Depth Density Achieves a Better Result for Semantic Segmentation with the Kinect System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
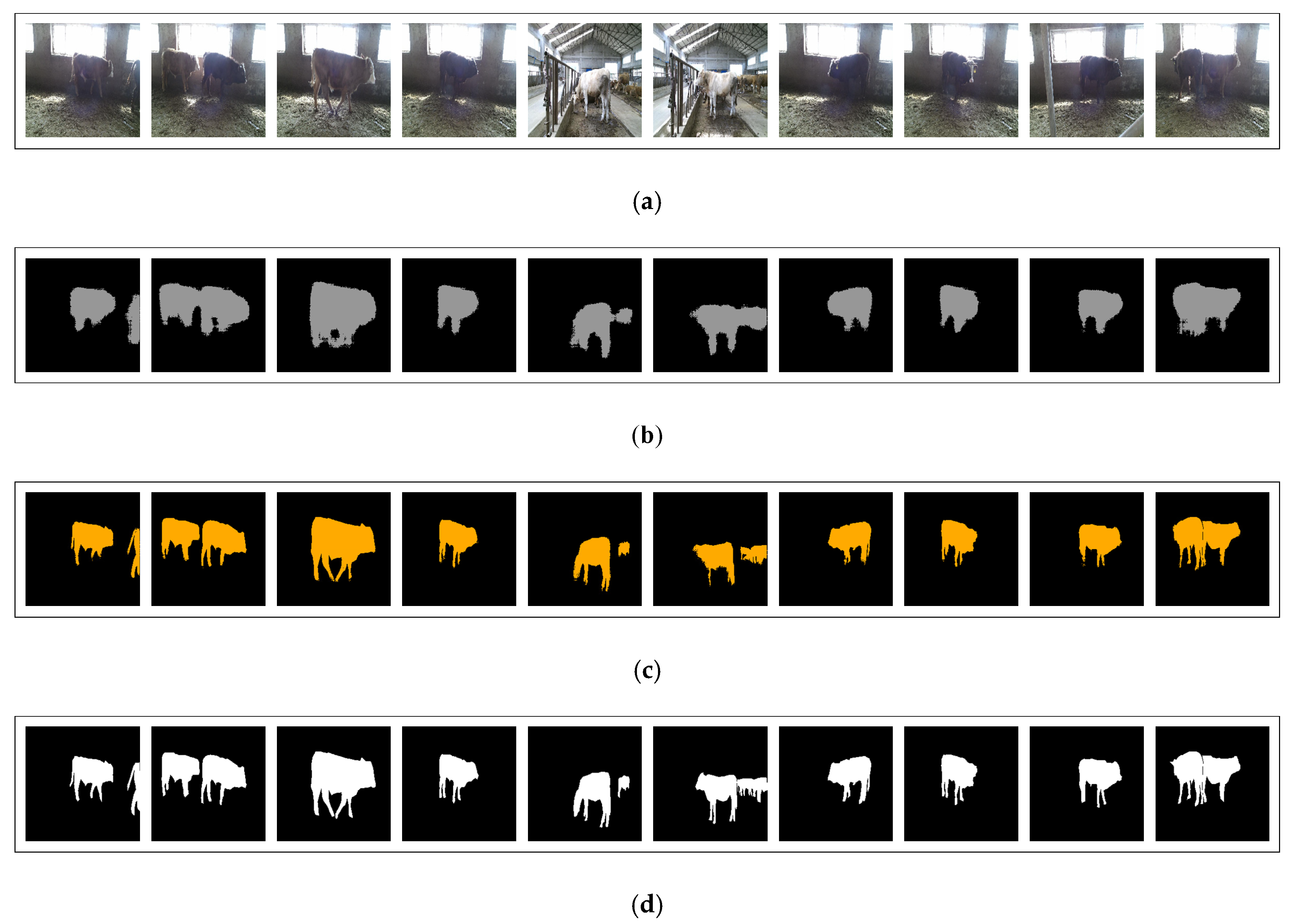
2.1. Experimental Materials and Setup
2.2. Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN) and up-Sampling
2.3. Depth Density
- The average depth of , and
- The depth distribution of the central pixel and its adjacent pixels in .
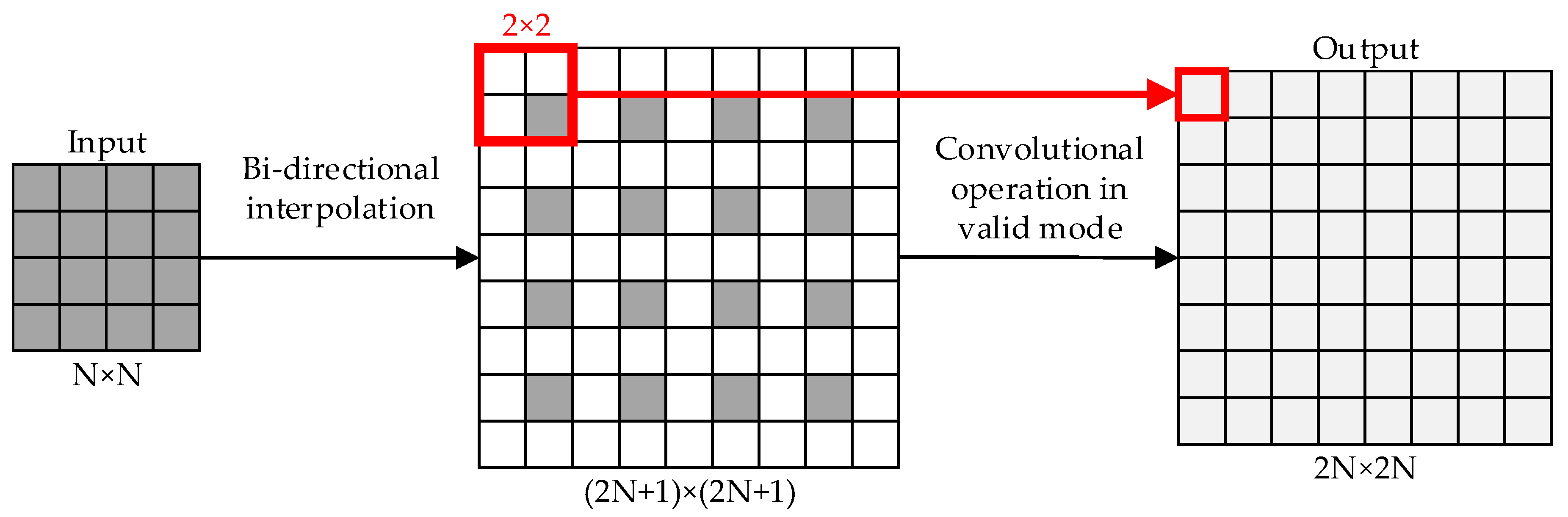
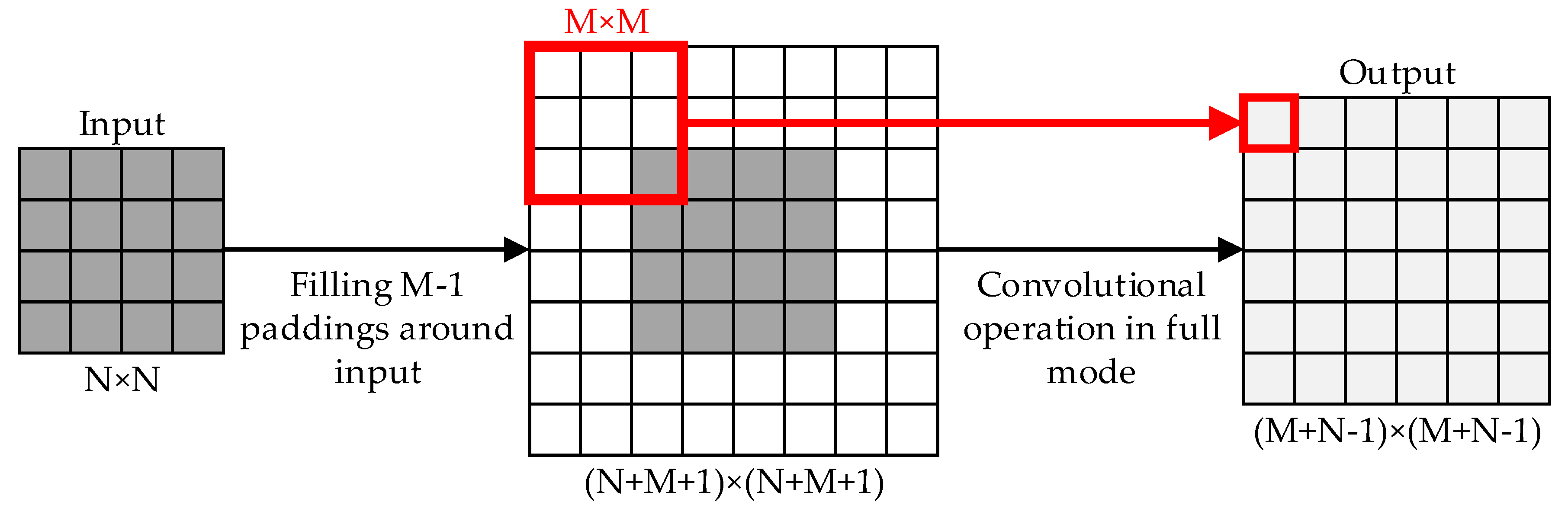
2.4. Analysis and Improvement of Depth Density
3. Results
3.1. Training of FCN
3.2. Metrics of Semantic Segmentation
3.3. The Improvement of Semantic Segmentation by Depth Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johannsen, W. The genotype conception of heredity. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schork, N.J. Genetics of complex disease: Approaches, problems, and solutions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebner, H.R.; Callicott, J.H.; Sommer, T. From the genome to the phenome and back: Linking genes with human brain function and structure using genetically informed neuroimaging. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilder, R.M.; Sabb, F.W.; Cannon, T.D. Phenomics: The systematic study of phenotypes on a genome-wide scale. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houle, D.; Govindaraju, D.R.; Omholt, S. Phenomics: The next challenge. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furbank, R.T.; Tester, M. Phenomics-technologies to relieve the phenotyping bottleneck. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.W.; Andrade, S.P.; Gore, M.A. Field-based phenomics for plant genetics research. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 133, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlgren, N.; Gehan, M.A.; Baxter, I. Lights, camera, action: High-throughput plant phenotyping is ready for a close-up. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 24, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorani, F.; Schurr, U. Future scenarios for plant phenotyping. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, A.; Bostrom, A.G.; Ball, J. Combining computer vision and deep learning to enable ultra-scale aerial phenotyping and precision agriculture: A case study of lettuce production. Horticult. Res. 2019, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mochida, K.; Koda, S.; Inoue, K. Computer vision-based phenotyping for improvement of plant productivity: A machine learning perspective. Gigascience 2019, 8, giy153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prey, L.; Von, B.M.; Schmidhalter, U. Evaluating RGB imaging and multispectral active and hyperspectral passive sensing for assessing early plant vigor in winter wheat. Sensors 2018, 18, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, L.R.; Bao, Y.; Tang, L. Automated morphological traits extraction for sorghum plants via 3D point cloud data analysis. Comp. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.O.; Liu, M.; Ma, X.D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of soybean canopies using multisource imaging for phenotyping analysis. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.J.; Xu, L.B.; Shi, S.G. A high throughput integrated hyperspectral imaging and 3D measurement system. Sensors 2018, 19, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.L.; Zhao, D.Z.; Huang, M. Image segmentation and bias correction using local inhomogeneous intensity clustering (LINC): A region-based level set method. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, T.; Wang, P.; Lee, S.H. Image compression with meanshift based inverse colorization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–14 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. Contour-aware network for semantic segmentation via adaptive depth. Neurocomputing 2018, 284, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.K.; Chang, T.; Li, S. Scene-aware deep networks for semantic segmentation of images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 69184–69193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Qiu, G.P. Integrating low-level and semantic features for object consistent segmentation. Neurocomputing 2013, 119, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.Q. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.S.; Qian, L.D.; Liang, D.; Wan, M.Z. Self-adversarial training and attention for multi-task wheat phenotyping. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Yang, C.K.; Tsai, M.J.; Kuo, Y.F. Identifying Fagaceae species in Taiwan using leaf images. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.G.; Moon, H.; Kwak, J.T. Deep convolutional neural network for classifying Fusarium Wilt of Radish from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 042621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milioto, A.; Lottes, P.; Stachniss, C. Real-time Blob-Wise Sugar Beets vs Weeds classification for monitoring fields using convolutional neural networks. ISPRS 2017, 4, W3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.Q.; He, K.M.; Girshick, R. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Omid, G.; Thomas, B.; Khalid, G.; Sansar, R.M.; Dirk, T.; Jagannath, A. Evaluation of different machine learning methods and deep-learning convolutional neural networks for landslide detection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.M. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zou, J.H.; He, K.M. Very deep convolutional neural networks for classification and detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2014. Available online: http://image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/2014/ (accessed on 19 January 2014).
- Lin, T.Y.; Roy, C.A.; Maji, S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shou, Z.; Chan, J.; Zareian, A. CDC: Convolutional-de-convolutional networks for precise temporal action localization in untrimmed videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]



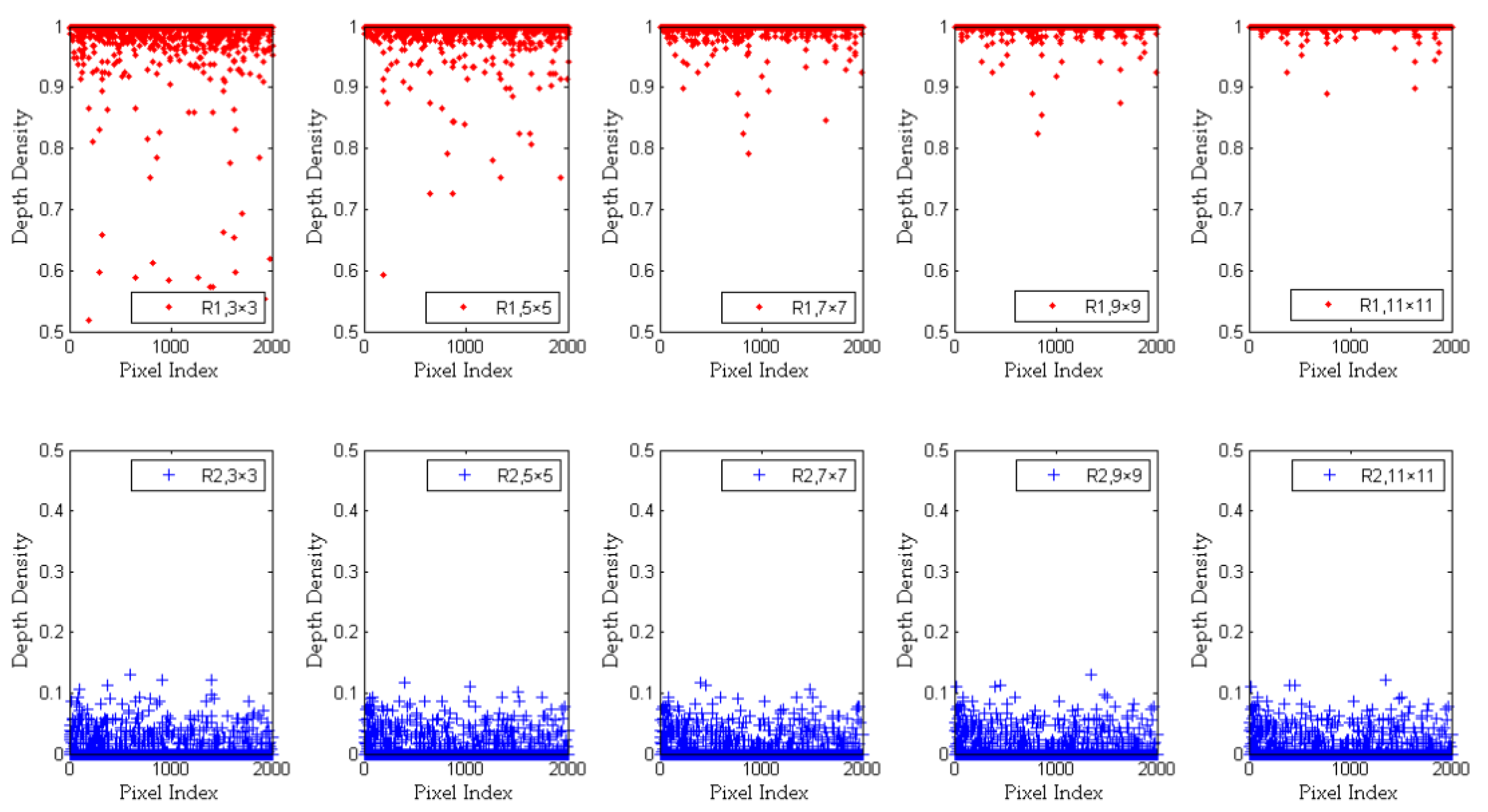



| The Value of s | Time Cost (s) |
|---|---|
| s = 3 | 16 |
| s = 5 | 37 |
| s = 7 | 69 |
| s = 9 | 111 |
| s = 11 | 163 |
| Results of Method | pa 1 | ma 2 | mIU 3 | f.w.IU 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN-8s | 0.963 | 0.961 | 0.857 | 0.935 |
| Depth density | 0.991 | 0.964 | 0.955 | 0.982 |
| Increment | 2.9% | 0.3% | 11.4% | 5.02% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, H.; Xu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, T. Depth Density Achieves a Better Result for Semantic Segmentation with the Kinect System. Sensors 2020, 20, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030812
Deng H, Xu T, Zhou Y, Miao T. Depth Density Achieves a Better Result for Semantic Segmentation with the Kinect System. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030812
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Hanbing, Tongyu Xu, Yuncheng Zhou, and Teng Miao. 2020. "Depth Density Achieves a Better Result for Semantic Segmentation with the Kinect System" Sensors 20, no. 3: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030812
APA StyleDeng, H., Xu, T., Zhou, Y., & Miao, T. (2020). Depth Density Achieves a Better Result for Semantic Segmentation with the Kinect System. Sensors, 20(3), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030812




