Precise Point Positioning on the Reliable Detection of Tropospheric Model Errors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PPP Data Processing
2.1. Modeling and Filtering
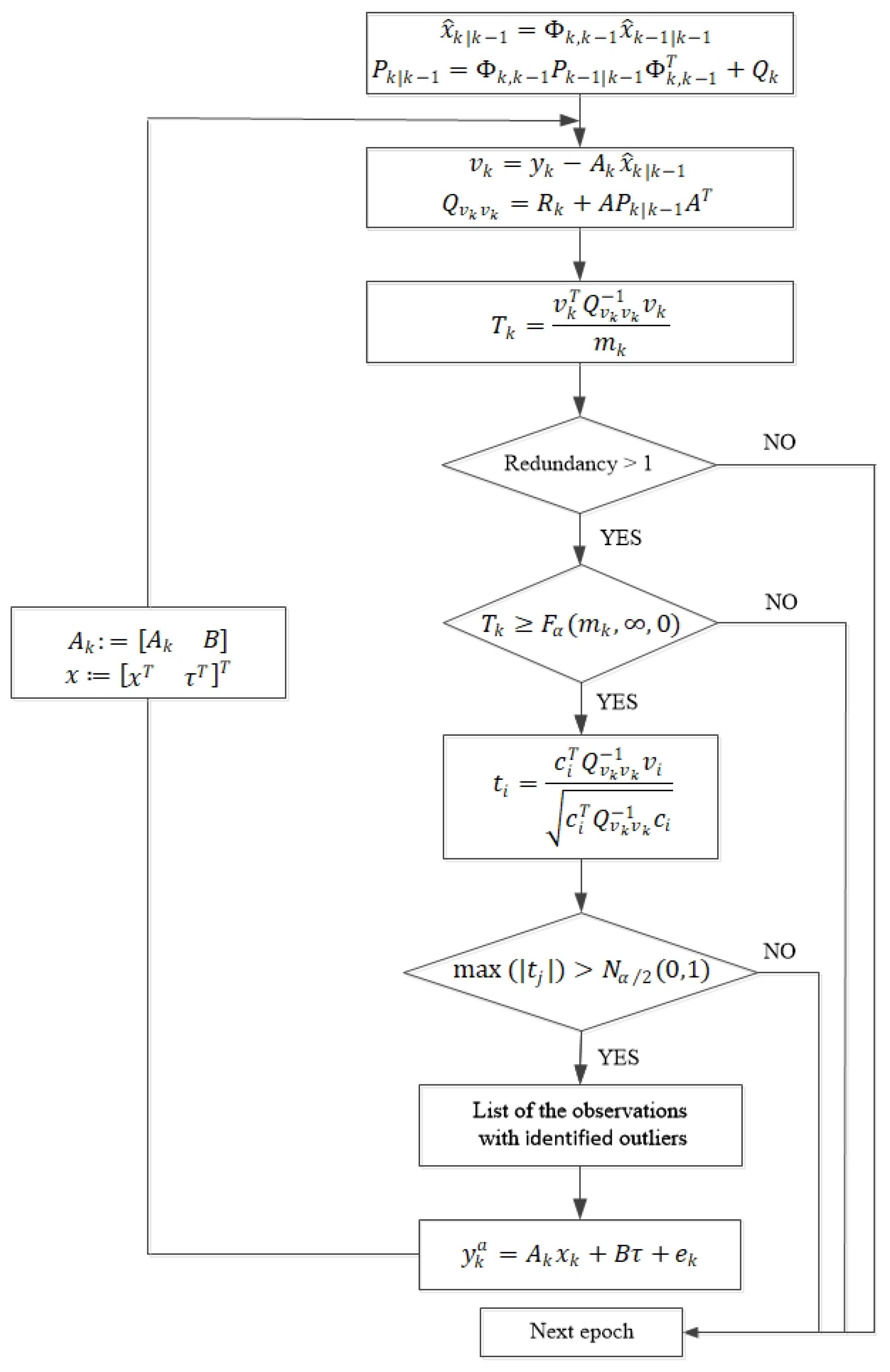
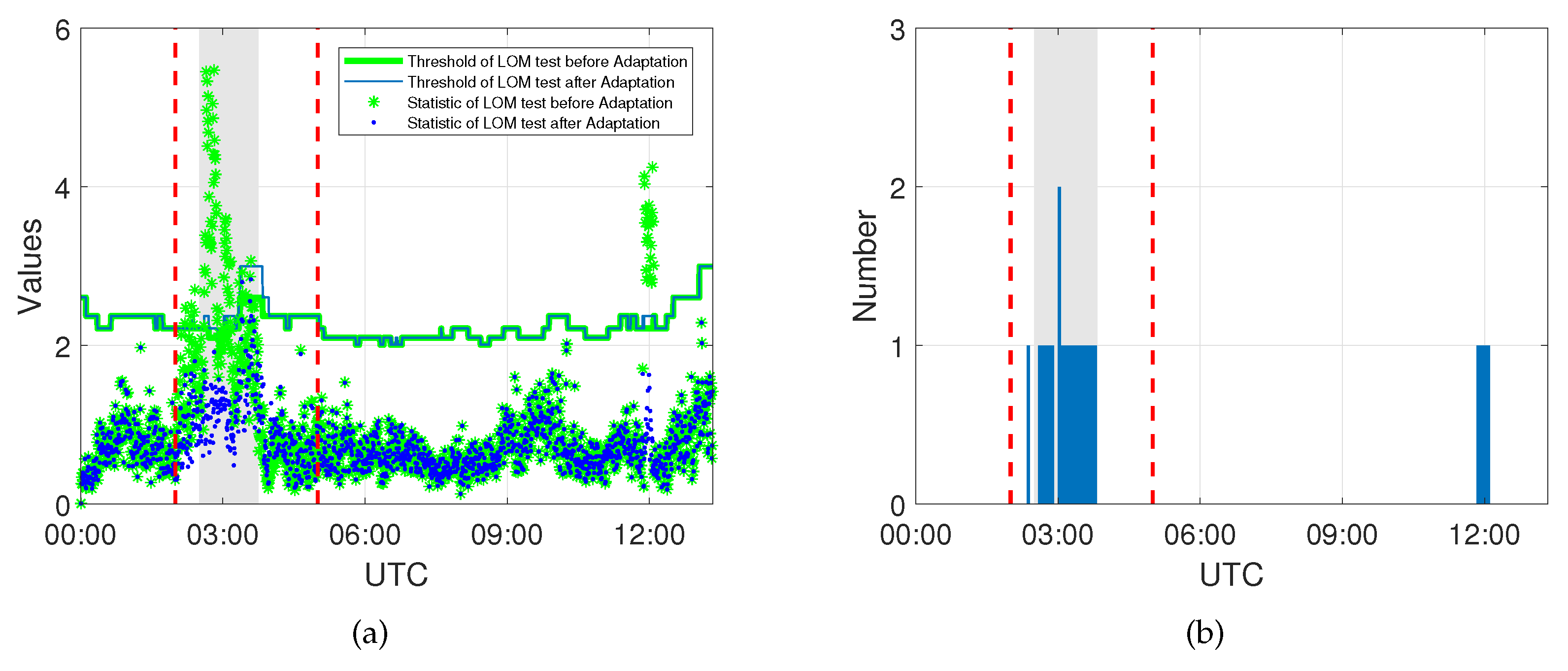
2.2. Detection, Identification and Adaptation
2.2.1. Detection
2.2.2. Identification
2.2.3. Adaptation
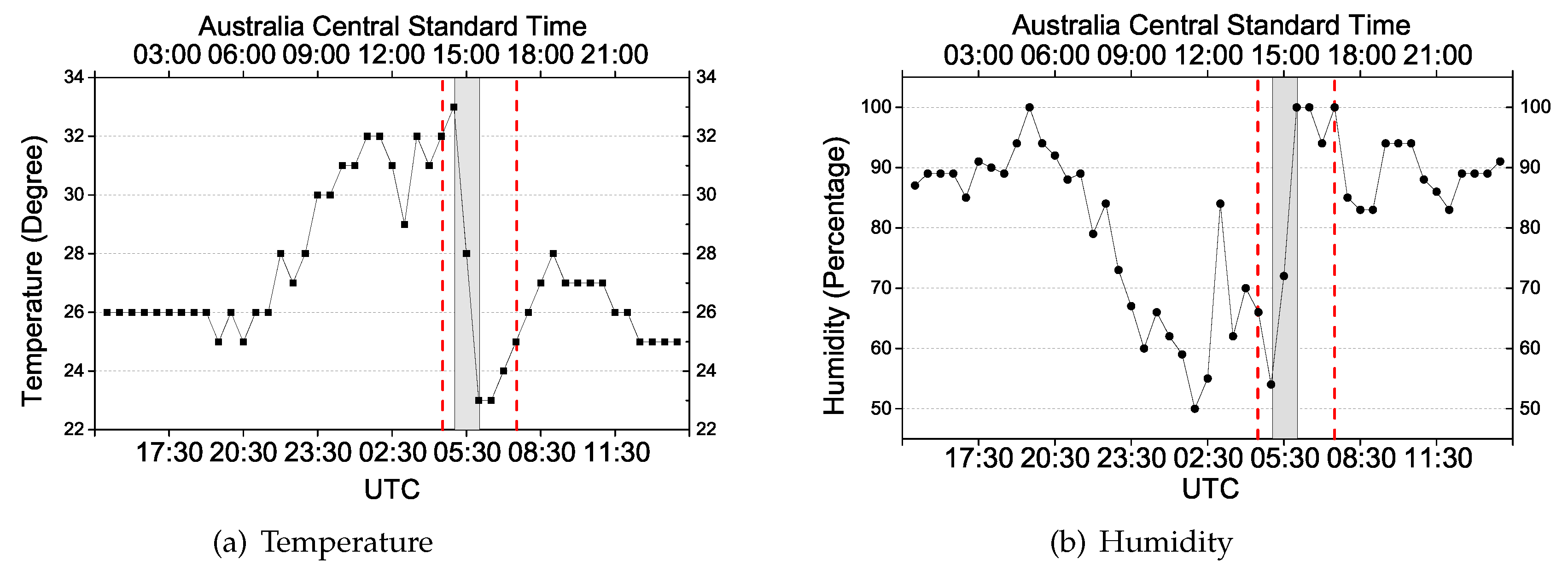
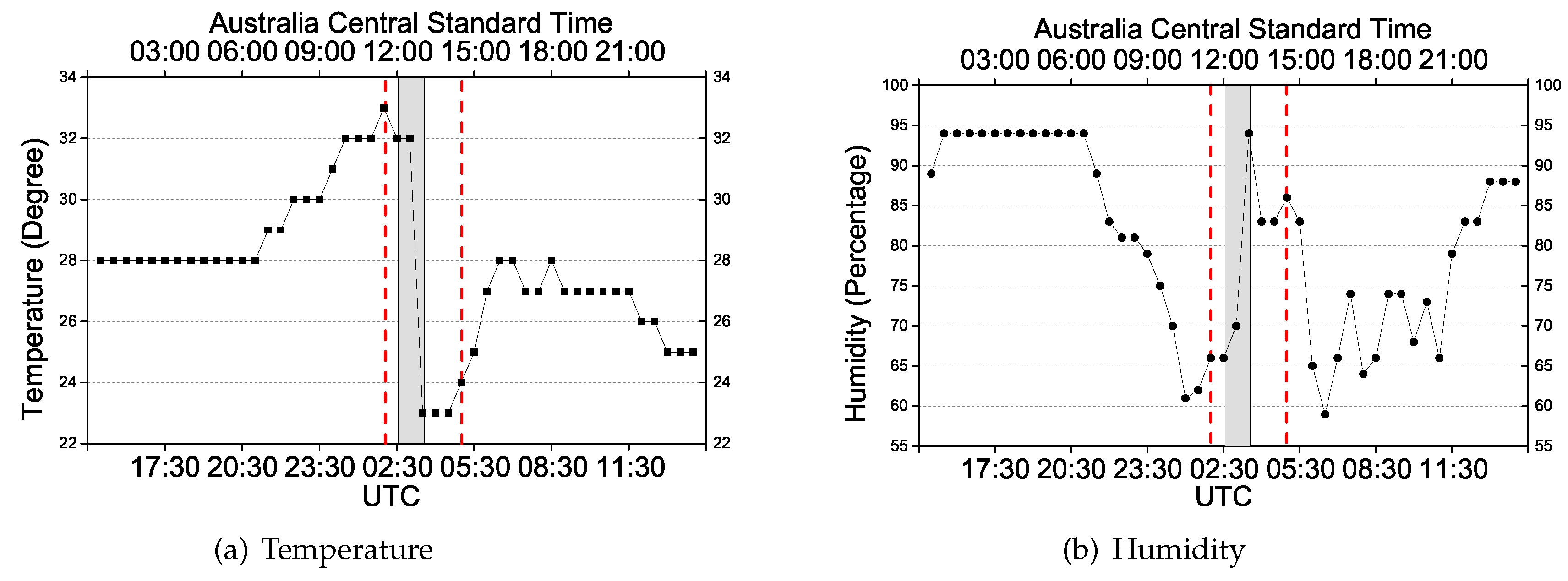
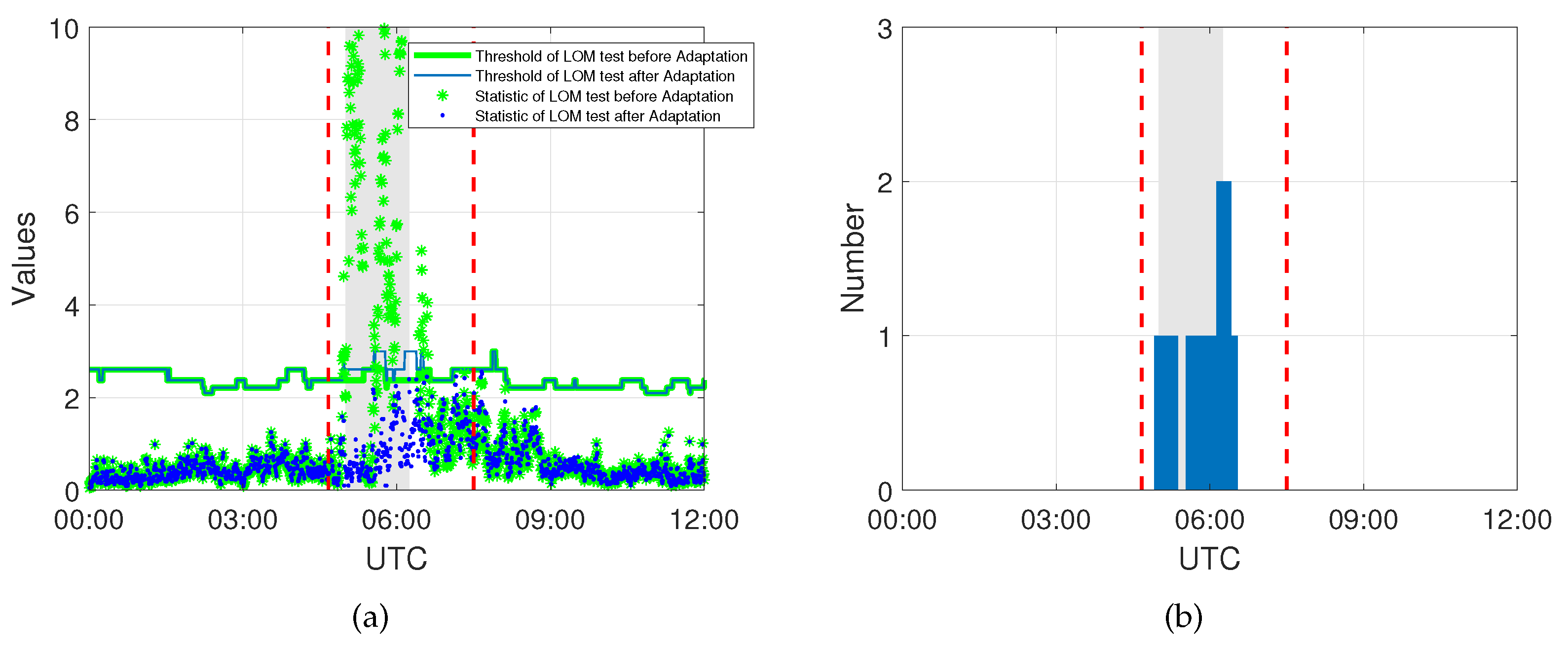
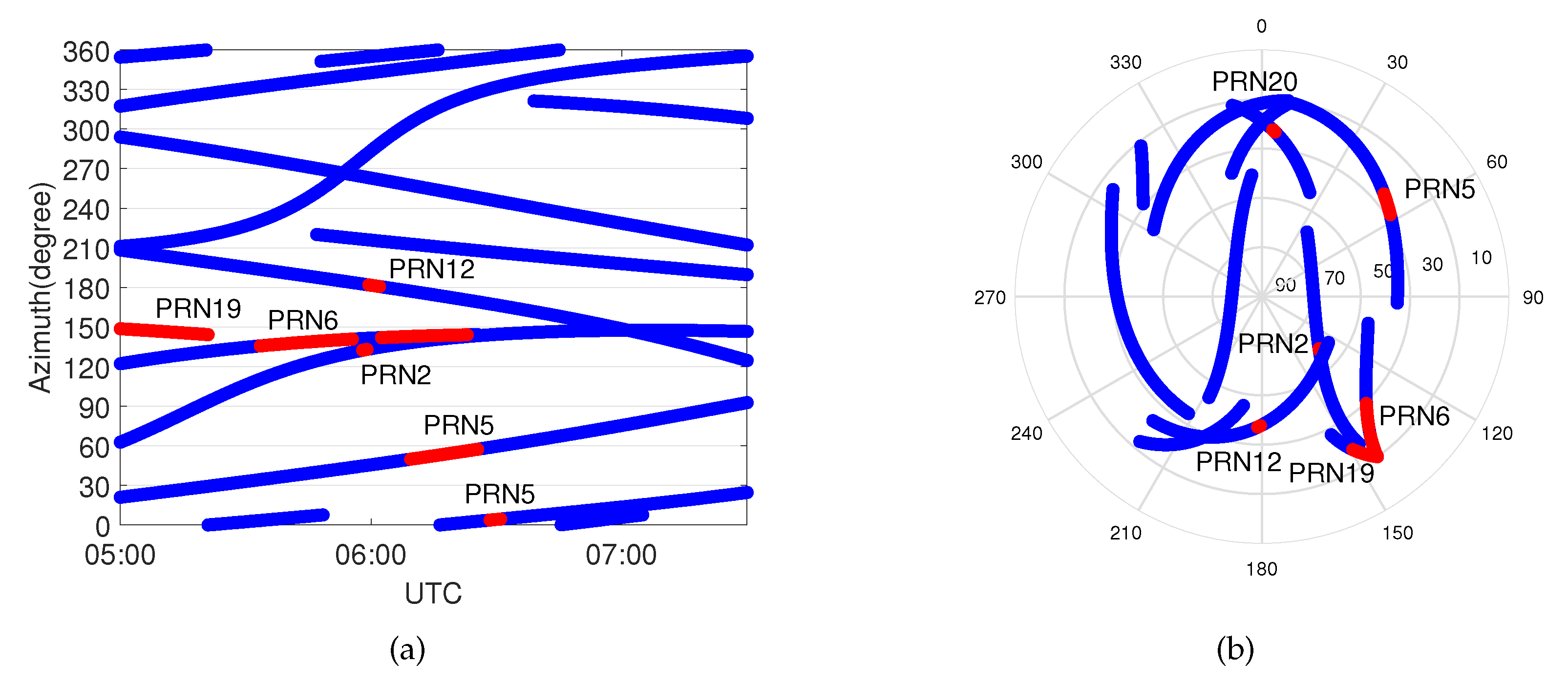
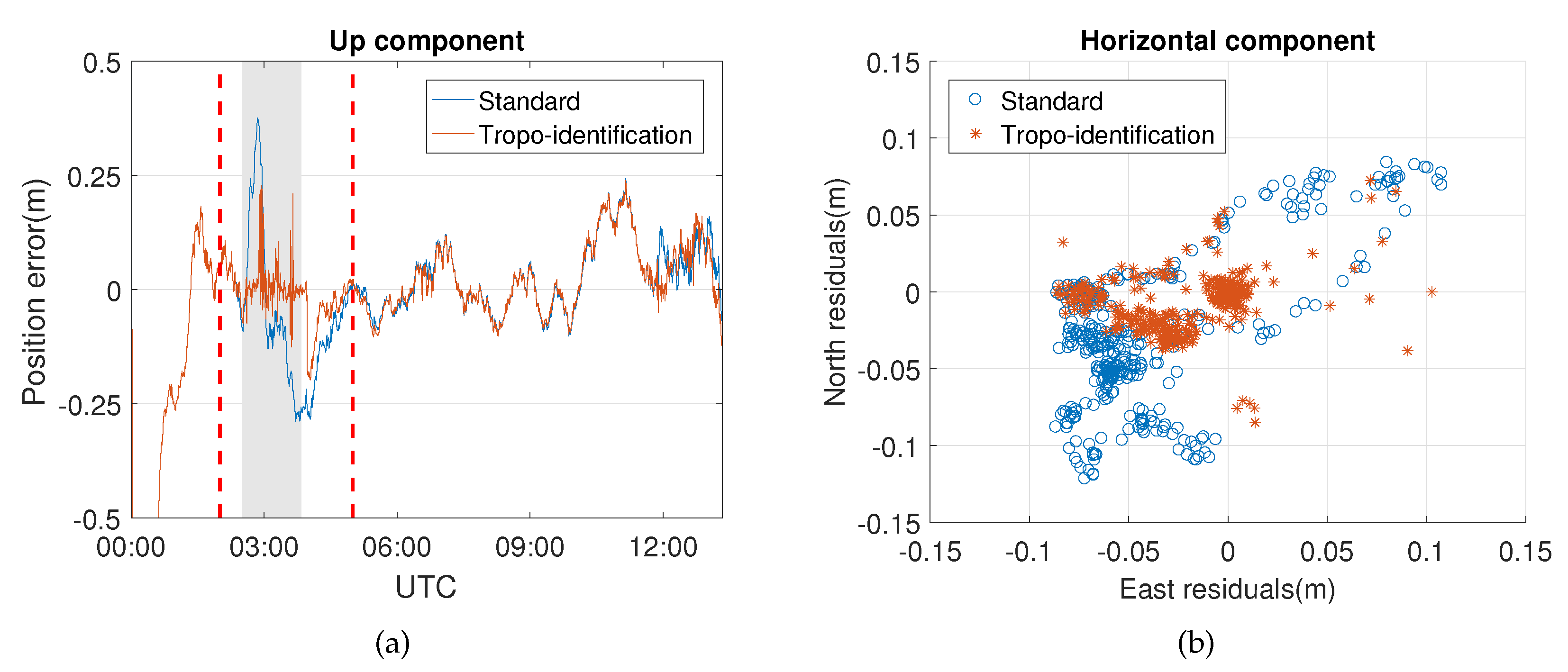
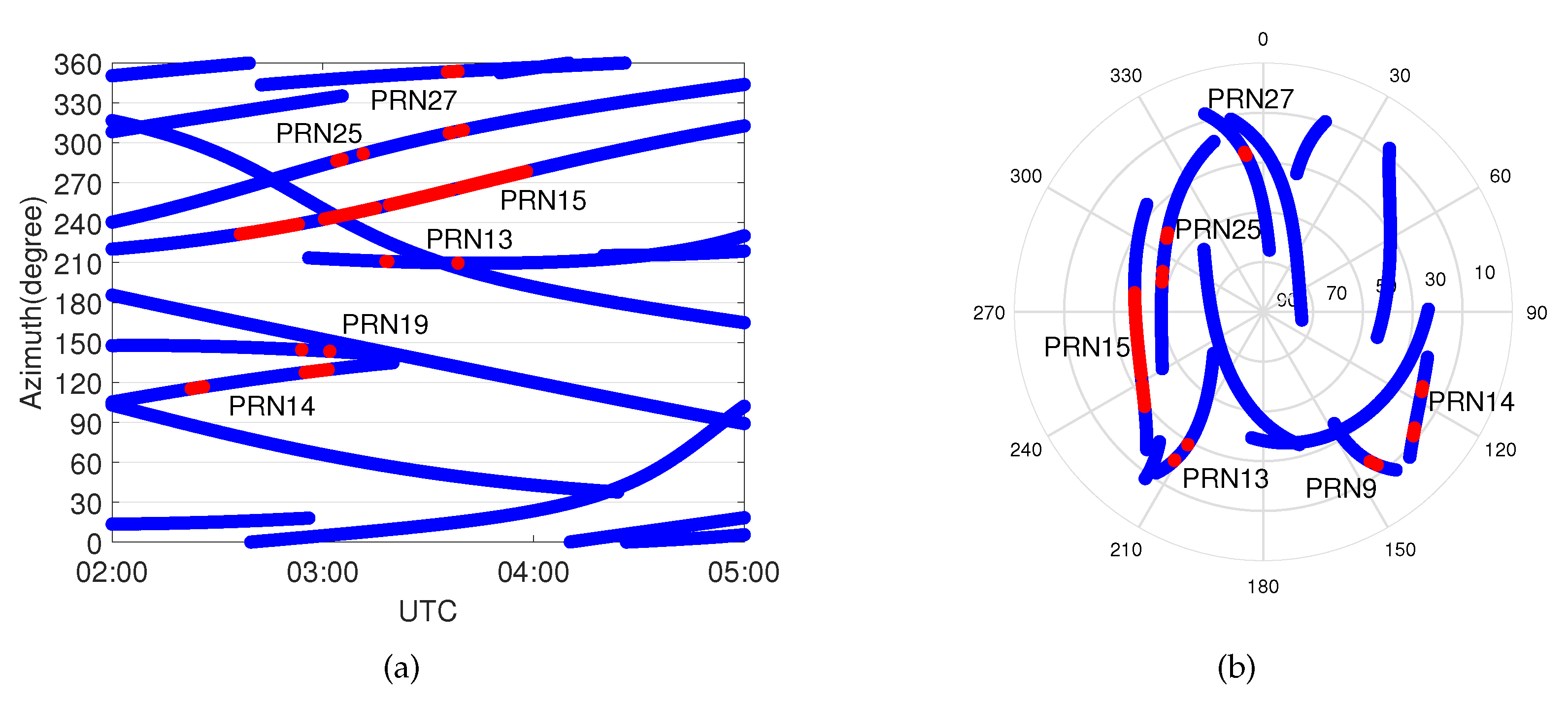
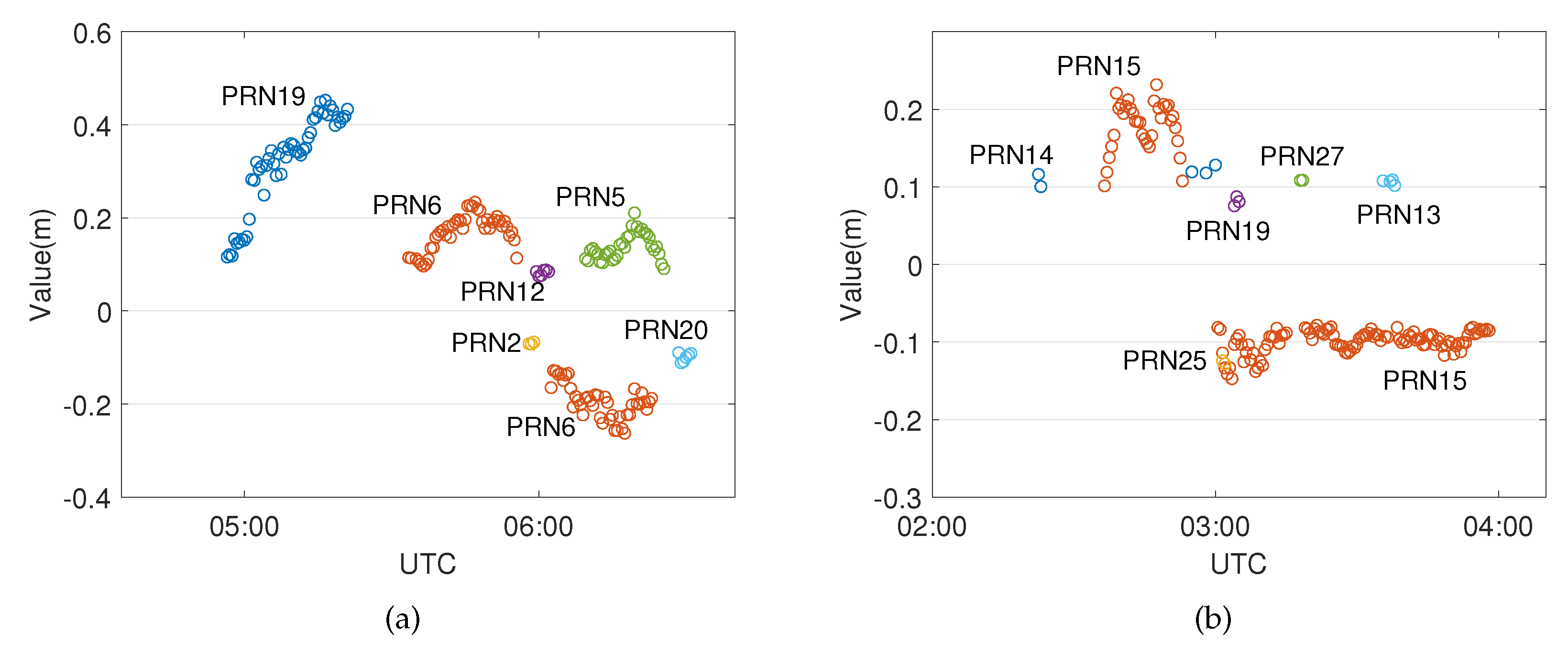
3. Case Studies and Results
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. In The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy; 2000 Florida Ave. NW: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; pp. 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, P.; Bevis, M.; Bock, Y.; Gutman, S.; Wolfe, D. GPS meteorology: Reducing systematic errors in geodetic estimates for zenith delay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 19, 3583–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teke, K.; Nilsson, T.; Böhm, J.; Hobiger, T.; Steigenberger, P.; García-Espada, S.; Haas, R.; Willis, P. Troposphere delays from space geodetic techniques, water vapor radiometers, and numerical weather models over a series of continuous VLBI campaigns. J. Geodesy 2013, 87, 981–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopfield, H.S. Two-quartic tropospheric refractivity profile for correcting satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 18, 4487–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Herring, T.A.; Shapiro, I.I.; Rogers, A.E.E.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.P.; Langley, R. The residual tropospheric propagation delay: How bad can it get? In Proceedings of the Conference on ION GPS, INSTITUTE of NAVIGATION, Nashville, TN, USA, 15–18 September 1998; Volume 11, pp. 729–738. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, R.; Santos, M.C.; Langley, R.B. UNB neutral atmosphere models: development and performance. In Proceedings of the Conference on ION NTM, INSTITUTE OF NAVIGATION, Monterey, CA, USA, 18–20 January 2006; pp. 564–573. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, R.F.; Langley, R.B.; Santos, M.C. UNB3m_pack: A neutral atmosphere delay package for radiometric space techniques. GPS Solut. 2008, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, N.; Dodson, A.; Chen, W. Assessment of EGNOS tropospheric correction model. J. Navig. 2001, 1, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, M.; Hoshinoo, K.; Matsunaga, K.; Kawai, M.; Nakao, H.; Langley, R.B.; Bisnath, S.B. Assessment of atmospheric delay correction models for the Japanese MSAS. In Proceedings of the Conference on ION NTM, INSTITUTE OF NAVIGATION, Long Beach, CA, USA, 22–24 January 2001; pp. 2341–2350. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Ou, J.; Li, H.; Li, Z. A new global zenith tropospheric delay model IGGtrop for GNSS applications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 17, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Ou, J.; Chai, Y.; Li, Z.; Liou, Y.A.; Wang, N. New versions of the BDS/GNSS zenith tropospheric delay model IGGtrop. J. Geod. 2015, 1, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Heinkelmann, R.; Schuh, H. Short note: a global model of pressure and temperature for geodetic applications. J. Geod. 2007, 10, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagler, K.; Schindelegger, M.; Böhm, J.; Krásná, H.; Nilsson, T. GPT2: Empirical slant delay model for radio space geodetic techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 6, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niell, A.E. Global mapping functions for the atmosphere delay at radio wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1996, 2, 3227–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niell, A.E. Preliminary evaluation of atmospheric mapping functions based on numerical weather models. Phys. Chem. Earth A 2001, 26, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Werl, B.; Schuh, H. Troposphere mapping functions for GPS and very long baseline interferometry from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts operational analysis data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, D.S. Atmospheric gradients from very long baseline interferometry observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 9, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Herring, T. Effects of atmospheric azimuthal asymmetry on the analysis of space geodetic data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 9, 20489–20502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.; Montenbruck, O. (Eds.) Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yasyukevich, Y.; Astafyeva, E.; Padokhin, A.; Ivanova, V.; Syrovatskii, S.; Podlesnyi, A. The 6 September 2017 X-class solar flares and their impacts on the ionosphere, GNSS, and HF radio wave propagation. Space Weather 2018, 8, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Xiong, C.; Chen, B.; Jin, X. Assessing the performance of GPS precise point positioning under different geomagnetic storm conditions during solar cycle 24. Sensors 2018, 6, 1784–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesmer, V.; Boehm, J.; Heinkelmann, R.; Schuh, H. Effect of different tropospheric mapping functions on the TRF, CRF and position time-series estimated from VLBI. J. Geodesy 2007, 81, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Chai, Y. Assessment of three tropospheric delay models (IGGtrop, EGNOS and UNB3m) based on precise point positioning in the Chinese region. Sensors 2016, 1, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steigenberger, P.; Tesmer, V.; Krügel, M.; Thaller, D.; Schmid, R.; Vey, S.; Rothacher, M. Comparisons of homogeneously reprocessed GPS and VLBI long time-series of troposphere zenith delays and gradients. J. Geodesy 2007, 81, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijer, F. Mapping function induced bias in tropospheric delay estimation using GPS. Phys. Chem. Earth A 2001, 26, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J. Robustness of GNSS integer ambiguity resolution in the presence of atmospheric biases. GPS Solut. 2014, 2, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobiger, T.; Shimada, S.; Shimizu, S.; Ichikawa, R.; Koyama, Y.; Kondo, T. Improving GPS positioning estimates during extreme weather situations by the help of fine-mesh numerical weather models. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2010, 72, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarda, W.A. Testing Procedure for Use in Geodetic Networks. In Publications on Geodesy; New Series; Netherlands Geodetic Commission: Delft, The Netherlands, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Quality control in geodetic networks. In Optimization and Design of Geodetic Networks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1985; pp. 526–547. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Salzmann, M.A. A recursive slippage test for use in state-space fltering. Manuscr. Geod. 1989, 14, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J. Quality control and GPS. In GPS for Geodesy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 271–318. [Google Scholar]
- Tiberius, C.C. Recursive data processing for kinematic GPS surveying. In Publications on Geodesy; Netherlands Geodetic Commission: Delft, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Perfetti, N. Detection of station coordinate discontinuities within the Italian GPS Fiducial Network. J. Geodesy 2006, 7, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.; Odijk, D.; Zhang, B. PPP-RTK: results of CORS network-based PPP with integer ambiguity resolution. J. Aeronaut. Astronaut. Aviat. Ser. A 2010, 4, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Zhai, G.; Chai, H. Study on the processing method of cycle slips under kinematic mode. In Theoretical and Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Odijk, D. Ionosphere-free phase combinations for modernized GPS. J. Surv. Eng. 2003, 4, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Khodabandeh, A. Review and principles of PPP-RTK methods. J. Geodesy 2015, 3, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P. An integrity and quality control procedure for use in multi sensor integration. In Proceedings of the Conference on ION GPS, INSTITUTE OF NAVIGATION, Colorado Spring, CO, USA, 19–21 September 1990; Volume 11, pp. 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Distributional theory for the DIA method. J. Geodesy 2018, 1, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tralli, D.M.; Lichten, S.M. Stochastic estimation of tropospheric path delays in Global Positioning System geodetic measurements. Bull. Géodésique 1990, 2, 127–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, P. Precision, cross correlation, and time correlation of GPS phase and code observations. GPS Solut. 2000, 2, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| STD of the zenith wet delay | 0.2 m [42] |
| Process noise of the zenith wet delay | 0.02 m/ |
| STD of the gradients | 0.01 m |
| Process noise of the gradients | 0.001 m/ |
| Interval 30 s | |
| STD of phase | 0.005 m [43] |
| STD of code | 0.5 m |
| Significance level |
| PRN | Phase | Code | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | RMS | Mean | RMS | |||||||||
| Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | |
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||
| 20 | ||||||||||||
| PRN | Phase | Code | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | RMS | Mean | RMS | |||||||||
| Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | Sta | Pro | Ipv(%) | |
| 13 | ||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||||||
| Mean | RMS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sta | Pro | Improve | Sta | Pro | Improve | |
| Up | ||||||
| East | ||||||
| North | ||||||
| 3D | ||||||
| Mean | RMS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sta | Pro | Improve | Sta | Pro | Improve | |
| Up | ||||||
| East | ||||||
| North | ||||||
| 3D | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Verhagen, S. Precise Point Positioning on the Reliable Detection of Tropospheric Model Errors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061634
Ma H, Verhagen S. Precise Point Positioning on the Reliable Detection of Tropospheric Model Errors. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061634
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hongyang, and Sandra Verhagen. 2020. "Precise Point Positioning on the Reliable Detection of Tropospheric Model Errors" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061634
APA StyleMa, H., & Verhagen, S. (2020). Precise Point Positioning on the Reliable Detection of Tropospheric Model Errors. Sensors, 20(6), 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061634






