Highly Selective Electrochemiluminescence Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted-quantum Dots for the Sensitive Detection of Cyfluthrin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Fabrication of MIP-QDs
2.4. Fabrication of the Nafion-MWCNTs/MIP-QDs/GCE
2.5. ECL Measurement
2.6. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
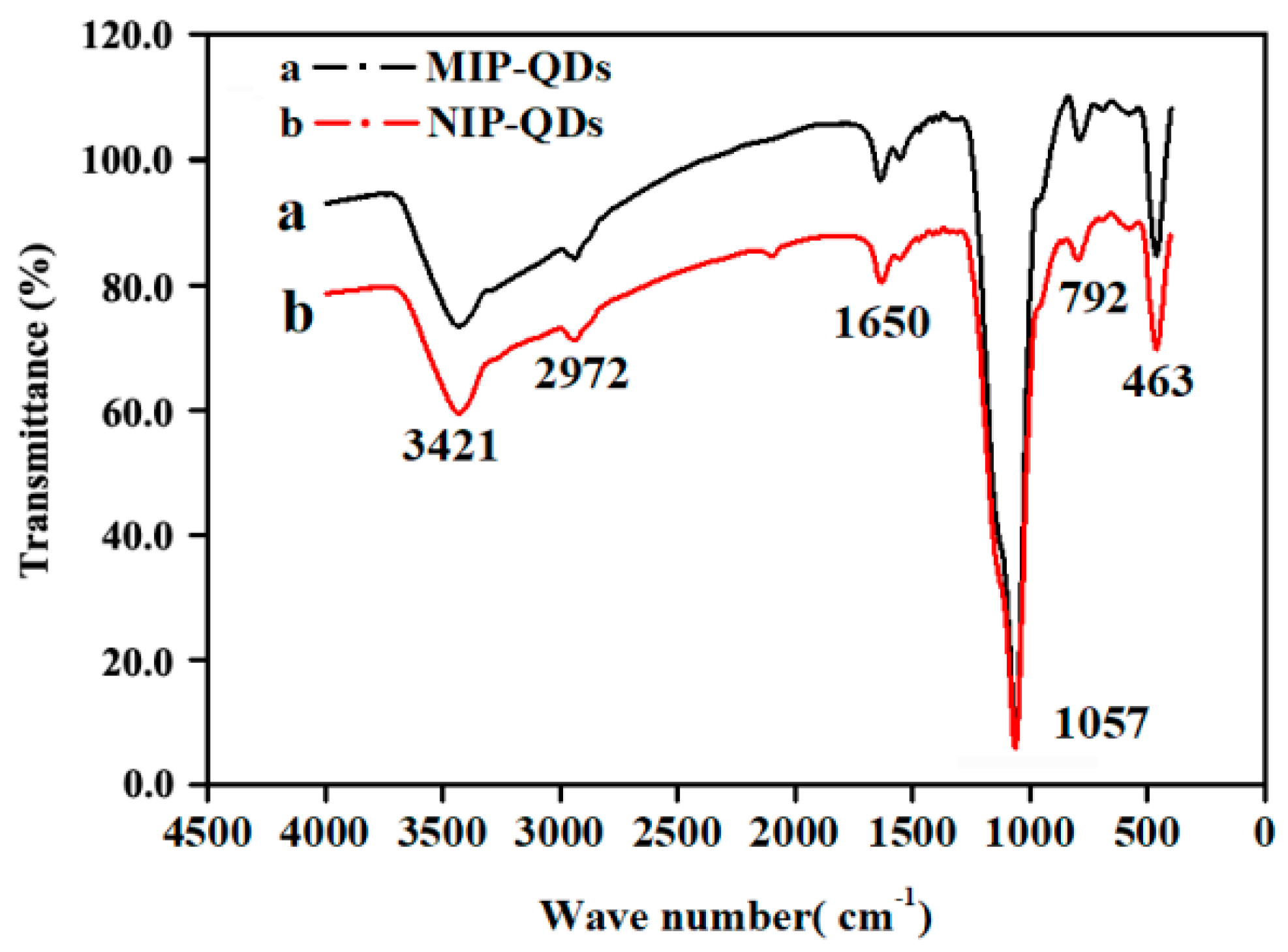
3.1. Characterization of MIP-CdSe-QDs
3.2. ECL Behavior and Mechanism of the MIECL Sensor
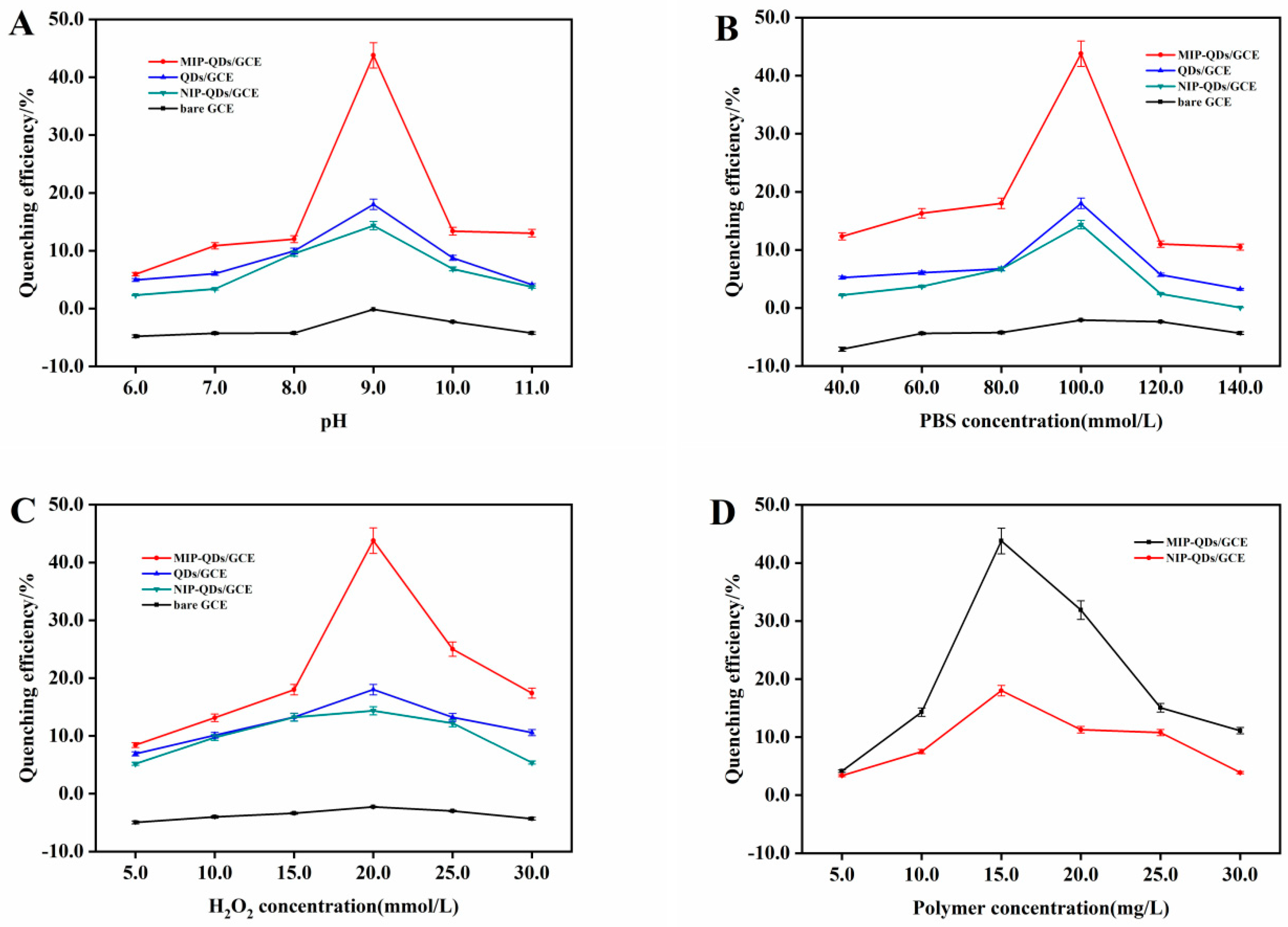
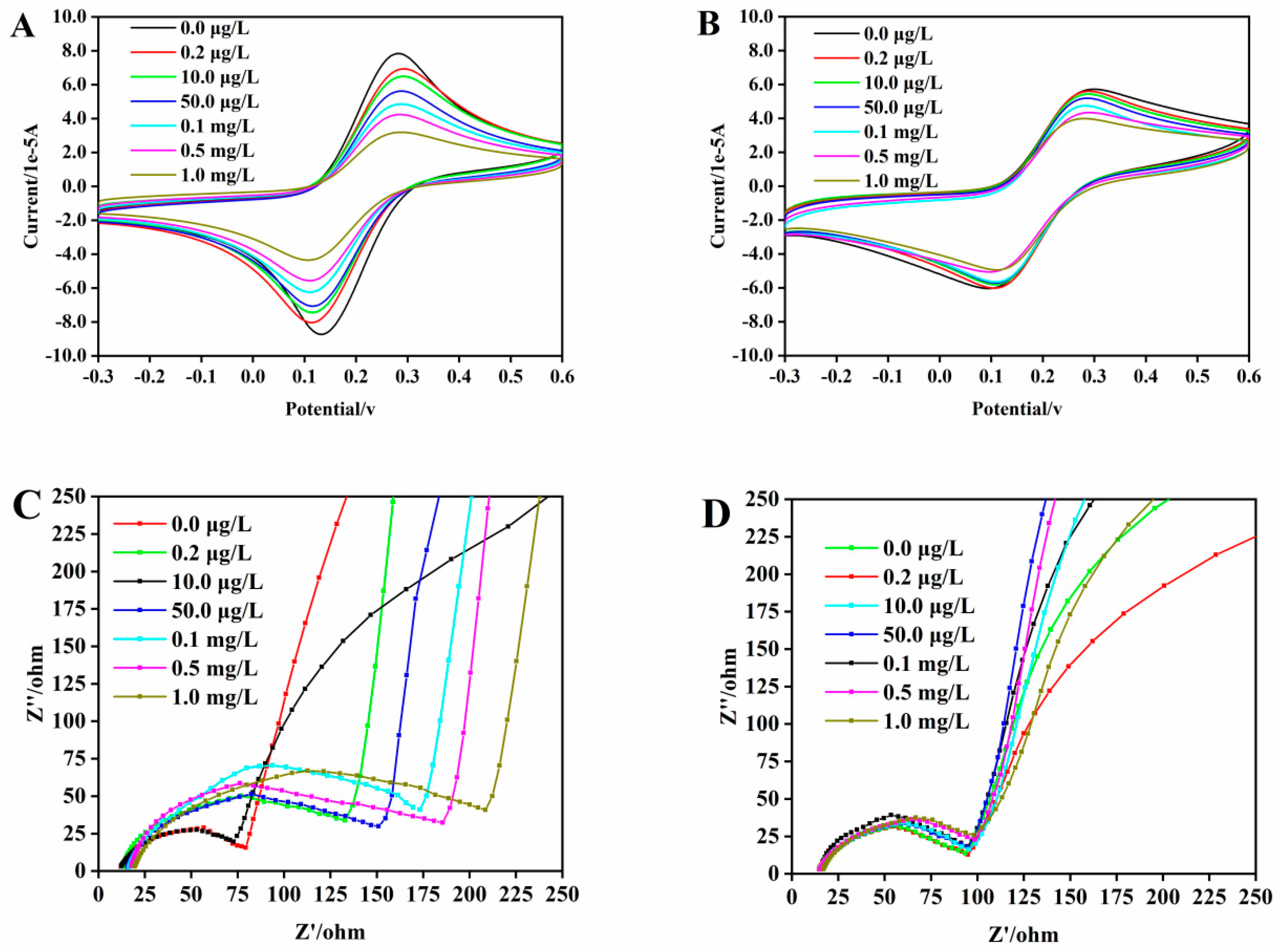
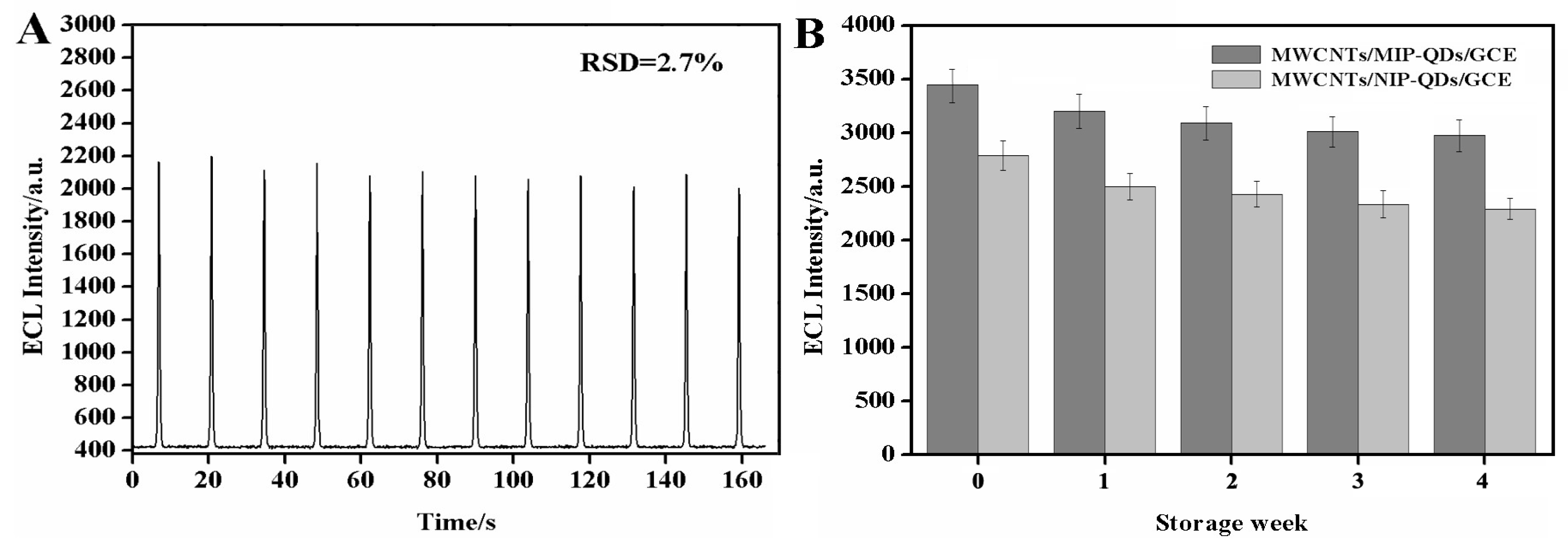
3.3. Optimization of the MIECL Sensor Conditions
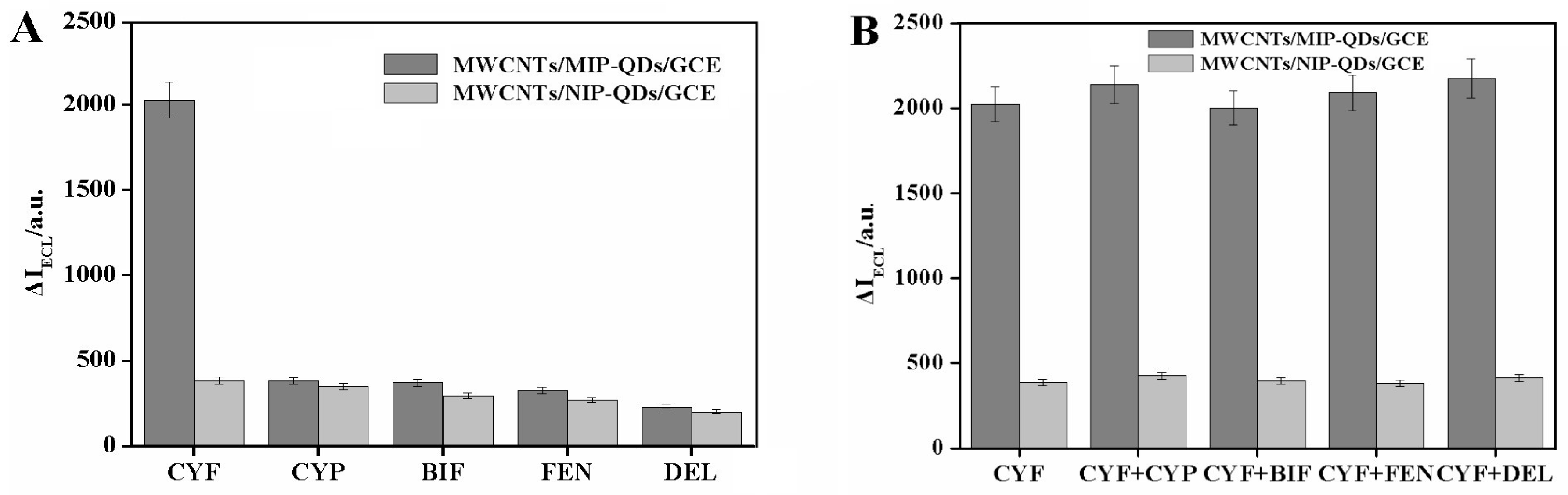
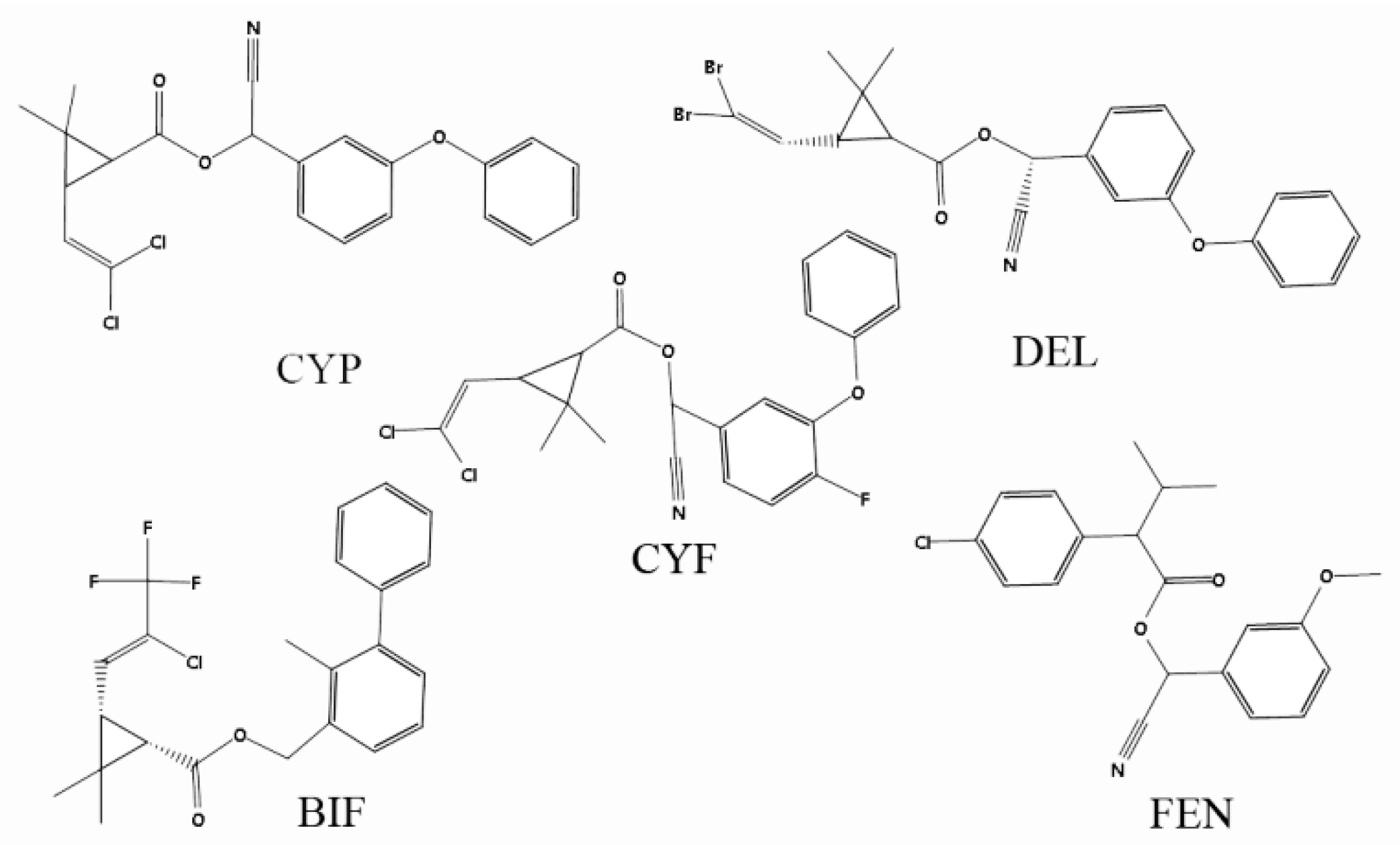
3.4. Selectivity Evaluation of the Developed MICEL Sensor
3.5. Application of the MIECL Sensor in the Fish and Seawater Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, G.P.; Zhao, Y.; Song, F.Q.; Liu, B. Isolation, identification and cyfluthrin-degrading potential of a novel Lysinibacillus sphaericus strain, FLQ-11-1. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, W.; Tiefenthaler, L.; Greenstein, D.J.; Maruya, K.A.; Bay, S.M.; Ritter, K.; Schiff, K. Pyrethroids in southern california coastal sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.F.; Ross, D.G.; Starr, J.M.; Scollon, E.J.; Wolansky, M.J.; Crofton, K.M.; Devito, M.J. Environmentally relevant pyrethroid mixtures: A study on the correlation of blood and brain concentrations of a mixture of pyrethroid insecticides to motor activity in the rat. Toxicology 2016, 359, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmet, Y.; Eyyup, R.; Mustafa, C. The effects of cyfluthrin on some biomarkers in the liver and kidney of Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4747–4752. [Google Scholar]
- Brander, S.M.; Gabler, M.K.; Fowler, N.L.; Connon, R.E.; Schlenk, D. Pyrethroid pesticides as endocrine disruptors: Molecular mechanisms in vertebrates with a focus on fishes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8977–8992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, J.; Peruga, A.; Pitarch, E.; Lopez, F.J.; Hernandez, F. Application of solid-phase microextraction for the determination of pyrethroid residues in vegetable samples by GC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.G.; Kurz, M.H.S.; Guimarães, M.C.M.; Martins, M.L.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R.; Ribeiro, J.N.S.; Gonçalves, F.F. Development and validation of a method for the analysis of pyrethroid residues in fish using GC–MS. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, A.; Randhawa, M.A.; Javed, M.S.; Muhammad, Z.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Murtaza, S. Dietary intake assessment of pyrethroid residues from okra and eggplant grown in peri-urban areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabot, C.; Fieu, M.; Giroud, B.; Buleté, A.; Casabianca, H.; Vulliet, E. Trace-level determination of pyrethroid, neonicotinoid and carboxamide pesticides in beeswax using dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Solanki, P.R.; Ansari, A.A.; Malhotra, B.D.; Ahmad, S. Iron oxide-chitosan hybrid nanobiocomposite based nucleic acid sensor for pyrethroid detection. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 46, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babamiri, B.; Salimi, A.; Hallaj, R. A molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for ultrasensitive HIV-1 gene detection using EuS nanocrystals as luminophore. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babamiri, B.; Salimi, A.; Hallaj, R.; Hasanzadeh, M. Nickel nanoclusters as a novel emitter for molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence based sensor toward nanomolar detection of creatinine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G. Electrochemiluminescent functional nucleic acids-based sensors for food analysis. Luminescence 2019, 34, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dennany, L.; Gerlach, M.; O’Carroll, S.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J.; Bertoncello, P. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensing properties of water soluble core-shell CdSe/ZnS quantum dots/Nafion composite films. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13984–13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, W.J.; Choi, J.P.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence 69: The Tris(2,2‘-bipyridine)ruthenium(II), (Ru(bpy)32+)/Tri-n-propylamine (TPrA) system revisited A new route involving TPrA •+ Cation Radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14478–14485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Fang, G.; Pan, M.; Yang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, S. A molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor based on upconversion nanoparticles enhanced by electrodeposited rGO for selective and ultrasensitive detection of clenbuterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 102, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, E. Recent advances based on nanomaterials as electrochemiluminescence probes for the fabrication of sensors. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Quinn, B.M.; Haram, S.K.; Pell, L.E.; Korgel, B.A.; Bard, A.J. Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 2002, 296, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenti, G.; Rampazzo, E.; Kesarkar, S.; Genovese, D.; Fiorani, A.; Zanut, A.; Palomba, F.; Marcaccio, M.; Paolucci, F.; Prodi, L. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from metal complexes-based nanoparticles for highly sensitive sensors applications. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2018, 367, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chullasat, K.; Nurerk, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Davis, F.; Bunkoed, O. A facile optosensing protocol based on molecularly imprinted polymer coated on CdTe quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective amoxicillin detection. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 254, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, J.; Khataee, A.; Oskoei, Y.M.; Fattahi, H.; Bagheri, N. Selective chemiluminescence method for the determination of trinitrotoluene based on molecularly imprinted polymer-capped ZnO quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10659–10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, S.; Nguyen, P.; D’Alton, L.; Hogan, C.F. Electrochemiluminescence energy transfer in mixed iridium-based redox copolymers immobilised as nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 313, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tao, H.; Li, J. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical luminescence sensor based on enzymatic amplification for ultratrace isoproturon determination. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Jiao, H.F.; Shi, X.Z.; Sun, A.L.; Wang, X.J.; Chai, J.Y.; Li, D.X.; Chen, J. Development and application of a novel fluorescent nanosensor based on FeSe quantum dots embedded silica molecularly imprinted polymer for the rapid optosensing of cyfluthrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 99, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.S.; Yan, J.B.; Hussin, T.; Liu, J.Y. Nafion-AC-based asymmetric capacitive deionization. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 225, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.T.; Shi, X.Z.; Jiao, H.F.; Sun, A.L.; Ding, H.; Zhang, R.R.; Pan, D.D.; Li, D.X.; Chen, J. Selective and sensitive determination of cypermethrin in fish via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-like method based on molecularly imprinted artificial antibody-quantum dot optosensing materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.C.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Quantum Dots: Electrochemiluminescent and photoelectrochemical bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9520–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Yan, K.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.R. A highly sensitive photoelectrochemical sensor for 4-aminophenol based on CdS-graphene nanocomposites and molecularly imprinted polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.T.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.P.; Sun, X.Y. A urea electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted chitosan film doping with CdS quantum dots. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 426, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Mao, L.; Liu, Z.; Su, H.; Yuan, S. Electrochemiluminescence sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes doped polyvinyl butyral film containing Ru(bpy)32+ as chemiluminescence reagent. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.Z.; Ju, H.X. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from a CdSe nanocrystal film and its sensing application in aqueous solution. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6871–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, T.; Amjadi, S. A tryptophan assay based on the glassy carbon electrode modified with a nano-sized tryptophan-imprinted polymer and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4493–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.Q.; Kitazumi, Y.; Shirai, O.; Kano, K. Enhanced direct electron transfer-type bioelectrocatalysis of bilirubin oxidase on negatively charged aromatic compound-modified carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 763, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, P.Z.; Mao, C.J.; Niu, H.L.; Jin, B.K.; Zhang, S.Y. Multifunctional reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/Fe3O4/CdSe nanocomposite for electrochemiluminescence immunosensor. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 190, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noipa, T.; Martwiset, S.; Butwong, N.; Tuntulani, T.; Ngeontae, W. Enhancement of the fluorescence quenching efficiency of DPPH• on colloidal nanocrystalline quantum dots in aqueous micelles. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, G.; He, X.; Zhou, C.; Ya, D.; Feng, J.; Yu, C.; Deng, B. Sensitive detection of hydroquinone based on electrochemiluminescence energy transfer between the exited ZnSe quantum dots and benzoquinone. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 266, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Zare, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Tavana, B. A new molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensor for monitoring 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) in natural waters and soil samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zeng, J.L.; Liu, J.H.; Deng, Q.; Fan, J.B.; Xiang, J.N. A novel fluorescent probe for copper ions based on polymer-modified CdSe/CdS core/shell quantum dots. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, S. Electrochemiluminescent graphene quantum dots enhanced by MoS2 as sensing platform: A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid assay. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 228, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Pan, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X. A precise and efficient detection of Beta-Cyfluthrin via fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymers with ally fluorescein as functional monomer in agricultural products. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.H.; Chen, L.G. Quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymer as fluorescence probe for detection of cyphenothrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Hao, T.F.; Xu, Y.Q.; Lu, K.; Li, H.J.; Yan, Y.S.; Zhou, Z.P. Facile polymerizable surfactant inspired synthesis of fluorescent molecularly imprinted composite sensor via aqueous CdTe quantum dots for highly selective detection of λ-cyhalothrin. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 224, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, E.; Shi, W.; Yan, Y. A lanthanide complex-based molecularly imprinted luminescence probe for rapid and selective determination of λ-cyhalothrin in the environment. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 6141–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Added (μg/kg, L) | Found (μg/kg, L) | RSD (%) (n = 3) | Recovery (%) (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 | 9.32 | 3.6 | 93.2 | |
| Fish | 20.0 | 19.72 | 3.2 | 98.6 |
| 50.0 | 47.87 | 2.2 | 95.7 | |
| 1.0 | 0.86 | 1.5 | 86.0 | |
| Seawater | 2.0 | 1.76 | 2.5 | 88.0 |
| 5.0 | 4.92 | 4.1 | 98.4 |
| Detection Method | Target Object | Linear Range (µg/kg, L) | LOD (µg/kg, L) | Recovery (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2-MPTMS @FMIPs | Beta-Cyfluthrin | 4.6–36.0 | 4.55 | 103.8–111.8 | [40] |
| Inorganic-organic MIP-coated QDs | Cyphenothrin | 37.5–3.0 × 104 | 3.40 | 88.5–97.1 | [41] |
| MIPs-OVDAC/CdTe QDs | λ-Cyhalothrin | 45.0–7.2 × 103 | 13.5 | 97.3–105.5 | [42] |
| MIP on FeSe QDs | Cyfluthrin | 10.0–2.0 × 102 | 1.00 | 88.0–113.9 | [24] |
| Dy(III)@SiO2@MIPs | λ-cyhalothrin | 4.5 × 103–4.5 × 105 | 719.7 | 102.7–107.9 | [43] |
| Nafion-MWCNTs/MIP-CdSe QDs | Cyfluthrin | 0.2–1.0 × 103 | 0.05 | 86.0–98.6 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Sun, A.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X. Highly Selective Electrochemiluminescence Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted-quantum Dots for the Sensitive Detection of Cyfluthrin. Sensors 2020, 20, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030884
Xu J, Zhang R, Liu C, Sun A, Chen J, Zhang Z, Shi X. Highly Selective Electrochemiluminescence Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted-quantum Dots for the Sensitive Detection of Cyfluthrin. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030884
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jinjin, Rongrong Zhang, Chenxi Liu, Aili Sun, Jiong Chen, Zeming Zhang, and Xizhi Shi. 2020. "Highly Selective Electrochemiluminescence Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted-quantum Dots for the Sensitive Detection of Cyfluthrin" Sensors 20, no. 3: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030884
APA StyleXu, J., Zhang, R., Liu, C., Sun, A., Chen, J., Zhang, Z., & Shi, X. (2020). Highly Selective Electrochemiluminescence Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted-quantum Dots for the Sensitive Detection of Cyfluthrin. Sensors, 20(3), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030884





