A Comparative Study of Brachial–Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity and Heart–Finger Pulse Wave Velocity in Korean Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
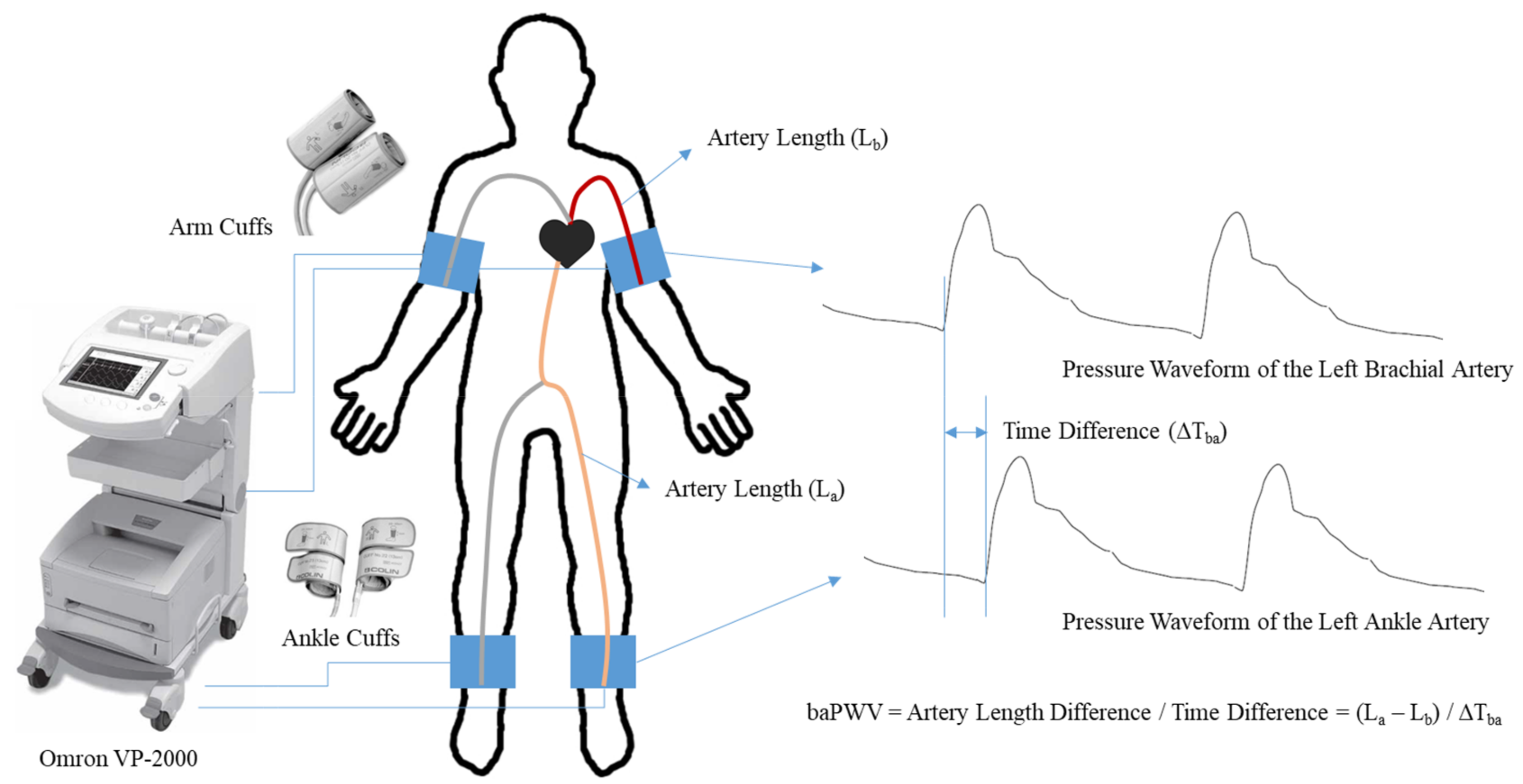
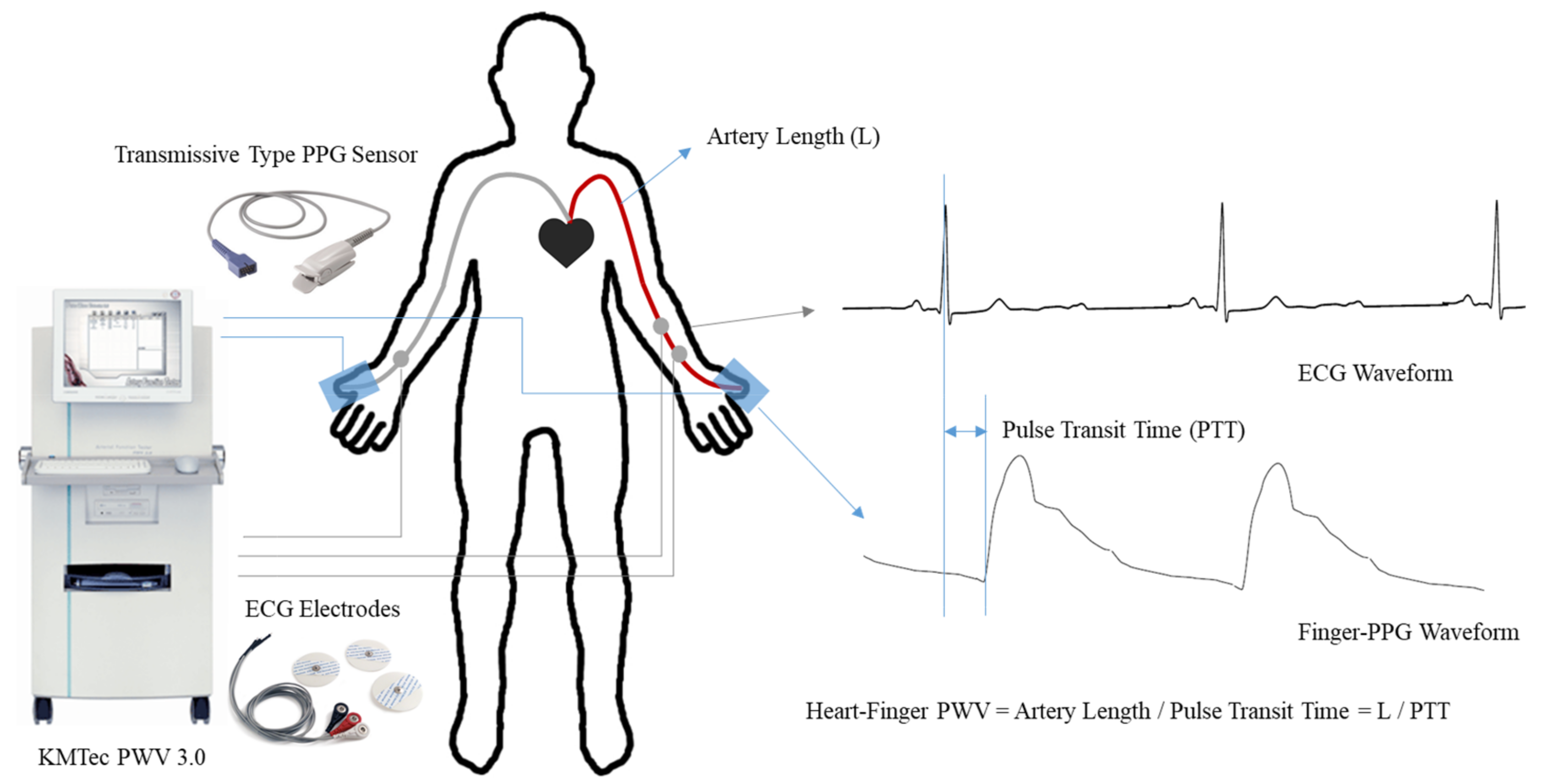
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Brachial–Ankle PWV and Heart–Finger PWV Measurements
3.2. Comparison of Heart–Finger PWV Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Asmar, R.; Gautier, I.; Laloux, B.; Guize, L.; Ducimetiere, P.; Benetos, A. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Katsahian, S.; Fassot, C.; Tropeano, A.-I.; Gautier, I.; Laloux, B.; Boutouyrie, P. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of fatal stroke in essential hypertension. Stroke 2003, 34, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattace-Raso, F.U.S.; van der Cammen, T.J.M.; Hofman, A.; van Popele, N.M.; Bos, M.L.; Schalekamp, M.A.D.H.; Asmar, R.; Reneman, R.S.; Hoeks, A.P.G.; Breteler, M.M.B.; et al. Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: the Rotterdam study. Circulation 2006, 113, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, S.M.T.; Dixon, L.J.; McVeigh, G.E. Arterial stiffness and pulse wave velocity: problems with terminology. Circulation 2004, 109, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terai, M.; Ohishi, M.; Ito, N.; Takagi, T.; Tatara, Y.; Kaibe, M.; Komai, N.; Rakugi, H.; Ogihara, T. Comparison of arterial functional evaluations as a predictor of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients: the non-invasive atherosclerotic evaluation in hypertension(NOAH) study. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoach, S.S.; Townsend, R.R. Vascular stiffness: its measurement and significance for epidemiologic and outcome studies. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashina, A.; Tomiyama, H.; Takeda, K.; Tsuda, H.; Arai, T.; Hirose, K.; Koji, Y.; Hori, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Validity, reproducibility, and clinical significance of noninvasive brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity measurement. Hypertens. Res. 2002, 25, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchikura, S.; Shoji, T.; Kimoto, E.; Shinohara, K.; Hatsuda, S.; Koyama, H.; Emoto, M.; Nishizawa, Y. Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity as an index of central arterial stiffness. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-Y.; Choi, D.-H.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, B.-B.; Ki, Y.-J.; Chung, J.-W.; Koh, Y.-Y.; Chang, K.-S.; Hong, S.-P. Predictive value of brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity for cardiovascular events. Am. J. Med Sci. 2013, 346, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.-S.; Li, Y.; Li, L.-H.; Huang, Q.-F.; Zeng, W.-F.; Kang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Wei, F.-F.; Li, G.-L.; et al. Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity as a predictor of mortality in elderly Chinese. Hypertension 2014, 64, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, T.-J.; Song, D.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.S.; Nam, C.M.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Heo, J.H. Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity is a strong predictor for mortality in patients with acute stroke. Hypertension 2014, 64, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.-M.; Yang, T.-Y.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chang, S.-T.; Hsiao, J.-F.; Pan, K.-L.; Jang, S.-J.; Hsu, J.-T. Relation of arterial stiffness assessed by brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity to complexity of coronary artery disease. Am. J. Med Sci. 2014, 348, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Avolio, A.; Seo, D.C.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Sung, K.-C. Relationship between brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity and incident hypertension according to 2017 ACC/AHA high blood pressure guidelines. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Tomiyama, H.; Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Kita, Y.; Inoguchi, T.; Maeda, Y.; Kohara, K.; Tabara, Y.; et al. Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity and the risk prediction of cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 2017, 69, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Cooper, M.Y.; Supak, J.A.; Tanaka, H. A new device for automatic measurements of arterial stiffness and ankle-brachial index. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, M.U.R.; Reddy, B.M.; Yashmaina, S.; Patnaik, A.N.; Rani, P.U. Validity and reproducibility of arterial pulse wave velocity measurement using new device with oscillometric technique: a pilot study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2005, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, H.; Yamashina, A.; Arai, T.; Hirose, K.; Koji, Y.; Chikamori, T.; Hori, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Doba, N.; Hinohara, S. Influences of age and gender on results of noninvasive brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity measurement—a survey of 12517 subjects. Atherosclerosis 2003, 166, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyai, N.; Utsumi, M.; Gowa, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Miyashita, K.; Takeda, S.; Arita, M. Age-specific nomogram of brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity in Japanese adolescents. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2013, 35, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiming, G.; Zhou, X.; Lv, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Xing, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Reference values of brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity according to age and blood pressure in a central Asia population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-B.; Hsu, P.-C.; Chen, Z.-L.; Wu, H.-T. Measuring pulse wave velocity using ECG and phothoplethysmography. J. Med Syst. 2011, 35, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fang, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, T. Reliability analysis of an integrated device of ECG, PPG and pressure pulse wave for cardiovascular disease. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 87, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Instruments, AFE4900 Ultra-Low Power, Integrated AFE for Wearable Optical, Electrical Bio-Sensing with FIFO. 2017. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/afe4900.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2017).
- Teng, X.F.; Zhang, Y.T. Continuous and noninvasive estimation of arterial blood pressure using a photoplethysmographic approach. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rundo, F.; Ortis, A.; Battiato, S.; Conoci, S. Advanced bio-inspired system for noninvasive cuff-less blood pressure estimation from physiological signal analysis. Computation 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazazzera, R.; Belhaj, Y.; Carrault, G. A new wearable device for blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmogram. Sensors 2019, 19, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slapnicar, G.; Mlakar, N.; Luštrek, M. Blood pressure estimation from photoplethysmogram using a spectro-temporal deep neural network. Sensors 2019, 19, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundo, F.; Ortis, A.; Battiato, S.; Conoci, S. Advanced multi-neural system for cuff-less blood pressure estimation through nonlinear HC-features. In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications, Prague, Czech Republic, 26–28 July 2019; Volume 1, pp. 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. Hypertension assessment via ECG and PPG signals: An evaluation using MIMIC database. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, D.N.; Shruthi, S. Digital processing of ECG and PPG signals for study of arterial parameters for cardiovascular risk assessment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing(ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 2–4 April 2015; pp. 1506–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Oreggia, D.; Guarino, S.; Parisi, A.; Pernice, R.; Adamo, G.; Mistretta, L.; di Buono, P.; Fallica, G.; Ferla, G.; Cino, A.C.; et al. Physiological parameters measurements in a cardiac cycle via a combo PPG-ECG system. In Proceedings of the AEIT International Annual Conference, Naples, Italy, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rundo, F.; Conoci, S.; Ortis, A.; Battiato, S. An advanced bio-inspired photoplethysmography(PPG) and ECG Pattern Recognition System for Medical Assessment. Sensors 2018, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeinia, E.K.; Azimib, I.; Rahmania, A.M.; Liljebergb, P.; Dutta, N. A Real-time PPG quality assessment approach for healthcare internet-of-things. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT), Leuven, Belgium, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 551–558. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, R.A.; Symeonides, C.N.; Webb, D.J.; Maxwell, S.R.J. Pulse transit time measured from the ECG: An unreliable marker of beat-to-beat blood pressure. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, J.; Pretty, C.; Kamoi, S.; Davidson, S.; Pironet, A.; Desaive, T.; Shaw, G.M.; Chase, J.G. Electrocardiogram R-wave is an unreliable indicator of pulse wave initialization. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wang, X.; Yin, L.; Li, Y. A wearable sensor for arterial stiffness monitoring based on machine learning algorithms. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, R.V.; Nabeel, P.M.; Joseph, J.; Sivaprakasam, M. Methodological and measurement concerns of local pulse wave velocity assessment. IEEE Int. Symp. Med. Meas. Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 92 | 93 |
| Age | 42 ± 13 | 42 ± 13 |
| Height (cm) | 172 ± 7 | 159 ± 5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23 ± 2 | 22 ± 2 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 124 ± 11 | 116 ± 10 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80 ± 8 | 75 ± 8 |
| MBP (mmHg) | 95 ± 8 | 88 ± 8 |
| PP (mmHg) | 44 ± 8 | 41 ± 8 |
| Right Arm Length (cm) | 85 ± 4 | 78 ± 3 |
| Left Arm Length (cm) | 84 ± 4 | 77 ± 3 |
| Brachial–Ankle PWV (cm/s) | 1297 ± 230 | 1195 ± 231 |
| Heart-Finger PWV (cm/s) | 391 ± 29 | 365 ± 25 |
| Gender | Age (Year) | No. of Subjects | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | RA Length (cm) | LA Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 20–24 | 13 | 177 ± 7 | 22 ± 1 | 123 ± 11 | 72 ± 8 | 87 ± 4 | 87 ± 4 |
| 25–29 | 6 | 175 ± 6 | 24 ± 1 | 117 ± 9 | 78 ± 7 | 88 ± 4 | 87 ± 4 | |
| 30–34 | 11 | 176 ± 6 | 23 ± 1 | 123 ± 14 | 80 ± 9 | 87 ± 4 | 86 ± 4 | |
| 35–39 | 14 | 173 ± 5 | 23 ± 2 | 123 ± 13 | 80 ± 9 | 85 ± 3 | 85 ± 3 | |
| 40–44 | 16 | 171 ± 4 | 23 ± 1 | 125 ± 8 | 83 ± 6 | 83 ± 3 | 83 ± 3 | |
| 45–49 | 5 | 172 ± 7 | 22 ± 2 | 123 ± 10 | 74 ± 13 | 85 ± 3 | 84 ± 4 | |
| 50–54 | 6 | 167 ± 4 | 23 ± 1 | 127 ± 12 | 83 ± 8 | 82 ± 1 | 82 ± 2 | |
| 55–59 | 6 | 165 ± 9 | 24 ± 1 | 132 ± 6 | 86 ± 4 | 82 ± 5 | 81 ± 4 | |
| 60–64 | 12 | 165 ± 4 | 22 ± 2 | 125 ± 10 | 81 ± 6 | 82 ± 2 | 81 ± 2 | |
| 65–69 | 3 | 169 ± 10 | 23 ± 1 | 134 ± 3 | 85 ± 4 | 84 ± 4 | 84 ± 3 | |
| Female | 20–24 | 10 | 162 ± 4 | 21 ± 1 | 113 ± 7 | 73 ± 8 | 79 ± 3 | 79 ± 3 |
| 25–29 | 10 | 160 ± 3 | 21 ± 2 | 109 ± 8 | 72 ± 7 | 78 ± 2 | 78 ± 2 | |
| 30–34 | 15 | 160 ± 3 | 21 ± 1 | 113 ± 9 | 74 ± 8 | 78 ± 2 | 77 ± 2 | |
| 35–39 | 7 | 161 ± 6 | 22 ± 2 | 111 ± 7 | 72 ± 9 | 78 ± 3 | 78 ± 3 | |
| 40–44 | 14 | 160 ± 6 | 21 ± 2 | 114 ± 11 | 70 ± 9 | 78 ± 4 | 78 ± 4 | |
| 45–49 | 5 | 161 ± 5 | 21 ± 2 | 117 ± 9 | 76 ± 7 | 78 ± 2 | 78 ± 2 | |
| 50–54 | 7 | 157 ± 3 | 22 ± 1 | 123 ± 12 | 83 ± 6 | 78 ± 3 | 77 ± 3 | |
| 55–59 | 14 | 157 ± 5 | 22 ± 1 | 120 ± 11 | 78 ± 9 | 77 ± 3 | 77 ± 3 | |
| 60–64 | 9 | 155 ± 5 | 23 ± 1 | 121 ± 15 | 78 ± 8 | 76 ± 3 | 76 ± 3 | |
| 65–69 | 2 | 155 ± 4 | 23 ± 2 | 122 ± 4 | 80 ± 6 | 78 ± 4 | 78 ± 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, J.; Baek, H.J. A Comparative Study of Brachial–Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity and Heart–Finger Pulse Wave Velocity in Korean Adults. Sensors 2020, 20, 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072073
Cho J, Baek HJ. A Comparative Study of Brachial–Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity and Heart–Finger Pulse Wave Velocity in Korean Adults. Sensors. 2020; 20(7):2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072073
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Jaegeol, and Hyun Jae Baek. 2020. "A Comparative Study of Brachial–Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity and Heart–Finger Pulse Wave Velocity in Korean Adults" Sensors 20, no. 7: 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072073
APA StyleCho, J., & Baek, H. J. (2020). A Comparative Study of Brachial–Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity and Heart–Finger Pulse Wave Velocity in Korean Adults. Sensors, 20(7), 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072073





