Decoding Attempted Hand Movements in Stroke Patients Using Surface Electromyography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Recordings—Surface EMG
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Pre-Processing and Feature Extraction
2.4.2. Classification
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO MONICA Project Principal Investigators. The world health organization monica project (monitoring trends and determinants in cardiovascular disease): A major international collaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorne, P.; Coupar, F.; Pollock, A. Motor recovery after stroke: A systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.S. The Copenhagen Stroke Study experience. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1996, 6, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaechter, J.D. Motor rehabilitation and brain plasticity after hemiparetic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 73, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, J.W. Motor learning: Its relevance to stroke recovery and neurorehabilitation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Nguyet, D.; Cohen, L.G.; Brasil-Neto, J.P.; Cammarota, A.; Hallett, M. Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 74, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Jiang, N.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Lin, C.; Prieto, G.A.; Moreno, J.C.; Pons, J.L.; Dremstrup, K.; Farina, D. A Closed-Loop Brain-Computer Interface Triggering an Active Ankle-Foot Orthosis for Inducing Cortical Neural Plasticity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 20, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Murguialday, A.; Broetz, D.; Rea, M.; Läer, L.; Yilmaz, Ö.; Msc, F.L.B.; Liberati, G.; Curado, M.R.; Garcia-Cossio, E.; Vyziotis, A.; et al. Brain–machine interface in chronic stroke rehabilitation: A controlled study. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte-Silva, K.; Piscitelli, D.; Norouzi-Gheidari, N.; Batalla, M.A.P.; Archambault, P.; Levin, M.F. Electromyogram-related neuromuscular electrical stimulation for restoring wrist and hand movement in Poststroke hemiplegia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2019, 33, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, E.; Russold, M.; Gfoehler, M.; Puchinger, M.; Weber, M.; Becker, S.; Krakow, K.; Immick, N.; Augsten, A.; Rossini, M.; et al. A Hybrid Robotic System for Arm Training of Stroke Survivors: Concept and First Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 3290–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jochumsen, M.; Niazi, I.K.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Jiang, N.; Farina, D.; Dremstrup, K. Comparison of spatial filters and features for the detection and classification of movement-related cortical potentials in healthy individuals and stroke patients. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 56003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochumsen, M.; Niazi, I.K.; Taylor, D.; Farina, D.; Dremstrup, K. Detecting and classifying movement-related cortical potentials associated with hand movements in healthy subjects and stroke patients from single-electrode, single-trial EEG. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 56013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochumsen, M.; Niazi, I.K.; Dremstrup, K.; Kamavuako, E.N. Detecting and classifying three different hand movement types through electroencephalography recordings for neurorehabilitation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 54, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Ushiba, J.; Nishimoto, A.; Abe, K.; Honaga, K.; Nishimura, A.; Mizuno, K.; Kodama, M.; Masakado, Y.; et al. A new therapeutic application of brain-machine interface (BMI) training followed by hybrid assistive neuromuscular dynamic stimulation (HANDS) therapy for patients with severe hemiparetic stroke: A proof of concept study. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2016, 34, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, N.P. High-density myoelectric pattern recognition toward improved stroke rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Garcia-Cossio, E.; Birbaumer, N.; Burdet, E.; Ramos-Murguialday, A. Is EMG a Viable Alternative to BCI for Detecting Movement Intention in Severe Stroke? IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 2790–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Murguialday, A.; García-Cossio, E.; Walter, A.; Cho, W.; Broetz, D.; Bogdan, M.; Cohen, L.G.; Birbaumer, N. Decoding upper limb residual muscle activity in severe chronic stroke. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochumsen, M.; Navid, M.S.; Rashid, U.; Haavik, H.; Niazi, I.K. EMG-versus EEG-Triggered Electrical Stimulation for Inducing Corticospinal Plasticity. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camona, C.; Wilkins, K.B.; Drogos, J.; Sullivan, J.E.; Dewald, J.P.A.; Yao, J. Improving hand function of severely impaired chronic hemiparetic stroke individuals using task-specific training with the ReIn-Hand system: A case series. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Lai, W.P.; Qian, Q.; Hu, X.; Tam, E.W.C.; Zheng, Y.-P. Translation of robot-assisted rehabilitation to clinical service: A comparison of the rehabilitation effectiveness of EMG-driven robot hand assisted upper limb training in practical clinical service and in clinical trial with laboratory configuration for chronic stroke. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Wilson, K.M.; Lock, B.A.; Kamper, D.G. Subject-specific myoelectric pattern classification of functional hand movements for stroke survivors. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 19, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Tong, R.K.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, P. Myoelectric pattern recognition for controlling a robotic hand: A feasibility study in stroke. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolla, M.; Ferrante, S.; Ferrigno, G.; Baldassini, D.; Molteni, F.; Guanziroli, E.; Cottini, M.C.; Seneci, C.; Pedrocchi, A. Artificial neural network EMG classifier for functional hand grasp movements prediction. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopke, J.V.; Hargrove, L.J.; Ellis, M.D. Applying LDA-based pattern recognition to predict isometric shoulder and elbow torque generation in individuals with chronic stroke with moderate to severe motor impairment. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subramaniam, S.; Varghese, R.; Bhatt, T. Influence of chronic stroke on functional arm reaching: Quantifying deficits in the ipsilesional upper extremity. Rehabil. Res. Pr. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, P. Myoelectric pattern identification of stroke survivors using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. J. Healthc. Eng. 2014, 5, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, P. Wavelet packet feature assessment for high-density myoelectric pattern recognition and channel selection toward stroke rehabilitation. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehman, M.Z.U.; Waris, A.; Gilani, S.O.; Jochumsen, M.; Niazi, I.K.; Jamil, M.; Farina, D.; Kamavuako, E.N. Multiday EMG-based classification of hand motions with deep learning techniques. Sensors 2018, 18, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gladstone, D.J.; Danells, C.J.; Black, S.E. The fugl-meyer assessment of motor recovery after stroke: A critical review of its measurement properties. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2002, 16, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgins, B.; Parker, P.; Scott, R.N. A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochumsen, M.; Waris, A.; Kamavuako, E.N. The effect of arm position on classification of hand gestures with intramuscular EMG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2018, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.Z.U.; Gilani, S.O.; Waris, A.; Niazi, I.K.; Slabaugh, G.; Farina, D.; Kamavuako, E.N. Stacked sparse autoencoders for EMG-based classification of hand motions: A comparative multi day analyses between surface and intramuscular EMG. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Barkhaus, P.E.; Zhang, X.; Rymer, W.Z. Characterizing the complexity of spontaneous motor unit patterns of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using approximate entropy. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 66010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Haider, A.; Taleb-Ahmed, A. A heterogeneous multi-core based biomedical application processing system and programming toolkit. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2019, 91, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugler, E.M.; Tomic, G.; Singh, A.; Hameed, S.; Lindberg, E.W.; Gaide, J.; Alqadi, M.; Robinson, E.; Dalzotto, K.; Limoli, C.; et al. Myoelectric Computer Interface Training for Reducing Co-Activation and Enhancing Arm Movement in Chronic Stroke Survivors: A Randomized Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2019, 33, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzolato, S.; Tagliapietra, L.; Cognolato, M.; Reggiani, M.; Müller, H.; Atzori, M. Comparison of six electromyography acquisition setups on hand movement classification tasks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
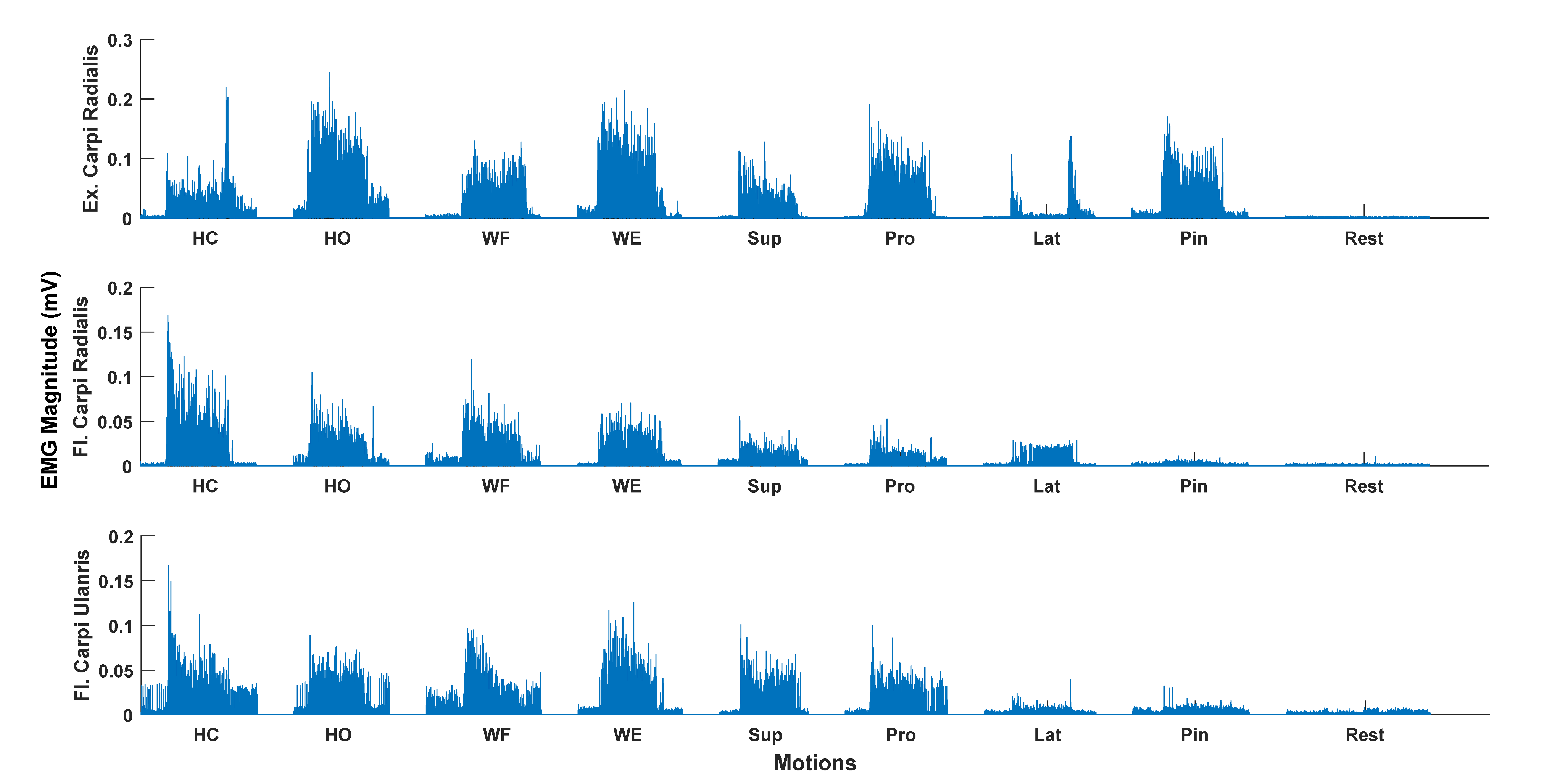
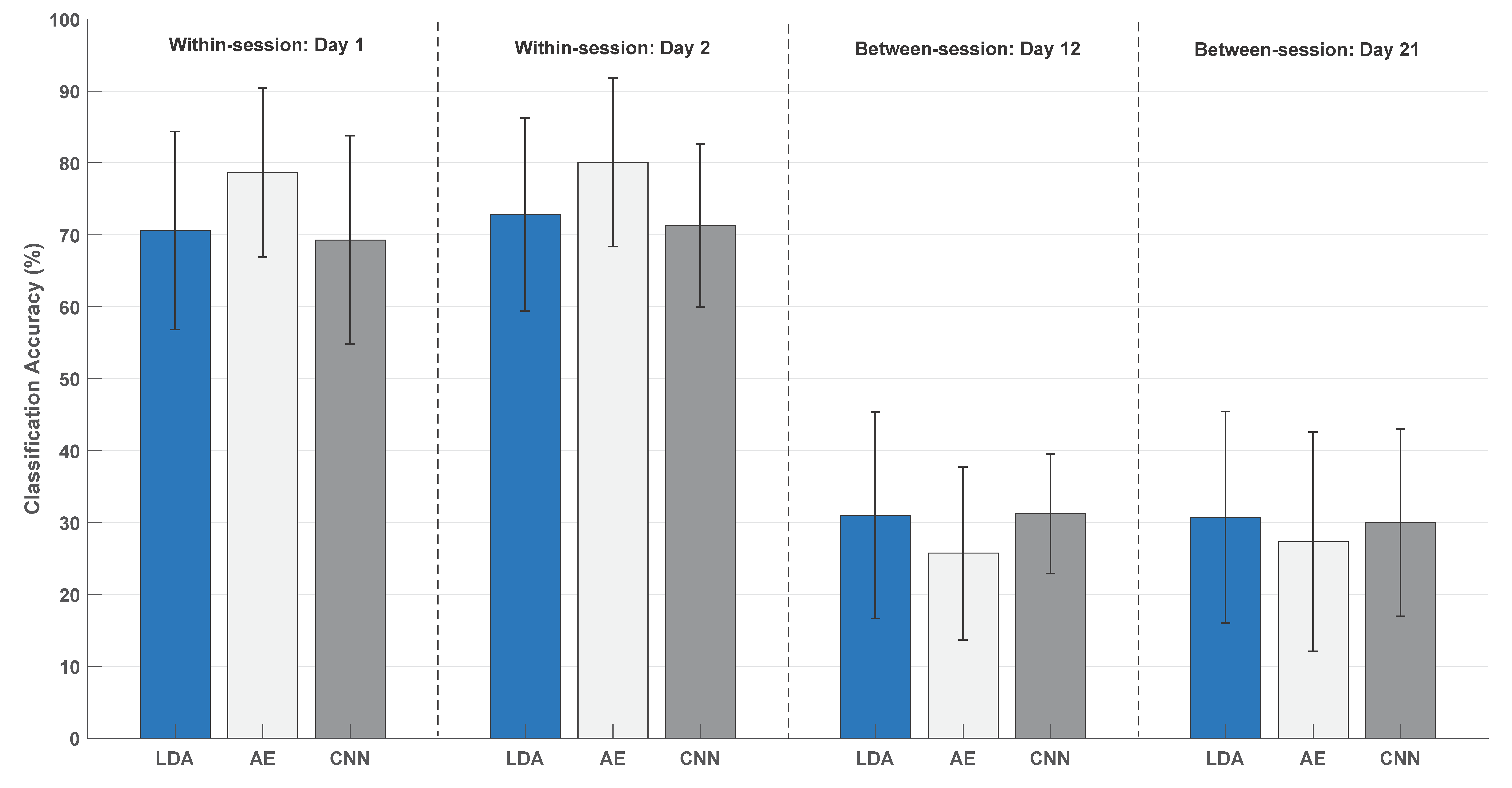
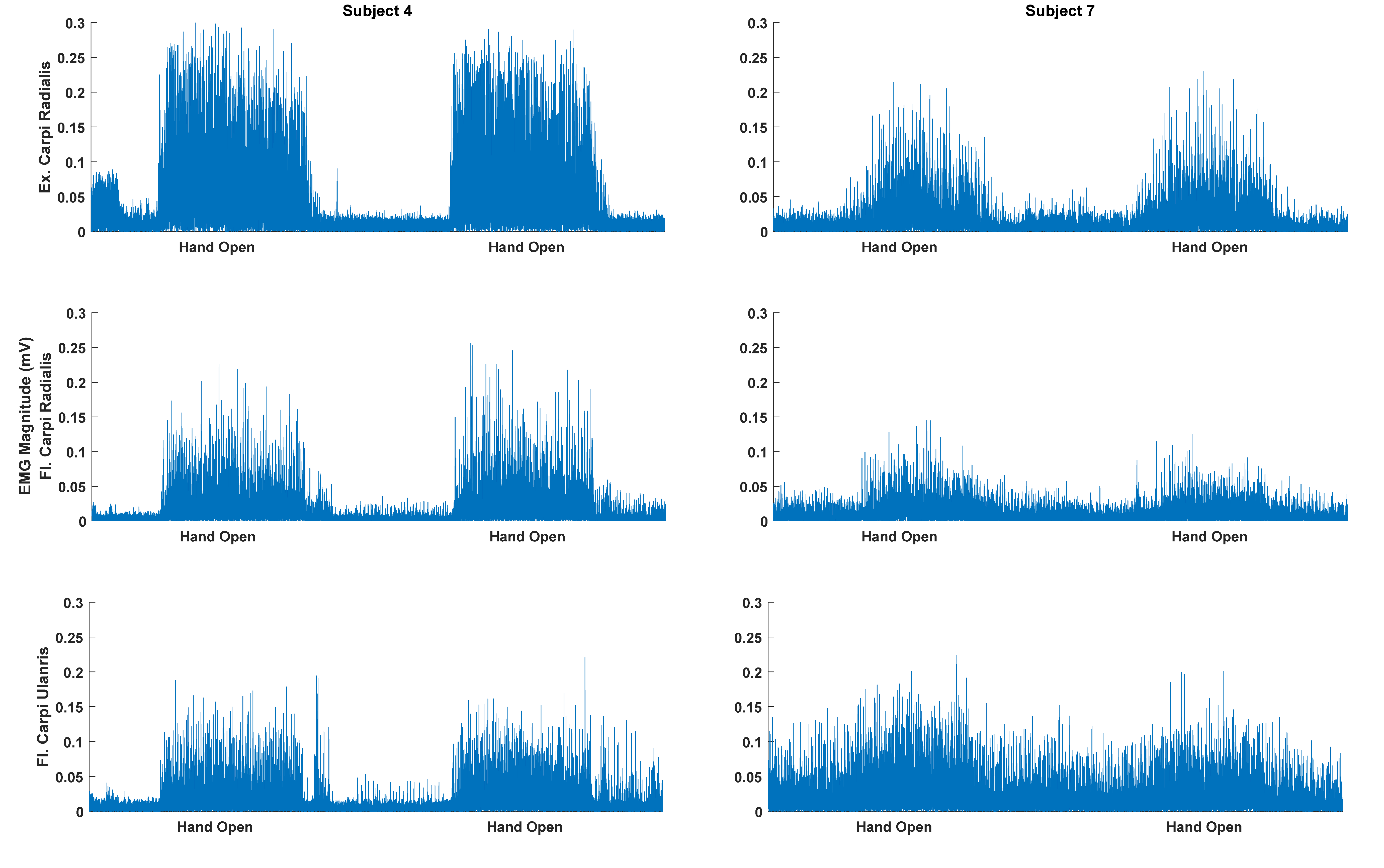
| Patient | Months Since Injury | Affected Side | Type of Injury | Fugl-Meyer [UL/LL/Total] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24 | Left | Ischemic | [55/22/77] |
| 2 | 17 | Right | Ischemic | [36/34/70] |
| 3 | 18 | Right | Ischemic | [23/28/51] |
| 4 | 32 | Left | Ischemic | [46/32/78] |
| 5 | 36 | Left | Ischemic | [26/18/44] |
| 6 | 5 | Right | Ischemic | [65/31/96] |
| 7 | 38 | Right | Ischemic | [17/22/39] |
| 8 | 2 | Left | Ischemic | [59/31/90] |
| 9 | 38 | Right | Ischemic | [55/30/85] |
| 10 | 6 | Left | Ischemic | [51/23/74] |
| 11 | 3 | Right | Ischemic | [56/24/80] |
| 12 | 5 | Left | Hemorrhagic | [44/20/64] |
| 13 | 66 | Right | Hemorrhagic | [28/18/46] |
| 14 | 19 | Left | Ischemic | [50/21/71] |
| 15 | 70 | Left | Hemorrhagic | [36/33/69] |
| Within-Session | Between-Session | |
|---|---|---|
| Linear discriminant analysis | 0.84 [0.54:0.95] | 0.88 [0.63:0.96] |
| Autoencoders | 0.88 [0.63:96] | 0.87 [0.62:0.96] |
| Convolutional neural network | 0.86 [0.58:0.95] | 0.69 [0.06:0.90] |
| HC | HO | WF | WE | Sup | Pro | Lat | Pin | Rest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | 72 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 2 |
| HO | 4 | 77 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| WF | 4 | 9 | 71 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| WE | 2 | 4 | 4 | 75 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| Sup | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 66 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| Pro | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 70 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| Lat | 9 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 8 | 56 | 9 | 6 |
| Pin | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 6 | 69 | 5 |
| Rest | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 92 |
| HC | HO | WF | WE | Sup | Pro | Lat | Pin | Rest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | 82 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 1 |
| HO | 3 | 83 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| WF | 2 | 7 | 80 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| WE | 1 | 4 | 4 | 79 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Sup | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 73 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| Pro | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 76 | 3 | 6 | 2 |
| Lat | 7 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 70 | 7 | 2 |
| Pin | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 77 | 3 |
| Rest | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 94 |
| HC | HO | WF | WE | Sup | Pro | Lat | Pin | Rest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | 70 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 13 | 3 | 1 |
| HO | 5 | 69 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| WF | 2 | 8 | 73 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| WE | 1 | 4 | 4 | 76 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 1 |
| Sup | 2 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 61 | 9 | 6 | 8 | 2 |
| Pro | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 68 | 4 | 7 | 2 |
| Lat | 13 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 55 | 10 | 4 |
| Pin | 2 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 68 | 2 |
| Rest | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 95 |
| HC | HO | WF | WE | Sup | Pro | Lat | Pin | Rest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | 41 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 13 | 6 | 18 | 5 | 1 |
| HO | 16 | 30 | 13 | 6 | 14 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 1 |
| WF | 16 | 9 | 39 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 2 |
| WE | 15 | 7 | 6 | 42 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 2 |
| Sup | 17 | 9 | 10 | 4 | 21 | 10 | 17 | 11 | 3 |
| Pro | 12 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 15 | 23 | 12 | 15 | 7 |
| Lat | 35 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 7 | 17 | 6 | 5 |
| Pin | 19 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 15 | 12 | 6 | 24 | 6 |
| Rest | 13 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 14 | 9 | 5 | 11 | 43 |
| HC | HO | WF | WE | Sup | Pro | Lat | Pin | Rest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | 29 | 9 | 16 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 22 | 6 | 1 |
| HO | 9 | 28 | 15 | 10 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 9 | 0 |
| WF | 16 | 9 | 40 | 8 | 13 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 1 |
| WE | 11 | 7 | 8 | 41 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 9 | 0 |
| Sup | 14 | 9 | 12 | 8 | 22 | 12 | 21 | 3 | 2 |
| Pro | 12 | 10 | 11 | 8 | 13 | 28 | 9 | 7 | 4 |
| Lat | 24 | 10 | 14 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 16 | 7 | 2 |
| Pin | 17 | 8 | 13 | 15 | 12 | 13 | 7 | 14 | 4 |
| Rest | 13 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 8 | 22 |
| HC | HO | WF | WE | Sup | Pro | Lat | Pin | Rest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | 30 | 8 | 19 | 5 | 14 | 4 | 14 | 7 | 1 |
| HO | 16 | 21 | 17 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 13 | 7 | 1 |
| WF | 8 | 11 | 49 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
| WE | 8 | 10 | 13 | 43 | 8 | 2 | 8 | 9 | 1 |
| Sup | 13 | 12 | 13 | 7 | 22 | 11 | 11 | 6 | 7 |
| Pro | 7 | 10 | 12 | 7 | 15 | 19 | 12 | 14 | 7 |
| Lat | 19 | 11 | 17 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 15 | 10 | 7 |
| Pin | 10 | 10 | 11 | 15 | 15 | 12 | 8 | 13 | 6 |
| Rest | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 12 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 66 |
| Correlation Coefficients | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Linear discriminant analysis | 0.29 | 0.30 |
| Autoencoders | 0.24 | 0.38 |
| Convolutional neural network | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| Classifier | Training (Seconds) | Test (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|
| Linear discriminant analysis (within-session) | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| Autoencoders (within-session) | 12.16 | 0.015 |
| Convolutional neural network (within-session) | 47.68 | 0.22 |
| Linear discriminant analysis (between-session) | 0.018 | 0.018 |
| Autoencoders (between-session) | 13.22 | 0.016 |
| Convolutional neural network (between-session) | 58.77 | 0.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jochumsen, M.; Niazi, I.K.; Zia ur Rehman, M.; Amjad, I.; Shafique, M.; Gilani, S.O.; Waris, A. Decoding Attempted Hand Movements in Stroke Patients Using Surface Electromyography. Sensors 2020, 20, 6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236763
Jochumsen M, Niazi IK, Zia ur Rehman M, Amjad I, Shafique M, Gilani SO, Waris A. Decoding Attempted Hand Movements in Stroke Patients Using Surface Electromyography. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236763
Chicago/Turabian StyleJochumsen, Mads, Imran Khan Niazi, Muhammad Zia ur Rehman, Imran Amjad, Muhammad Shafique, Syed Omer Gilani, and Asim Waris. 2020. "Decoding Attempted Hand Movements in Stroke Patients Using Surface Electromyography" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236763
APA StyleJochumsen, M., Niazi, I. K., Zia ur Rehman, M., Amjad, I., Shafique, M., Gilani, S. O., & Waris, A. (2020). Decoding Attempted Hand Movements in Stroke Patients Using Surface Electromyography. Sensors, 20(23), 6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236763







