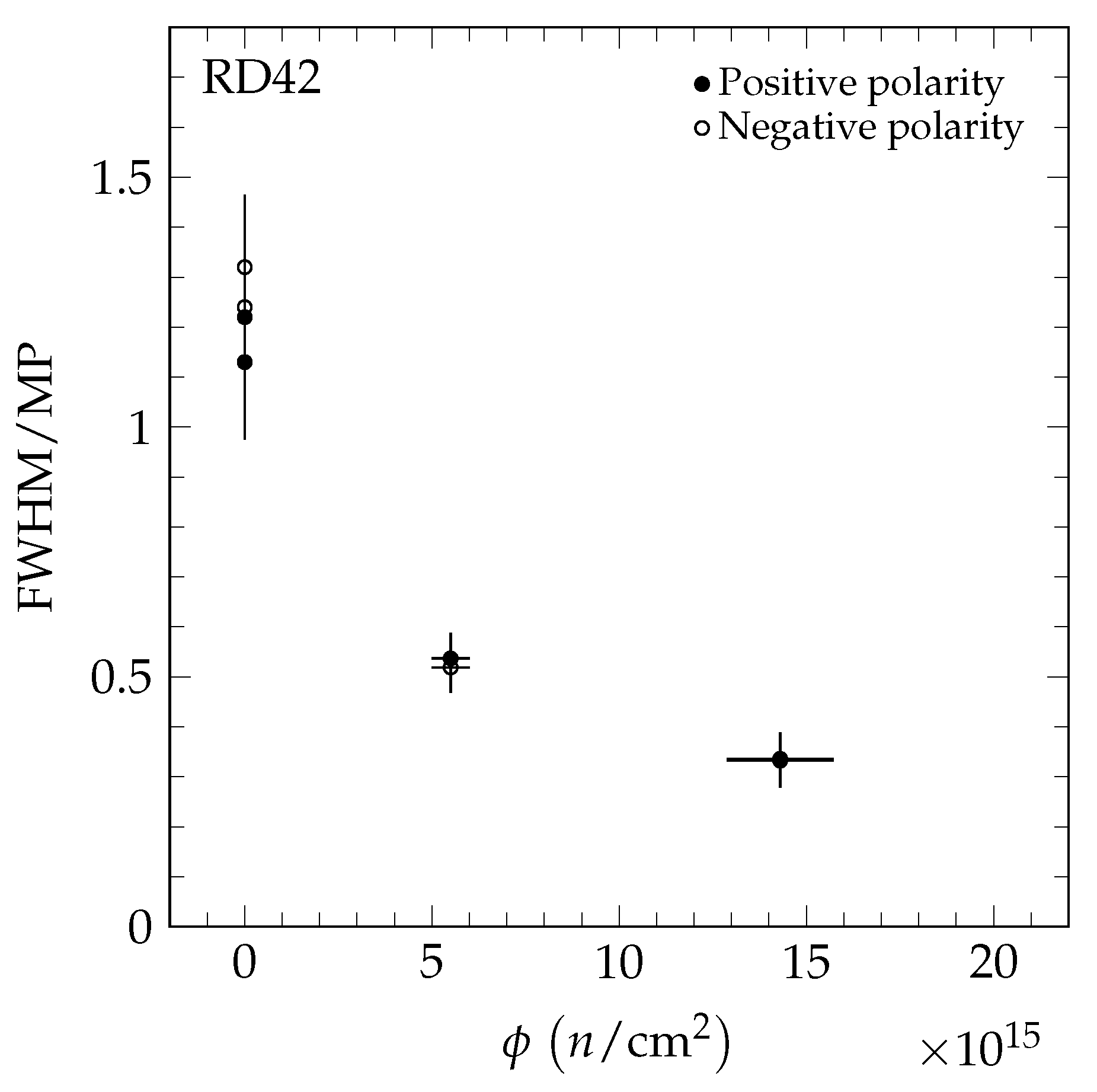
8. Measurement of the / Ratio
9. Comparison with Silicon
10. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CERN The European Organization for Nuclear Research, CH-1211, Genève 23, Switzerland. Available online: https://home.cern/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Apollinari, G.; Brüning, O.; Nakamoto, T.; Lucio, R. High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC): Preliminary Design Report, Chapter 1: High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider HL-LHC; CERN Yellow Reports: Monographs, CERN-2015-005; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollinari, G.; Béjar, A.I.; Brüning, O.; Fessia, P.; Lamont, M.; Rossi, L.; Tavian, L. High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC): Technical Design Report V.0.1; CERN Yellow Reports: Monographs, Volume 4/2017 CERN-2017-007-M; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäni, L.; Alexopoulos, A.; Artuso, M.; Bachmair, F.; Bartosik, M.; Beck, H.; Bellini, V.; Belyaev, V.; Bentele, B.; Bes, A.; et al.; (On behalf of the RD42 Collaboration) A study of the radiation tolerance of poly-crystalline and single-crystalline CVD diamond to 800 MeV and 24 GeV protons. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 465103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Samples Used in this Study Were Electronic Grade CVD Diamond Purchased from Element Six Technologies, Global Innovation Centre, Fermi Ave., Harwell, OX11 0QR, United Kingdom and II-VI Incorporated, 375 Saxonburg Blvd., Saxonburg, PA 16056-9499, USA. Available online: http://www.iiviinfrared.com (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Bachmair, F. CVD Diamond Sensors in Detectors for High Energy Physics. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotite Silver Paint D-550. Fujikura Kasei Co., LTD. 6-15, Shibakoen 2-chome, Minato-ku, Tokyo 105-0011 Japan. Available online: https://www.fkkasei.co.jp/english/product/electric/dotite/05.html (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Integrated Detector and Electronics (IDE) AS Designed the VA Circuits. Available online: http://www.ideas.no (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Zhao, S. Characterization of the Electrical Properties of Polycrystalline Diamond Films. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 1994. Available online: http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1394810346 (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center (CYRIC), Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan. Available online: http://www.cyric.tohoku.ac.jp (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Snoj, L.; Žerovnik, G.; Trkov, A. Computational analysis of irradiation facilities at the JSI TRIGA reactor. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrožič, K.; Žerovnik, G.; Snoj, L. Computational analysis of the dose rates at JSI TRIGA reactor irradiation facilities. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 130, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krištof, E.S. Characterization of neutron flux in the exposure channel F19 of the TRIGA Mark II reactor in Ljubljana. Nucl. Energy Cent. Eur. 1998, 98, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), 5232 Villigen, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.psi.ch (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- CERN IRRAD Proton Facility. Available online: https://ps-irrad.web.cern.ch/ps-irrad/external.php (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Glaser, M.; Ravotti, F.; Moll, M. Dosimetry assessments in the irradiation facilities at the CERN-PS accelerator. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2006, 53, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäni, L. Top Quarks and Diamonds. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colledani, C.; Dulinski, W.; Turchetta, R.; Djama, F.; Rudge, A.; Weilhammer, P. A Submicron Precision Silicon Telescope for Beam Test Purposes. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1996, 372, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, D. CVD Diamond Sensors for Particle Detection and Tracking. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.S.; Han, S.; Kania, D.R.; Zhao, S.; Gan, K.K.; Kagan, H.; Kass, R.; Malchow, R.; Morrow, F.; Palmer, W.F.; et al. Particle- and photoinduced conductivity in type-IIa diamonds. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muškinja, M.; Cindro, V.; Gorišek, A.; Kagan, H.; Kramberger, G.; Mandić, I.; Mikuž, M.; Phan, S.; Smith, D.S.; Zavrtanik, M. Investigation of charge multiplication in single crystalline CVD diamond. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2017, 841, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, K. Zum Mechanismus des lichtelektrischen Primärstromes in isolierenden Kristallen. Z. Phys. 1932, 77, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The RD42 Collaboration; Hartjes, F.; Adam, W.; Bauer, C.; Berdermann, E.; Bergonzo, P.; Bogani, F.; Borchi, E.; Brambilla, A.; Bruzzi, M.; et al. Parameterisation of Radiation Effects on CVD Diamond for Proton Irradiation. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 1999, 78, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsung, J.W.; Havranek, M.; Hügging, F.; Kagan, H.; Krüger, H.; Wermes, N. Signal and noise of diamond pixel detectors at high radiation fluences. J. Instrum. 2012, 7, P09009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthoff, M.; de Boer, W.; Müller, S. Simulation of beam induced lattice defects of diamond detectors using FLUKA. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2014, 735, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramberger, G.; Cindro, V.; Mandić, I.; Mikuž, M.; Zavrtanik, M. Determination of effective trapping times for electrons and holes in irradiated silicon. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2002, 476, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindro, V.; Kramberger, G.; Lozano, M.; Mandić, I.; Mikuž, M.; Pellegrini, G.; Pulko, J.; Ullan, M.; Zavrtanik, M. Radiation damage in p-type silicon irradiated with neutrons and protons. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2009, 599, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RD50 Collaboration. Available online: http://rd50.web.cern.ch/rd50/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Jacoboni, C.; Canali, C.; Ottaviani, G.; Alberigi Quaranta, A. A review of some charge transport properties of silicon. Solid-State Electron. 1977, 20, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





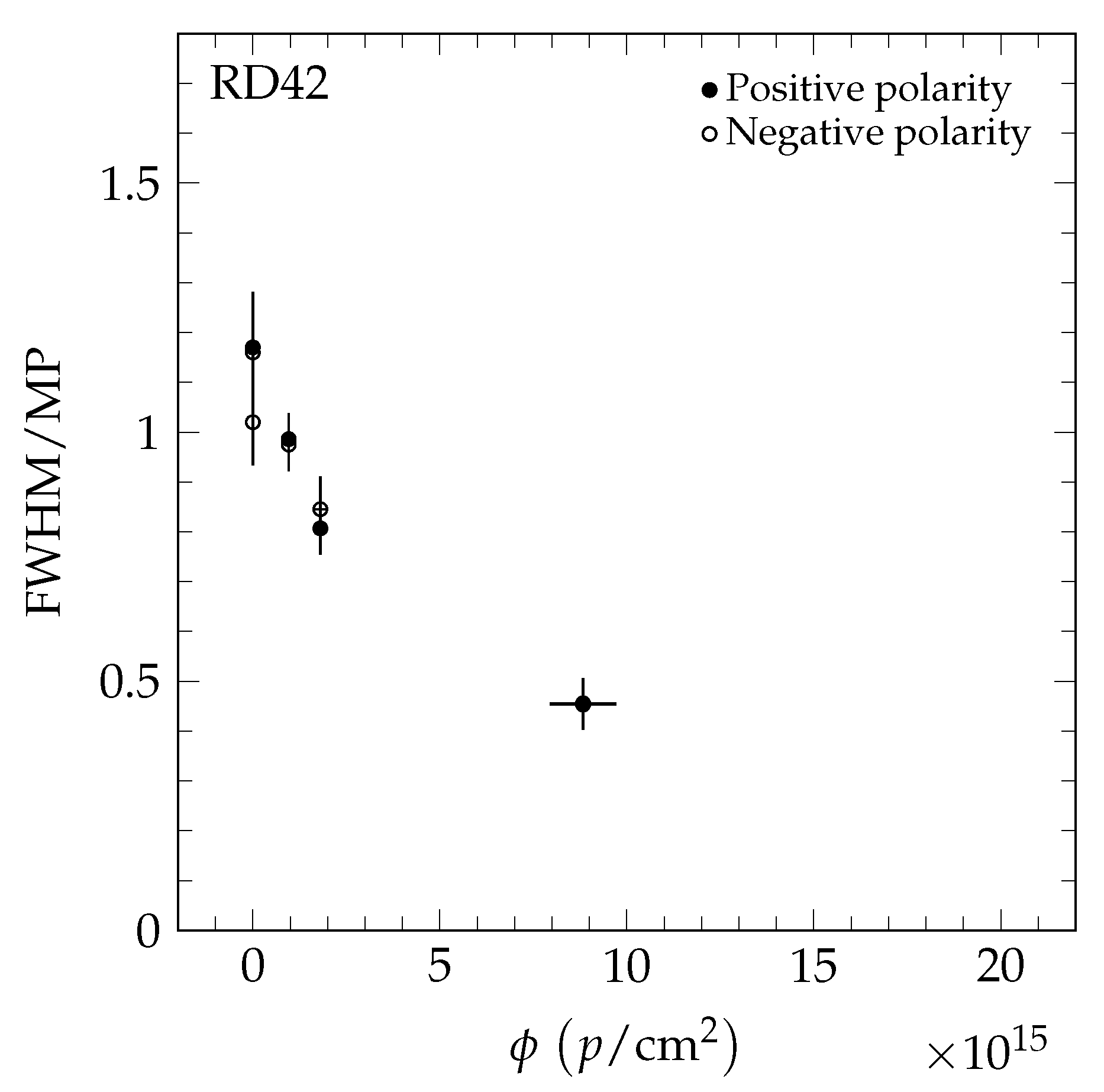
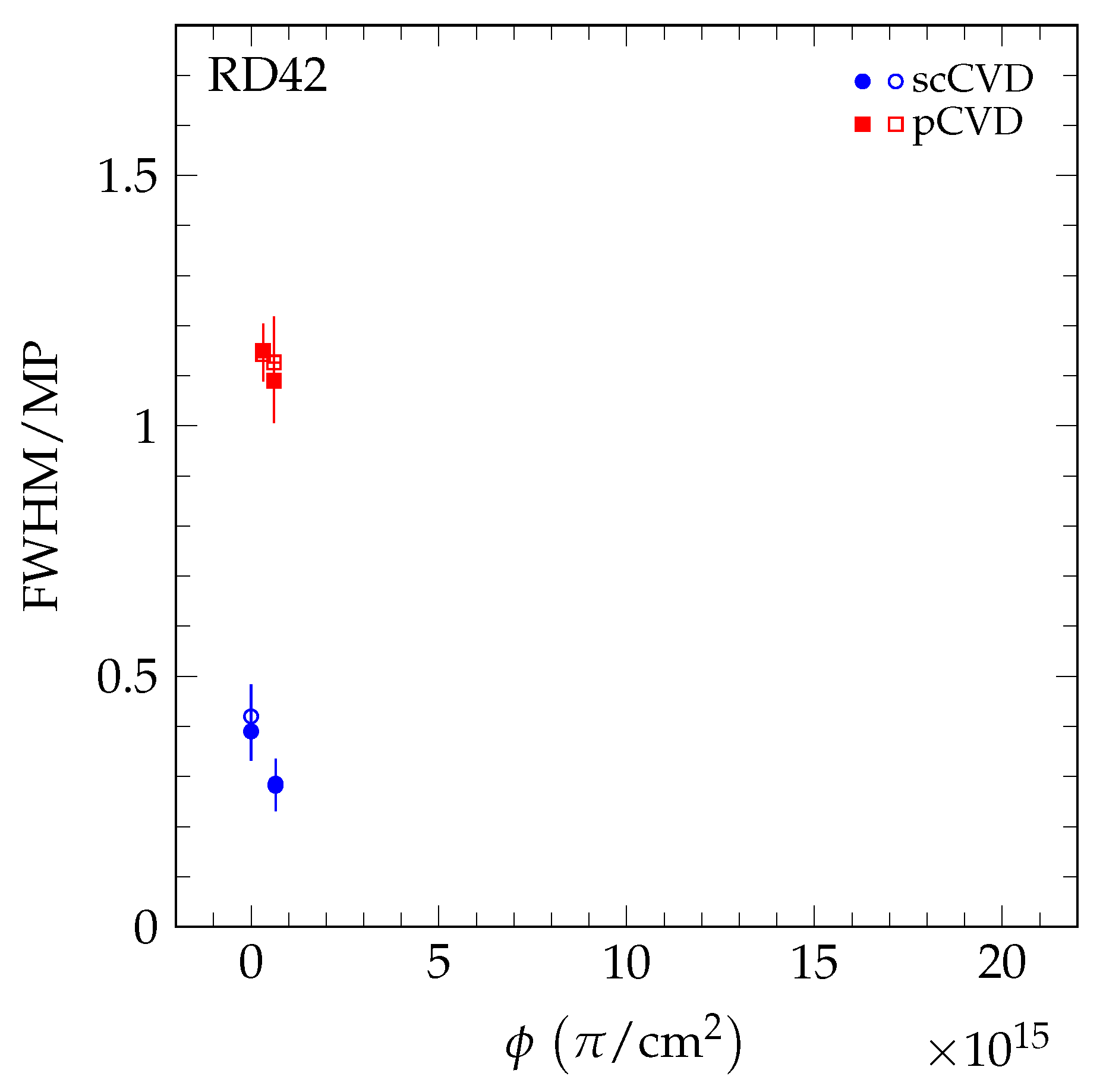
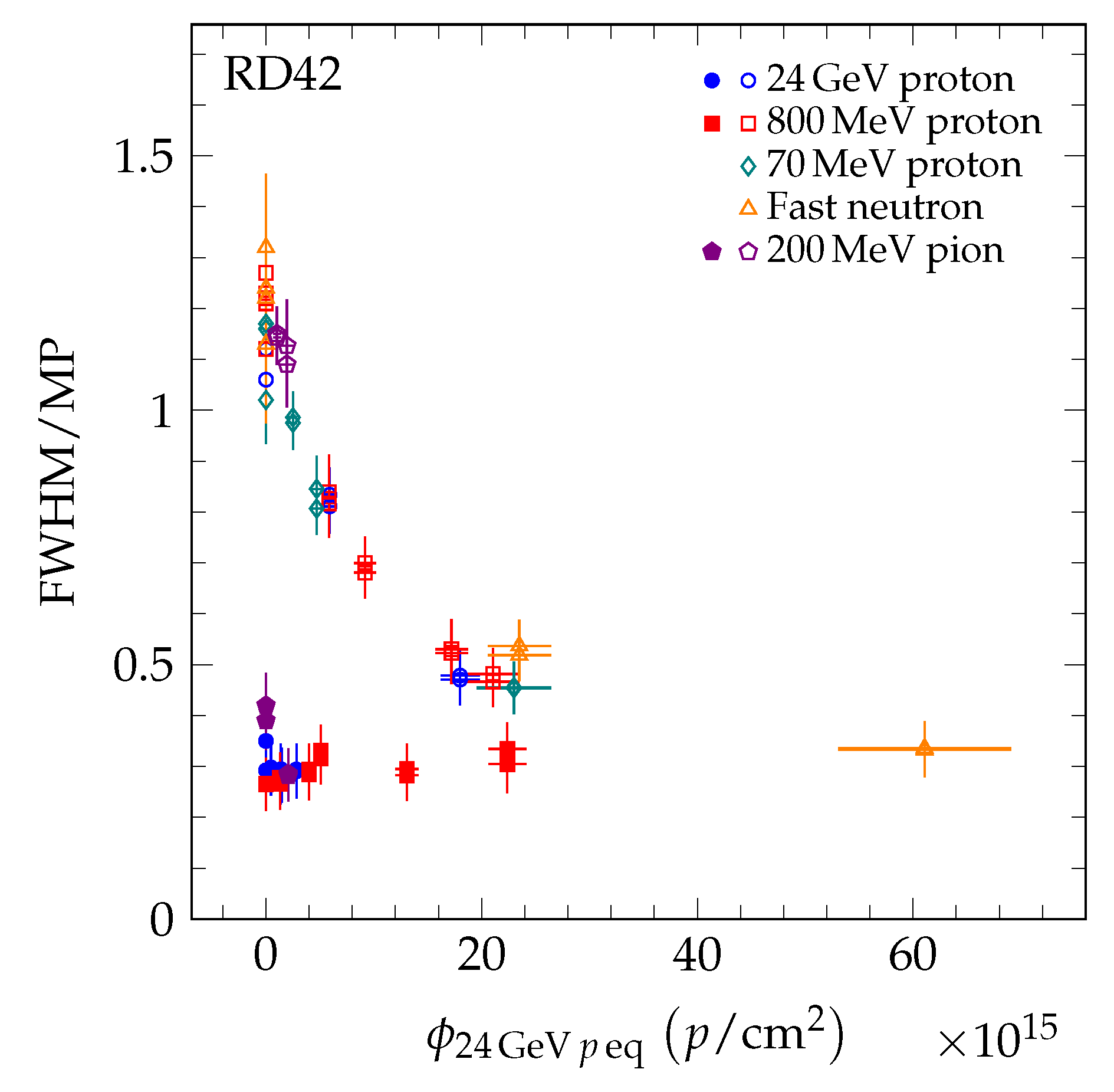


| Diamond | Type | Thickness () | Area (mm) | Initial ccd () | Fluence (10 p/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | pCVD | 518 | 10 × 10 | 227/238 | 0 |
| 8.8 ± 0.9 | |||||
| Sample 2 | pCVD | 506 | 10 × 10 | 216/216 | 0 |
| 0.96 ± 0.10 | |||||
| 1.81 ± 0.18 |
| Diamond | Type | Thickness () | Area (mm) | Initial ccd () | Fluence (10 n/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 3 | pCVD | 512 | 5 × 5 | 214/204 | 0 |
| 14.3 ± 1.4 | |||||
| Sample 4 | pCVD | 510 | 10 × 10 | 295/292 | 0 |
| 5.5 ± 0.5 |
| Diamond | Type | Thickness () | Area (mm) | Initial ccd () | Fluence (10 /cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 5 | scCVD | 497 | 5 × 5 | 497/497 | 0 |
| 0.65 ± 0.14 | |||||
| Sample 6 | pCVD | 520 | 5 × 5 | 222 | 0 |
| 0.32 ± 0.07 | |||||
| Sample 7 | pCVD | 508 | 5 × 5 | 228 | 0 |
| 0.61 ± 0.14 |
| Particle Species | |
|---|---|
| 24 GeV protons | 1.0 |
| 800 MeV protons | 1.67 ± 0.09 |
| 70 MeV protons | 2.60 ± 0.29 |
| 25 MeV protons | 4.4 ± 1.2 |
| Fast neutrons | 4.3 ± 0.4 |
| 200 MeV pions | 3.2 ± 0.8 |
| Diamond j | (m) | (10/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 340 ± 21 | 4.7 ± 0.6 |
| Sample 2 | 318 ± 15 | 5.1 ± 0.6 |
| Sample 3 | 291 ± 21 | 5.5 ± 0.7 |
| Sample 4 | 531 ± 27 | 3.0 ± 0.4 |
| Sample 5 | 11,000 ± 20,000 | 0.15 ± 0.31 |
| Sample 6 + 7 | 420 ± 60 | 3.8 ± 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bäni, L.; Alexopoulos, A.; Artuso, M.; Bachmair, F.; Bartosik, M.R.; Beck, H.C.; Bellini, V.; Belyaev, V.; Bentele, B.; Bes, A.; et al. A Study of the Radiation Tolerance of CVD Diamond to 70 MeV Protons, Fast Neutrons and 200 MeV Pions. Sensors 2020, 20, 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226648
Bäni L, Alexopoulos A, Artuso M, Bachmair F, Bartosik MR, Beck HC, Bellini V, Belyaev V, Bentele B, Bes A, et al. A Study of the Radiation Tolerance of CVD Diamond to 70 MeV Protons, Fast Neutrons and 200 MeV Pions. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226648
Chicago/Turabian StyleBäni, Lukas, Andreas Alexopoulos, Marina Artuso, Felix Bachmair, Marcin Ryszard Bartosik, Helge Christoph Beck, Vincenzo Bellini, Vladimir Belyaev, Benjamin Bentele, Alexandre Bes, and et al. 2020. "A Study of the Radiation Tolerance of CVD Diamond to 70 MeV Protons, Fast Neutrons and 200 MeV Pions" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226648
APA StyleBäni, L., Alexopoulos, A., Artuso, M., Bachmair, F., Bartosik, M. R., Beck, H. C., Bellini, V., Belyaev, V., Bentele, B., Bes, A., Brom, J.-M., Chiodini, G., Chren, D., Cindro, V., Claus, G., Collot, J., Cumalat, J., Curtoni, S., Dabrowski, A. E., ... Unno, Y., on behalf of the RD42 Collaboration. (2020). A Study of the Radiation Tolerance of CVD Diamond to 70 MeV Protons, Fast Neutrons and 200 MeV Pions. Sensors, 20(22), 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226648










