Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
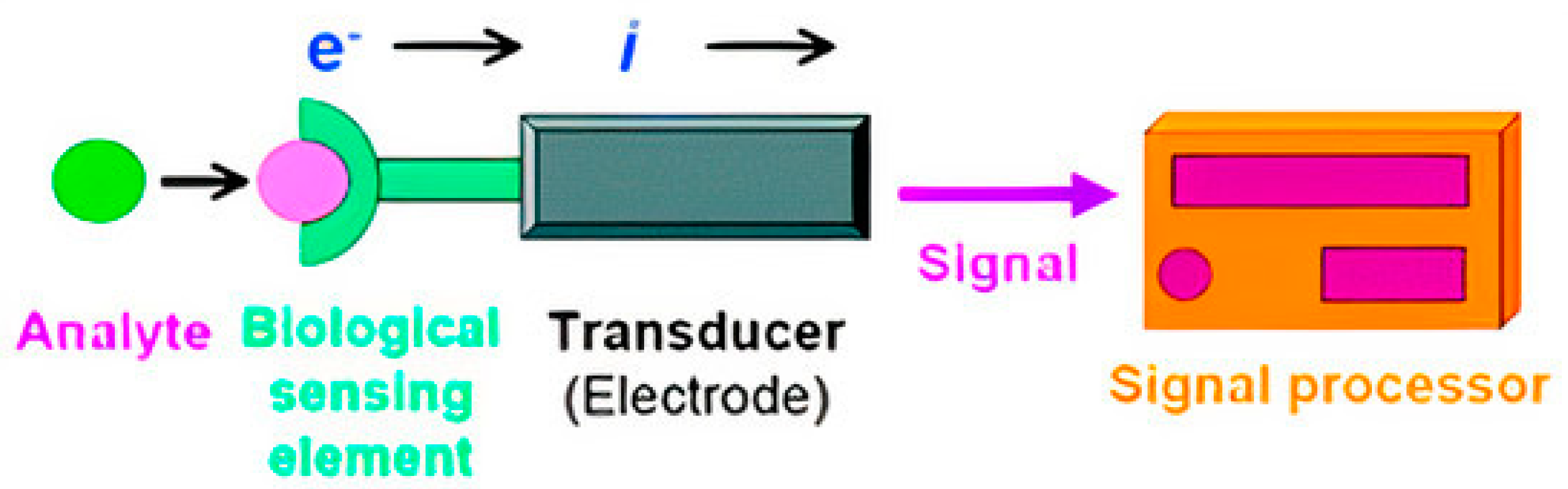
2. Biosensors
2.1. Operating Principles
2.2. Types of Biosensors
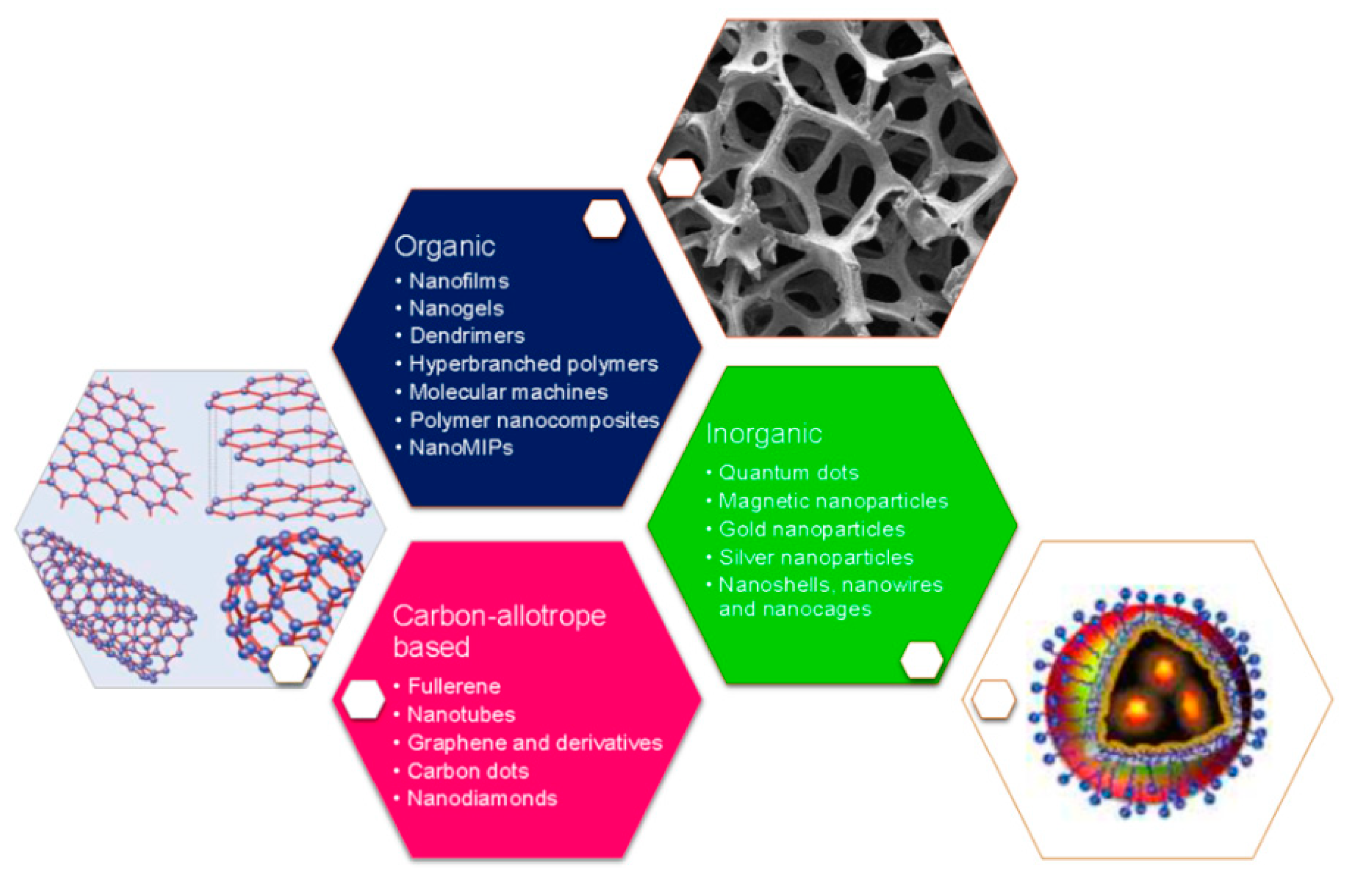
3. Biosensors Nanotechnological Features for Bacterial and Viral Detection
3.1. Nanoparticles
3.2. Graphene Quantum Dots
3.3. Electrospun Nanofibers
4. Bacterial and Viral Pathogens Detected through Biosensors and Nano-Biosensors
4.1. Bacterial Pathogen Detection
4.2. Viral Pathogen Detection
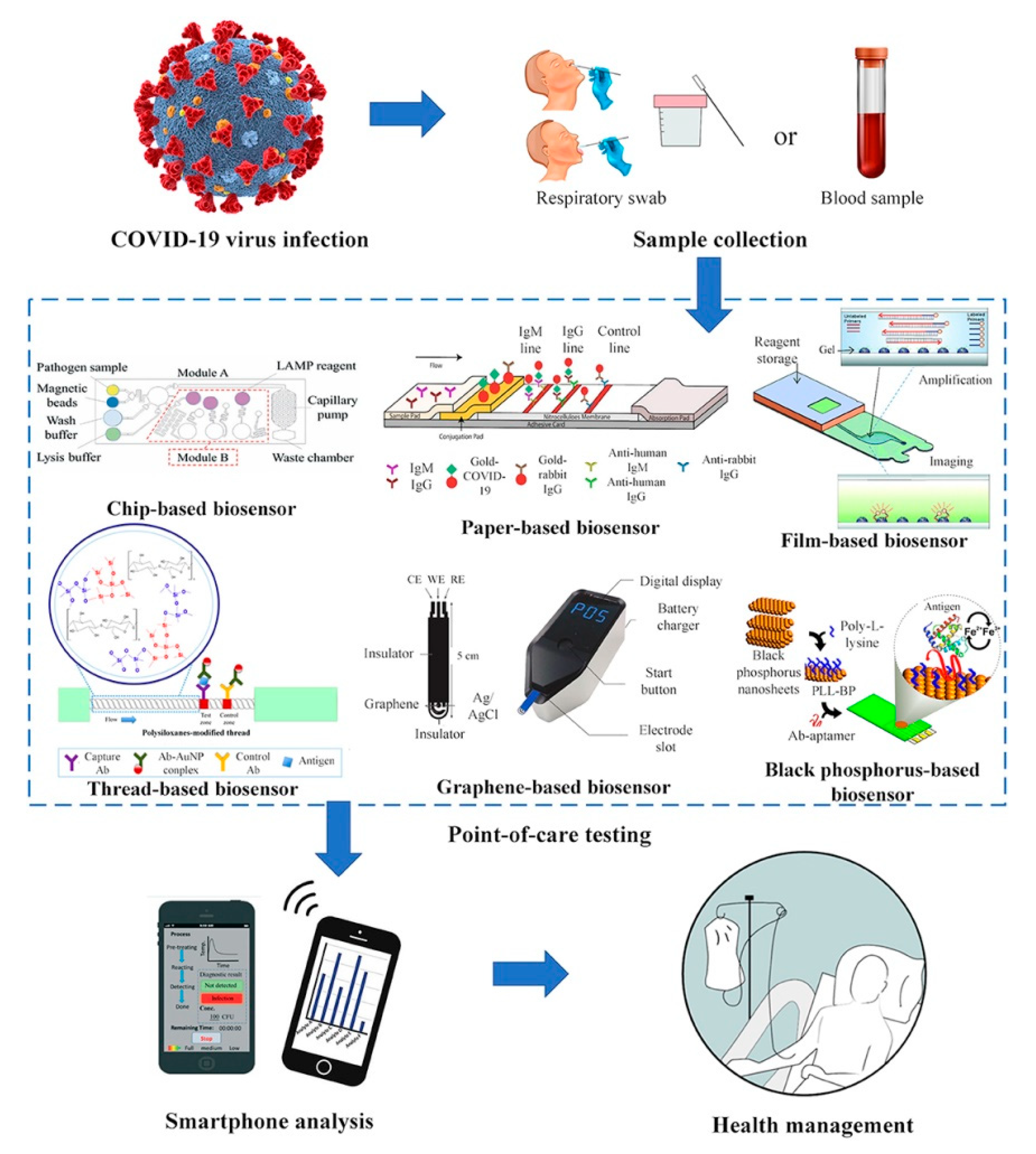
COVID-19 Pandemic
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode Systems for Continuous Monitoring in Cardiovascular Surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimuthu, A.; Vijayan, A.N.; Murali, P.; Korrapati, P.S. Nano-biosensors and their relevance in tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, S.K.; Girigoswami, K. Diagnostic biosensors in medicine—A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmipriya, T.; Gopinath, S.C.B. 1—An Introduction to Biosensors and Biomolecules. In Nanobiosensors for Biomolecular Targeting; Gopinath, S.C.B., Lakshmipriya, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, K.; Meng, E. A review of implantable biosensors for closed-loop glucose control and other drug delivery applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, M.K.; Zarrintaj, P.; Bagheri, B.; Kim, Y.C.; Ganjali, M.R.; Saeb, M.R. Nanotechnology-based biosensors in drug delivery. In Nanoengineered Biomaterials for Advanced Drug Delivery; Mozafari, M., Ed.; Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesche, C.; Baeumner, A.J. Biosensors to support sustainable agriculture and food safety. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Ozguz, V.; Niazi, J.H.; Qureshi, A. Graphene-interfaced electrical biosensor for label-free and sensitive detection of foodborne pathogenic E. coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliy, O.I.; Zaitsev, B.D.; Larionova, O.S.; Borodina, I.A. Virus Detection Methods and Biosensor Technologies. Biophysics 2019, 64, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Yang, Q.; Ullah, M.W.; Wang, S. Bacterial biosensing: Recent advances in phage-based bioassays and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.S.; Ho, J.S.; Tan, C.H.; Wong, J.P.S.; Ng, L.C.; Toh, C.-S. Development of an electrochemical membrane-based nanobiosensor for ultrasensitive detection of dengue virus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 725, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, N.; Kumari, A.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, T.; Tripathi, K.M. Nano-carbon based sensors for bacterial detection and discrimination in clinical diagnosis: A junction between material science and biology. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Gade, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Marcato, P.D.; Durán, N. Biomedical applications of nanobiosensors: The state-of-the-art. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, V.X.T.; Wong, T.I.; Zheng, X.T.; Tan, Y.N.; Zhou, X. Colorimetric biosensors for point-of-care virus detections. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, R.C.; Schommer, S.; Hoehn, D.; Grant, S.A. Development of an optical biosensor using gold nanoparticles and quantum dots for the detection of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Atti, D.; Zavaglia, M.; Tombelli, S.; Bertacca, G.; Cavazzana, A.O.; Bevilacqua, G.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Development of combined DNA-based piezoelectric biosensors for the simultaneous detection and genotyping of high risk Human Papilloma Virus strains. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 383, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Cai, H.; Park, M.; Wall, T.A.; Stott, M.A.; Alfson, K.J.; Griffiths, A.; Carrion, R.; Patterson, J.L.; Hawkins, A.R.; et al. Multiplexed efficient on-chip sample preparation and sensitive amplification-free detection of Ebola virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J. A novel electrochemical biosensor for HIV-related DNA detection based on toehold strand displacement reaction and cruciform DNA crystal. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 822, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.E.; Tabei, F.; Park, S.J.; Askarian, B.; Kim, K.H.; Moallem, G.; Chong, J.; Kwon, O. Smartphone with optical, physical, and electrochemical nanobiosensors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monošík, R.; Stred’anský, M.; Šturdík, E. Application of Electrochemical Biosensors in Clinical Diagnosis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2012, 26, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobed, A.; Baradaran, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Agazadeh, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Rezaee, M.A.; Mosafer, J.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Hamblin, M.R. Advances in detection of fastidious bacteria: From microscopic observation to molecular biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosova, A.; Konry, T.; Cosnier, S.; Trakht, I.; Lutwama, J.; Rwaguma, E.; Chepurnov, A.; Muhlberger, E.; Lobel, L.; Marks, R.S. Development of a highly sensitive, field operable biosensor for serological studies of Ebola virus in central Africa. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encarnação, J.M.; Rosa, L.; Rodrigues, R.; Pedro, L.; da Silva, F.A.; Gonçalves, J.; Ferreira, G. Piezoelectric biosensors for biorecognition analysis: Application to the kinetic study of HIV-1 Vif protein binding to recombinant antibodies. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 132, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitdikov, R.A.; Wilkins, E.S.; Yates, T.; Hjelle, B. Detection of Hantavirus Using a New Miniaturized Biosensor Device. J. Appl. Res. 2007, 7, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, R.E. Biosensor Platforms for Rapid Detection of E. coli Bacteria. In Recent Advances on Physiology, Pathogenesis and Biotechnological Applications; Samie, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvano, F.; Pilloton, R.; Albanese, D. A novel impedimetric biosensor based on the antimicrobial activity of the peptide nisin for the detection of Salmonella spp. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. DNA nanotechnology-enabled biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Surana, R.K.; Jha, S.K. Smartphone based optical biosensor for the detection of urea in saliva. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 269, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, L.; Huang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, N.; Lin, J. A capillary biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella using Fe-nanocluster amplification and smart phone imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Michelini, E.; Zangheri, M.; Di Fusco, M.; Calabria, D.; Simoni, P. Smartphone-based biosensors: A critical review and perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C. Integrated nanobiosensor technology for biomedical application. Nanobiosens. Dis. Diagn. 2012, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Srinivasan, B.; Tung, S. Development and Applications of Portable Biosensors. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, P. Biosensors and their applications—A review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2016, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejcova, L.; Michalek, P.; Rodrigo, M.M.; Heger, Z.; Krizkova, S.; Vaculovicova, M.; Hynek, D.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Nanoscale virus biosensors: State of the art. Nanobiosens. Dis. Diagn. 2015, 4, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malon, R.S.P.; Sadir, S.; Balakrishnan, M.; Córcoles, E.P. Saliva-Based Biosensors: Noninvasive Monitoring Tool for Clinical Diagnostics. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 962903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.L. Noninvasive glucose monitoring using saliva nano-biosensor. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Rajakumari, R. Chapter 1—Nanobiosensors for Biomedical Application: Present and Future Prospects. In Characterization and Biology of Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, V.; Fichera, M.; Giannazzo, F.; Libertino, S.; Scandurra, A.; Reins, M.; Sinatra, F. Fabrication and characterization of the sensing element for glucose biosensor applications. In Sensors and Microsystems; World Scientific: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, S.; Alluri, N.R.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Kim, S.J. Unconventional active biosensor made of piezoelectric BaTiO3 nanoparticles for biomolecule detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Mahato, K.; Ealla, K.K.R.; Asthana, A.; Chandra, P. Chitosan stabilized gold nanoparticle mediated self-assembled gliP nanobiosensor for diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Raza, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Vikrant, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhardwaj, N. Advances in nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for the detection of microbial toxins, pathogenic bacteria in food matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 2020, 123379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xing, Y.; Lin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, J. Monolayer graphene chemiresistive biosensor for rapid bacteria detection in a microchannel. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanman, S.; Kanatharana, P.; Chotigeat, W.; Deachamag, P.; Thavarungkul, P. Highly sensitive capacitive biosensor for detecting white spot syndrome virus in shrimp pond water. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 173, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, B. Disease-Related Detection with Electrochemical Biosensors: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Lu, Y.C.; Lai, J.J. Recent Advances in Biosensors for Nucleic Acid and Exosome Detection. Chonnam. Med. J. 2019, 55, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Menzies, N.W.; Lombi, E.; Sekine, R.; Blamey, F.P.C.; Hernandez-Soriano, M.C.; Cheng, M.; Kappen, P.; Peijnenburg, W.; Tang, C.; et al. Silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S-NPs) are taken up by plants and are phytotoxic. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aljaro, C.; Cella, L.N.; Shirale, D.J.; Park, M.; Muñoz, F.J.; Yates, M.V.; Mulchandani, A. Carbon nanotubes-based chemiresistive biosensors for detection of microorganisms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, R.; Dehghani, S.; Karimi, B.; Yousefi, M.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Abnous, K.; Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M. Siderophore-based biosensors and nanosensors; new approach on the development of diagnostic systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, A.; Farooq, R.; Rehman, M.U.; Khan, R.; Majid, S.; Ganaie, M.A. Aptamer based nanobiosensors: Promising healthcare devices. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A. Microbial biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro-Leránoz, A.B.; Santano, D.; Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R. Trends in the design of wavelength-based optical fibre biosensors (2008–2018). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.D.; Nguyen, B.H.; Van Hieu, N.; Tran, H.V.; Nguyen, H.L.; Nguyen, P.X. Electrochemical detection of short HIV sequences on chitosan/Fe3O4 nanoparticle based screen printed electrodes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazerges, M.; Bedioui, F. Analysis of the evolution of the detection limits of electrochemical DNA biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3705–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.R.; Patel, M.K.; Kaushik, A.; Pandey, M.K.; Kotnala, R.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Sol-Gel Derived Nanostructured Metal Oxide Platform for Bacterial Detection. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaninejad, Z.; Yousefi, F.; Movahedpour, A.; Ghasemi, Y.; Dokanehiifard, S.; Rezaei, S.; Aryan, R.; Savardashtaki, A.; Mirzaei, H. Electrochemical-based biosensors for microRNA detection: Nanotechnology comes into view. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 581, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.; Shankar, P.M.; Mutharasan, R. A review of fiber-optic biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Peña, E.; Valdés, M.G.; Glahn-Martínez, B.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Fluorescence based fiber optic and planar waveguide biosensors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 943, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Cheng, W. Soft and stretchable electrochemical biosensors. Mater. Today Nano 2019, 7, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skládal, P. Piezoelectric biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.N. Development of Biosensors from Biopolymer Composites. In Biopolymer Composites in Electronics; Sadasivuni, K.K., Ponnamma, D., Kim, J., Cabibihan, J.J., AlMaadeed, M.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 353–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-free optical biosensors for food and biological sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopsky, V.N.; Alieva, E.V. Imaging biosensor based on planar optical waveguide. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 115, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Gu, B.; An, Q.F.; Yang, C.; Guan, Y.L.; Yong, K.T. Recent development of fiber-optic chemical sensors and biosensors: Mechanisms, materials, micro/nano-fabrications and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 376, 348–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Zhou, X. Optical biosensors based on refractometric sensing schemes: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 144, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, P.; Martinez, M.; Hernandez, C.; Adhikari, A.R.; Mao, Y.; Materon, L.; Lozano, K. Development of chromatic biosensor for quick bacterial detection based on polyvinyl butyrate-polydiacetylene nonwoven fiber composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 121, 109284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Choi, S.-H.; Lee, H.; Lim, Y. A fluorescent supramolecular biosensor for bacterial detection via binding-induced changes in coiled-coil molecular assembly. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Heidarzadeh, H.; Taghipour, A.; Rostami, A.; Baghban, H.; Dolatyari, M.; Rostami, G. Evaluation of single virus detection through optical biosensor based on microsphere resonator. Optik 2014, 125, 3599–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tong, R.; Xia, F.; Peng, Y. Current status of optical fiber biosensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arwin, H. TIRE and SPR-Enhanced SE for Adsorption Processes. In Ellipsometry of Functional Organic Surfaces and Films; Hinrichs, K., Eichhorn, K.-J., Eds.; Springer Series in Surface Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 249–264. ISBN 978-3-642-40128-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jebelli, A.; Oroojalian, F.; Fathi, F.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; De la Guardia, M. Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensors for microRNAs detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.D.; Kant, R. Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic chemical and biosensors utilizing bulk and nanostructures. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 101, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, E.O.; Corrigan, D.K. A review of microfabricated electrochemical biosensors for DNA detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 134, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.L.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P.; Carrara, S.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical biosensors and nanobiosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Wang, F.; Li, C. A label-free electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive detection of gliotoxin based on DNA nanostructure/MXene nanocomplexes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathelié, M.; Cohen, T.; Gammoudi, I.; Martin, A.; Béven, L.; Delville, M.H.; Grauby, C. Silica nanoparticles-assisted electrochemical biosensor for the rapid, sensitive and specific detection of Escherichia coli. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 292, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, M.W.; Park, C.Y.; Choi, C.S.; Kailasa, S.K.; Park, J.P.; Park, T.J. Development of a rapid and sensitive electrochemical biosensor for detection of human norovirus via novel specific binding peptides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M. Overview of Piezoelectric Biosensors, Immunosensors and DNA Sensors and Their Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Santucci, A.; Spiriti, M.M.; Mascini, M. A DNA-based piezoelectric biosensor: Strategies for coupling nucleic acids to piezoelectric devices. Talanta 2006, 68, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombelli, S. Piezoelectric biosensors for medical applications. In Biosensors for Medical Applications; Higson, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.Q.; Luo, J.K.; Nguyen, N.T.; Walton, A.J.; Flewitt, A.J.; Zu, X.T.; Li, Y.; McHale, G.; Matthews, A.; Iborra, E.; et al. Advances in piezoelectric thin films for acoustic biosensors, acoustofluidics and lab-on-chip applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 31–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lin, C.-S.; Chen, S.-H.; Ye, R.; Wu, V.C.H. A piezoelectric immunosensor for specific capture and enrichment of viable pathogens by quartz crystal microbalance sensor, followed by detection with antibody-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Nasirian, V.; Mansouri, K.; Barati, A.; Veisi-Raygani, A.; Kashanian, S. A highly sensitive quantum dots-DNA nanobiosensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer for rapid detection of nanomolar amounts of human papillomavirus 18. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 136, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golichenari, B.; Nosrati, R.; Farokhi, A.; Abnous, K.; Vaziri, F.; Behravan, J. Nano-biosensing approaches on tuberculosis: Defy of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Katyal, V.; Malik, V.; Asatkar, A.; Inwati, G.; Mukherjee, T.K. Nanobiosensors: Concepts and Variations. ISRN Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 327435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Lee, C.; Kwon, O.S. Conducting Polymer Based Nanobiosensors. Polymers 2016, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.; Merkoci, A. Nanobiosensors in diagnostics. Nanobiomedicine 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.D.; Baker, H.A.; Ortiz, M.V.; Kentsis, A.; Heller, D.A. HIV Detection via a Carbon Nanotube RNA Sensor. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Takemura, K.; Park, E.Y. Plasmonic Nanomaterial-Based Optical Biosensing Platforms for Virus Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Eivazzadeh, R.; Pashazadeh, P.; Hejazi, M.; Gharaatifar, N.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Baradaran, B.; de la Guardia, M. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic virus. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, G.; Zhao, L.; Lai, K.W. Carbon Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors: A Review of Design and Applications. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2019, 13, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Applications of Graphene Quantum Dots in Biomedical Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, M.; Altintas, Z. Nanomaterials for Healthcare Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 25221775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Yáñez, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Carbon Dots and Graphene Quantum Dots in Electrochemical Biosensing. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, A.; Tomar, R.S. Detection of pathogenic bacteria using nanobiosensors. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, O.; Seo, M.; Kato, T.; Kawahito, S.; Park, E. An ultrasensitive SiO2-encapsulated alloyed CdZnSeS quantum dot-molecular beacon nanobiosensor for norovirus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, S.; Taj, A.; Zia, R.; Hayat, H.; Shaheen, A.; Awan, F.R.; Bhatti, H.; Khan, W.; Bajwa, S. Chapter 19—Nanosensors for the detection of viruses. In Nanosensors for Smart Cities; Han, B., Tomer, V.K., Nguyen, T.A., Farmani, A., Kumar Singh, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Gupta, V.K. Chapter 4—Synthesis, Classification, and Properties of Nanomaterials. In Nanomaterial and Polymer Membranes; Saleh, T.A., Gupta, V.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 83–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, A.; Neogy, S.; Raorane, B.S.; Adhikari, S. Room temperature ionic liquid assisted rapid synthesis of amorphous Se nanoparticles: Their prolonged stabilization and antioxidant studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 253, 123369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, P.N.; Sangeetha, K.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Barhoum, A. Chapter 12—Nanomaterials history, classification, unique properties, production and market. In Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architecture Nanostructures; Barhoum, A., Makhlouf, A.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 341–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qadi, S.; Remuñan, C. Nanopartículas metálicas: Oro. In Nanotecnología Farmacéutica: Realidades y Posibilidades Farmacoterapéuticas; Vila, J.L., Ed.; Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia: Madrid, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, P.; Puente, A.; Castro, A.; Santos do Nascimento, L.A.; Balu, A.M.; Luque, R.; Alvarado, C. Nanomaterials and catalysis for green chemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 24, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuthu, K.; Cha, B.S.; Kim, S.; Park, K.S. Eco-friendly synthesis and biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: A review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, B.; Johnson, M.E.; Montoro, A.R.; Murphy, K.E.; Winchester, M.R.; Vega, J.R. Silver Nanoparticles: Technological Advances, Societal Impacts, and Metrological Challenges. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, V.; Vega, J. Gold, silver, copper and silicone hybrid nanostructure cytotoxicity. Int. J. Rec. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 15478–15486. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Bhatt, D.; Lim, D.K.; Kim, K.-H.; Deep, A. Optical detection of waterborne pathogens using nanomaterials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H.; Amini, B. A fluorescence Nano-biosensors immobilization on Iron (MNPs) and gold (AuNPs) nanoparticles for detection of Shigella spp. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, K.; Adegoke, O.; Takahashi, N.; Kato, T.; Li, T.C.; Kitamoto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, T.; Park, E. Versatility of a localized surface plasmon resonance-based gold nanoparticle-alloyed quantum dot nanobiosensor for immunofluorescence detection of viruses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarnaphaet, P.; Pechprasarn, S. Graphene-Based Materials for Biosensors: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safardoust, H.; Salavati, M.; Amiri, O.; Hassanpour, M. Preparation of highly luminescent nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and their application as a probe for detection of Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat, M.H.; Abdullah, J.; Yusof, N.A.; Sulaiman, Y.; Wasoh, H.; Noh, M.F.; Issa, R. PNA biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide/water soluble quantum dots for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Dai, S.; Miao, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, L.; Vargas, R.; Pacheco, J.; Vega, J. Electrospun nanofibers: A nanotechnological approach for drug delivery and dissolution optimization in poorly water-soluble drugs. ADMET DMPK 2020, 8, 325–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, N. Electrospun fibers: A guiding scaffold for research and regeneration of the spinal cord. Neu Reg. Res. 2016, 11, 1764–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Ezazi, N.Z.; Liu, D.; Santos, H. Electrospun Fibrous Architectures for Drug Delivery, Tissue Engineering and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1802852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrč, T.; Baumgartner, S.; Roškar, R.; Planinšek, O.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J.; Kocbek, P. Electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers as a potential oromucosal delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Z.; Liu, T.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. Electrospinning Nanoparticles-Based Materials Interfaces for Sensor Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliheidari, N.; Aliahmad, N.; Agarwal, M.; Dalir, H. Electrospun Nanofibers for Label-Free Sensor Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslakci, N.N.; Ulusoy, S.; Oksuz, A.U. Investigation of the effects of plasma-treated chitosan electrospun fibers onto biofilm formation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R.; Khan, W.S. Chapter 9—\ Electrospun nanofibers for nanosensor and biosensor applications. In Synthesis and Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers; Asmatulu, R., Khan, W.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, G.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Long, B.; Peng, B.; Zhu, J. A reusable electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive detection of mercury ions with an anionic intercalator supported on ordered mesoporous carbon/self-doped polyaniline nanofibers platform. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafi, A.K.; Wali, Q.; Jose, R.; Biswas, T.K.; Yusoff, M.M. A glassy carbon electrode modified with SnO2 nanofibers, polyaniline and hemoglobin for improved amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4443–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.; Braiek, M.; Chateaux, J.F.; Jaffrezic, N.; Lagarde, F. Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Interfaces for Biosensing Devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supraja, P.; Tripathy, S.; Krishna, S.R.; Singh, V.; Singh, S.G. Label free, electrochemical detection of atrazine using electrospun Mn2O3 nanofibers: Towards ultrasensitive small molecule detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundera, S.; Mohamed, M.S.; Perumal, V.; Mohamed, M.S.; Mohamed, N.M. Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensing Applications. In Nanobiosensors for Biomolecular Targeting; Gopinath, S.C., Lakshmipriya, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftoonazad, N.; Ramaswamy, H. Design and testing of an electrospun nanofiber mat as a pH biosensor and monitor the pH associated quality in fresh date fruit (Rutab). Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Gong, M.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J. An electrochemiluminescence biosensor for detection of CdkN2A/p16 anti-oncogene based on functional electrospun nanofibers and core-shell luminescent composite nanoparticles. Talanta 2018, 187, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, L.; Coon, B.; Pitner, C.L.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Functionalized electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers for on-chip concentration of E. coli cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nartker, S.; Miller, H.; Hochhalter, D.; Wiederoder, M.; Wiederoder, S.; Setterington, E.; Drzal, L.; Alocilja, E. Surface functionalization of electrospun nanofibers for detecting E. coli O157:H7 and BVDV cells in a direct-charge transfer biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, J.; Amaral, A.J.; Pasparakis, G.; Williams, G.R.; Rosal, R. Electrospun boronic acid-containing polymer membranes as fluorescent sensors for bacteria detection. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 121, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Krishna, S.R.; Singh, V.; Swaminathan, S.; Singh, S.G. Electrospun manganese (III) oxide nanofiber based electrochemical DNA-nanobiosensor for zeptomolar detection of dengue consensus primer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Seeram, R. A review on recent advances in application of electrospun nanofiber materials as biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbod, F.; Mazloum, M. Chapter 5—Typically used nanomaterials-based noncarbon materials in the fabrication of biosensors. In Electrochemical Biosensors; Ensafi, A.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 99–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, S.; Jose, M.V.; Andersen, J.D.; Russell, A.J. Electrospun gold nanofiber electrodes for biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Electromechanical biosensors for pathogen detection. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Wu, V.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lin, C.S. Using oligonucleotide-functionalized Au nanoparticles to rapidly detect foodborne pathogens on a piezoelectric biosensor. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 73, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Mukherjee, M.D.; Sumana, G.; Gupta, R.K.; Sood, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Biosensors for pathogen detection: A smart approach towards clinical diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.M.; Bock, W.J.; Mikulic, P.; Chinnappan, R.; Ng, A.; Tolba, M.; Zourob, M. Long period grating based biosensor for the detection of Escherichia coli bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; De, A.; Chaudhuri, C.R.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Sen, P. Label free polyaniline based impedimetric biosensor for detection of E. coli O157:H7 Bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Alocilja, E.C. Gold nanoparticle-labeled biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of bacterial pathogens. J. Biol. Eng. 2015, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.; Valles, C.; Benito, A.; Maser, W.; Rius, F.X.; Riu, J. Graphene-based potentiometric biosensor for the immediate detection of living bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Marrakchi, M.; Xu, D.; Dong, H.; Andreescu, S. Biosensors based on modularly designed synthetic peptides for recognition, detection and live/dead differentiation of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, M.; Gupta, V.; Tomar, M. Flower-like ZnO nanostructure based electrochemical DNA biosensor for bacterial meningitis detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsahi, S.; Lerner, M.B.; Goldstein, J.M.; Lee, J.; Tang, X.; Bagarozzi, D.A.; Pan, D.; Locascio, L.; Walker, A.; Barron, F.; et al. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, V.D.; Wu, K.; Perez, A.M.; Wang, J.P. Giant Magnetoresistance-based Biosensor for Detection of Influenza A Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Viezzi, S.; Mazerat, S.; Marks, R.S.; Vidic, J. Rapid and label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for detecting hepatitis A virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, H.A.M.; Zucolotto, V. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for zika virus identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, C.; Khanuja, M.; Chaudhary, N.; Pundir, C.S.; Narang, J. Detection of chikungunya virus DNA using two-dimensional MoS 2 nanosheets based disposable biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoori, Z.; Salimian, S.; Kharrazi, S.; Adabi, M.; Saber, R. Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on gold nanorods for detecting hepatitis B virus. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Hong, Y.W.; Yuan, R.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Huang, Y.W.; Lu, P.; Chen, Y.; Arthur, Y.; Su, L.; et al. Simple Strategy for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Avian Influenza a H7N9 Virus Based on Intensity-Modulated SPR Biosensor and New Generated Antibody. Anal Chem. 2018, 90, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzaihan, M.; Hashim, U.; Arshad, M.K.; Kasjoo, S.R.; Rahman, S.F.; Ruslinda, A.R.; Fathil, M.; Adzhri, R.; Shahimin, M. Electrical detection of dengue virus (DENV) DNA oligomer using silicon nanowire biosensor with novel molecular gate control. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Maurya, P.K.; Chandra, P. Fundamentals and commercial aspects of nanobiosensors in point-of-care clinical diagnostics. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Applications of commercial biosensors in clinical, food, environmental, and biothreat/biowarfare analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Advances in nano-scaled biosensors for biomedical applications. Analyst 2013, 138, 4427–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.; Seca, A.M.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M. Targeting human pathogenic bacteria by siderophores: A proteomics review. J. Proteom. 2016, 145, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdinasab, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Tang, X.; Marty, J.L. Detection of antibiotics in food: New achievements in the development of biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ye, Z.Z.; Si, C.Y.; Ying, Y.B. Application of Aptamer Based Biosensors for Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, J.; Lakshmaiah, J.; Wu, H.F. TiO2 nanoparticle assisted mass spectrometry as biosensor of Staphylococcus aureus, key pathogen in nosocomial infections from air, skin surface and human nasal passage. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 27, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubab, M.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Olaimat, A.N.; Oh, D.H. Biosensors for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaifan, G.; Alhogail, S.; Zourob, M. Rapid and low-cost biosensor for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahari, H.; Hedayati, M.; Akbari, B.; Kakoolaki, S.; Hosseini, H.; Anvar, A. Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin detection using potentiometric nanobiosensor for microbial electrode approach with the effects of pH and temperature. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starodub, N.F.; Ogorodniichuk, J.; Lebedeva, T.; Shpylovyy, P. Immune biosensors based on the SPR and TIRE: Efficiency of their application for bacteria determination. In Proceedings of the Biophotonics—Riga 2013; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 9032, p. 90320X. [Google Scholar]
- Vaisocherová, H.; Víšová, I.; Ermini, M.L.; Špringer, T.; Song, X.C.; Mrázek, J.; Lamacová, J.; Lynn, S.; Sedivak, P.; Homola, J. Low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor for multi-step detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens in complex food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchini, F.; Fajs, L.; Cosnier, S.; Marks, R.S. Vibrio cholerae detection: Traditional assays, novel diagnostic techniques and biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmani, A.; Kamali, M.; Amini, B.; Kooshki, H.; Amini, A.; Hasani, L. Highly sensitive and accurate detection of Vibrio cholera O1 OmpW gene by fluorescence DNA biosensor based on gold and magnetic nanoparticles. Process. Biochem. 2018, 65, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Rong, Z.; Long, F.; Liu, Q. Portable evanescent wave fiber biosensor for highly sensitive detection of Shigella. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 132, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, N.; Baghersad, M.H.; Kamali, M. Precise, direct, and rapid detection of Shigella Spa gene by a novel unmodified AuNPs-based optical genosensing system. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 162, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.N.; Yoon, J.; Jin, C.E.; Koo, B.; Han, K.; Shin, Y.; Lee, T. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella based on microfluidic enrichment with a label-free nanobiosensing platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Recent progress in the construction of nanozyme-based biosensors and their applications to food safety assay. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 121, 115668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, T.G.; Martins, R.C.; Fernandes, E.; Cardoso, S.; Rivas, J.; Freitas, P.P. Detection of BCG bacteria using a magnetoresistive biosensor: A step towards a fully electronic platform for tuberculosis point-of-care detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, H.S.; Su, Z.; Ward, A.; Tang, X. Carbon Nanotube Thin Film Biosensors for Sensitive and Reproducible Whole Virus Detection. Theranostics 2012, 2, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banga, I.; Tyagi, R.; Shahdeo, D.; Gandhi, S. Chapter 1—Biosensors and Their Application for the Detection of Avian Influenza Virus. In Nanotechnology in Modern Animal Biotechnology; Maurya, P.K., Singh, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidzworski, D.; Pranszke, P.; Grudniewska, M.; Król, E.; Gromadzka, B. Universal biosensor for detection of influenza virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepeli, Y.; Ülkü, A. Electrochemical biosensors for influenza virus a detection: The potential of adaptation of these devices to POC systems. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, S.; Baradaran, B.; Hejazi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; de la Guardia, M. Recent trends in rapid detection of influenza infections by bio and nanobiosensor. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Tiwari, S.; Jayant, R.D.; Vashist, A.; Nikkhah, R.; El-Hage, N.; Nair, M. Electrochemical Biosensors for Early Stage Zika Diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Luo, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, C.; Jin, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Jiang, L.; He, H. Development and evaluation of a polydiacetylene based biosensor for the detection of H5 influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 219, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, S.M.; Hong, K.; Kim, Y.; Park, C.; Sohn, H.; Min, J. Label-free localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor composed of multi-functional DNA 3 way junction on hollow Au spike-like nanoparticles (HAuSN) for avian influenza virus detection. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 182, 110341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.; Monsalve, D.M.; Pacheco, Y.; Acosta, Y.; Ramírez, C.; Ansari, A.A.; Gershwin, M.; Anaya, J. Ebola virus disease: An emerging and re-emerging viral threat. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 106, 102375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharsany, A.B.; McKinnon, L.R.; Lewis, L.; Cawood, C.; Khanyile, D.; Maseko, D.V.; Goodman, T.; Beckett, S.; Govender, K.; George, G.; et al. Population prevalence of sexually transmitted infections in a high HIV burden district in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: Implications for HIV epidemic control. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, E.; Dieterle, M.E.; Kleinfelter, L.M.; Slough, M.M.; Chandran, K.; Jangra, R.K. Chapter Six—Hantavirus entry: Perspectives and recent advances. In Advances in Virus Research; Kielian, M., Mettenleiter, T.C., Roossinck, M.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 185–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastri, E.; Kobinger, G.; Vairo, F.; Montaldo, C.; Mboera, L.E.; Ansunama, R.; Zumla, A.; Ippolito, G. Ebola Virus Disease: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Management, and Prevention. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 953–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérens, A.; Bigaillon, C.; Delaune, D. Ebola virus disease: Biological and diagnostic evolution from 2014 to 2017. Méd. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.N. Recent Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Ebola Virus Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2019, 41, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walldorf, J.A.; Cloessner, E.A.; Hyde, T.B.; MacNeil, A.; Bennett, S.D.; Carter, R.J.; Redd, J.; Marston, B. Considerations for use of Ebola vaccine during an emergency response. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7190–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Tiwari, S.; Dev Jayant, R.; Marty, A.; Nair, M. Towards detection and diagnosis of Ebola virus disease at point-of-care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilkhani, H.; Farhad, S. A novel electrochemical DNA biosensor for Ebola virus detection. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 557, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baca, J.T.; Severns, V.; Lovato, D.; Branch, D.W.; Larson, R.S. Rapid Detection of Ebola Virus with a Reagent-Free, Point-of-Care Biosensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 8605–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iordache, L.; Launay, O.; Bouchaud, O.; Jeantils, V.; Goujard, C.; Boue, F.; Cacoub, P.; Hanslik, T.; Mahr, A.; Lambotte, O.; et al. Autoimmune diseases in HIV-infected patients: 52 cases and literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Mondal, A.; Roberts, A.; Gandhi, S. Chapter One—Biosensor platforms for rapid HIV detection. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, A.; Karbalaie, M.H.; Keshavarz, M.; Ghaffari, H.; Asoodeh, A.; Monavari, S.H.; Keyvani, H. Current diagnostic methods for HIV. Future Virol. 2017, 12, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, H.; Lidstone, E.A.; Jahangir, M.; Inci, F.; Hanhauser, E.; Henrich, T.J.; Kuritzkes, D.; Cunningham, B.; Demirci, U. Nanostructured Optical Photonic Crystal Biosensor for HIV Viral Load Measurement. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Han, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, J. Sensitive electrochemical DNA sensor for the detection of HIV based on a polyaniline/graphene nanocomposite. J. Mater. 2019, 5, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetcha, S.; Wilkins, E.; Yates, T.; Hjelle, B. Rapid and sensitive handheld biosensor for detection of hantavirus antibodies in wild mouse blood samples under field conditions. Talanta 2002, 58, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Du, H.; Wang, P.; Bai, X. Hantavirus infection: A global zoonotic challenge. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogola, J.L.; Martins, G.; Caetano, F.R.; Ricciardi, T.; Duarte, C.N.; Marcolino, L.H.; Bergamini, M. Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for quick detection of anti-hantavirus antibody. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 842, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.; Gogola, J.L.; Caetano, F.R.; Kalinke, C.; Jorge, T.R.; Duarte, C.N.; Bergamini, F.; Marcolino, L. Quick electrochemical immunoassay for hantavirus detection based on biochar platform. Talanta 2019, 204, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzin, L.; Shamsipur, M.; Samandari, L.; Sheibani, S. HIV biosensors for early diagnosis of infection: The intertwine of nanotechnology with sensing strategies. Talanta 2020, 206, 120201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panghal, A.; Flora, S.J. Chapter 4—Viral agents including threat from emerging viral infections. In Handbook on Biological Warfare Preparedness; Flora, S.J., Pachauri, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rohaimi, A.H.; Al-Otaibi, F. Novel SARS-CoV-2 outbreak and COVID19 disease; A systemic review on the global pandemic. Genes Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Hasan, M.R.; Hossain, S.I.; Ahommed, M.S.; Daizy, M. Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic viruses with electrochemical biosensor: State of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 2020, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Akbar khan, S.; Lai, C.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Xia, S.; Chen, B.; et al. Detection of COVID-19: A review of the current literature and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 2020, 112455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, E.; Eissa, S.; Ismail, A.; Zourob, M. Diagnostic techniques for COVID-19 and new developments. Talanta 2020, 220, 121392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, C.; He, Q.; Chen, J.; Yu, D.; Li, J.; Zhai, S.; Qin, Z.; Du, K.; Chu, Z.; et al. Current and Perspective Diagnostic Techniques for COVID-19. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalandra, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Verma, D.; Dalal, N.; Sharma, M.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Solanki, P. Strategies and perspectives to develop SARS-CoV-2 detection methods and diagnostics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.; Lindsley, A.; Courter, J.; Assa’ad, A. Clinical testing for COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Nagpal, S.; Kaushik, S.; Mendiratta, S. COVID-19 diagnostic approaches: Different roads to the same destination. Virus Dis. 2020, 31, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, I. Trends and Innovations in Biosensors for COVID-19 Mass Testing. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Tiwari, S.; Jain, R. Protein based biomarkers for non-invasive Covid-19 detection. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R. Development of Point-of-Care Biosensors for COVID-19. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, C. Fast, portable tests come online to curb coronavirus pandemic. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Feng, A.; Li, T. Consistency analysis of COVID-19 nucleic acid tests and the changes of lung CT. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yi, Y.; Luo, X.; Xiong, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, W.; et al. Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 2, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevarajan, I.; Nguyen, T.; Koutsakos, M.; Druce, J.; Caly, L.; van de Sandt, C.; Jia, X.; Nicholson, S.; Catton, M.; Cowie, B.; et al. Breadth of concomitant immune responses prior to patient recovery: A case report of non-severe COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhu, F.; Guo, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, T. Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Health C for D and R. EUA Authorized Serology Test Performance. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/eua-authorized-serology-test-performance (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Ghaffari, A.; Meurant, R.; Ardakani, A. COVID-19 Serological Tests: How Well Do They Actually Perform? Diagnostics 2020, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, E.; Dincer, C. The impact of biosensing in a pandemic outbreak: COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zou, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, B.; Lv, S.; Mu, Y. A “sample-in-multiplex-digital-answer-out” chip for fast detection of pathogens. Lab. Chip 2020, 20, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, N.C.; Fusco, V.; Maruccio, G.; Primiceri, E.; Batt, C.A. Micro- and nanotechnology-based approaches to detect pathogenic agents in food. In Nanobiosensors; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 475–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Yin, J.; Lv, S.; Wang, B.; Mu, Y. Advanced “lab-on-a-chip” to detect viruses—Current challenges and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Farokh, A. Opportunities and Challenges for Biosensors and Nanoscale Analytical Tools for Pandemics: COVID-19. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7783–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palestino, G.; Garcia, I.; Gonzalez, O.; Rosales, S. Can nanotechnology help in the fight against COVID-19? Exp. Rev. Anti-Innefect Ther. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermisoglou, E.; Panáček, D.; Jayaramulu, K.; Pykal, M.; Frébort, I.; Kolář, M.; Hajdúch, M.; Zboril, R.; Otyepka, M. Human virus detection with graphene-based materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 2020, 112436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.; Papi, M. Can graphene take part in the fight against COVID-19? Nano Today 2020, 33, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.; et al. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, H.S. Diagnostic methods and potential portable biosensors for coronavirus disease 2019. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, D.; Bhatia, H.; Sai, V.V.; Satija, J. P-FAB: A Fiber-Optic Biosensor Device for Rapid Detection of COVID-19. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Multiplex reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Gai, Z.; Tao, Y.; Schmitt, J.; Kullak, G.A.; Wang, J. Dual-Functional Plasmonic Photothermal Biosensors for Highly Accurate Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5268–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujawar, M.A.; Gohel, H.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Srinivasan, S.; Hickman, N.; Kaushik, A. Nano-enabled biosensing systems for intelligent healthcare: Towards COVID-19 management. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Peng, R.; Baravik, I.K.; Liu, X. Fighting COVID-19: Integrated Micro- and Nanosystems for Viral Infection Diagnostics. Matter 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Device | Target Pathogen | LOD | Response Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long-period fiber grating using bacteriophage T4 covalently immobilized on optical fiber surface. | E. coli | 103 CFU/mL | 20 min | [142] |
| Label free polyaniline based impedimetric. | E. coli O157:H7 | 102 CFU/mL | - | [143] |
| Electrochemical biosensor using antibody-modified NPs (polymer-coated magnetic NPs and carbohydrate-capped AuNPs). | E. coli O157:H7 | 101 CFU/mL | 45 min | [144] |
| Graphene-based potentiometric. | S. aureus | 1 CFU/mL | 10–15 min | [145] |
| Aptamer based biosensor and dual florescence resonance energy transfer from QDs to carbon NPs. | Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Salmonella typhimurium | 25 CFU/mL and 35 CFU/mL, respectively | 80 min | [116] |
| Impedimetric biosensor based on site specifically attached engineered antimicrobial peptides. | Pseudomona aeruginosa | 102 CFU/mL | 30 min | [146] |
| Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on flower-like ZnO nanostructures. | Neisseria meningitides | 5 ng/μL | - | [147] |
| Graphene-enabled biosensor with a highly specific immobilized monoclonal antibody. | Zika virus | 0.45 nM | 4–8 min | [148] |
| Giant magnetoresistance biosensor. | Influenza A virus | 1.5 × 102 TCID50/mL | - | [149] |
| Electrochemical biosensor based on DNA hybridization. | Hepatitis A virus | 6.94 fg/μL | 15 min | [150] |
| Impedimetric electrochemical DNA biosensor for label free detection. | Zika virus | 25 nM | 1.5 h | [151] |
| Two-dimensional molybdenum disulphide nanosheets based disposable biosensor. | Chikungunya virus | 3.4 nM | 3 h | [152] |
| Electrochemical DNA biosensor using gold nanorods. | Hepatitis B virus | 2.0 × 10−12 mol/L | 5 h | [153] |
| Intensity-modulated surface plasmon resonance (IM-SPR) biosensor | Avian influenza A H7N9 virus | 144 copies/mL | 10 min | [154] |
| Silicon nanowire biosensor. | Dengue virus | 2.0 fM | - | [155] |
| Manufacturer | Device | Target | Clinical Combined Specificity | Clinical Combined Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbott | SARS-CoV-2 IgG chemilumininescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) | Nucleocapsid | 99.9% | 100% |
| Access Bio, Inc. | CareStart COVID-19 IgM/IgG | Spike and Nucleocapsid | 98.9% | 98.4% |
| Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy Enterprise Co. Ltd. | Wantai SARS-CoV-2 Ab rapid test | Spike | 98.8% | 100% |
| Biohit Healthcare (Hefei) | Biohit SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG antibody test kit | Nucleocapsid | 95.0% | 96.7% |
| Cellex | Cellex Qsars-CoV-2 IgG/IgM rapid test lateral flow immunoassay | Spike and nucleocapsid | 96.0% | 93.8% |
| DiaSorin | LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 IgG CMIA | Spike | 99.3% | 97.6% |
| Hangzhou Biotest Biotech | COVID-19 IgG/IgM rapid test cassette | Spike | 100% | 100% |
| Hangzhou Laihe Biotech | LYHER novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) IgM/IgG antibody combo test kit (colloidal gold) | Spike | 98.8% | 100% |
| Healgen | COVID-19 IgG/IgM rapid test cassette | Spike | 97.5% | 100% |
| Megna Health, Inc. | Rapid COVID-19 IgM/IgG combo test kit | Nucleocapsid | 95% | 100% |
| Salofa Oy | Siena-Clarity COVIBLOCK COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid test cassette | Spike | 98.8% | 93.3% |
| Xiamen Biotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | BIOTIME SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM rapid qualitative test | Spike | 96.2% | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo-Henríquez, L.; Brenes-Acuña, M.; Castro-Rojas, A.; Cordero-Salmerón, R.; Lopretti-Correa, M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R. Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens. Sensors 2020, 20, 6926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236926
Castillo-Henríquez L, Brenes-Acuña M, Castro-Rojas A, Cordero-Salmerón R, Lopretti-Correa M, Vega-Baudrit JR. Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236926
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo-Henríquez, Luis, Mariana Brenes-Acuña, Arianna Castro-Rojas, Rolando Cordero-Salmerón, Mary Lopretti-Correa, and José Roberto Vega-Baudrit. 2020. "Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236926
APA StyleCastillo-Henríquez, L., Brenes-Acuña, M., Castro-Rojas, A., Cordero-Salmerón, R., Lopretti-Correa, M., & Vega-Baudrit, J. R. (2020). Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens. Sensors, 20(23), 6926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236926






