Gait Recognition and Understanding Based on Hierarchical Temporal Memory Using 3D Gait Semantic Folding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Proposed GRU-GSFSL Framework
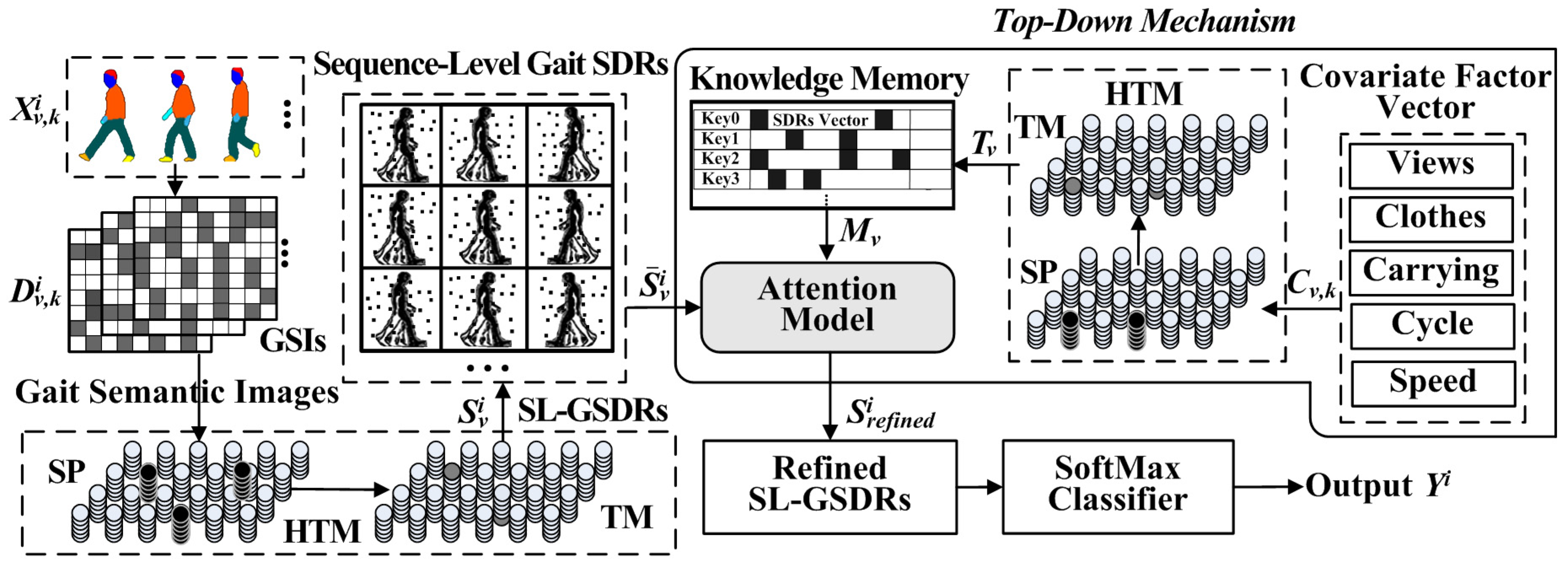
3.1. Overview
3.2. 3D Parametric Body Model
3.3. 3D Parametric Gait Semantic Data Extraction under Covariate Conditions
3.4. Semantic Folding Representation of Gait Features
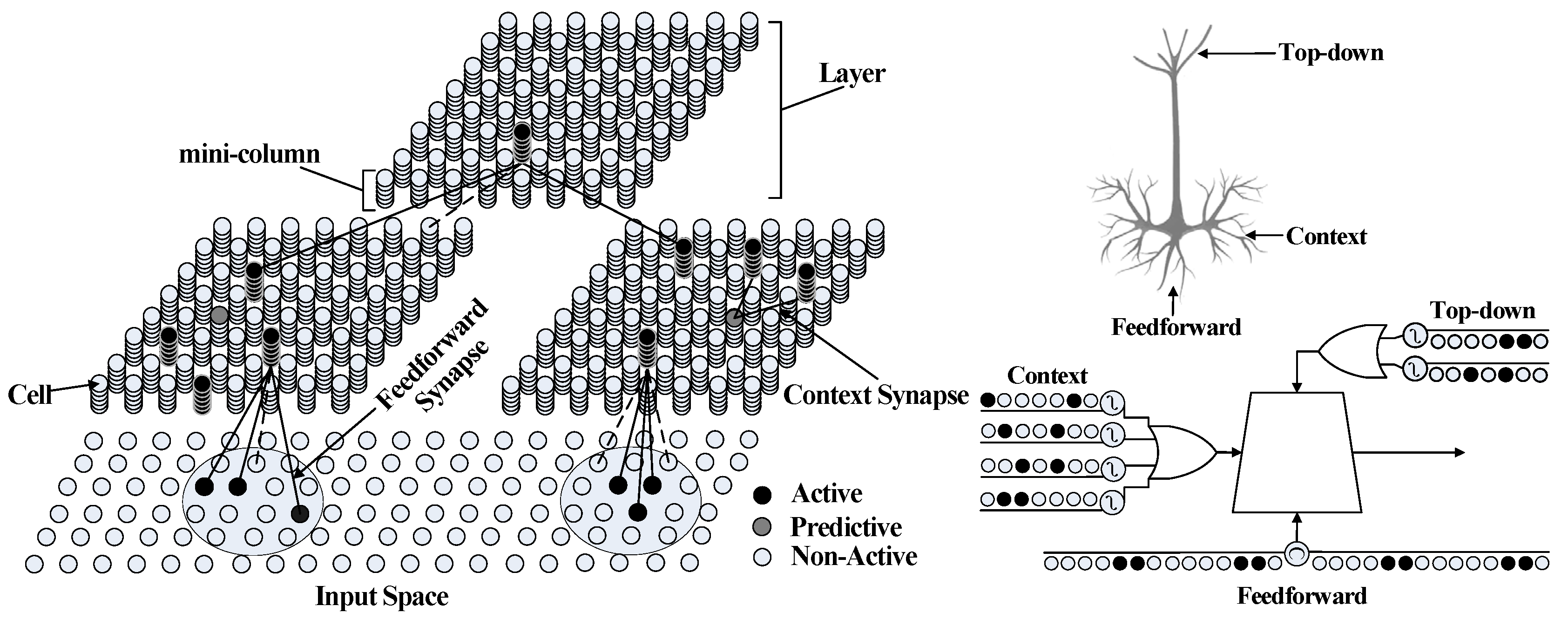
3.5. HTM-Based Sequence Learning Network for Gait Semantic Feature Learning
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiments on CMU Motion of the Body Dataset
4.2. Experiments on the CASIA B Dataset
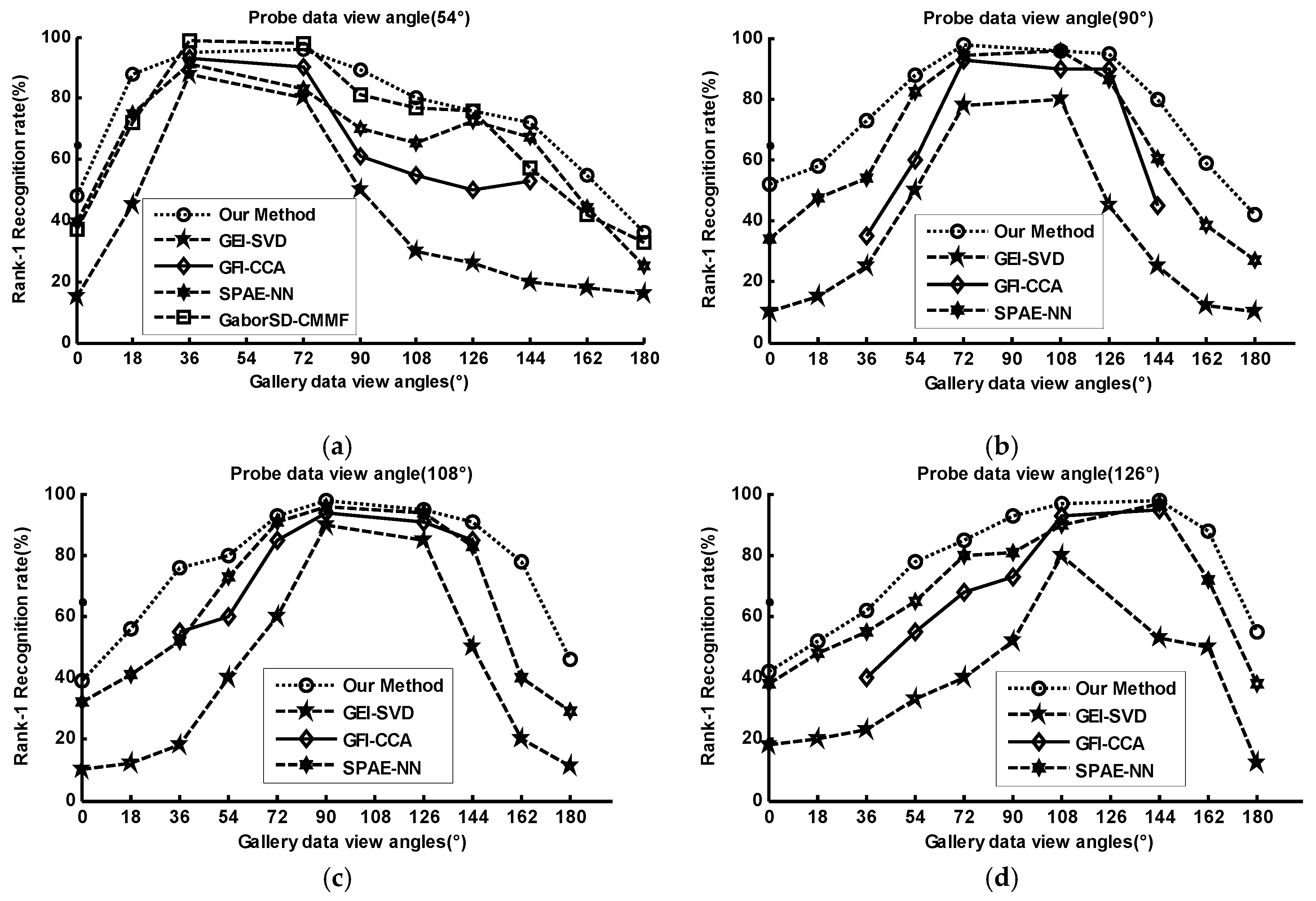
4.2.1. One Gallery View under Normal Conditions
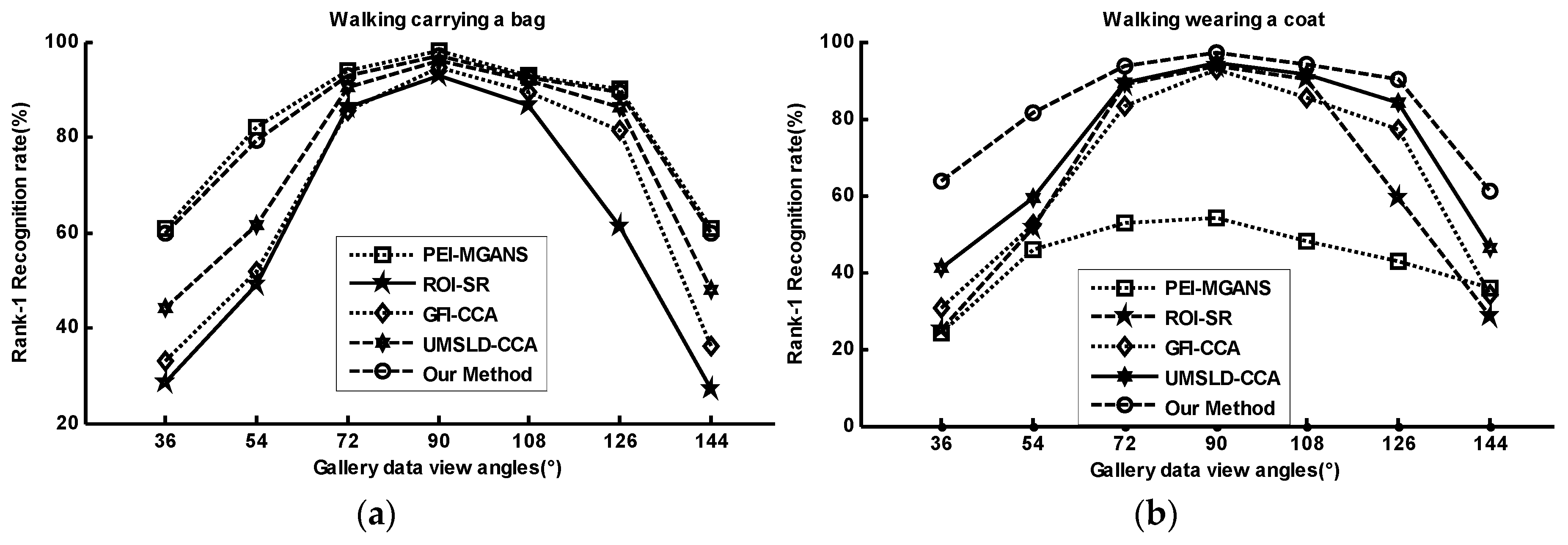
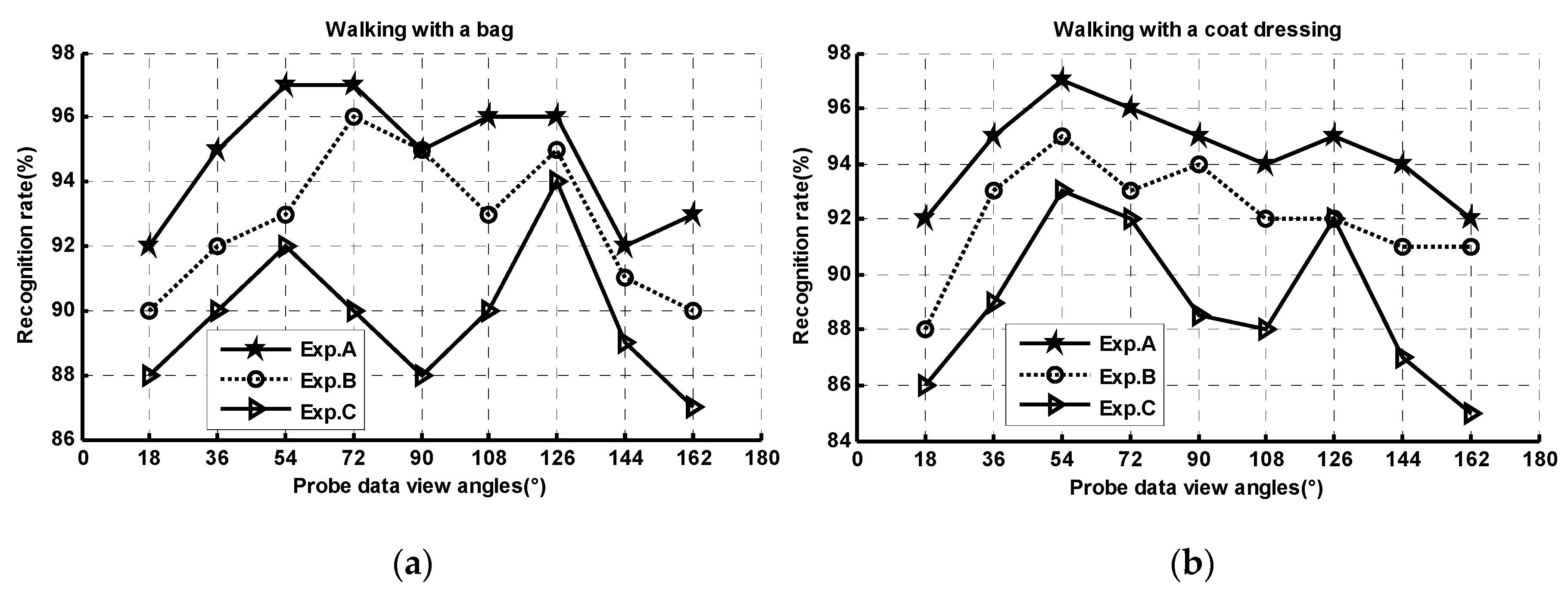
4.2.2. Multi-View Gait Recognition under Various Conditions
4.3. Experiments on TUM-IITKGP Database with Flexible Probe Frames
4.4. Experiments on KY4D Databases with Curved Trajectories
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jasvinder, P.S.; Sanjeev, J.; Sakshi, A.; Uday, P.S. Vision-Based Gait Recognition: A Survey. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 70497–70527. [Google Scholar]
- Yiwei, H.; Junping, Z.; Hongming, S.; Wang, L. Multi-task GANs for View-Specific Feature Learning in Gait Recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 14, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ben, X.; Peng, Z.; Lai, Z.; Yan, R.; Zhai, Z.; Meng, W. A general tensor representation framework for cross-view gait recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 90, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Gaitset: Regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2019, Hawaii, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Bhanu, B. Individual Recognition Using Gait Energy Image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, N.; Makihara, Y.; Muramatsu, D.; Echigo, T.; Yagi, Y. Multi-view large population gait dataset and its performance evaluation for cross-view gait recognition. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 2018, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.; Wang, C.; Cheng, F.; Zeng, W. Fusion of spatial-temporal and kinematic features for gait recognition with deterministic learning. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 67, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.; Ahmad, S.; Dubinsky, D. Cortical Learning Algorithm and Hierarchical Temporal Memory. Numenta Whitepaper, 2011; pp. 1–68. Available online: http://numenta.org/resources/HTM_CorticalLearningAlgorithms.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Yuwei, C.; Subutai, A.; Jeff, H. The HTM Spatial Pooler—A Neocortical Algorithm for Online Sparse Distributed Coding. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Jay, K.C.-C.; Peng, J. Gait recognition via GEI subspace projections and collaborative representation classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 1932–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liang, J.; Zhao, H.; Hu, H.; Tian, J. Frame difference energy image for gait recognition with incomplete silhouettes. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, K.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S. Gait recognition without subject cooperation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, T.H.W.; Cheung, K.H.; Liu, J.N.K. Gait flow image: A silhouette-based gait representation for human identification. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sural, S.; Mukherjee, J. Gait recognition using Pose Kinematics and Pose Energy Image. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastaniotis, D.; Theodorakopoulos, I.; Theoharatos, C.; Economou, G.; Fotopouulos, S. A framework for gait-based recognition using Kinect. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2015, 68, 32–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Ding, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y. Action and gait recognition from recovered 3-D human joints. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2010, 40, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Sandau, M.; Heimbürger, R.V.; Jensen, K.E.; Moeslund, T.B.; Aanæs, H.; Alkjær, T.; Simonsen, E.B. Reliable Gait Recognition Using 3D Reconstructions and Random Forests–An Anthropometric Approach. J. Forensic Sci. 2016, 61, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Fernández, D.; Madrid-Cuevas, F.J.; Carmona-Poyato, A.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Muñoz-Salinas, R.; Medina-Carnicer, R. Viewpoint-independent gait recognition through morphological descriptions of 3D human reconstructions. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, I.F.; Hong, S.; Lee, H.; Ahn, S.; Toh, K.-A.; Kim, E. Multi-view gait recognition fusion methodology. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Singapore, 3–5 June 2008; pp. 2101–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Kusakunniran, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Gait Recognition under Various Viewing Angles Based on Correlated Motion Regression. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2012, 22, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, D.; Shiraishi, A.; Makihara, Y.; Uddin, M.Z.; Yagi, Y. Gait-Based Person Recognition Using Arbitrary View Transformation Model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, D.; Makihara, Y.; Yagi, Y. View Transformation Model Incorporating Quality Measures for Cross-View Gait Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 46, 1602–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fernández, D.; Madrid-Cuevas, F.J.; Carmona-Poyato, A.; Muñoz-Salinas, R.; Medina-Carnicer, R. A new approach for multi-view gait recognition on unconstrained paths. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 38, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, T. A Comprehensive Study on Cross-View Gait Based Human Identification with Deep CNNs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Wang, C.; Zheng, T. Individual identification using a gait dynamics graph. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 83, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Anguelov, D.; Srinivasan, P.; Koller, D.; Thrun, S.; Rodgers, J.; Davis, J. SCAPE: Shape Completion and Animation of People. ACM Trans. Graph. 2015, 24, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastioni, M.; Simone, R. Ideas and methods for modeling 3D human figures: The principal algorithms used by MakeHuman and their implementation in a new approach to parametric modeling. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Bangalore Annual Conference, COMPUTE 2008, Bangalore, India, 18–20 January 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Tang, J.; Tjahjadi, T.; Xiao, X. Robust arbitrary view gait recognition based on parametric 3D human body reconstruction and virtual posture synthesis. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 60, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Luo, J.; Tjahjadi, T.; Guo, F. Robust Arbitrary-View Gait Recognition based on 3D Partial Similarity Matching. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CMU. Carnegie-Mellon Mocap Database. 2003. Available online: http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Liang, X.; Gong, K.; Shen, X.; Lin, L. Look into Person: Joint Body Parsing & Pose Estimation Network and a New Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 871–885. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Qiu, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. DeepFashion: Powering Robust Clothes Recognition and Retrieval with Rich Annotations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1096–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Su, Z.; Fu, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Luo, X. A data-driven editing framework for automatic 3D garment modeling. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 12597–12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.; Ahmad, S. Why Neurons Have Thousands of Synapses, a Theory of Sequence Memory in Neocortex. Front. Neural Circuits 2016, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, K.; Dong, L.; Pan, C.; Xu, W.; Yang, K. Deep Learning Based Joint Resource Scheduling Algorithms for Hybrid MEC Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.-J.; Wostmann, M.; Obleser, J. Selective attention to auditory memory neurally enhances perceptual precision. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 16094–16104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Xu, B. Modeling Attention and Memory for Auditory Selection in a Cocktail Party Environment. In Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2018), New Orleans, Louisiana, 26 April 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, Ł.; Nachum, O.; Roy, A.; Bengio, S. Learning to remember rare events. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, R.; Shi, J. The CMU Motion of Body (MoBo) Database; Technical Report CMU-RI-TR-01-18; Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Liu, Y.; Collins, R. Shape variation-based frieze pattern for robust gait recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 18–23 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, D.S.; Tjahjadi, T. Silhouette-based gait recognition using Procrustes shape analysis and elliptic Fourier descriptors. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 3414–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusakunniran, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Automatic gait recognition using weighted binary pattern on video. In Proceedings of the Sixth IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, Genova, Italy, 2–4 September 2009; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Wang, C. Silhouette-based gait recognition via deterministic learning, Advances in Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference, Beijing, China, 9–11 June 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June April 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Tan, D.; Tan, T. A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; pp. 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Kusakunniran, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Multiple views gait recognition using view transformation model based on optimized gait energy image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 1058–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, K.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S. Cross-view gait recognition using correlation strength. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, London, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y. Invariant feature extraction for gait recognition using only one uniform model. Neurocomputing 2017, 239, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.S.; Tjahjadi, T. Robust view-invariant multiscale gait recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H. Enhanced gabor feature based classification using a regularized locally tensor discriminant model for multiview gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; He, R.; Tan, T. Robust view transformation model for gait recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 2073–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Makihara, Y.; Sagawa, R.; Mukaigawa, Y.; Echigo, T.; Yagi, Y. Gait recognition using a view transformation model in the frequency domain. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Rida, I.; Jiang, X.; Marcialis, G.L. Human Body Part Selection by Group Lasso of Motion for Model-Free Gait Recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H. Multiview Gait Recognition Based on Patch Distribution Features and Uncorrelated Multilinear Sparse Local Discriminant Canonical Correlation Analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 24, 617–630. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, M.; Sural, S.; Rigoll, G. Gait Recognition in the Presence of Occlusion: A New Dataset and Baseline Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conferences on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision (WSCG), Plzen, Czech Republic, 31 January–3 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita, Y.; Ogawara, K.; Kurazume, R. Identification of people walking along curved trajectories. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 48, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Carnicer, R.M. Pyramidal fisher motion for multiview gait recognition. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2014, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 1692–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Seely, R.; Samangooei, S.; Lee, M.; Carter, J.; Nixon, M. The University of Southampton Multi-Biometric Tunnel and introducing a novel 3D gait dataset. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, Arlington, VA, USA, 29 September–1 October 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]









| Exp. | Gallery Set | Attention Model Training Set | Probe Set | Gallery/Probe Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Slow walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Fast walk | Fast walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| B | Slow walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Ball-carrying | Ball-carrying | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| C | Slow walk | Slow and 5 subjects of inclined walk | inclined walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| D | Fast walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Fast walk | Slow walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| E | Fast walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Fast and Ball-carrying walk | Ball-carrying | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| F | Fast walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Fast and inclined walk | Inclined walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| G | Inclined walk | Slow and 5 subjects of inclined walk | Slow walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| H | Inclined walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Fast and inclined walk | Fast walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| I | Inclined walk | Slow and 5 subjects of Ball-carrying and inclined walk | Ball-carrying | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| J | Ball-carrying | Slow and 5 subjects of Ball-carrying walk | Slow walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| K | Ball-carrying | Slow and 5 subjects of Fast and Ball-carrying walk | Fast walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| L | Ball-carrying | Slow and 5 subjects of Ball-carrying and inclined walk | Inclined walk | 25 × 3 × 4 |
| Exp. | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSVB | 82% | 77% | - | 80% | 61% | - | - | - | - | 89% | 73% | - |
| WBP | 92% | 73% | 92% | 61% | - | - | - | - | 75% | 63% | - | |
| STM | 94% | 93% | 91% | 84% | - | - | - | - | 82% | 82% | - | |
| SGRVDL | 96% | 87% | 92% | 88% | - | - | - | - | 87% | 88% | - | |
| PEI | 100% | 92% | 60% | 88% | 60% | 72% | 76% | 80% | 48% | 92% | 84% | 76% |
| Our | 100% | 94% | 90% | 93% | 92% | 95% | 90% | 92% | 94% | 95% | 95% | 92% |
| Methods | Probe | 36° | 54° | 72° | 90° | 108° | 126° | 144° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI-MGR [50] | Bag | 88% | 90% | 78% | 80% | 82% | 83% | 91% |
| Coat | 70% | 80% | 72% | 75% | 77% | 73% | 68% | |
| GFI-CCA [48] | Bag | 83% | 80% | 76% | 71% | 75% | 70% | 73% |
| Coat | 45% | 59% | 50% | 42% | 36% | 34% | 48% | |
| GEI-GaitSet [4] | Bag | 92% | 89% | 83% | 81% | 84% | 90% | 92% |
| Coat | 81% | 77% | 72% | 70% | 71% | 74% | 74% | |
| GRU-HTM | Bag | 86% | 82% | 79% | 75% | 78% | 80% | 83% |
| Coat | 75% | 74% | 69% | 66% | 68% | 70% | 69% | |
| GRU-GSFSL-A | Bag | 91% | 88% | 85% | 84% | 87% | 89% | 88% |
| Coat | 81% | 83% | 85% | 88% | 82% | 81% | 80% | |
| GRU-GSFSL-B | Bag | 92% | 91% | 90% | 89% | 92% | 91% | 89% |
| Coat | 88% | 90% | 92% | 91% | 91% | 92% | 89% | |
| GRU-GSFSL | Bag | 92% | 94% | 94% | 95% | 93% | 93% | 93% |
| Coat | 93% | 95% | 96% | 94% | 94% | 95% | 93% |
| Probe/Gallery View | 54°/36° | 90°/108° | 126°/144° | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Method | Bag | 91.6% | 92.8% | 90.6% |
| Coat | 92.4% | 92.0% | 93.2% | |
| HBPS-GLM | Bag | 76.4% | 73.7% | 76.9% |
| Coat | 87.9% | 91.1% | 86.2% | |
| RLTDA | Bag | 80.8% | 76.5% | 72.3% |
| Coat | 69.4% | 72.1% | 64.6% | |
| Robust VTM | Bag | 40.7% | 58.2% | 59.4% |
| Coat | 35.4% | 50.3% | 61.3% | |
| FT-SVD | Bag | 26.5% | 33.1% | 38.6% |
| Coat | 19.8% | 20.6% | 32% | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Tjahjadi, T. Gait Recognition and Understanding Based on Hierarchical Temporal Memory Using 3D Gait Semantic Folding. Sensors 2020, 20, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061646
Luo J, Tjahjadi T. Gait Recognition and Understanding Based on Hierarchical Temporal Memory Using 3D Gait Semantic Folding. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jian, and Tardi Tjahjadi. 2020. "Gait Recognition and Understanding Based on Hierarchical Temporal Memory Using 3D Gait Semantic Folding" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061646
APA StyleLuo, J., & Tjahjadi, T. (2020). Gait Recognition and Understanding Based on Hierarchical Temporal Memory Using 3D Gait Semantic Folding. Sensors, 20(6), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061646





