Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Building Blocks of Smart Textile Systems
2. Search Method
3. Conductive Materials for Textiles
3.1. Conductive Inks
3.2. Carbon-Based Conductive Materials
3.3. Intrinsically Conductive Polymers
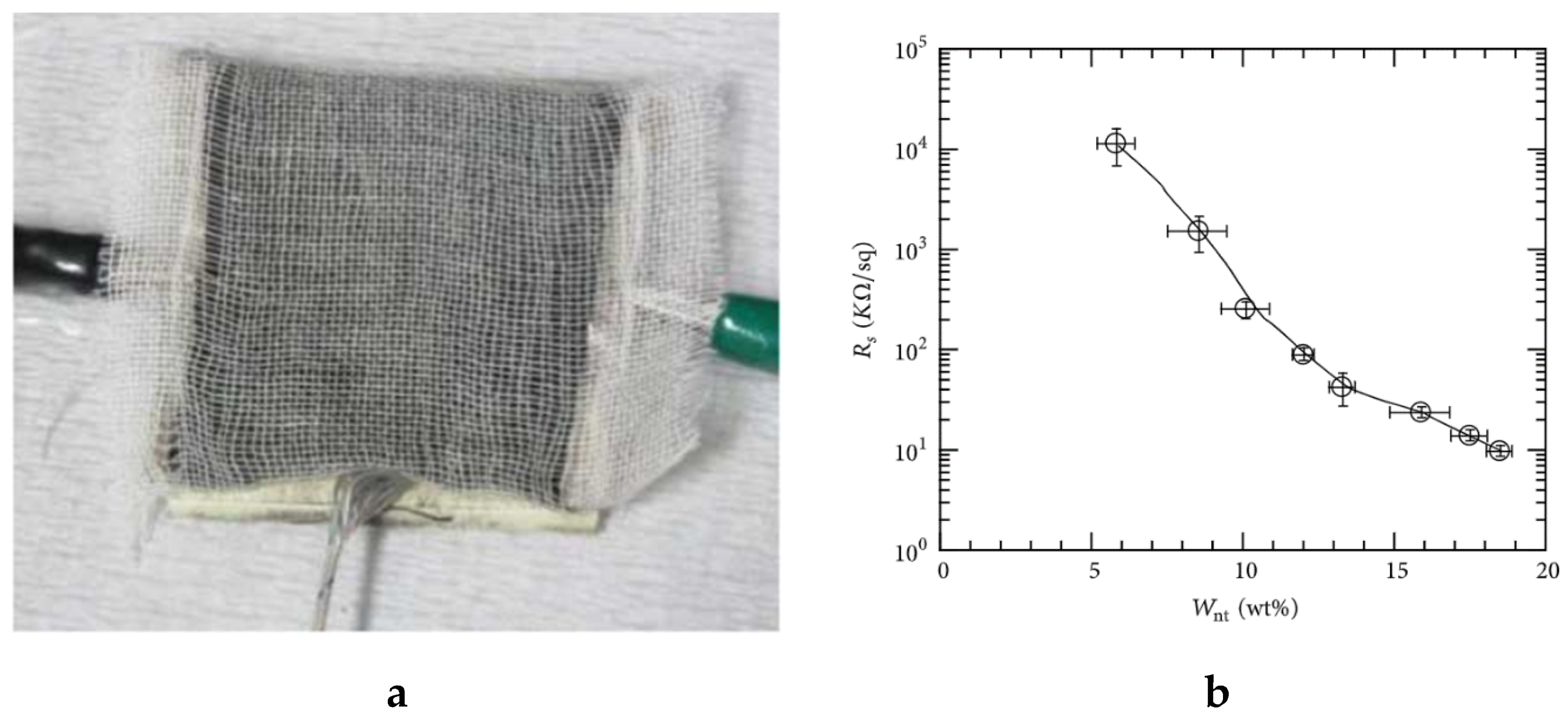
3.4. Conductive Polymer Composites
4. Integration Techniques of Conductive Materials on/into a Textile Structure
4.1. Integration of Conductive Compounds
4.1.1. Fiber Spinning
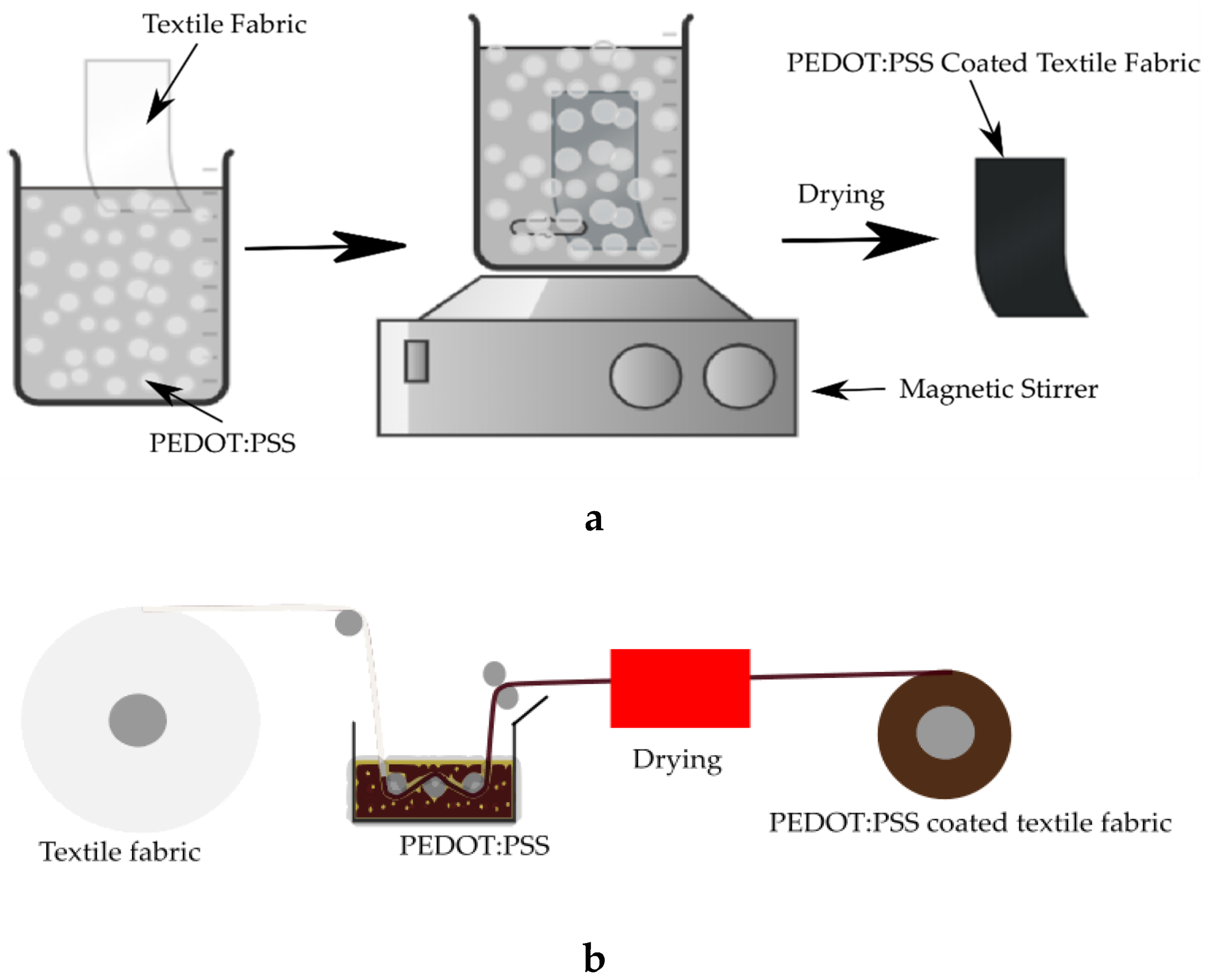
4.1.2. Dip-Coating
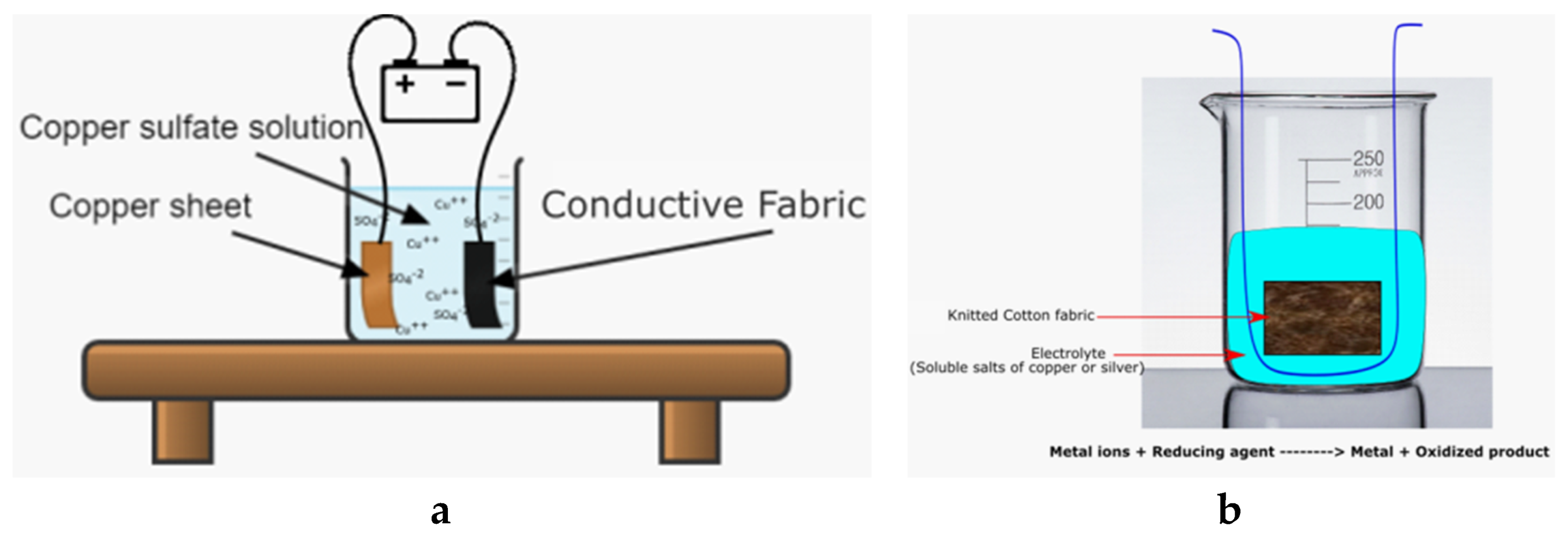
4.1.3. Plating
4.1.4. Screen Printing
4.1.5. Spray-Coating
4.1.6. Transfer Printing
4.1.7. Inkjet Printing
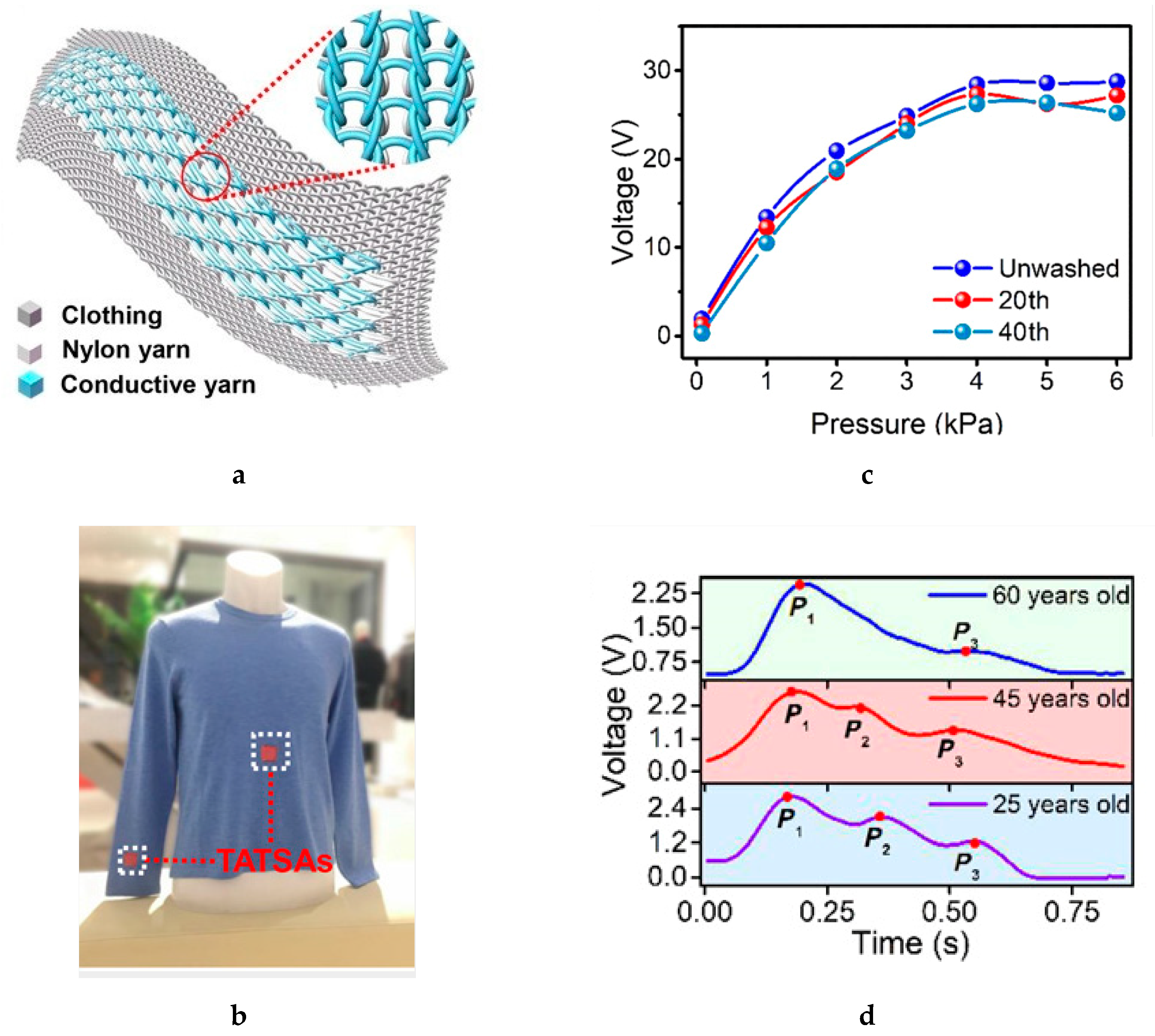
4.2. Integration of Conductive Yarn and Conductive Filament Fiber
4.2.1. Weaving
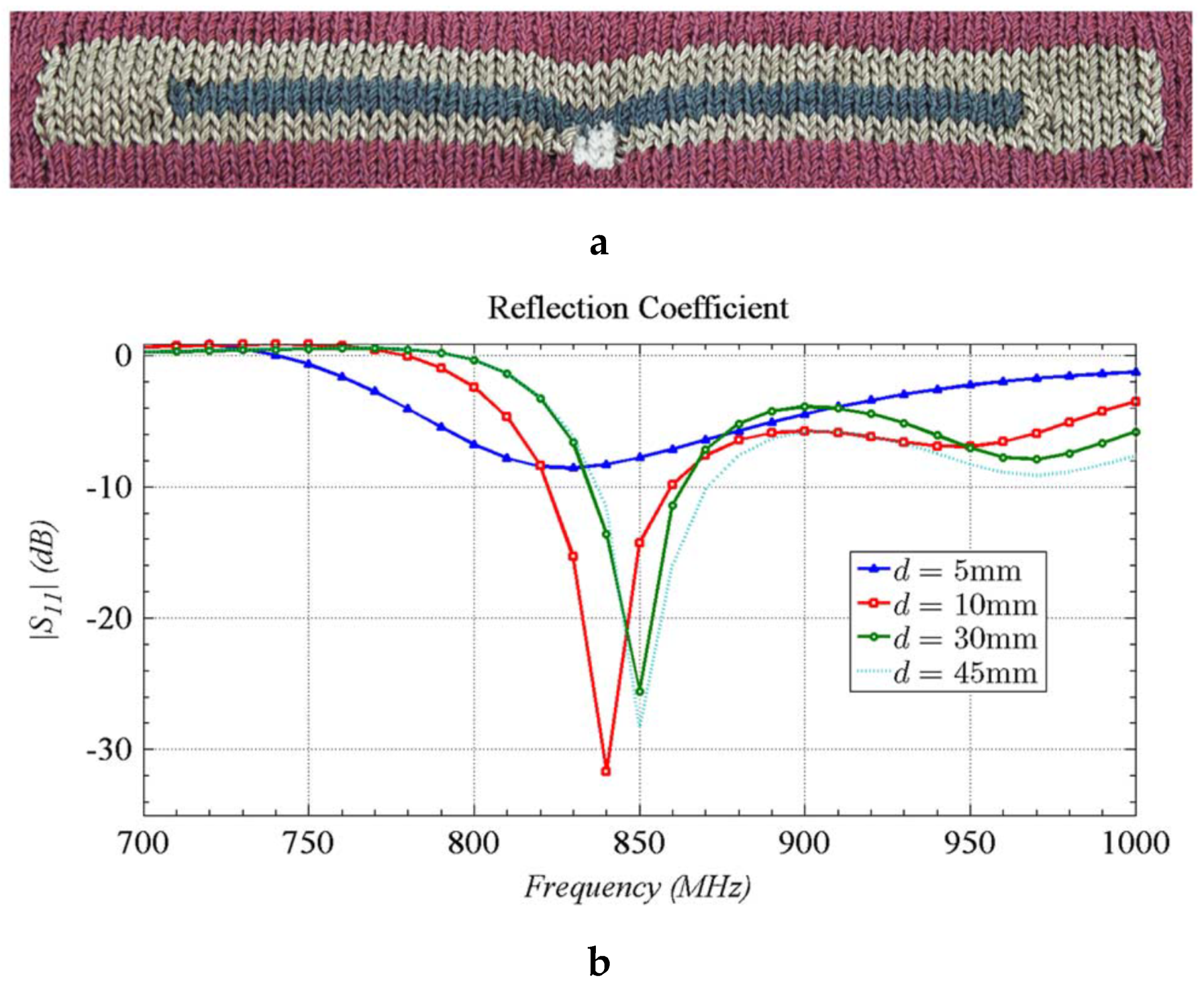
4.2.2. Knitting
4.2.3. Embroidery
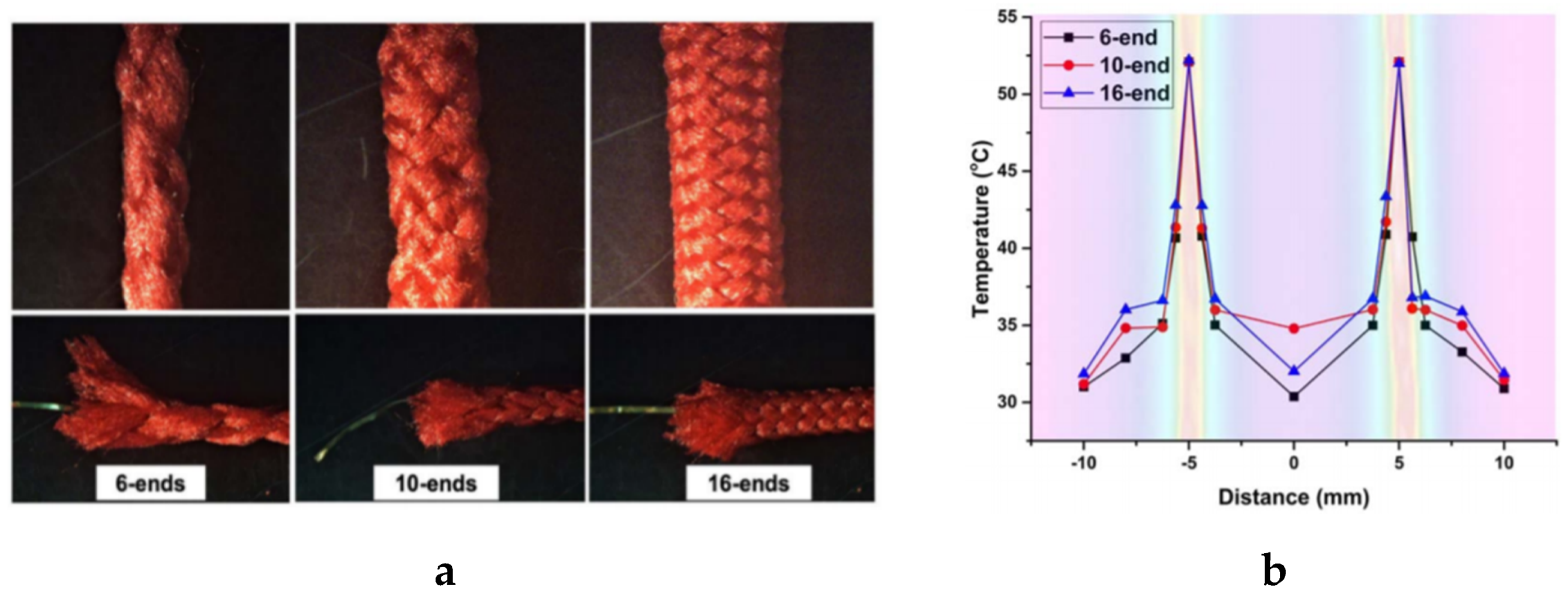
4.2.4. Braiding
4.3. Integration of Conductive Sheets: Laminating
5. Outlook and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tseghai, G.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. The Status of Textile-Based Dry EEG Electrodes. Autex Res. J. 2020. Ahead of Print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CENTEXBEL VKC. Smart Textiles. 2019. Available online: https://www.centexbel.be/en/lexicon/smart-textiles (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Steele, J.R.; Gho, S.A.; Campbell, T.E.; Richards, C.J.; Beirne, S.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G. The Bionic Bra: Using electromaterials to sense and modify breast support to enhance active living. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2018, 5, 205566831877590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dadi, H.H. Literature over View of Smart Textiles; Boras University: Boras, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X. Smart Fibres, Fabrics and Clothing, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedin, S.; Razal, J.M.; Innis, P.C.; Jeiranikhameneh, A.; Beirne, S.; Wallace, G.G. Knitted Strain Sensor Textiles of Highly Conductive All-Polymeric Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21150–21158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jug, L.; Meng, E.; Lee, C.; Jug, L.; Meng, E. High strain biocompatible polydimethylsiloxane-based conductive graphene and multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite strain sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 183511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyedin, M.Z.; Razal, J.M.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. Strain-responsive polyurethane/PEDOT:PSS elastomeric composite fibers with high electrical conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahid, M.; Papadopoulou, E.L.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Strain-responsive mercerized conductive cotton fabrics based on PEDOT:PSS/grapheme. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Zein, A.; Hupp, C.; Cochrane, C. Development of a Flexible Strain Sensor Based on PEDOT: PSS for Thin Film Structures. Sensors 2017, 17, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pani, D.; Dess, A.; Saenz-cogollo, J.F.; Barabino, G.; Fraboni, B.; Bonfiglio, A. Fully Textile, PEDOT:PSS Based Electrodes for Wearable ECG Monitoring Systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Cho, G. PU nanoweb-based textile electrode treated with single-walled carbon nanotube/silver nanowire and its application to ECG monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Tao, X.; Koncar, V.; Coulon, D.; Tarlet, J. Ambulatory Evaluation of ECG Signals Obtained Using Washable Textile-Based Electrodes Made with. Sensors 2019, 19, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Achilli, A.; Bonfiglio, A.; Pani, D. Design and characterization of screen-printed textile electrodes for ECG monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 8, 4097–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Stylios, G.K. A hybrid textile electrode for electrocardiogram (ECG) measurement and motion tracking. Materials 2018, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, G.M.; Cao, F.; Torah, R.; Yang, K.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. A smart textile based facial EMG and EOG computer interface. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 14, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.O.; Kang, T.; Park, J.; Choi, Y. Knit Band Sensor for Myoelectric Control of Surface EMG-Based Prosthetic Hand. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8578–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niijima, A.; Isezaki, T.; Aoki, R.; Watanabe, T. hitoeCap: Wearable EMG Sensor for Monitoring Masticatory Muscles with PEDOT-PSS Textile Electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Maui, HI, USA, 11–15 September 2017; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Golparvar, A.J.; Yapici, M.K. Electrooculography by Wearable Graphene Textiles. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8971–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Liao, L.-D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, I.-J.; Lin, B.-S.; Chang, J.-Y. Novel Dry Polymer Foam Electrodes for Long-Term EEG Measurement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahi, A.; Rai, P.; Oh, S.; Ramasamy, M.; Harbaugh, R.E.; Varadan, V.K. Neural activity based biofeedback therapy for Autism spectrum disorder through wearable wireless textile EEG monitoring system. Nanosens. Biosens. Info-Tech Sens. Syst. 2014, 9060, 90600D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Jian, J.; Tu, T.; Yang, Z.; Ling, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Wearable humidity sensor based on porous graphene network for respiration monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weremczuk, J.; Tarapata, G.; Jachowicz, R. Humidity Sensor Printed on Textile with Use of Ink-Jet Technology. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, M.A.B.; Vryonides, P.; Nikolaou, S. Humidity sensor devices using PEDOT:PSS. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–25 July 2015; pp. 1366–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.-G.; Park, J.-K.; Yun, G.-H.; Choi, H.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Yook, J.-G. A real-time humidity sensor based on a microwave oscillator with conducting polymer PEDOT:PSS film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslik, J.; Andersson, H.; Forsberg, V.; Engholm, M.; Zhang, R.; Olin, H. PEDOT:PSS temperature sensor ink-jet printed on paper substrate. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, C12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zang, Y.; Huang, D.; Di, C.-A.; Zhu, D. Flexible and self-powered temperature–pressure dual-parameter sensors using microstructure-frame-supported organic thermoelectric materials. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.F.; Lee, K.-F.; Lee, M.-Y. Development of a flexible PDMS capacitive pressure sensor for plantar pressure measurement. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Nigusse, A.B.; Langenhove, L.V. Development and evaluation of resistive pressure sensors from electro-conductive textile fabric. In Proceedings of the Second International Forum on Textiles for Graduate Students (IFTGS) 2018, Tianjin, China, 30 September 2018; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Macharia, D.K.; Ahmed, S.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Mwasiagi, J.I.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, M. UV/NIR-Light-Triggered Rapid and Reversible Color Switching for Rewritable Smart Fabrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 13370–13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarini, M.; Vasile, F.; Natali, D. Inkjet printed hybrid light sensors based on titanium dioxide and Inkjet printed hybrid light sensors based on titanium dioxide and PEDOT:PSS. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Khasim, S.; Ahmed, F.; Dhananjaya, K.N. Fabrication of gas sensor device using poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly (styrenesulfonate)-doped reduced graphene oxide organic thin films for detection of ammonia gas at room temperature. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkeldei, T.; Zysset, C.; Münzenrieder, N.; Tröster, G. An electronic nose on flexible substrates integrated into a smart textile. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Lin, T.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, D.; Cui, Z. Double layer printed high performance OLED based on PEDOT:PSS/Ir(bt)2acac:CDBP. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 115112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, G.; Park, J. Improved Intrapixel Thickness Uniformity of Slot-Coated PEDOT:PSS Films for OLEDs via Dilution and Predrying Treatments. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 4506–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, J.-L.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Wei, B.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.-H.; Yang, Y. Highly efficient red fluorescent organic light-emitting diodes by sorbitol-doped PEDOT:PSS. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 225302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X. Handbook of Smart Textiles, 1st ed.; Springer Science+Business Media: Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Koncar, V. Smart Textiles and Their Applications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- van Langenhove, L. Advances in Smart Medical Textiles: Treatments and Health Monitoring; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L. Intelligent Macromolecules for Smart Devices: From Materials Synthesis to Device Applications; Springer: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein, T. Multidisciplinary Know-How for Smart-Textiles Developers, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.; Park, T.H.; Yoon, H.; Hur, J.; Park, J.-J. Textile Speaker Using Polyvinylidene Fluoride/ZnO Nanopillar on Au Textile for Enhancing the Sound Pressure Level. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.; Luthy, K.; Muth, J.; Mattos, L.S.; Braly, J.; Seyam, A.-F.M.; Ghosh, T.; Dhawan, A.; Natarajan, K. Developing portable acoustic arrays on a large-scale e-textile substrate. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2004, 16, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthy, K.A.; Mattos, L.S.; Braly, J.C.; Grant, E.; Muth, J.F.; Dhawan, A.; Natarajan, K.; Ghosh, T.; Seyam, A. Initial Development of a Portable Acoustic Array on a Large-Scale E-Textile Substrate. MRS Proc. 2002, 736, D3.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briedis, U.; Valisevskis, A.; Grecka, M. Development of a Smart Garment Prototype with Enuresis Alarm Using an Embroidery-machine-based Technique for the Integration of Electronic Components. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 104, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, A.O.; Torah, R.N.; Yang, K.; Tudor, J.; Beeby, S.P. Durability of screen printed electrical interconnections on woven textiles. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 65th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Chen, T. Nano Energy Beyond energy harvesting-multi-functional triboelectric nanosensors on a textile. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Darabi, S.; Hultmark, S.; Ryan, J.D.; Andersson, B.; Ström, A.; Müller, C. Roll-to-Roll Dyed Conducting Silk Yarns: A Versatile Material for E-Textile Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OpenBCI. Ultracortex ‘Mark IV’ EEG Headset. 2019. Available online: https://openbci.com/ (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Hertleer, C.; Rogier, H.; Member, S.; Vallozzi, L.; van Langenhove, L. A Textile Antenna for Off-Body Communication Integrated Into Protective Clothing for Firefighters. IEEE Trans. Propag. 2009, 57, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannadhasan, S.; Shagar, A.C. Design and Analysis of U-Shaped Microstrip Patch Antenna. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Information, Communication and Bio-Informatics (AEEICB17) Design, Chennai, India, 27–28 February 2017; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Roshni, S.B.; Jayakrishnan, M.P.; Mohanan, P.; Surendran, K.P. Design and fabrication of an E-shaped wearable textile antenna on PVB-coated hydrophobic polyester fabric. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Fumeaux, C.; Chivers, B.; Shepherd, R. A 5.8-GHz Flexible Microstrip-Fed Slot Antenna Realized in PEDOT:PSS Conductive Polymer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; Volume 2015, pp. 1317–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Sun, T.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W. Synthesis of freestanding PEDOT:PSS/PVA@Ag NPs nanofiber film for high-performance flexible thermoelectric generator. Polymer 2019, 167, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Arumugam, S.; Tudor, J.; Beeby, S. Screen Printed Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs) on Woven Polyester Cotton Fabric for Wearable Energy Harvesting Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 13753–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Lim, S.; Sim, J.Y.; Jeon, J.S.; No, K.; Park, S.; Hong, S. Nano Energy Intrinsically stretchable multi-functional fiber with energy harvesting and strain sensing capability. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuri, A.; Colella, S.; Listorti, A.; Rizzo, A.; Mele, C.; Esposito, C. GO/glucose/PEDOT:PSS ternary nanocomposites for fl exible supercapacitors. Compos. Part B 2018, 148, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Facile one-step hydrothermal synthesis of PEDOT:PSS/MnO2 nanorod hybrids for high-rate supercapacitor electrode materials. Ionics 2018, 25, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.D.; Smoukov, S.K.; Wang, T. Multidimensional performance optimization of conducting polymer-based supercapacitor electrodes. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1857–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuramdhani, I.; Malengier, B.; Deferme, W.; de Mey, G.; van Langenhove, L. Charge-Discharge Characteristics of Textile Energy Storage Devices Having Different PEDOT:PSS Ratios and Conductive Yarns Configuration. Polymers 2019, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahariar, H.; Kim, I.; Soewardiman, H.; Jur, J.S. Inkjet Printing of Reactive Silver Ink on Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6208–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.L.; Saleh, S.M.; Yudin, M.B.M.; Harun, F.K.C.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Tuantranont, A.; Wicaksono, D.H. Graphene Ink-Coated Cotton Fabric-Based Flexible Electrode for Electrocardiography. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Conference on Instrumentation, Communications, Information Technology, and Biomedical Engineering (ICICI-BME), Bandung, Indonesia, 6–7 November 2017; pp. 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangakameshwaran, N.; Santhoskumar, A.U. Cotton Fabric Dipped in Carbon Nano Tube Ink for Smart Textile Applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2014, 63, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.-C.; Ku, H.-J.; Cho, C.-J.; Chen, W.-C.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Rwei, S.-P.; Borsali, R.; Kuo, C.-C. An intrinsically stretchable and ultrasensitive nanofiber-based resistive pressure sensor for wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tian, M.; Qu, L.; Zhu, S.; Han, G. Multifunctional cotton fabrics with graphene/polyurethane coatings with far-infrared emission, electrical conductivity, and ultraviolet-blocking properties. Carbon 2015, 95, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, B.S.; Chen, W.; Doty, C.; Xu, C.; Kotov, N.A. Smart Electronic Yarns and Wearable Fabrics for Human Biomonitoring made by Carbon Nanotube Coating with Polyelectrolytes. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, R.; Khair, N.; Ahmed, D.M.; Shahariar, H. Fabrication of low cost and scalable carbon-based conductive ink for E-textile applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugetsu, B.; Sano, E.; Yu, H.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, T. Graphene oxide as dyestuffs for the creation of electrically conductive fabrics. Carbon 2010, 48, 3340–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulan, L.; Zhi, L.; Lan, C.; Sihao, C.; Dayang, W.; Fangyin, D. Reduced Graphene Oxide Coated Silk Fabrics with Conductive Property for Wearable Electronic Textiles Application. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, S.J.P.; Yang, K.; Braveenth, R.; Raagulan, K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, C.-M.; Jung, M.J.; Chai, K.Y. MWCNT Coated Free-Standing Carbon Fiber Fabric for Enhanced Performance in EMI Shielding with a Higher Absolute EMI SE. Materials 2017, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lou, C.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Liang, T.; Wei, Z.; Run, M.; Yan, X.; Liu, X. Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.J.; Mieno, T. Conductive Cotton Textile from Safely Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Qiang, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; You, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ye, C. Multi-functional and Highly Conductive Textiles with Ultra-high Durability through ‘Green’ Fabrication Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 406, 127140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Tabor, J.; Ghosh, T.K. Electrically Conductive Coatings for Fiber-Based E-Textiles. Fibers 2019, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, S.; Chakrabarty, T.; Singh, A.K.; Shahi, V.K. Polymer thin films embedded with metal nanoparticles for electrochemical biosensors applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A. Polypyrrole Based Electro-Conductive Cotton Yarn. J. Text. Sci. Eng. 2014, 4, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Pani, D.; Bonfiglio, A. Characterization of Screen-Printed Textile Electrodes Based on Conductive Polymer for ECG Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology Conference, Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.N.A.; Mohanta, K. Preparation of Highly Conductive Yarns by an Optimized Impregnation Process. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 47, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón, R.; Pérez, J.J.; Andrade-Caicedo, H. Electrical performance of PEDOT:PSS-based textile electrodes for wearable ECG monitoring: A comparative study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kellomäki, T.; Virkki, J.; Merilampi, S.; Ukkonen, L. Towards Washable Wearable Antennas: A Comparison of Coating Materials for Screen-Printed Textile-Based UHF RFID Tags. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Xu, L.; Yan, D.-X.; Li, Z.-M. Conductive polymer composites with segregated structures. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1908–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A. Textile/Polypyrrole Composites for Sensory Applications. J. Compos. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; van Langenhove, L. Development of a Flex and Stretchy Conductive Cotton Fabric Via Flat Screen Printing of PEDOT:PSS/PDMS Conductive Polymer Composite. Sensors 2020, 20, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feller, J.F.; Grohens, Y. Electrical response of Poly(styrene)/carbon black conductive polymer composites (CPC) to methanol, toluene, chloroform and styrene vapors as a function of filler nature and matrix tacticity. Synth. Met. 2005, 154, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadim, M.F.; Imani, A.; Farzi, G. Synthesis of PPy–silver nanocomposites via in situ oxidative polymerization. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Bac, L.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, J.-C. Synthesis and Characterization of Conducting Polyaniline-Copper Composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 7728–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loryuenyong, V.; Khadthiphong, A.; Phinkratok, J.; Watwittayakul, J.; Supawattanakul, W.; Buasri, A. The fabrication of graphene-polypyrrole composite for application with dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, H.-H.; Wang, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-X. Thermoelectric behavior of PEDOT:PSS/CNT/graphene composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2018, 38, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafti, A.; Manero, R.B.R.; Borg, A.M.; Althoefer, K.; Howard, M.J. Embroidered Electromyography: A Systematic Design Guide. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 25, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, X.; Tennant, A.; Langley, R.J.; Hurley, W.; Dias, T. A knitted textile waveguide. In Proceedings of the 2014 Loughborough Antennas and Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 10–11 November 2014; Volume 1, pp. 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkonen, J.; Pouta, E. Flexible Wire-Component for Weaving Electronic Textiles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 66th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 May–3 June 2016; pp. 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Xu, N.; Kan, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Wet-Spinning Assembly of Continuous, Highly Stable Hyaluronic/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Microfibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pragya, A.; Singh, H.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, H.; Shankar, P. Designing and investigation of braided-cum-woven structure for wearable heating textile. Eng. Res. Express 2020, 2, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhu, L.; Xue, J.; Hao, L.; Jin, L.; He, Y.; Cheng, B. A Novel Two-Step Method for Fabricating Silver Plating Cotton Fabrics. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baurley, S. Interactive and experiential design in smart textile products and applications. Pres. Ubiquit. Comput. 2004, 8, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.; Choi, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Yeo, S.Y. Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black. Polymers 2020, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, J.C. Electrically Conductive Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid/Polyacrylonitrile Composite Fibers Prepared by Wet Spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzuan, N.A.M.; Sulong, A.B.; Somalu, M.R. Extrusion Process of Polypropylene Composites Reinforced Milled Carbon Fibre for Conductive Polymer Composite Application. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences: 4th Engineering Science and Technology International Conference (ESTIC 2018), Padang, West Sumatra, Indonesia, 28–29 August 2018; Volume 248, p. 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerfeldt, M.; Nilsson, E.; Gillgard, P.; Walkenström, P. Textile piezoelectric sensors—Melt spun bi-component poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibres with conductive cores and poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene)-poly(styrene sulfonate) coating as the outer electrode. Fash. Text. 2014, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tuo, X. Preparation of polypyrrole coated cotton conductive fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Coulon, D.; Koncar, V. Washable and Reliable Textile Electrodes Embedded into Underwear Fabric for Electrocardiography (ECG) Monitoring. Materials 2018, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Fante, K.A.; van Langenhove, L. Knitted Cotton Fabric Strain Sensor by In-situ Polymerization of Pyrrole. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Textiles & Mass Customization, Marrakech, Morocco, 13–15 November 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 827, p. 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mule, A.R.; Dudem, B.; Patnam, H.; Graham, S.A.; Yu, J.S. Wearable Single-Electrode-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Conductive Polymer-Coated Textiles for Self-Power Electronics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16450–16458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maqdasi, Z.; Hajlane, A.; Renbi, A.; Ouarga, A.; Chouhan, S.S.; Joffe, R. Conductive Regenerated Cellulose Fibers by Electroless Plating. Fibers 2019, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardianto, H.; Mey, G.D.; Malengier, B.; Hertleer, C.; Langenhove, V. Characterization of Carbon-Nickel thermocouples integrated in textile fabrics. In Proceedings of the AUTEX2019: 19th World Textile Conference on Textiles at the Crossroads, Ghent, Belgium, 11–15 June 2019; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.M.; Thilagavathi, G. Design and Development of Textile Electrodes for EEG Measurement using Copper Plated Polyester Fabrics. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2014, 8, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. A wearable, anti-bacterial strain sensor prepared by silver plated cotton/spandex blended fabric for human motion monitoring. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, W.; Wright, T.; Caven, B.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Flexible Textile Strain Sensor Based on Copper-Coated Lyocell Type Cellulose Fabric. Polymers 2019, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willfahrt, A. Screen Printing Technology for Energy Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping Univeristy, Linköping, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kazani, I. Study of Screen-Printed Electroconductive Textile Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nigusse, A.B.; Malengier, B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Tseghai, G.B.; van Langenhove, L. Development of Washable Silver Printed Textile Electrodes for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzetuska, E.; Puchalski, M.; Krucińska, I. Chemically Driven Printed Textile Sensors Based on Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 16816–16828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Etana, B.B.; van Langenhove, L. PEDOT:PSS/PDMS-coated cotton fabric for ECG electrode. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 16–19 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauraya, A.; Whittow, W.G.; Vardaxoglou, J.C.; Li, Y.; Torah, R.; Yang, K.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Inkjet printed dipole antennas on textiles for wearable communications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Arumugam, S.; Krishnan, C.; Charlton, M.D.B.; Beeby, S.P. Encapsulated Textile Organic Solar Cells Fabricated by Spray Coating. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Li, Y.; Senthilarasu, S.; Torah, R.; Kanibolotsky, A.L.; Inigo, A.R.; Skabara, P.J.; Beeby, S.P. Fully spray-coated organic solar cells on woven polyester cotton fabric for wearable energy harvesting applications. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 5561–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maheshwari, N.; Abd-Ellah, M.; Goldthorpe, I.A. Transfer printing of silver nanowire conductive ink for e-textile applications. Flex. Print. Electron. 2019, 4, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, B.; Son, Y.K.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, I.-Y. A flexible textile wristwatch using Transfer Printed Textile Circuit technique. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–15 January 2012; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauraya, A.; Seager, R.; Whittow, W.; Zhang, S.; Vardaxoglou, Y. Embroidered Frequency Selective Surfaces on textiles for wearable applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 11–12 November 2013; pp. 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-naiemy, Y.; Elwi, T.A.; Khaleel, H.R.; Al-rizzo, H. A Systematic Approach for the Design, Fabrication, and Testing of Microstrip Antennas Using Inkjet Printing Technology A Systematic Approach for the Design, Fabrication, and Testing of Microstrip Antennas Using Inkjet Printing Technology. ISRN Commun. Netw. 2012, 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidmar, T.; Topič, M.; Dzik, P.; Krašovec, U.O. Inkjet printing of sol-gel derived tungsten oxide inks. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 125, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Brent, J.R.; Ding, H.; Yang, J.; Lewis, D.J.; O’Brien, P.; Derby, B. Fully printed high performance humidity sensors based on two-dimensional materials. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5599–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidik, H.; Dupont, D.; Bedek, G. Development of a radiative heat fluxmeter with a textile substrate. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2018, 271, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, D.; Choi, A.Y.; Kim, Y.T. Flexible single-strand fiber-based woven-structured triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered electronics. APL Mater. 2018, 6, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patron, D.; Mongan, W.; Kurzweg, T.P.; Fontecchio, A.; Dion, G.; Anday, E.K.; Dandekar, K.R. On the Use of Knitted Antennas and Inductively Coupled RFID Tags for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, A.; Hurley, W.; Dias, T. Knitted, textile, high impedance surface with integrated conducting vias. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; He, Q.; Meng, K.; Tan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Machine-knitted washable sensor array textile for precise epidermal physiological signal monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moradi, B.; Fernández-García, R.; Gil, I. E-textile embroidered metamaterial transmission line for signal propagation control. Materials 2018, 11, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Estrada, M.; Moradi, B.; Fernández-Garcia, R.; Gil, I. Impact of manufacturing variability and washing on embroidery textile sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alharbi, S.; Chaudhari, S.; Inshaar, A.; Shah, H.; Zou, C.; Harne, R.L.; Kiourti, A. E-Textile Origami Dipole Antennas with Graded Embroidery for Adaptive RF Performance. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadzade, B.; Hashmi, R.M.; Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Gharaei, R.; Rehman, S.U.; Abbasi, Q.H. Recent Advances in Fabrication Methods for Flexible Antennas in Wearable Devices: State of the Art. Sensors 2019, 19, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The mechanics of the braiding process. In Braiding Technology for Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 177–209.
- Vanveerdeghem, P.; van Torre, P.; Stevens, C.; Knockaert, J.; Rogier, H. Synchronous Wearable Wireless Body Sensor Network Composed of Autonomous Textile Nodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 18583–18610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michael, S. Method for Preparing Fabric Laminate. U.S. Patent No. 3383263, 14 May 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; McCutcheon, J.W. Tapes and Articles Therefrom. U.S. Patent No. 2016/0333232 A1, 19 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Overcoming the Efficiency Barrier of Textile Antennas: A Transmission Lines Approach. Proceedings 2019, 32, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; van Langenhove, L. PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Textiles and Their Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, E.; Rahiminejad, S.; Enoksson, P. Evaluation of 3D printed materials used to print WR10 horn antennas. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 757, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, T.; Williams, J. 3D Printing; Chery Lake Publishing: Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bellacicca, A.; Santaniello, T.; Milani, P. Embedding electronics in 3D printed structures by combining fused filament fabrication and supersonic cluster beam deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Chen, K.; Dunn, C.K.; Wu, J.; Li, V.C.F.; Qi, H.J. 3D Printing of Highly Stretchable, Shape-Memory, and Self-Healing Elastomer toward Novel 4D Printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7381–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, S.; Goh, G.L.; Yap, Y.L.; Yu, H.; Yeong, W.Y.; Tran, T. Development of bendable strain sensor with embedded microchannels using 3D printing. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2017, 263, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muth, J.T.; Vogt, D.M.; Truby, R.L.; Mengüç, Y.; Kolesky, D.B.; Wood, R.J.; Lewis, J.A. Embedded 3D Printing of Strain Sensors within Highly Stretchable Elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6307–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayate, A.; Jain, P.K. A Review on 4D Printing Material Composites and Their Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20474–20484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Van Langenhove, L. Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors 2020, 20, 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910
Tseghai GB, Malengier B, Fante KA, Nigusse AB, Van Langenhove L. Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseghai, Granch Berhe, Benny Malengier, Kinde Anlay Fante, Abreha Bayrau Nigusse, and Lieva Van Langenhove. 2020. "Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910
APA StyleTseghai, G. B., Malengier, B., Fante, K. A., Nigusse, A. B., & Van Langenhove, L. (2020). Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors, 20(23), 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910