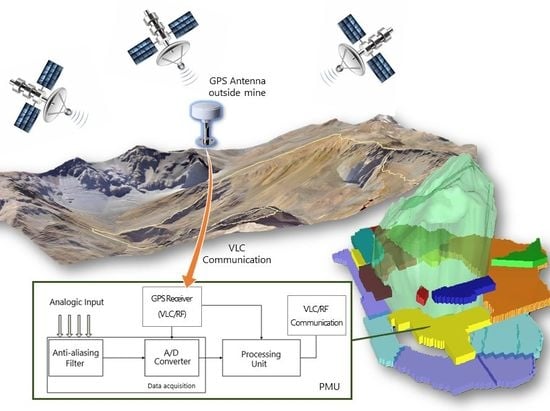
A Hybrid VLC-RF Portable Phasor Measurement Unit for Deep Tunnels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Technologies Used to Provide Positioning and Wireless Communication in a Tunnel
- Acoustic systems: Acoustic signals are mechanical waves. The estimation of the acoustic position can be based on ultrasound or audible sound. The estimated range of acoustic positioning systems is about 10 m due to the specific decay profile of the channel. Trilateration-based methods can be easily implemented using these types of systems using a microphone array on the receiver side. Acoustic systems are severely affected by multipath propagation, directivity of transducers and noise. In addition, increasing the signal strength is not a viable alternative, since a huge amount of energy is required, reducing the battery life [22].
- Inertial Navigation Systems (INS): INS estimates the position, speed and orientation of the mobile node from an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU). This type of systems operates without infrastructure requirement. When the initial position and orientation of the mobile device are known, the subsequent positions, orientations and speeds can be continuously updated by the Dead Reckoning (DR) without the need for external reference positions. The accuracy of the position propagated depends largely on the quality of the position and orientation that was initially provided. Accelerometer measurements are also affected by noise. Because of this, the INS decreases its accuracy over the distance traveled, this being its main problem [23].
- Signage and maps: Signage and maps are traditionally the most available approach for human navigation in indoor environments. The actual position is provided by static signaling and, to help the mobile user reach his destination. Today, new signs and maps are replacing this traditional approach. For example, cameras and mobile devices can replace the user’s vision and reasoning to provide positioning and navigation. The use of a camera to scan unique “markers” is proposed. By doing so, the single mark provides information to a mobile phone application to determine the actual position [24].
- Magnetic field: Unlike electromagnetic waves, magnetic waves are able to penetrate the interior walls of buildings. Because of this, magnetic field based location systems do not suffer from several disadvantages found in electromagnetic systems. The second type of location systems based on magnetic fields use artificially generated magnetic fields. In this type of systems a variable electric current is used that circulates in concentric coils to create the artificial and controlled magnetic field (Lenz effect). Usually, artificially induced magnetic fields have a short coverage range (less than 3 m) and, due to this, their application is limited to small volumes. This means that there is no feasibility of using these systems for underground mining [25].
3. System Description
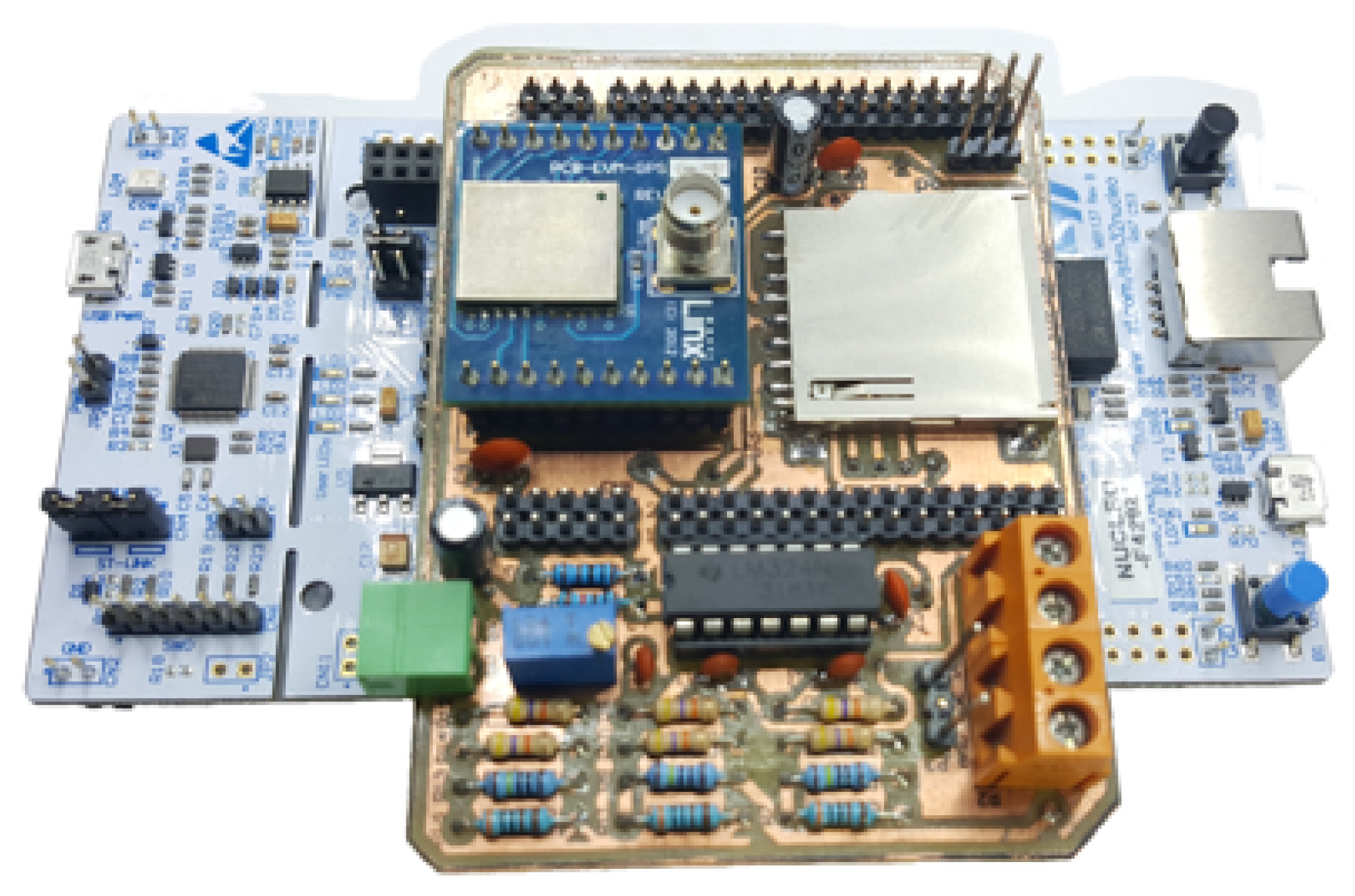
4. Materials and Methods
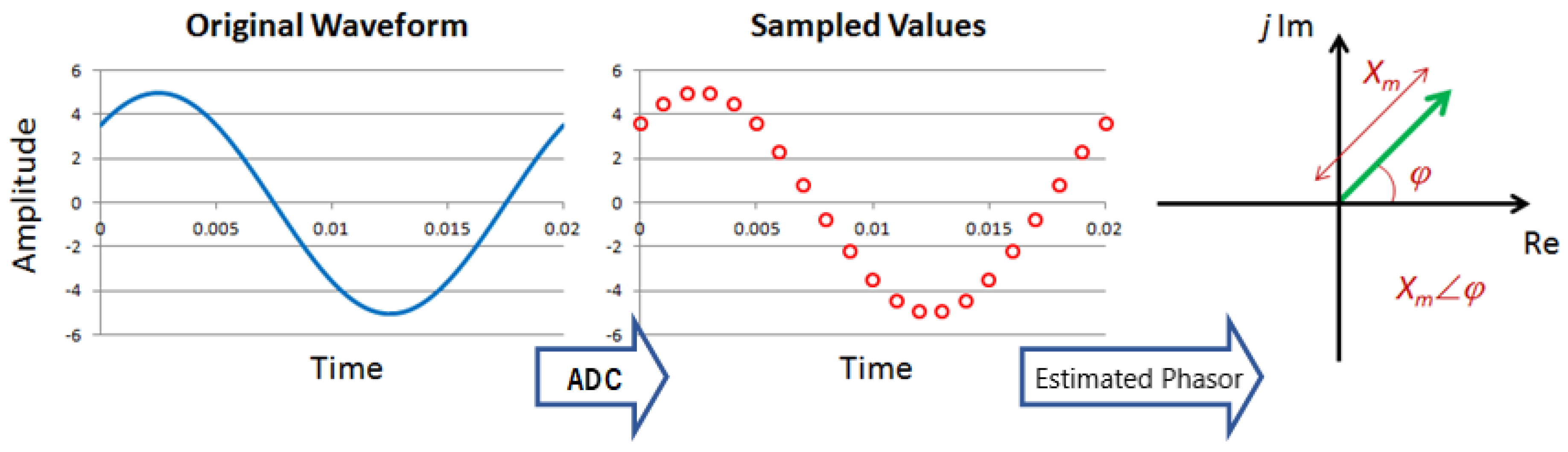
4.1. Phasor Measurement Unit
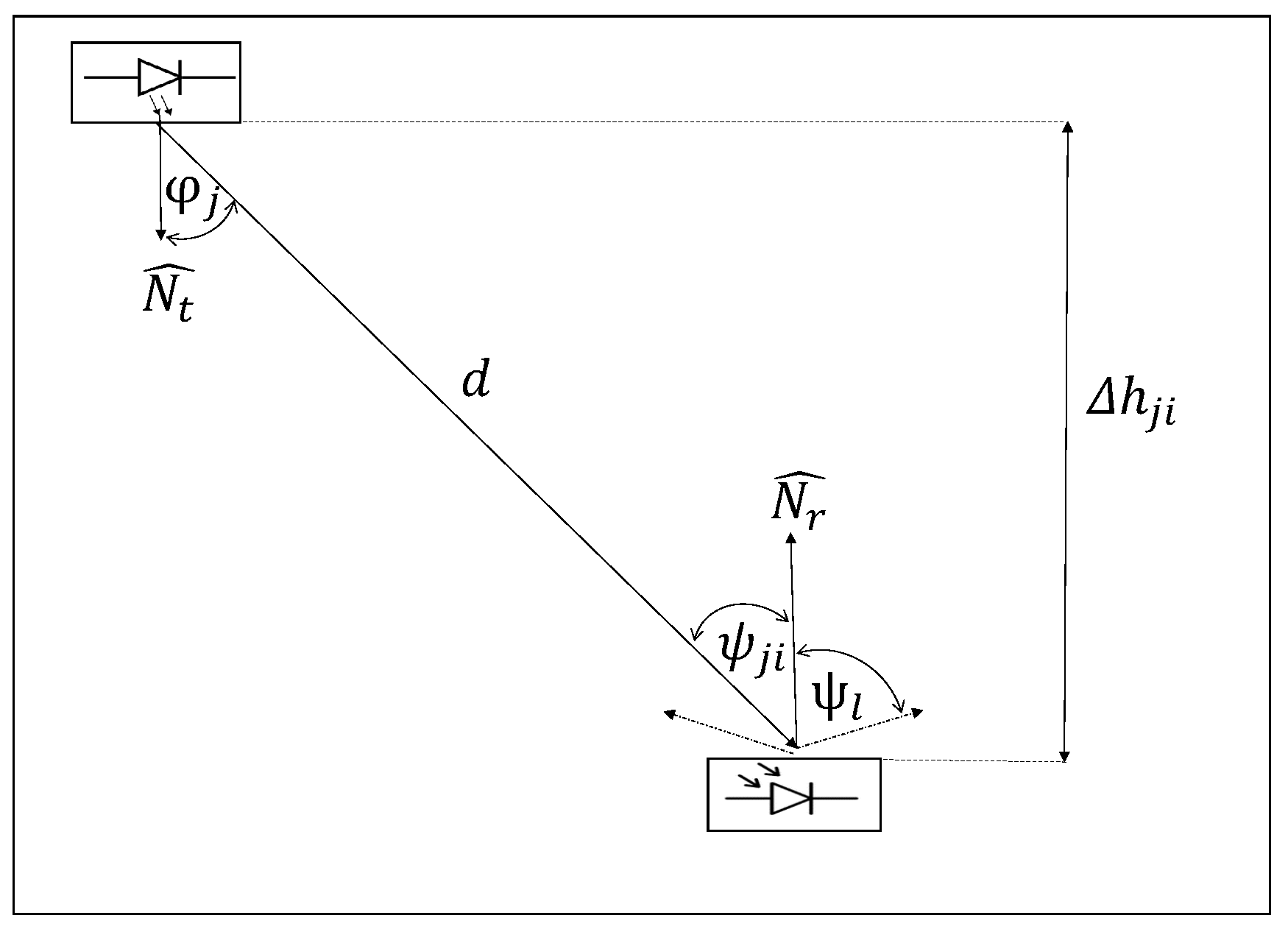
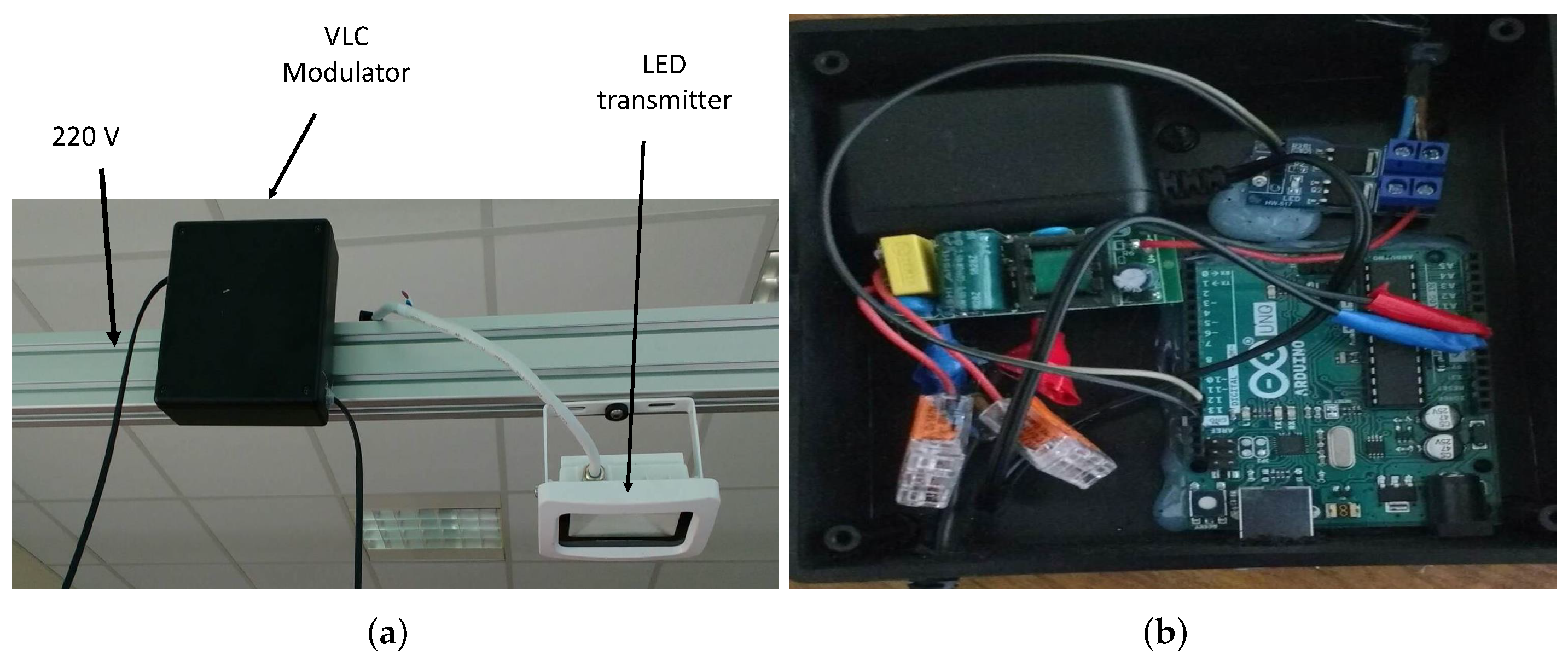
4.2. Visible Light Communication System
4.3. Single Hop Range Free Methods
4.3.1. Cell of Origin
4.3.2. Convex Position Estimation
4.3.3. Centroid
5. Results and Discussion
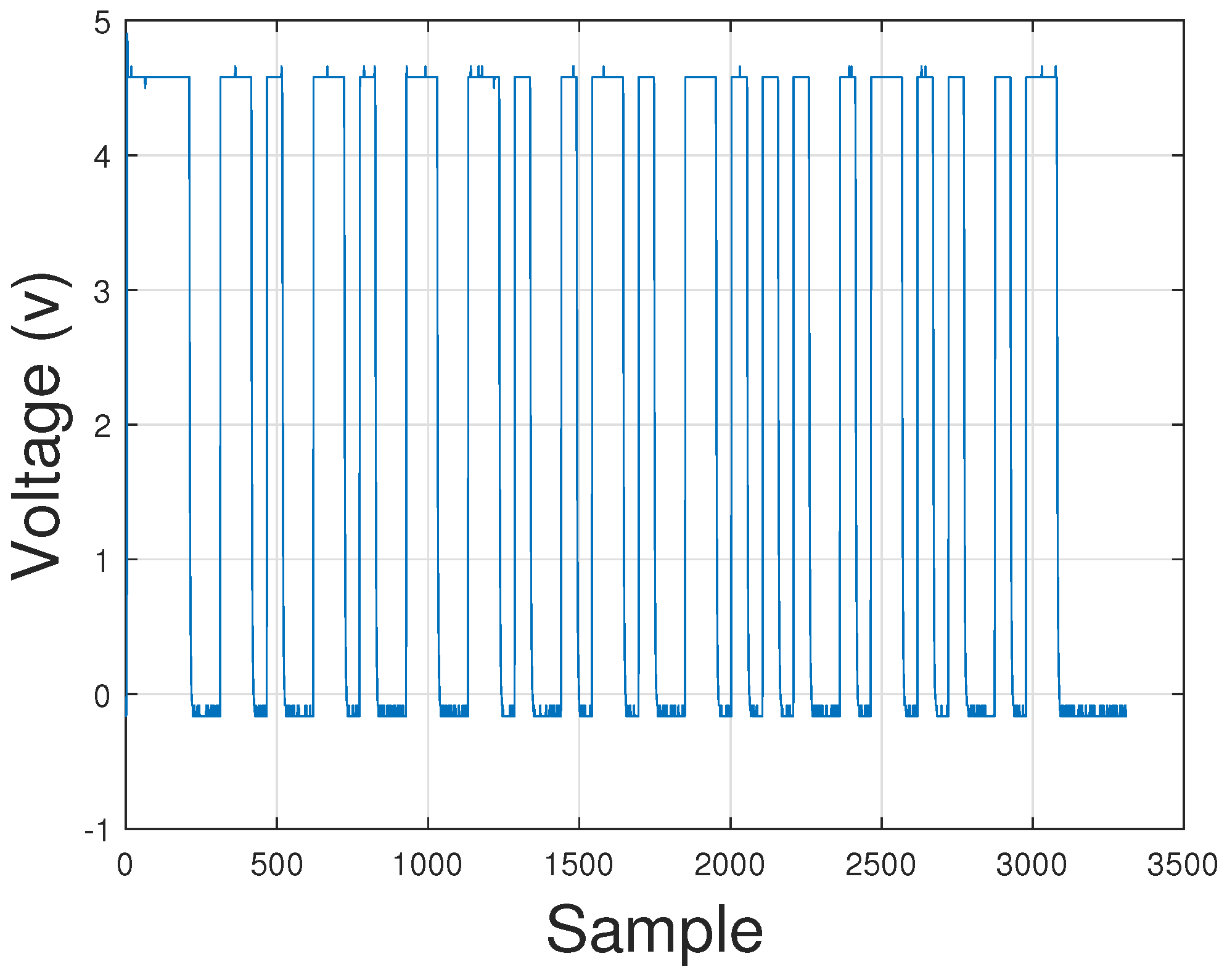
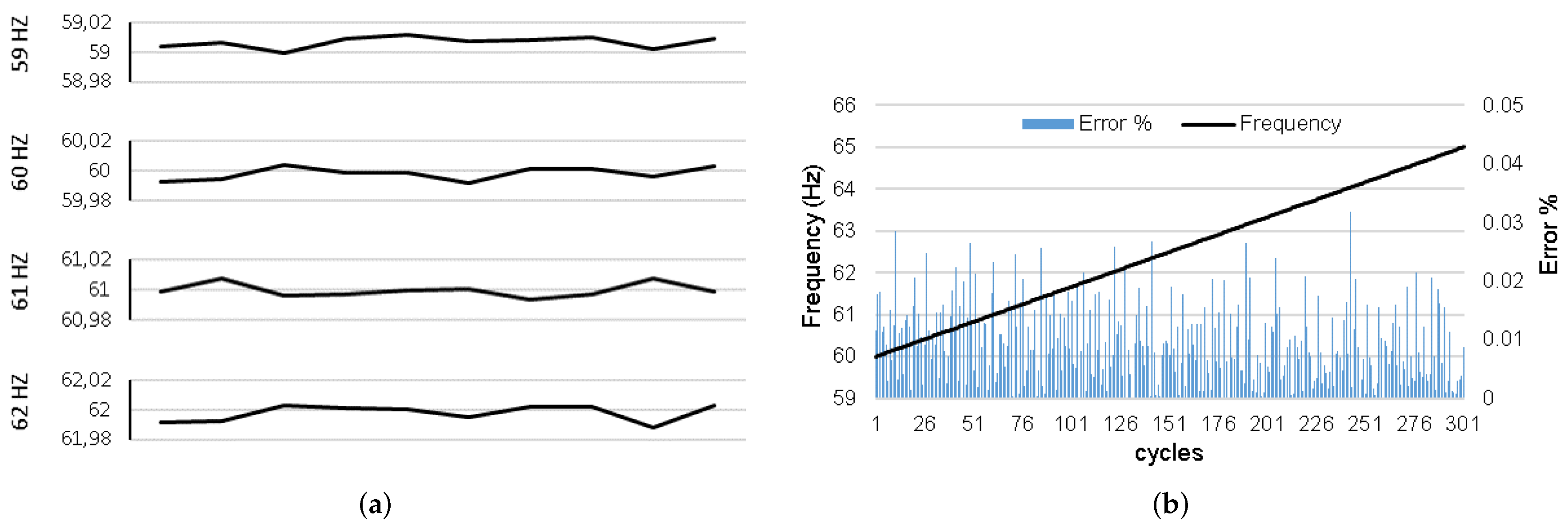
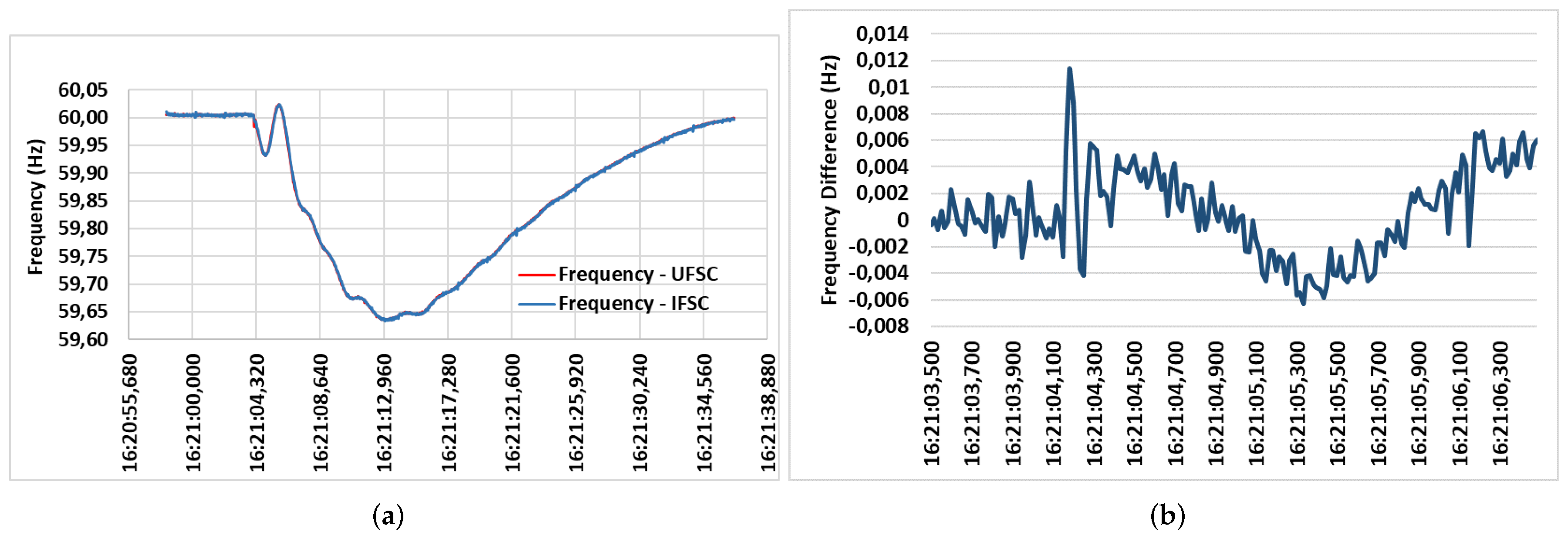
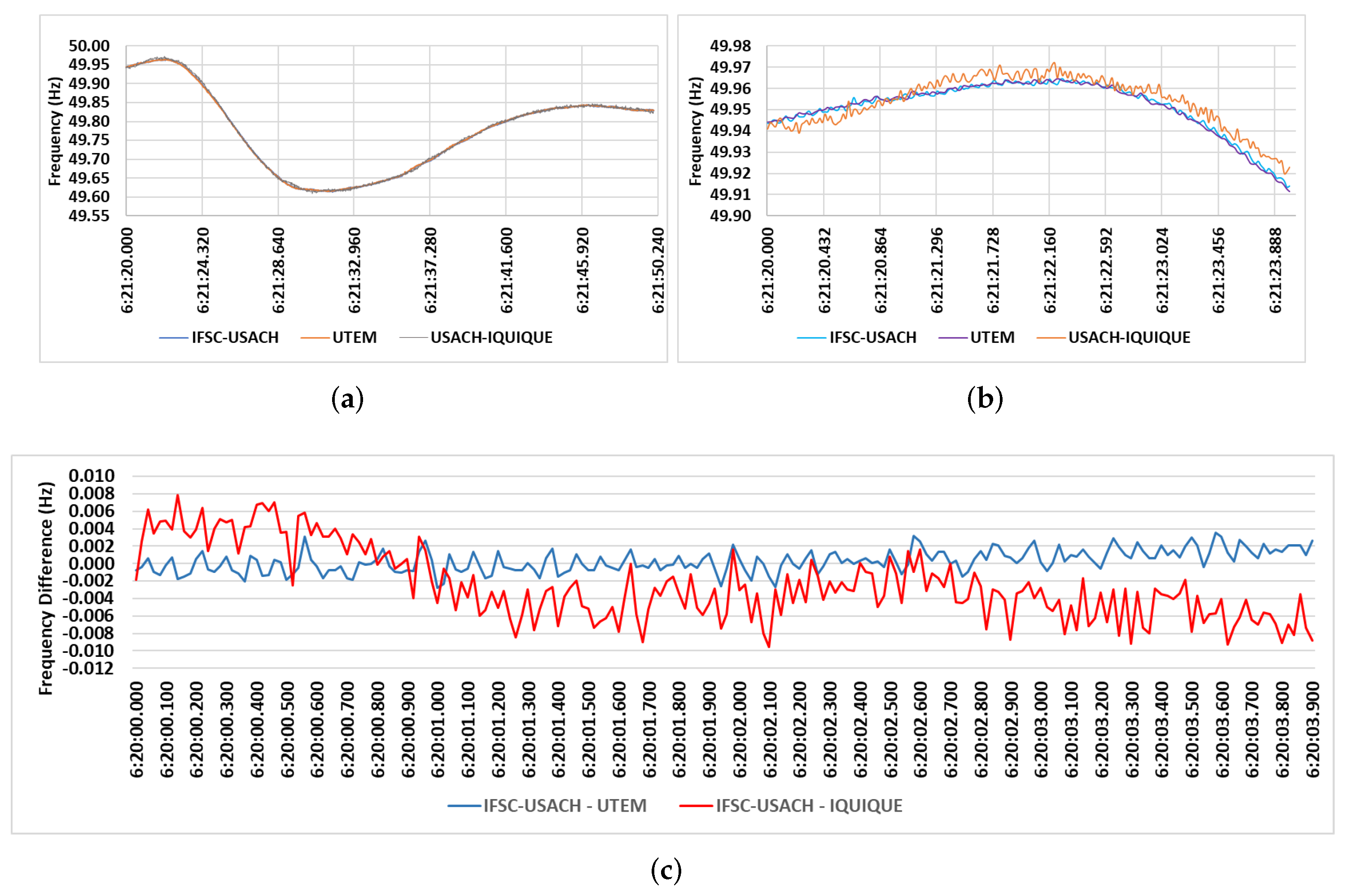
5.1. Analysis and Results of the PMU
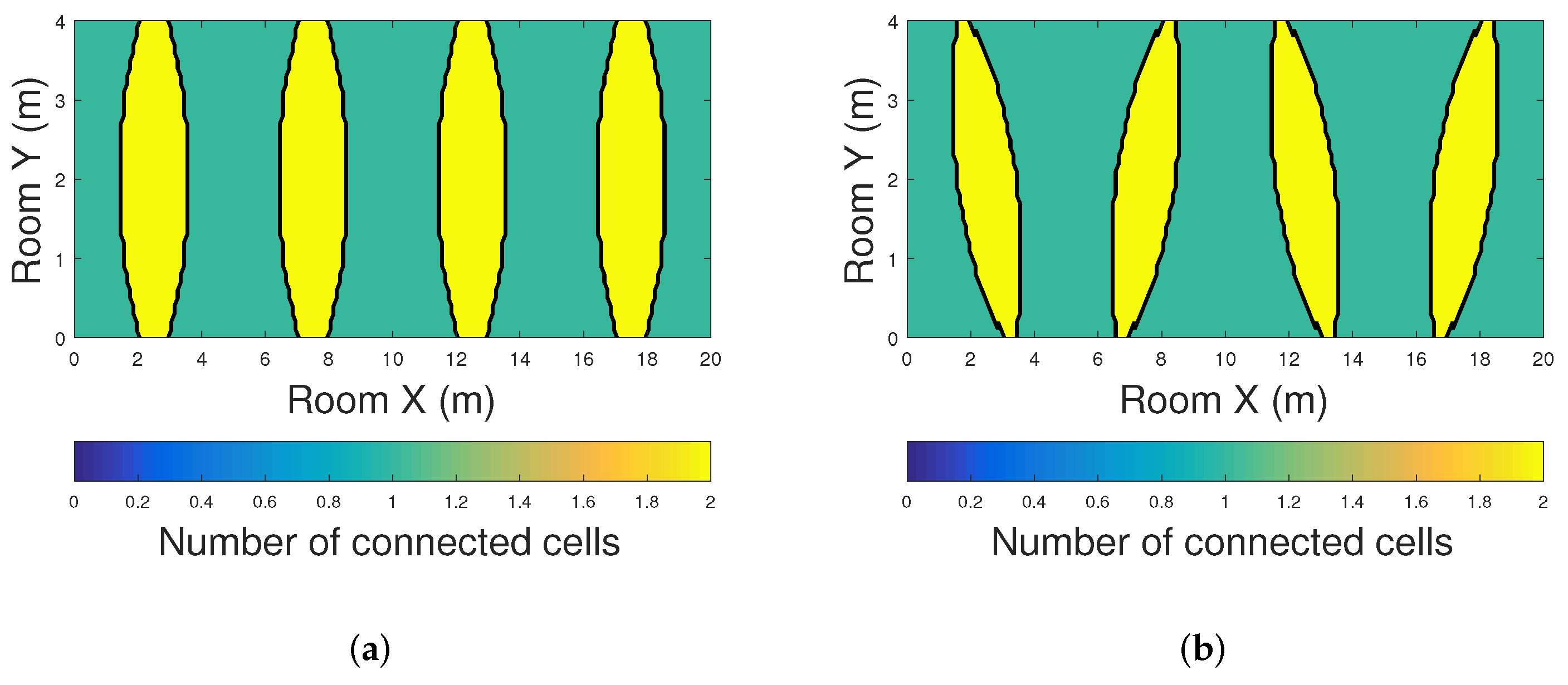
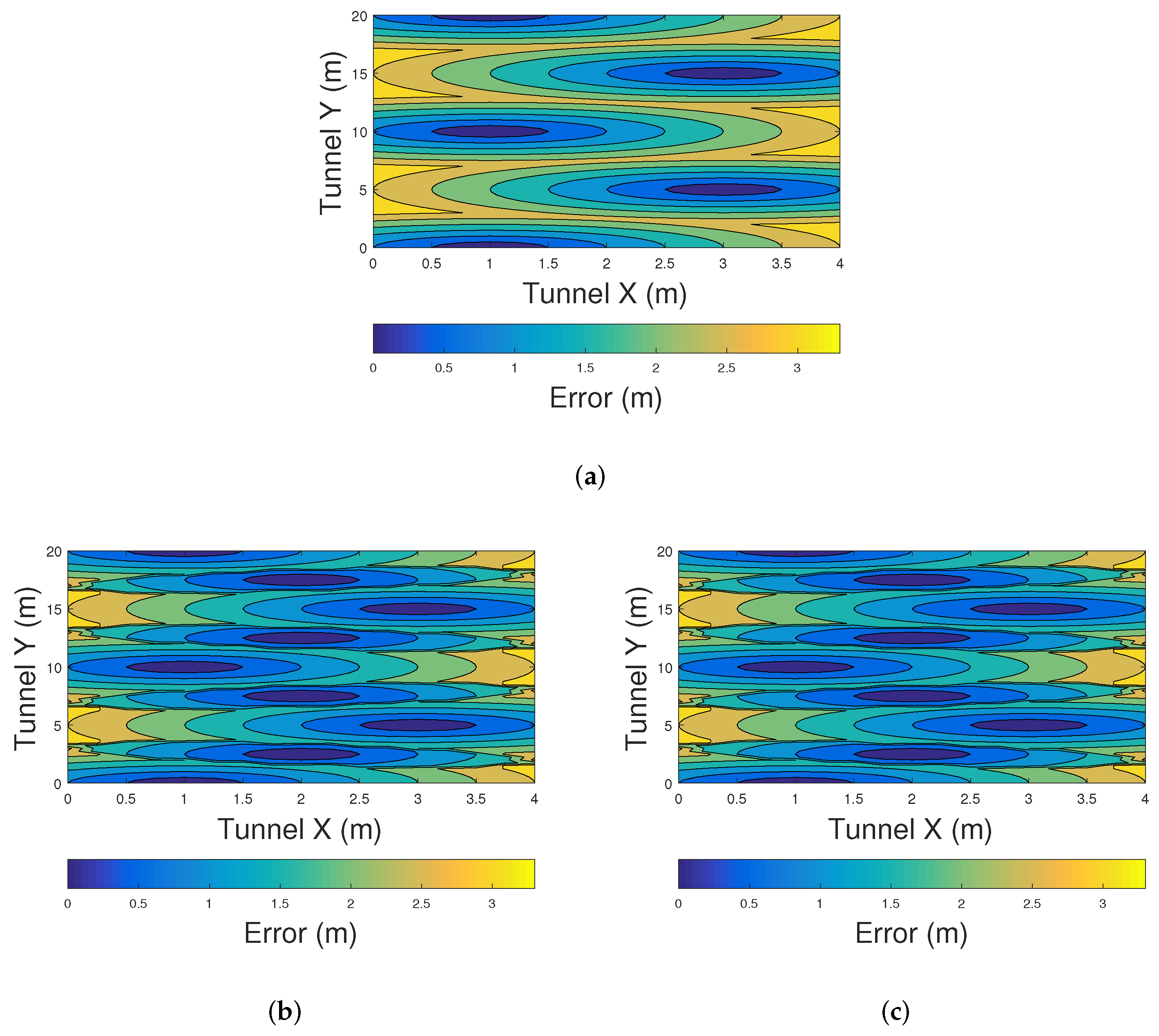
5.2. Analysis and Results for Range Free Positioning Methods
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
- “Soto, I. and Lagos, C.”, Título: “Sistema y método de comunicación a través de luz visible para túneles subterráneos”. Country: CHILE, N°: CL3778-2015.
- “Soto, I. and Lagos, C.”, Title: “System and method for communication by means of visible light for underground tunnels”. Country: USA, N°: US2019/0007143A1.
- “Soto, I. and Lagos, C.”, Title: “Sistema y método de comunicación a través de luz visible para túneles subterráneos”. Country: COLOMBIA, N°: Colombian Patent 36068.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Analogic-Digital Converter |
| COO | Cell of Origin |
| CPE | Convex Position Estimation |
| DD | Direct Detection |
| DR | Dead Reckoning |
| EPS | Electric Power System |
| FOV | Field of View |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IFSC | Federal Institute of Santa Catarina |
| IM | Intensity Modulation |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| INS | Inertial Navigation Systems |
| IR | Infrared |
| LED | Light-Emitting Diode |
| Li-Fi | Light Fidelity |
| LOS | Line of Sight |
| MF | Medium Frequency |
| OWC | Optical Wireless Communication |
| PD | Photodetector |
| PDC | Phasor Data Concentrator |
| PMU | Phasor Measurement Unit |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| Rx | Receiver |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| SHF | Super High Frequency |
| SPMS | Synchronized Phasor Measurement System |
| Tx | Transmitter |
| UFSC | University of Santa Catarina |
| UHF | Ultra High Frequency |
| USACH | University of Santiago of Chile |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
| VHF | Very High Frequency |
| VLC | Visible Light Communication |
| VLP | Visible Light Positioning |
| VSAT | Very Small Aperture Trminal |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless Fidelity |
References
- Wache, M.; Murray, D.C. Application of Synchrophasor Measurements for distribution networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–28 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Misra, S.; Xue, G.; Yang, D. Smart grid—The new and improved power grid: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 14, 944–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.N.; Zatta, J.K.; Vieira, P.C.C.; Schlichting, L.C.M. A low cost prototype of a Phasor Measurement Unit using Digital Signal Processor. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Biennial Congress of Argentina (ARGENCON 2016), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, R.N.; Cavalcante, L.H.; Zatta, J.K.; Schlichting, L.C.M. A Phasor Measurement Unit based on discrete fourier transform using digital signal processor. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON 2016), Curitiba, Brazil, 20–23 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Phadke, A.G.; Thorp, J.S. History and applications of phasor measurements. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Von Meier, A.; Culler, D.; McEachern, A.; Arghandeh, R. Micro-synchrophasors for distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.H.; Yoo, M. An in-Depth Survey of Visible Light Communication Based Positioning Systems. Sensors 2016, 16, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarkan, S.; Güzelgöz, S.; Arslan, H.; Murphy, R. Underground mine communications: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemlooy, Z.; Alves, L.N.; Zvanovec, S.; Khalighi, M.A. Visible Light Communications; Taylor & Francis Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, C.W.; Liu, Y.; Yeh, C.H.; Sung, J.Y.; Liu, Y.L. A practical in-home illumination consideration to reduce data rate fluctuation in visible light communication. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2015, 22, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, F.; Firoozabadi, A.; Adasme, P.; Soto, I.; Krommenacker, N.; Azurdia-Meza, C. A novel strategy for LED re-utilization for visible light communications. Optik 2017, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturralde, D.; Azurdia-Meza, C.; Krommenacker, N.; Soto, I.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Becerra, N. A new location system for an underground mining environment using visible light communications. In Proceedings of the 2014 9th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks & Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Manchester, UK, 23–25 July 2014; pp. 1165–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Iturralde, D.; Seguel, F.; Soto, I.; Azurdia, C.; Khan, S. A new VLC system for localization in underground mining tunnels. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2017, 15, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios Játiva, P.; Román Cañizares, M.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.A.-M.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Dehghan Firoozabadi, A.; Seguel, F.; Montejo-Sánchez, S.; Soto, I. Interference Mitigation for Visible Light Communications in Underground Mines Using Angle Diversity Receivers. Sensors 2020, 20, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borkute, A.; Padole, A. Li-Fi (Light Fidelity)—The future technology In Wireless communication. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.U.; Naeem, A.; Pasha, M.A.; Jadoon, T.; Yuen, C. Indoor Positioning Using Visible LED Lights. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 48, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzalan, M.; Jazizadeh, F. Indoor Positioning Based on Visible Light Communication. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, F.; Krommenacker, N.; Charpentier, P.; Soto, I. Visible light positioning based on architecture information: Method and performance. IET Commun. 2019, 13, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan Firoozabadi, A.; Azurdia-Meza, C.; Soto, I.; Seguel, F.; Krommenacker, N.; Iturralde, D.; Charpentier, P.; Zabala-Blanco, D. A Novel Frequency Domain Visible Light Communication (VLC) Three-Dimensional Trilateration System for Localization in Underground Mining. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguirre, D.; Firoozabadi, A.D.; Seguel, F.; Soto, I. Proposed energy based method for light receiver localization in underground mining. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Automatica (ICA-ACCA), Curico, Chile, 19–21 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentealba, D.; Soto, I.; Liu, K.; Martinez, A.J. Tracking system with VLC for underground mine using multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 First South American Colloquium on Visible Light Communications (SACVLC), Santiago, Chile, 13 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeil, R.; Pichler, M.; Schuster, S.; Hammer, F. Robust Acoustic Positioning for Safety Applications in Underground Mining. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2876–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Du, J.; Xu, D. Navigation and positioning system applied in underground driverless vehicle based on IMU. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Robots and Intelligent System (ICRIS), Changsha, China, 26–27 May 2018; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Abrudan, T.E.; Xiao, Z.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. Underground Incrementally Deployed Magneto-Inductive 3-D Positioning Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4376–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Myung, H. Resilient underground localization using magnetic field anomalies for drilling environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for Wireless Personal Area Networks. 2002. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1016473 (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- IEEE. P802.15.7/D3a, Aug 2018—IEEE Approved Draft Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Part 15.7: Short-Range Optical Wireless Communications. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8569020 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- IEEE. PC37.242/D11, Oct 2012—IEEE Approved Draft Guide for Synchronization, Calibration, Testing, and Installation of Phasor Measurement Units (PMU) for Power System Protection and Control. 2012. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6473804 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Seguel, F.; Soto, I.; Adasme, P.; Krommenacker, N.; Charpentier, P. Potential and challenges of VLC based IPS in underground mines. In Proceedings of the 2017 First South American Colloquium on Visible Light Communications (SACVLC), Santiago, Chile, 13 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Forooshani, A.E.; Bashir, S.; Michelson, D.G.; Noghanian, S. A survey of wireless communications and propagation modeling in underground mines. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1524–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G.; Lagace, R.L.; Strong, P.F. Theory of the Propagation of UHF Radio Waves in Coal Mine Tunnels. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1975, 23, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, D. VSAT Communications Networks—An Overview. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1988, 26, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C. Earthquake performance of telecommunications infrastructure in Christchurch 2010/2011. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 33rd International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 9–13 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. IEEE Standard for Synchrophasor Measurements for Power Systems IEEE Power & Energy Society. 2012. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.2011.6111219 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- IEEE. IEEE Standard for Synchrophasor Measurements for Power Systems-C37.118.1-2011. 2011. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6111219 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Barry, J.R.; Kahn, J.M.; Krause, W.J.; Lee, E.A.; Messerschmitt, D.G. Simulation of multipath impulse response for indoor wireless optical channels. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1993, 11, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komine, T.; Nakagawa, M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2004, 50, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Instruments. OPA657 1.6-GHz, Low-Noise, FET-Input Operational Amplifier. 2015. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=3&ved=2ahUKEwjeubC5t6rnAhWafXAKHaymBnMQFjACegQIAhAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.ti.com%2Flit%2Fpdf%2Fsbos197&usg=AOvVaw3u_e-TA5QsKl0xQx8zziJK (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Nordic Semiconductor. nRF905 Product Specification. 2008. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=2ahUKEwiJ6_eIt6rnAhXLUt4KHT6VCmsQFjAAegQIAxAB&url=https%3A%2F%2Finfocenter.nordicsemi.com%2Fpdf%2FnRF905_PS_v1.5.pdf&usg=AOvVaw2BjTupw1Y-NjS1-38RUDcV (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- 109th Congress. Mine Improvement and New Emergency Response. 2006. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/senate-bill/2803 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Seguel, F.; Krommenacker, N.; Charpentier, P.; Bombardier, V.; Soto, I. Convex polygon positioning for homogeneous optical wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Nantes, France, 24–27 September 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.P.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 716. [Google Scholar]
- Bulusu, N.; Heidemann, J.; Estrin, D. GPS-less low-cost outdoor localization for very small devices. IEEE Pers. Commun. 2000, 7, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, M.; Su, H.; Chen, M.; Ming, Z.; Yang, L.T. Balance of security strength and energy for a PMU monitoring system in smart grid. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, I.; Adasme, P.; San-Juan, E.; Valencia, C.; Azurdia-Meza, C. New triangular VLC cell plus protocol to uplink the data in VSAT/GPS format. In Proceedings of the IEEE CHILECON 2019, Valparaíso, Chile, 29–31 October 2019; p. 5. [Google Scholar]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soto, I.; Nilson Rodrigues, R.; Massuyama, G.; Seguel, F.; Palacios Játiva, P.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Krommenacker, N. A Hybrid VLC-RF Portable Phasor Measurement Unit for Deep Tunnels. Sensors 2020, 20, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030790
Soto I, Nilson Rodrigues R, Massuyama G, Seguel F, Palacios Játiva P, Azurdia-Meza CA, Krommenacker N. A Hybrid VLC-RF Portable Phasor Measurement Unit for Deep Tunnels. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoto, Ismael, Rafael Nilson Rodrigues, Gabriel Massuyama, Fabian Seguel, Pablo Palacios Játiva, Cesar A. Azurdia-Meza, and Nicolas Krommenacker. 2020. "A Hybrid VLC-RF Portable Phasor Measurement Unit for Deep Tunnels" Sensors 20, no. 3: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030790
APA StyleSoto, I., Nilson Rodrigues, R., Massuyama, G., Seguel, F., Palacios Játiva, P., Azurdia-Meza, C. A., & Krommenacker, N. (2020). A Hybrid VLC-RF Portable Phasor Measurement Unit for Deep Tunnels. Sensors, 20(3), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030790