Coupling of Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with Sampled-Current Voltammetry on an Electrode Array: Application to Lead Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Part
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Electrodes
2.3. Electrochemical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Electrochemical Signal
3.1.1. Cyclic Voltammetry Analysis
3.1.2. Electrodeposition Potential
3.1.3. Electrodeposition Time
3.2. Anodic Stripping Voltammetry on an Electrode Array
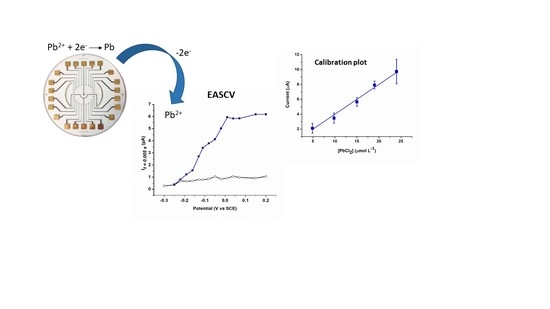
3.3. Lead Calibration Curve Established by Coupling Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with EASCV
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EU. Directive 98/83/CE of Council of 3 November 1998 onthe quality of water intended for human consumption. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 1998, L330, 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Yu, X.-Y.; Xiong, S.-Q.; Liu, J.-H.; Huang, X.-J. Electrochemical Detection of Arsenic(III) Completely Free from Noble Metal: Fe3O4 Microspheres-Room Temperature Ionic Liquid Composite Showing Better Performance than Gold. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasraoui, R.; Floner, D.; Geneste, F. Analytical performances of a flow electrochemical sensor for preconcentration and stripping voltammetry of metal ions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 629, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasraoui, R.; Floner, D.; Geneste, F. Improvement in performance of a flow electrochemical sensor by using carbamoyl-arms polyazamacrocycle for the preconcentration of lead ions onto the electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasraoui, R.; Floner, D.; Paul-Roth, C.; Geneste, F. Flow electroanalytical system based on cyclam-modified graphite felt electrodes for lead detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 638, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feier, B.; Fizesan, I.; Meriadec, C.; Ababou Girard, S.; Cristea, C.; Sandulescu, R.; Geneste, F. Influence of the electrografting method on the performances of a flow electrochemical sensor using modified electrodes for trace analysis of copper (II). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 744, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feier, B.; Floner, D.; Cristea, C.; Bodoki, E.; Sandulescu, R.; Geneste, F. Flow electrochemical analyses of zinc by stripping voltammetry on graphite felt electrode. Talanta 2012, 98, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feier, B.; Floner, D.; Cristea, C.; Sandulescu, R.; Geneste, F. Development of a novel flow sensor for copper trace analysis by electrochemical reduction of 4-methoxybenzene diazonium salt. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 31, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Economou, A.; Fielden, P.R. Mercury film electrodes: developments, trends and potentialities for electroanalysis. Analyst 2003, 128, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, J.; Brand, M.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Determination of sub-μg l-1 concentrations of copper by anodic stripping voltammetry at the gold electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 387, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, Y.; Brand, M.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Trace determination of mercury by anodic stripping voltammetry at the rotating gold electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 424, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, S.; Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Gold-based screen-printed sensor for detection of trace lead. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, B. Gold ultramicroelectrodes for on-site monitoring of trace lead. Electroanalysis 1993, 5, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, B. Mercury-free disposable lead sensors based on potentiometric stripping analysis of gold-coated screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tian, B. Screen-printed electrodes for stripping measurements of trace mercury. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 274, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, K.; Justino, C.I.L.; Freitas, A.C.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Disposable sensors for environmental monitoring of lead, cadmium and mercury. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 64, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothimuthu, P.; Wilson Robert, A.; Herren, J.; Haynes Erin, N.; Heineman William, R.; Papautsky, I. Lab-on-a-chip sensor for detection of highly electronegative heavy metals by anodic stripping voltammetry. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonfil, Y.; Brand, M.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Characteristics of subtractive anodic stripping voltammetry of Pb and Cd at silver and gold electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 464, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, Y.; Brand, M.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Determination of mercury and copper in waste water by anodic-stripping voltammetry at the gold electrode. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, Y.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Determination of nanomolar concentrations of lead and cadmium by anodic-stripping voltammetry at the silver electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 457, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, G.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Determination of trace metals by underpotential deposition-stripping voltammetry at solid electrodes. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazerie, I.; Didier, P.; Razan, F.; Hapiot, P.; Coulon, N.; Girard, A.; de Sagazan, O.; Floner, D.; Geneste, F. A General Approach Based on Sampled-Current Voltammetry for Minimizing Electrode Fouling in Electroanalytical Detection. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignard, L.; Denoual, M.; Lavastre, O.; Floner, D.; Geneste, F. Sampled voltammetry on an electrode array for the renewal of the electrode surface and the analytical solution during the analysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 689, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazerie, I. Développement de capteurs électrochimiques basés sur de la voltammétrie par échantillonnage de courant sur réseau d’électrodes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rennes 1, Rennes, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Engelsmann, K.; Lorenz, W.J.; Schmidt, E. Underpotential deposition of lead on polycrystalline and single-crystal gold surfaces. Part II. Kinetics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1980, 114, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsmann, K.; Lorenz, W.J.; Schmidt, E. Underpotential deposition of lead on polycrystalline and single-crystal gold surfaces. Part I. Thermodynamics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1980, 114, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamelin, A.; Katayama, A.; Picq, G.; Vennereau, P. Surface characterization by underpotential deposition: lead on gold surfaces. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1980, 113, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirowa-Eisner, E.; Bonfil, Y.; Tzur, D.; Gileadi, E. Thermodynamics and kinetics of upd of lead on polycrystalline silver and gold. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 552, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, V.A.; Bruckenstein, S. Rotating ring-disk electrode study of the adsorption of lead on gold in 0.5M potassium chloride. Anal. Chem. 1973, 45, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koper, M.T.M. Stripping voltammetry and chronoamperometry of an adsorbed species with repulsive lateral interactions. Z. Phys. Chem. 2003, 217, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melroy, O.; Kanazawa, K.; Gordon, J.G., II; Buttry, D. Direct determination of the mass of an underpotentially deposited monolayer of lead on gold. Langmuir 1986, 2, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, D.; Crummett, W.B. Guidelines for data acquisition and data quality evaluation in environmental chemistry. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandil, A.; Idrissi, L.; Amine, A. Stripping voltammetric determination of mercury(II) and lead(II) using screen-printed electrodes modified with gold films, and metal ion preconcentration with thiol-modified magnetic particles. Microchim. Acta 2010, 170, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Adverse health effects of heavy metals in children. In Children’s Health and the Environment WHO Training Package for the Health Sector World; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 77, pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]












| Method | Sensitivity (mA mol−1 L) | Regression Coefficient | LOD (mg L−1) | LOQ (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EASCV 0.005 s | 307 | 0.994 | 1.16 | 1.41 |
| EASCV 0.007 s | 148 | 0.995 | 1.16 | 1.39 |
| Linear voltammetry | 1.64 | 0.977 | 1.02 | 1.03 |
| Working Electrode | Electrodeposition Time | Stirring Conditions | Detection Limit (g L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold screen-printed electrode | 120 s | Yes | 0.5 | [12] |
| Gold-coated ultra-microelectrode | 15 min | No | 0.3 | [13] |
| Gold-coated screen-printed electrode | 20 min 4 min 10 min | Yes Yes No | 0.1 0.6 3 | [14] |
| Gold-coated screen-printed electrode | 120 s | Yes | 0.5 | [33] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazerie, I.; Geneste, F. Coupling of Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with Sampled-Current Voltammetry on an Electrode Array: Application to Lead Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051327
Mazerie I, Geneste F. Coupling of Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with Sampled-Current Voltammetry on an Electrode Array: Application to Lead Detection. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051327
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazerie, Isabelle, and Florence Geneste. 2020. "Coupling of Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with Sampled-Current Voltammetry on an Electrode Array: Application to Lead Detection" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051327
APA StyleMazerie, I., & Geneste, F. (2020). Coupling of Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with Sampled-Current Voltammetry on an Electrode Array: Application to Lead Detection. Sensors, 20(5), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051327