Influence of Mg Doping Levels on the Sensing Properties of SnO2 Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Thin Film Synthesis and Processing
2.2. Characterization Methods
2.3. Gas Sensing Measurements
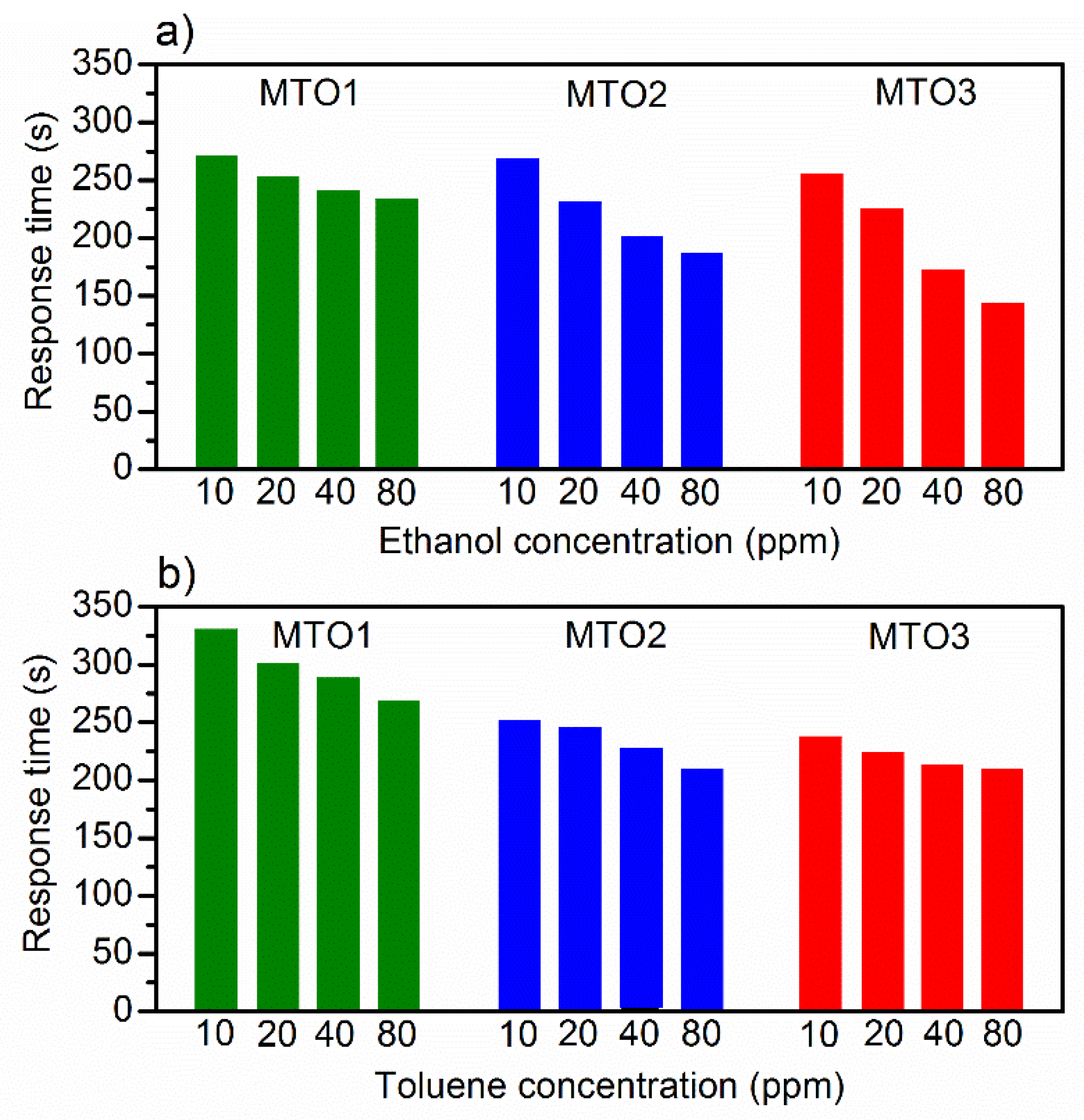
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Films Analysis and Characterization
3.2. Gas Sensing Properties
3.3. Gas Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schütze, A.; Baur, T.; Leidinger, M.; Reimringer, W.; Jung, R.; Conrad, T.; Sauerwald, T. Highly Sensitive and Selective VOC Sensor Systems Based on Semiconductor Gas Sensors: How to? Environment 2017, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.-W.; Lee, J.-H. Toward breath analysis on a chip for disease diagnosis using semiconductor-based chemiresistors: Recent progress and future perspectives. LAB CHIP 2017, 17, 3537–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Kumar, D. Mg-doped TiO2 thin films deposited by low cost technique for CO gas monitoring. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, S.; Gràcia, I.; Lednický, T.; Vojkuvka, L.; Figueras, E.; Hubálek, J.; Cané, C. Highly hydrogen sensitive micromachined sensors based on aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposited ZnO rods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, S.; Selina, S.; Annanouch, F.E.; Gràcia, I.; Llobet, E.; Blackman, C. Aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition of gas sensitive SnO2 and Au-functionalised SnO2 nanorods via a non-catalysed vapour solid (VS) mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallejos, S.; Gràcia, I.; Figueras, E.; Cané, C. Nanoscale heterostructures based on Fe2O3@ WO3-x nanoneedles and their direct integration into flexible transducing platforms for toluene sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18638–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Toluene and ethanol sensing performances of pristine and PdO-decorated flower-like ZnO structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Xie, E. Enhanced gas sensing performance of electrospun Pt-functionalized NiO nanotubes with chemical and electronic sensitization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7410–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, M.; Šetka, M.; Chmela, O.; Gràcia, I.; Figueras, E.; Cané, C.; Vallejos, S. Cerium Oxide-Tungsten Oxide Core-Shell Nanowire-Based Microsensors Sensitive to Acetone. Biosensors 2018, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xu, L.; Gui, Y. Recent advances of SnO2-based sensors for detecting fault characteristic gases extracted from power transformer oil. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belmonte, J.C.; Manzano, J.; Arbiol, J.; Cirera, A.; Puigcorbe, J.; Vila, A.; Sabate, N.; Gracia, I.; Cane, C.; Morante, J. Micromachined twin gas sensor for CO and O2 quantification based on catalytically modified nano-SnO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Hou, H. Charge imbalance induced oxygen-adsorption enhances the gas-sensing properties of Al-doped SnO2 powders. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 124, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-g.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J. Pt-doped SnO2 thin film based micro gas sensors with high selectivity to toluene and HCHO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-M.; Lo, Y.-J. Reducing gas-sensing performance of Ce-doped SnO2 thin films through a cosputtering method. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Ma, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Cheng, L.; Mao, Y.; Luo, J.; Gengzang, D. Preparation of Pr-doped SnO2 hollow nanofibers by electrospinning method and their gas sensing properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 605, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X.; Sun, P.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Lu, G. Hydrothermal preparation and gas sensing properties of Zn-doped SnO2 hierarchical architectures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Shah, N.A.; Bhatti, A.S.; Malik, M.A. Effects of Mg doping on optical and CO gas sensing properties of sensitive ZnO nanobelts. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 6080–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, S.; Khojier, K. Role of substrate temperature on the ammonia gas sensing performance of Mg-doped ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique: Application in breath analysis devices. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, E.; Gowrishankar, S.; Gopalakrishnan, N. Effect of Mg doping in the gas-sensing performance of RF-sputtered ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, K.; Srinivasan, D.; Christopher, J.B. Fabrication of highly c-axis Mg doped ZnO on c-cut sapphire substrate by rf sputtering for hydrogen sensing. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Elec. 2017, 28, 11979–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, C.-H.; Woo, H.-S.; Abdel-Hady, F.; Wazzan, A.; Lee, J.-H. Vapor-phase growth of urchin-like Mg-doped ZnO nanowire networks and their application to highly sensitive and selective detection of ethanol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.-M.; Lee, C.-S.; Wang, R.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Highly sensitive and selective ethanol sensors using magnesium doped indium oxide hollow spheres. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2017, 54, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Xie, Z.; Li, Q.; Niu, H. On the possibility of p-type doping of SnO2 with Mg: A first-principles study. J. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 101, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, S.M.N. Modeling and Spray Pyrolysis Processing of Mixed Metal Oxide Nano-Composite Gas Sensor Films. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA, 2014. Available online: http://purl.fcla.edu/fcla/etd/CFE0005817 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Falcony, C.; Aguilar-Frutis, M.A.; García-Hipólito, M. Spray pyrolysis technique; high-K dielectric films and luminescent materials: A review. Micromachines 2018, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touidjen, N.H.; Bendahmane, B.; Lamri Zeggar, M.; Mansour, F.; Aida, M. SnO2 thin film synthesis for organic vapors sensing at ambient temperature. Sens. Biosensing Res. 2016, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bendahmane, B.; Touidjen, N.H.; Mansour, F. Characterization of SnO2 Thin Films Fabricated by Chemical Spray Pyrolysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Algiers, Algeria, 19–21 November 2019; IEEE, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, S.; Grácia, I.; Chmela, O.; Figueras, E.; Hubálek, J.; Cané, C. Chemoresistive micromachined gas sensors based on functionalized metal oxide nanowires: Performance and reliability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shajira, P.; Bushiri, M.J.; Nair, B.B.; Prabhu, V.G. Energy band structure investigation of blue and green light emitting Mg doped SnO2 nanostructures synthesized by combustion method. J. Lumin. 2014, 145, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, N.; Bharati, A.; Saha, S.; Sen, D.; Chattopadhyay, K. Effect of Mg doping on the electrical properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.; Tsakiridis, P.; Hristoforou, E. Structural and electrical properties of undoped SnO2 films developed by a low cost CVD technique with two different methods: Comparative study. J. Opt. Adv. Mat. 2005, 7, 2693–2706. Available online: https://dspace.lib.ntua.gr/xmlui/handle/123456789/16827 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Kwoka, M.; Ottaviano, L.; Passacantando, M.; Santucci, S.; Czempik, G.; Szuber, J. XPS study of the surface chemistry of L-CVD SnO2 thin films after oxidation. Thin Solid Films 2005, 490, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, F.H.; Gonzalez, I.; Coaquira, J.A.; Hidalgo, P.; Brito, H.F.; Ardisson, J.D.; Macedo, W.A.; Morais, P.C. Structural and surface study of praseodymium-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by the polymeric precursor method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8711–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Y. Enhanced SaOS-2 cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation on Mg-incorporated micro/nano-topographical TiO2 coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, M.; Mo, J.; Deng, C.; Zhu, M. Tribochemical Behavior of Pure Magnesium During Sliding Friction. Metals 2019, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubecký, F.; Kindl, D.; Hubík, P.; Mičušík, M.; Dubecký, M.; Boháček, P.; Vanko, G.; Gombia, E.; Nečas, V.; Mudroň, J. A comparative study of Mg and Pt contacts on semi-insulating GaAs: Electrical and XPS characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 395, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Bhatti, H.S.; Singh, K. Europium doping effect on 3D flower-like SnO2 nanostructures: Morphological changes, photocatalytic performance and fluorescence detection of heavy metal ion contamination in drinking water. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37450–37466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayanthi, K.; Chawla, S.; Sood, K.; Chhibara, M.; Singh, S. Dopant induced morphology changes in ZnO nanocrystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5869–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithyavathy, N.; Arunmetha, S.; Vinoth, M.; Sriram, G.; Rajendran, V. Fabrication of Nanocomposites of SnO2 and MgAl2O4 for Gas Sensing Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ju, D.; Chen, Z.; Han, R.; Zhai, T.; Yu, H.; Liu, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, B. A novel hetero-structure sensor based on Au/Mg-doped TiO2/SnO2 nanosheets directly grown on Al2O3 ceramic tubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoang, N.D.; Van Duy, N.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Hieu, N. Design of SnO2/ZnO hierarchical nanostructures for enhanced ethanol gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Hao, Y.; Du, H.; Li, X. Toluene sensing properties of porous Pd-loaded flower-like SnO2 microspheres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Fabrication of porous α-Fe2O3 nanoshuttles and their application for toluene sensors. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30840–30849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, J.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, T. Nanoparticles-assembled Co3O4 nanorods p-type nanomaterials: One-pot synthesis and toluene-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Skariah, B. Spray deposited Mg-doped SnO2 thin film LPG sensor: XPS and EDX analysis in relation to deposition temperature and doping. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 625, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Conduction model of metal oxide gas sensors. J. Electroceram. 2001, 7, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, S.; Roggen, J.; Maes, G. FT-IR characterization of tin dioxide gas sensor materials under working conditions. Spectrochim. Acta A 1995, 51, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Mahapatra, R.; Mondal, B.; Maruyama, T.; Ghosh, R. Ultrafast and reversible gas-sensing properties of ZnO nanowire arrays grown by hydrothermal technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 3019–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tamaki, J.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. Grain size effects on gas sensitivity of porous SnO2-based elements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 3, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, D. The role of noble metals in the chemistry of solid-state gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1990, 1, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ederth, J.; Smulko, J.; Kish, L.B.; Heszler, P.; Granqvist, C.G. Comparison of classical and fluctuation-enhanced gas sensing with PdxWO3 nanoparticle films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

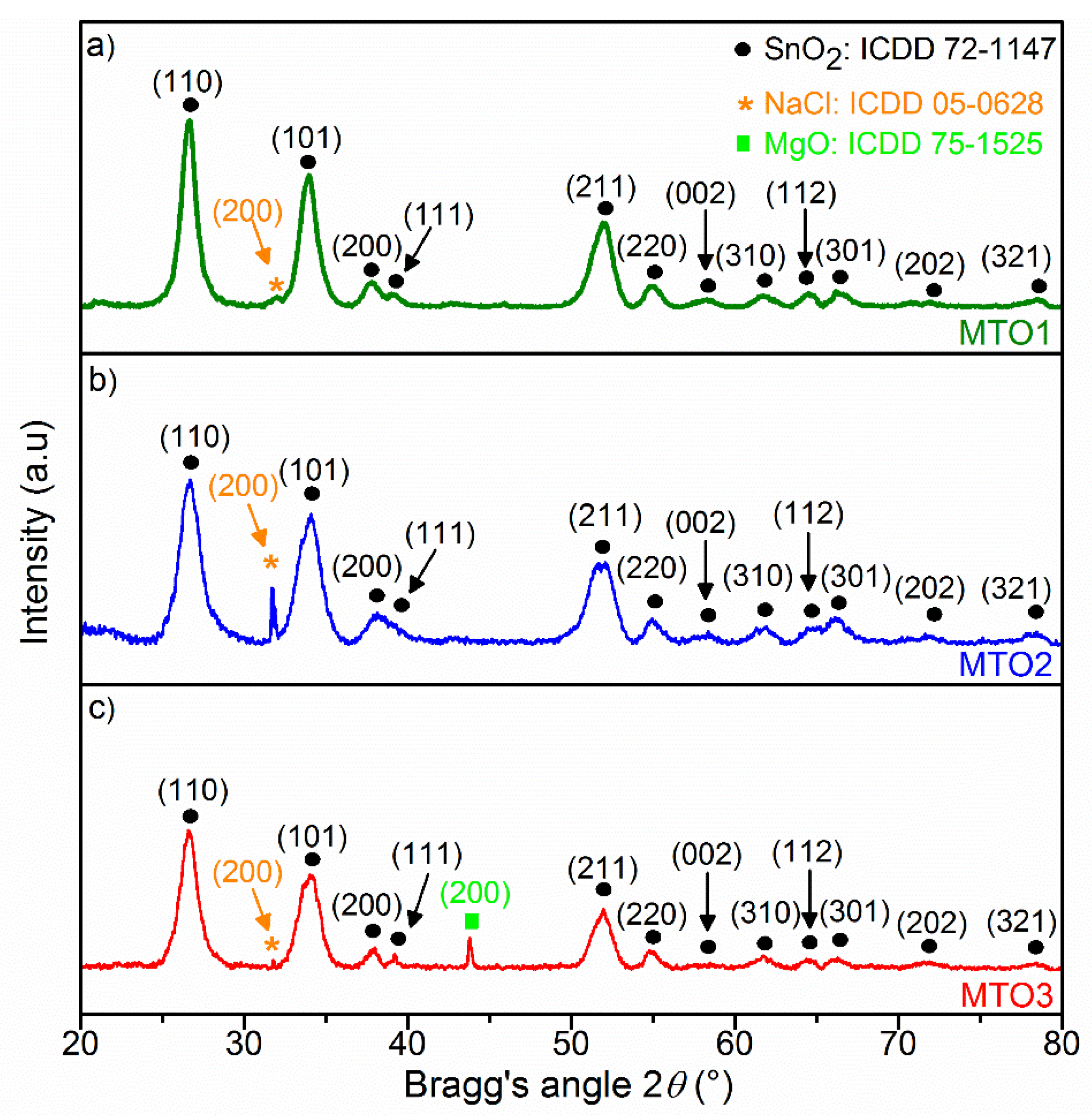
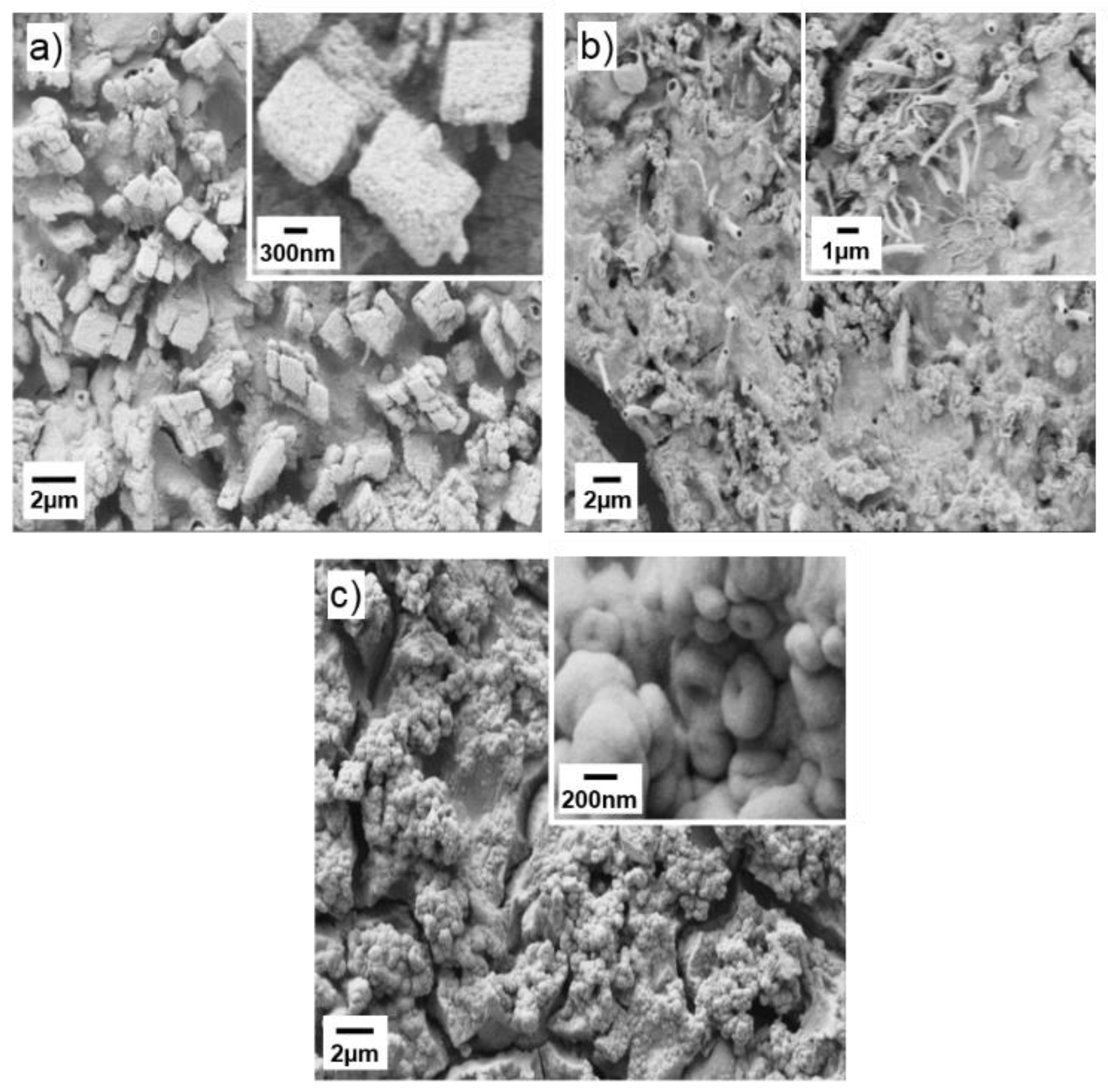
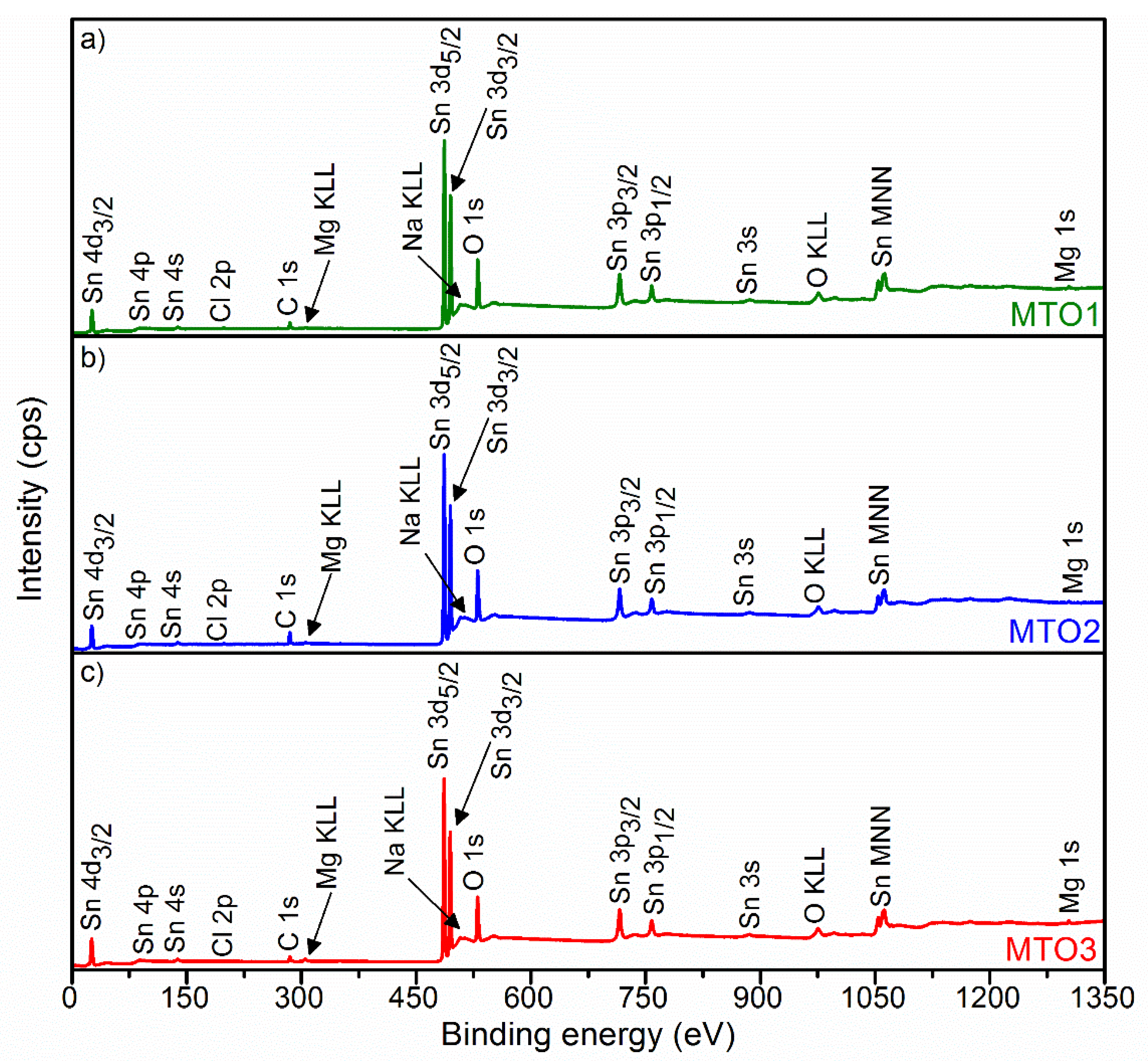
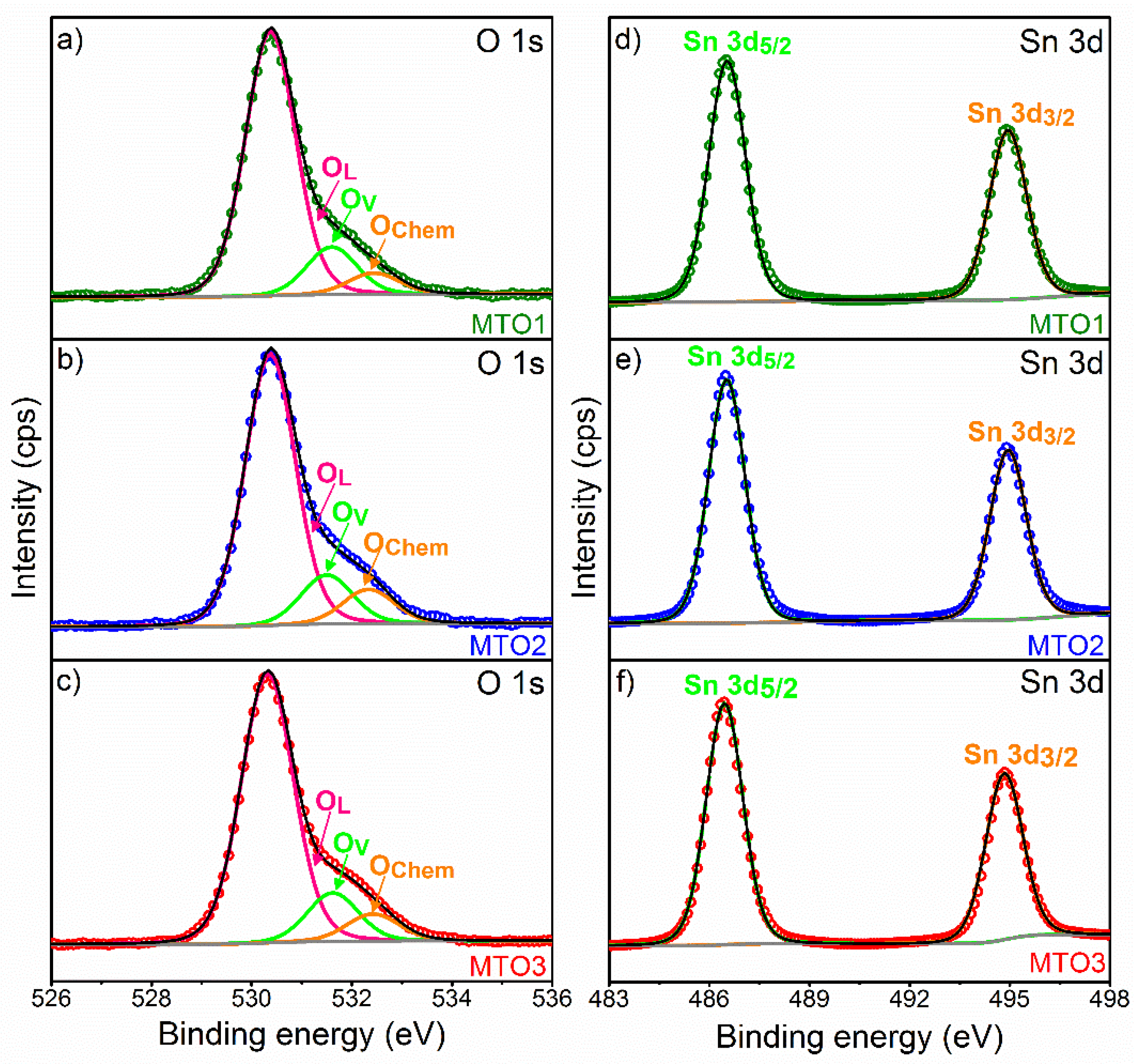
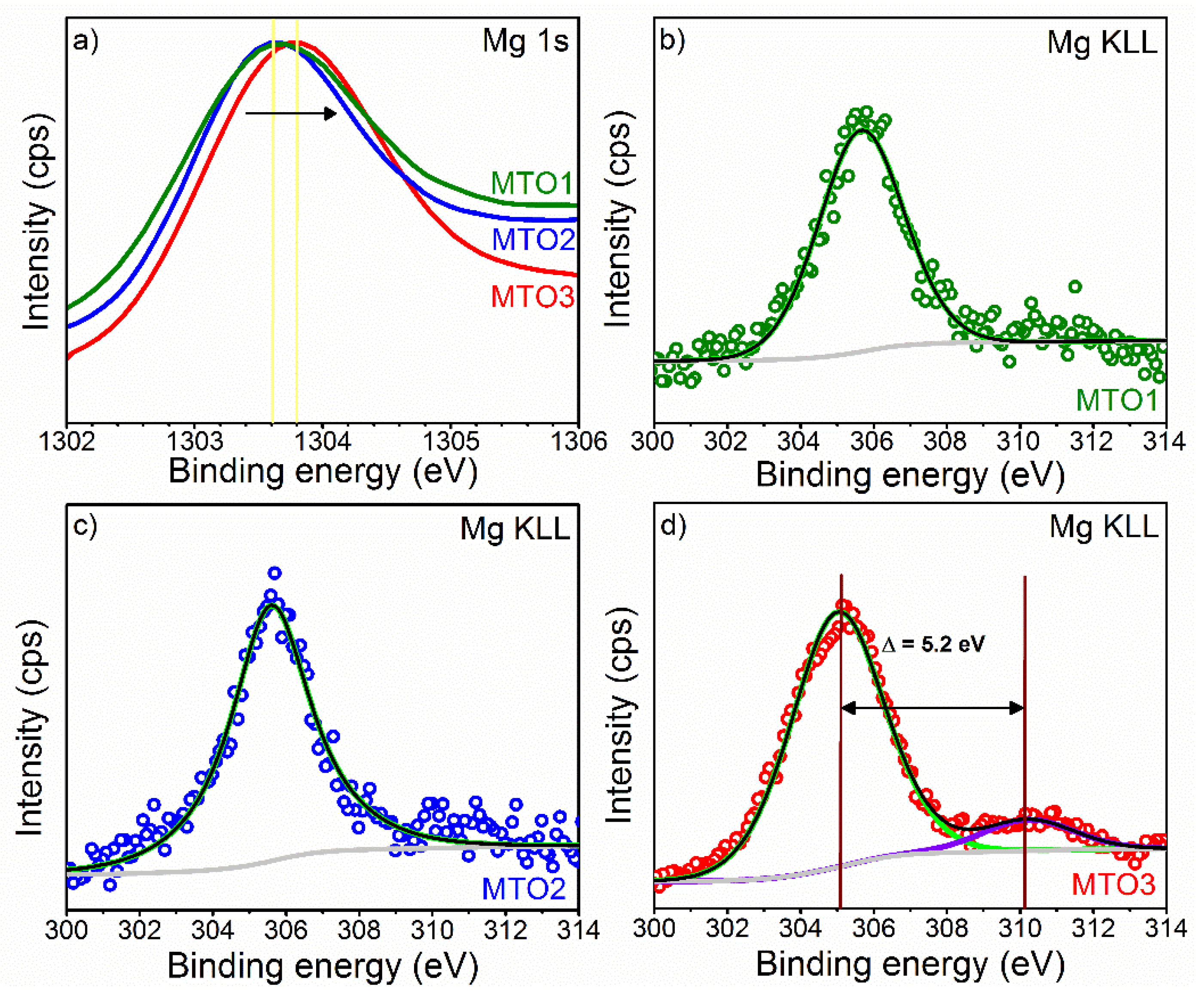
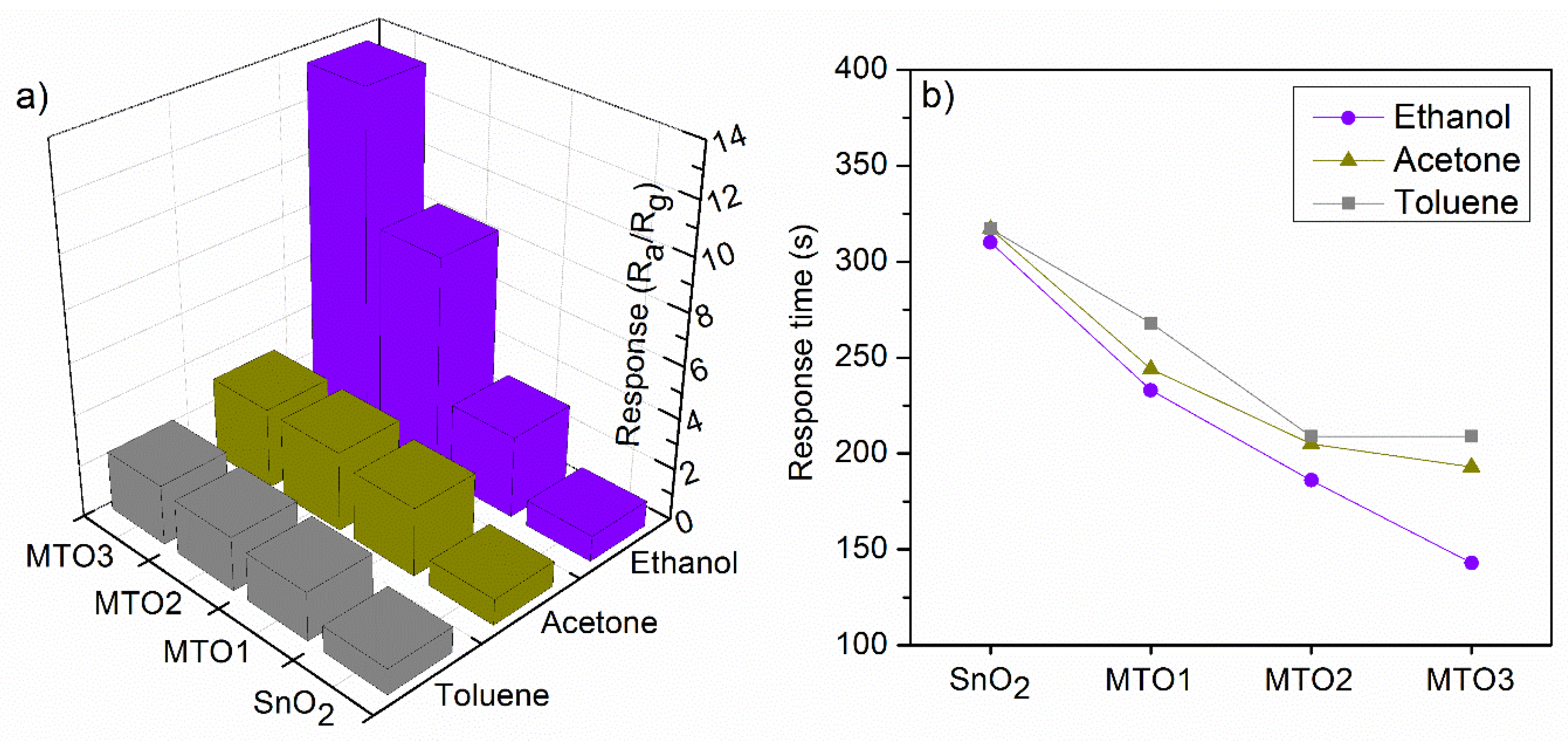

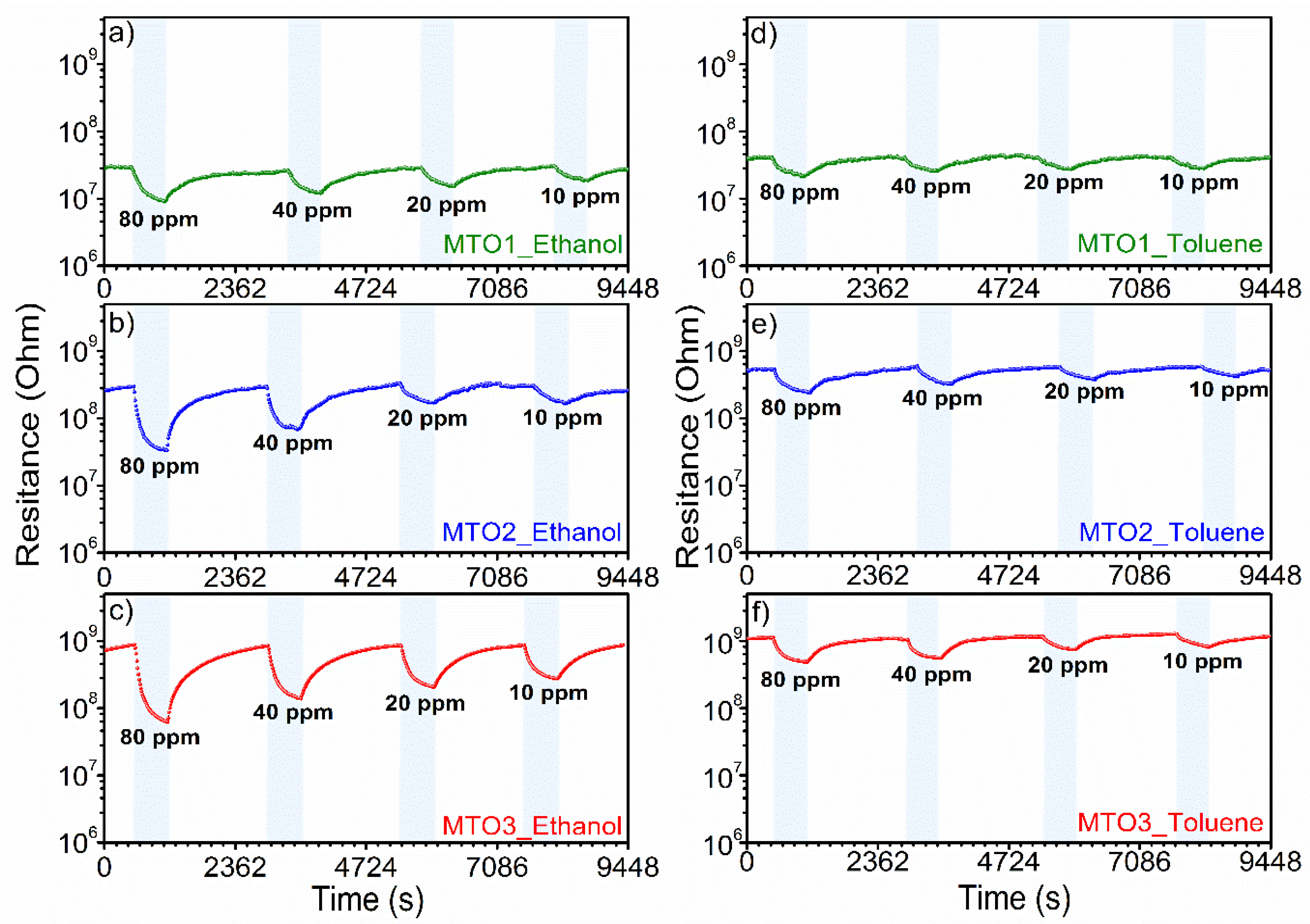
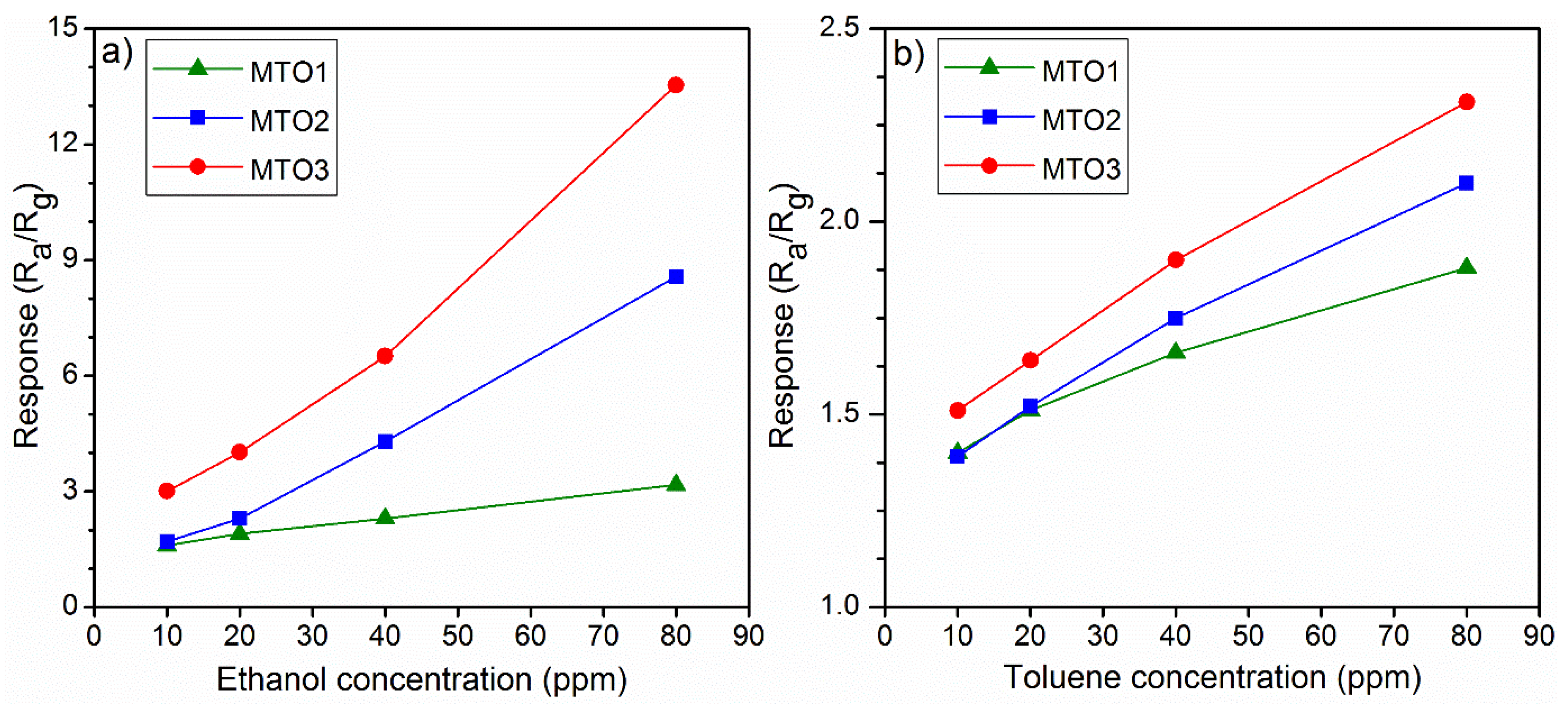


| Sample | Unit Cell Parameters | Unit Cell Volume | Average Crystallite Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a=b (Å) | c (Å) | α = β = γ | V = a2c (Å3) | D (nm) | |
| SnO2 | 4.732 | 3.187 | 90° | 71.39 | 26 * |
| MTO1 | 4.739 | 3.187 | 90° | 71.58 | 9.8 |
| MTO2 | 4.742 | 3.181 | 90° | 71.51 | 9.6 |
| MTO3 | 4.742 | 3.181 | 90° | 71.51 | 9.5 |
| Material | Method | Morphology | Concentration (ppm) | Top (°C) | Ra/Rg | tres (s) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-doped SnO2 | Spray pyrolysis | Nanospheres | Ethanol 80 | 160 | 13.5 | 143 | This work |
| SnO2/ MgAl2O4 | solid-state and sol-gel | Nanocomposites | Ethanol 100 | 227 | 3.33 * | -- | [39] |
| Au/Mg-TiO2/SnO2 | Hydrothermal | Heterostructure nanosheets | Ethanol 50 | 260 | 7 | -- | [40] |
| Mg-doped ZnO | RF magnetron sputtering | Rod-like | Ethanol 50 | 100 | 2.32 * | -- | [19] |
| Ce-doped SnO2 | Cosputtering | Nanostructures | Ethanol 100 | 225 | 5 | 4 | [14] |
| Zn-doped SnO2 | Hydrothermal | Hierarchical architectures | Ethanol 100 | 213 | 13.8 | -- | [16] |
| SnO2/ZnO | Hydrothermal | Nanostructures | Ethanol 100 | 400 | 6.2 | -- | [41] |
| Al-doped SnO2 | Chemical synthesis | powders | Ethanol 100 | 280 | 35.25 | -- | [12] |
| Pr-doped SnO2 | Electro-spinning | Hollow nanofibers | Ethanol 100 | 300 | 28.62 | 168 | [15] |
| Mg-doped SnO2 | Spray pyrolysis | Nanospheres | Toluene 80 | 160 | 2.3 | 209 | This work |
| SnO2 | Hydrothermal | Flower microstructures | Toluene 10 | 250 | 1 | -- | [42] |
| Pt-doped SnO2 | LPCVD | Island-like structures | Toluene 25 | 440 | 6 | -- | [13] |
| PdO-decorated ZnO | Hydrothermal | Flower nanostructures | Toluene 100 | 160 | 1.9 | -- | [7] |
| Fe2O3 | Hydrothermal | Nanoshuttles | Toluene 100 | 440 | 2.3 | 5 | [43] |
| Co3O4 | Solvothermal | Nanorods | Toluene 200 | 120 | 3 | -- | [44] |
| WO3 | Vapor phase synthesis | Nanoneedles | Toluene 100 | 250 | 2.2 | 398 | [6] |
| Pt@WO3 | Vapor phase synthesis | NPs@NNs | Toluene 100 | 250 | 7 | 100 | [6] |
| Fe2O3@WO3 | Vapor phase synthesis | NPs@NNs | Toluene 100 | 250 | 8 | 150 | [6] |
| Mg-doped SnO2 | Spray pyrolysis | Leaf-like grains | LPG 1000 | 285 | 1.4 * | -- | [45] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bendahmane, B.; Tomić, M.; Touidjen, N.E.H.; Gràcia, I.; Vallejos, S.; Mansour, F. Influence of Mg Doping Levels on the Sensing Properties of SnO2 Films. Sensors 2020, 20, 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072158
Bendahmane B, Tomić M, Touidjen NEH, Gràcia I, Vallejos S, Mansour F. Influence of Mg Doping Levels on the Sensing Properties of SnO2 Films. Sensors. 2020; 20(7):2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072158
Chicago/Turabian StyleBendahmane, Bouteina, Milena Tomić, Nour El Houda Touidjen, Isabel Gràcia, Stella Vallejos, and Farida Mansour. 2020. "Influence of Mg Doping Levels on the Sensing Properties of SnO2 Films" Sensors 20, no. 7: 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072158
APA StyleBendahmane, B., Tomić, M., Touidjen, N. E. H., Gràcia, I., Vallejos, S., & Mansour, F. (2020). Influence of Mg Doping Levels on the Sensing Properties of SnO2 Films. Sensors, 20(7), 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072158






