Analysis and Correction of the Magnetometer’s Position Error in a Cross-Shaped Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
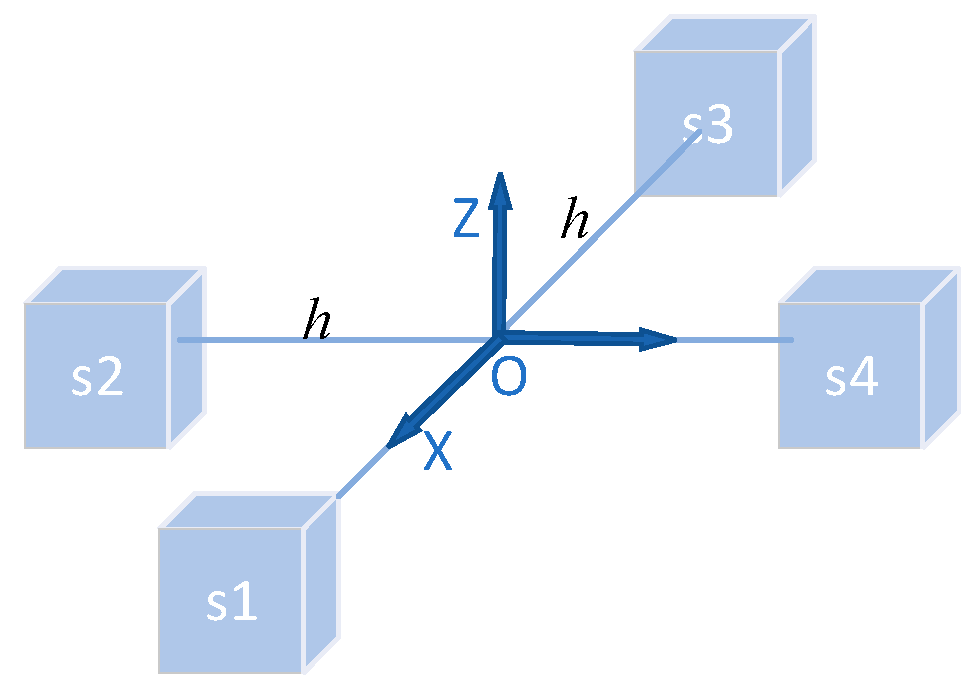
2. Magnetic Gradient Tensor and Location Theory
3. The Analysis and Correction of Magnetometer’s Position Error
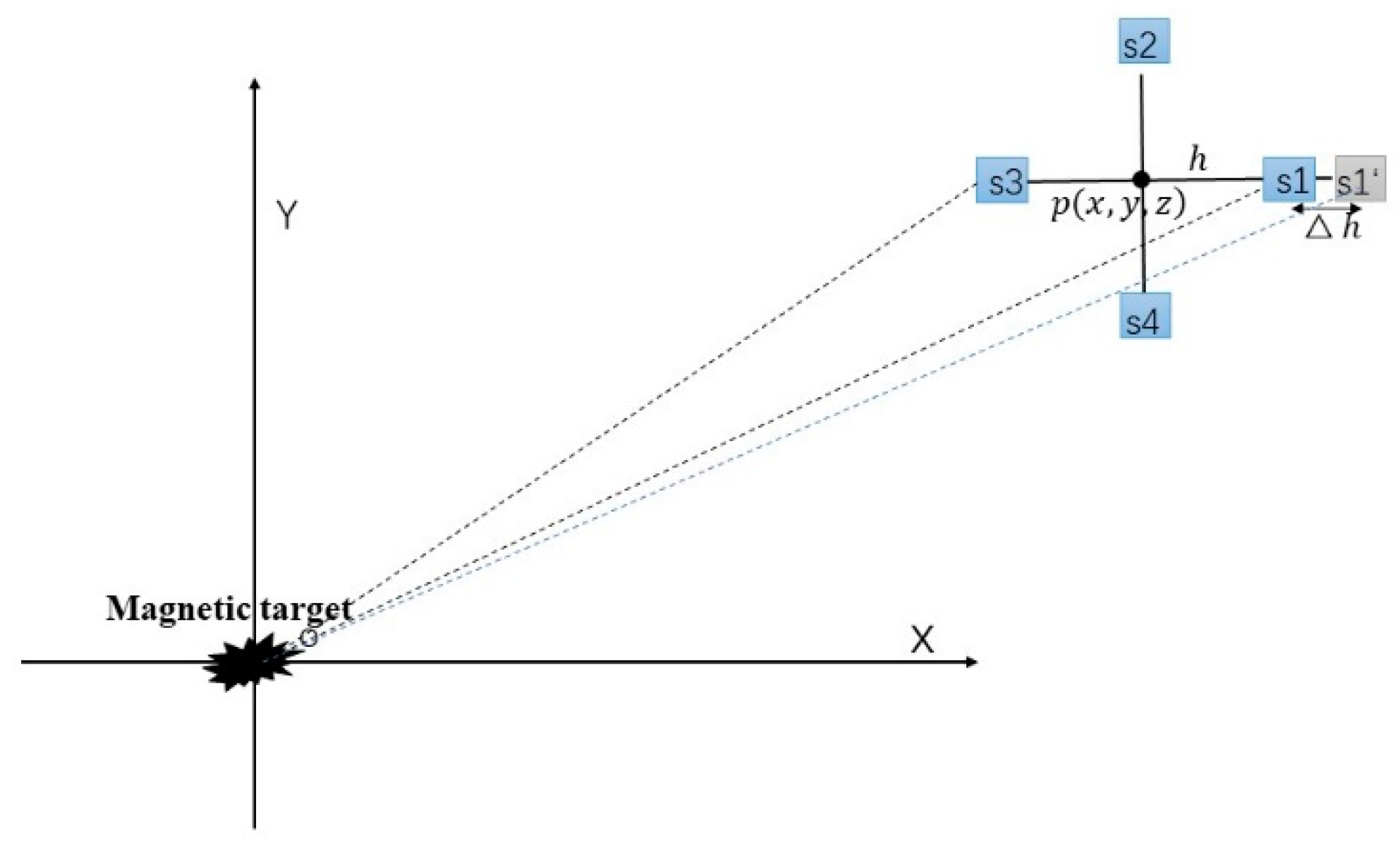
3.1. Analysis of Locating Error
3.2. The Correction Method for Magnetometer’s Position Error
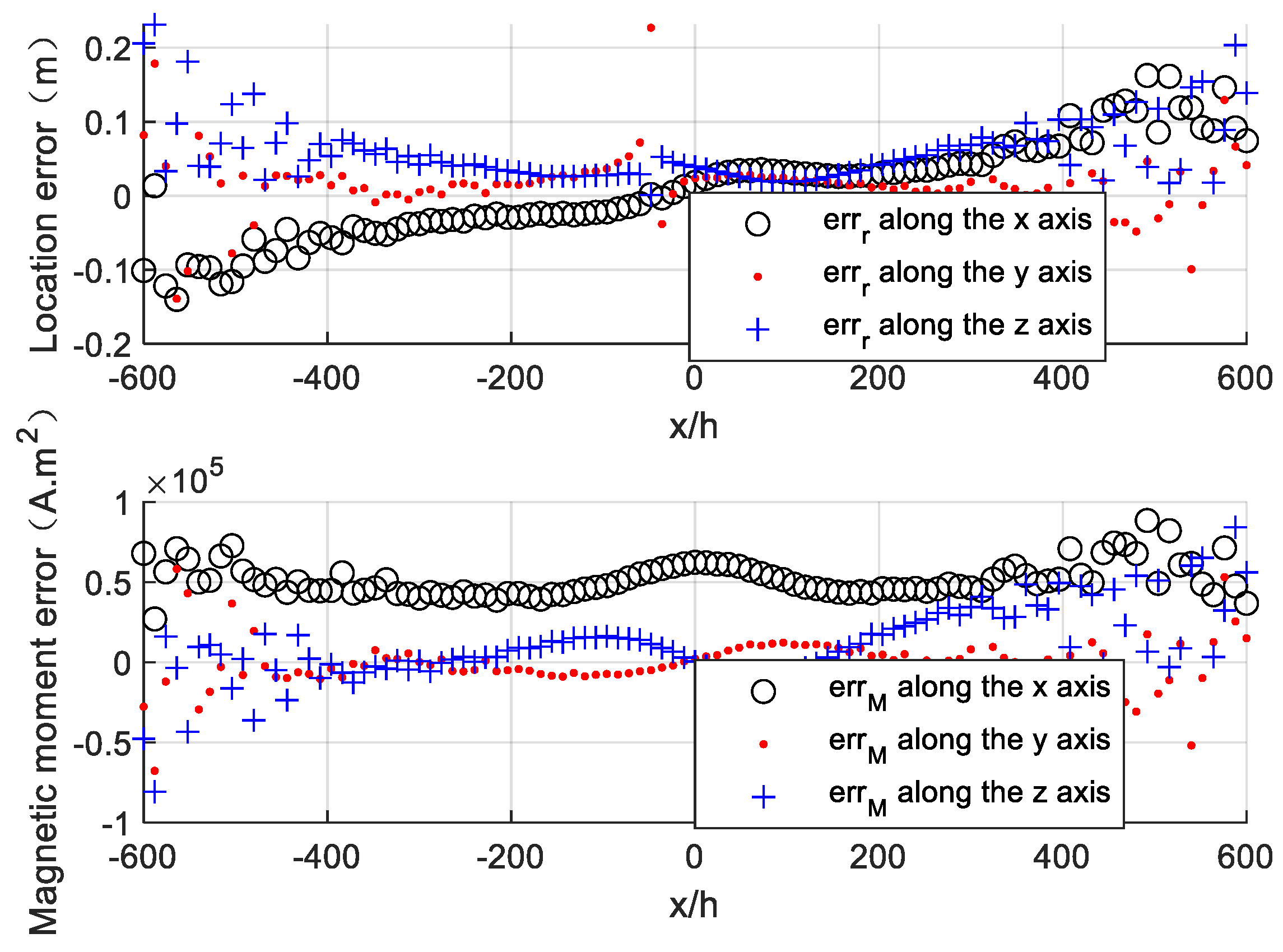
4. Numerical Simulation
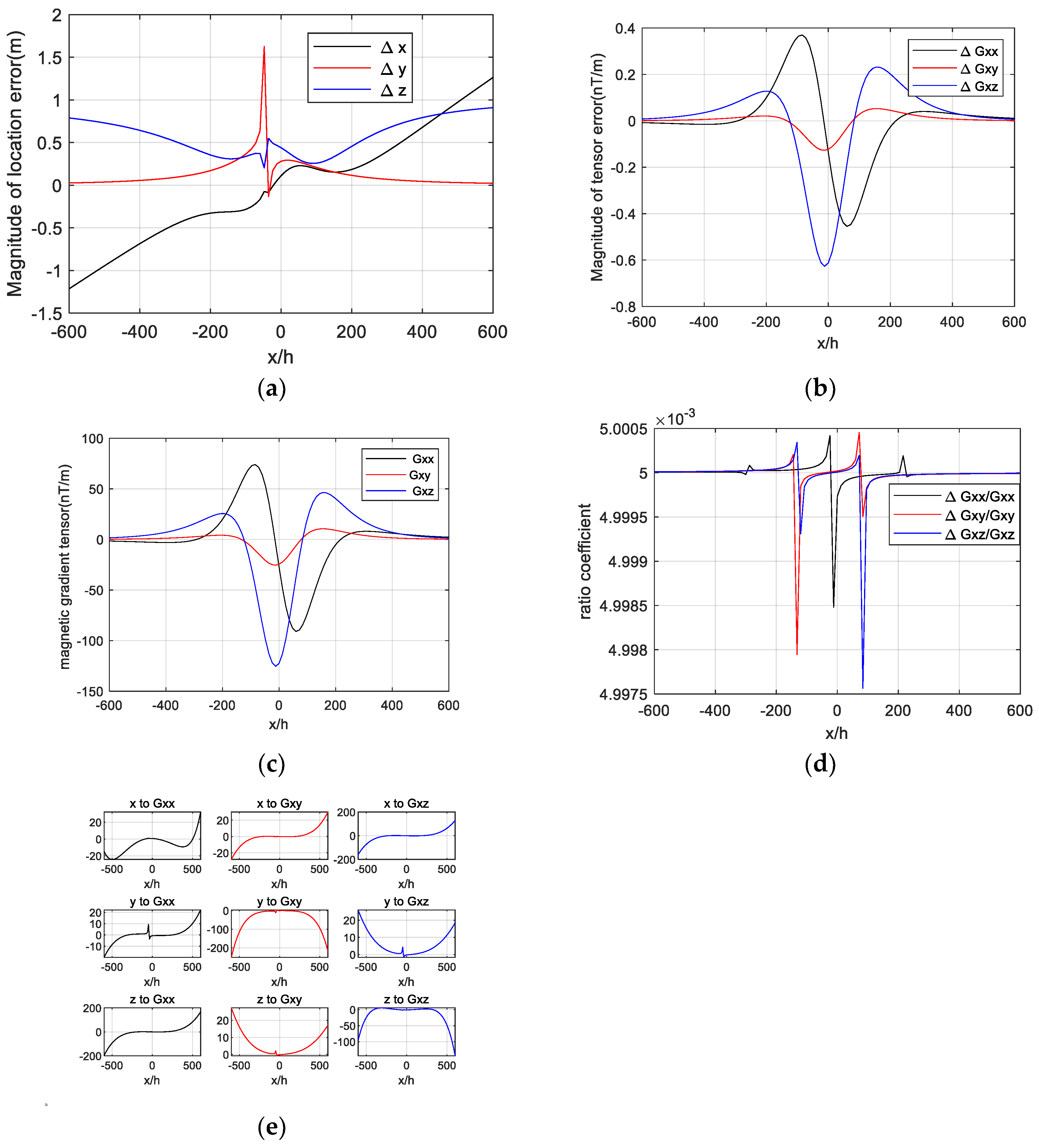
4.1. Influence Assessment
- A magnetic object, which can be seen as a magnetic dipole, is used as a target and placed at the origin of the coordinates. Its magnetic moment is assumed as , , and .
- The baseline length of the magnetic gradient tensor system is 0.5 m and the precision of the magnetometer is 1 pT.
- A 600 m straight survey line containing 100 observation points is designed. It starts from point to point .
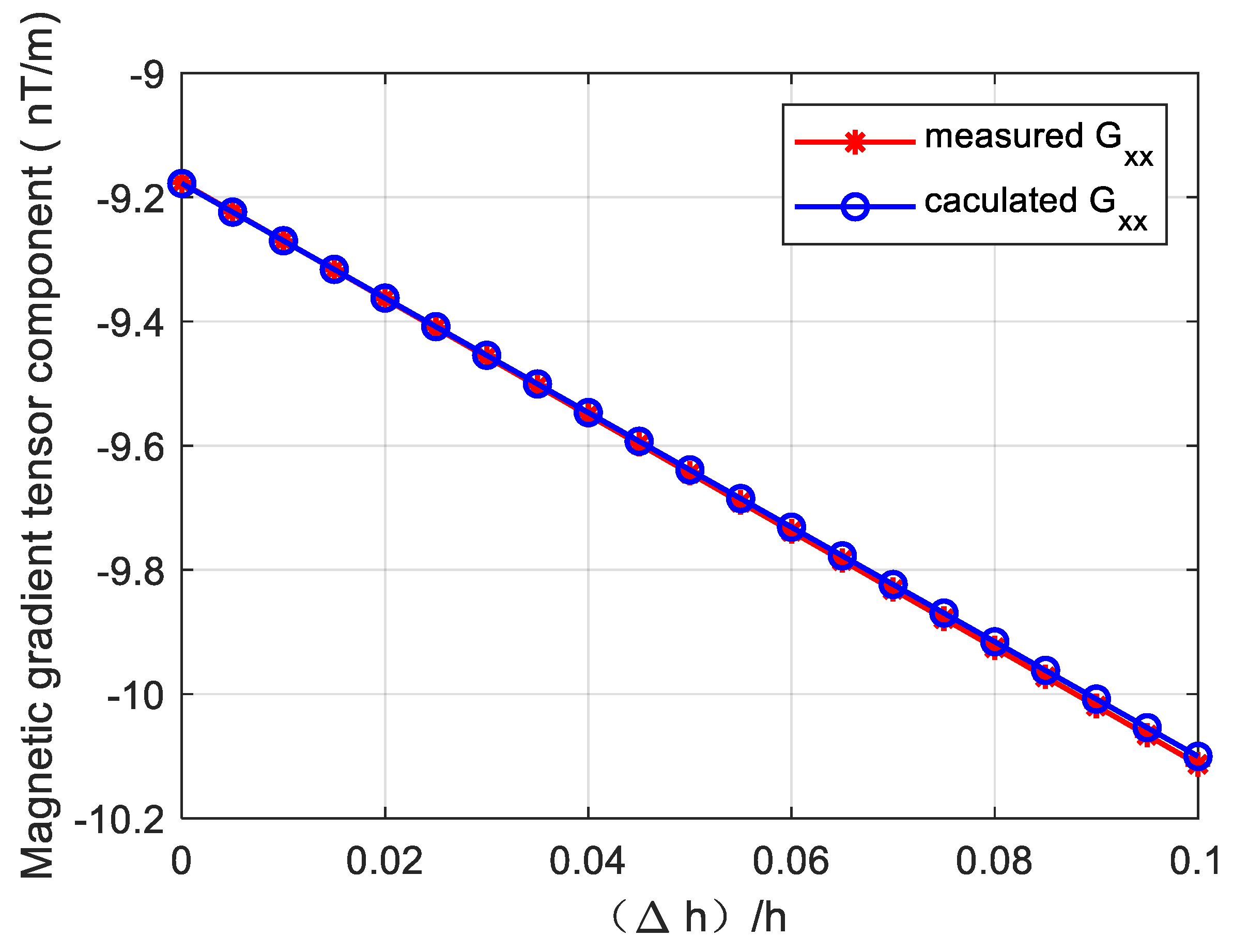
4.2. Error Correction
- A magnetic object with known magnetic moment (, , and ) is placed at the origin of the coordinates.
- Preset , , ……, .
- The baseline length of the magnetometer array is 0.5 m and the precision of the magnetometer is 1 pT. The measurement points, which are used to estimate , can be selected arbitrarily. Herein, two points, (20, 20, 100) and (−300, 20, 100) m, with the same Y and Z of the survey line in Section 4.1, are selected to exemplify the correction method.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- The magnetic moment of the magnetic object: , , and .
- and .
- The observation point is arbitrarily selected as .
References
- Nabighian, M.N.; Grauch, V.J.S.; Hansen, R.O.; Lafehr, T.R.; Phillips, J.D.J.G. The historical development of the magnetic method in exploration. Geophysics 2005, 70, 33ND. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W. Calibration of Magnetometer Arrays in Magnetic Field Gradients. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2019, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.A. New methods for interpretation of magnetic vector and gradient tensor data I: Eigenvector analysis and the normalised source strength. Explor. Geophys. 2018, 45, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingzhu, L.; Zhining, L.; Yingtang, Z.; Gang, Y.; Hong-bo, F. Research Progress of Magnetic Gradient Tensor System and its Error Calibration. J. Acad. Armored Force Eng. 2017, 31, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansheng, W.; Mingji, Z.; Ning, Z.; Qiang, G. Calculation and correction of magnetic object positioning error caused by magnetic field gradient tensor measurement. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2018, 29, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Jun-wei, L. Comparative Analysis of Magnetic Gradient Tensor System Structure. Command. Control Simul. 2019, 41, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merayo, J.M.G.; Brauer, P.; Primdahl, F.; Petersen, J.R.; Nielsen, O.V. Scalar calibration of vector magnetometers. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousaloo, H.S.; Sharifi, G.; Mahdian, J.; Nodeh, M.T. Complete Calibration of Three-Axis Strapdown Magnetometer in Mounting Frame. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 7886–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre-Egziabher, D.; Elkaim, G.H.; Powell, J.D.; Parkinson, B.W. A Non-Linear, Two-Step Estimation Algorithm for Calibrating Solid-State Strapdown Magnetometers. In Proceedings of the International St Petersburg Conference on Navigation Systems, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 28–30 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, G.; Shenggang, Y.; Bin, L. Study on the steering differential calibration method for magnetic gradiometer base on tri-axis fluxgate. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yanling, H. Correction of fluxgate field gradiometer based on FLANN. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Tech. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 39, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yanling, H. Error correction of magnetic field component gradiometer based on FLANN and least-squares. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 33, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W. A Novel Calibration Method for Magnetometer Array in Nonuniform Background Field. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yongjun, W.; Zhi, L. Inter-Triad Misalignment of Vector Field Sensors in Attitude and Heading Reference Systems and Its Calibration. Chin. J. Sens. Actuators 2017, 30, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Lv, J.W.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z.T.; Huang, J.L. Integrated Calibration for the Cross Magnetic Gradiometer. J. Magn. 2017, 22, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-Z.; Li, Z.-N.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Yin, G. Fast rotation calibration of sensor array in magnetic gradient tensor system. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2018, 26, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.; Oeschger, J. Generalized magnetic gradient contraction based method for detection, localization and discrimination of underwater mines and unexploded ordnance. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2005 MTS/IEEE, Washington, DC, USA, 17–23 September 2005; Volume 1322, pp. 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, Y.; Yingtang, Z.; Zhining, L.; Hongbo, F.; Guoquan, R. Detection of ferromagnetic target based on mobile magnetic gradient tensor system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 402, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.; Lee, K.; Oeschger, J. Improved magnetic STAR methods for real-time, point-by-point localization of unexploded ordnance and buried mines. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2008, Quebec, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gang, Y.; Yingtang, Z.; Hongbo, F.; Guang, Z.; Guoquan, R. Linear calibration method of magnetic gradient tensor system. Measurement 2014, 56, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, T.; Suzuki, S.; Ando, S. A Closed-Form Formula for Magnetic Dipole Localization by Measurement of Its Magnetic Field and Spatial Gradients. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3291–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number | (20, 20, 100) m | (−300, 20, 100) m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.001 | 0.0007 | 0.0003 | 0.001 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.002 | 0.0017 | 0.0003 | 0.0019 | 0.0001 |
| 3 | 0.003 | 0.0027 | 0.0003 | 0.0029 | 0.0001 |
| 4 | 0.004 | 0.0036 | 0.0004 | 0.0039 | 0.0001 |
| 5 | 0.005 | 0.0045 | 0.0005 | 0.0049 | 0.0001 |
| 6 | 0.007 | 0.0062 | 0.0008 | 0.0068 | 0.0002 |
| 7 | 0.008 | 0.0071 | 0.0009 | 0.0077 | 0.0003 |
| 8 | 0.01 | 0.0089 | 0.0011 | 0.0096 | 0.0004 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J. Analysis and Correction of the Magnetometer’s Position Error in a Cross-Shaped Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer. Sensors 2020, 20, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051290
Yan Y, Ma Y, Liu J. Analysis and Correction of the Magnetometer’s Position Error in a Cross-Shaped Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051290
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Youyu, Yan Ma, and Jianguo Liu. 2020. "Analysis and Correction of the Magnetometer’s Position Error in a Cross-Shaped Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051290
APA StyleYan, Y., Ma, Y., & Liu, J. (2020). Analysis and Correction of the Magnetometer’s Position Error in a Cross-Shaped Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer. Sensors, 20(5), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051290





