Colorimetric Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with Signal Enhancement Using Size-Based Filtration on a Finger-Powered Microfluidic Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
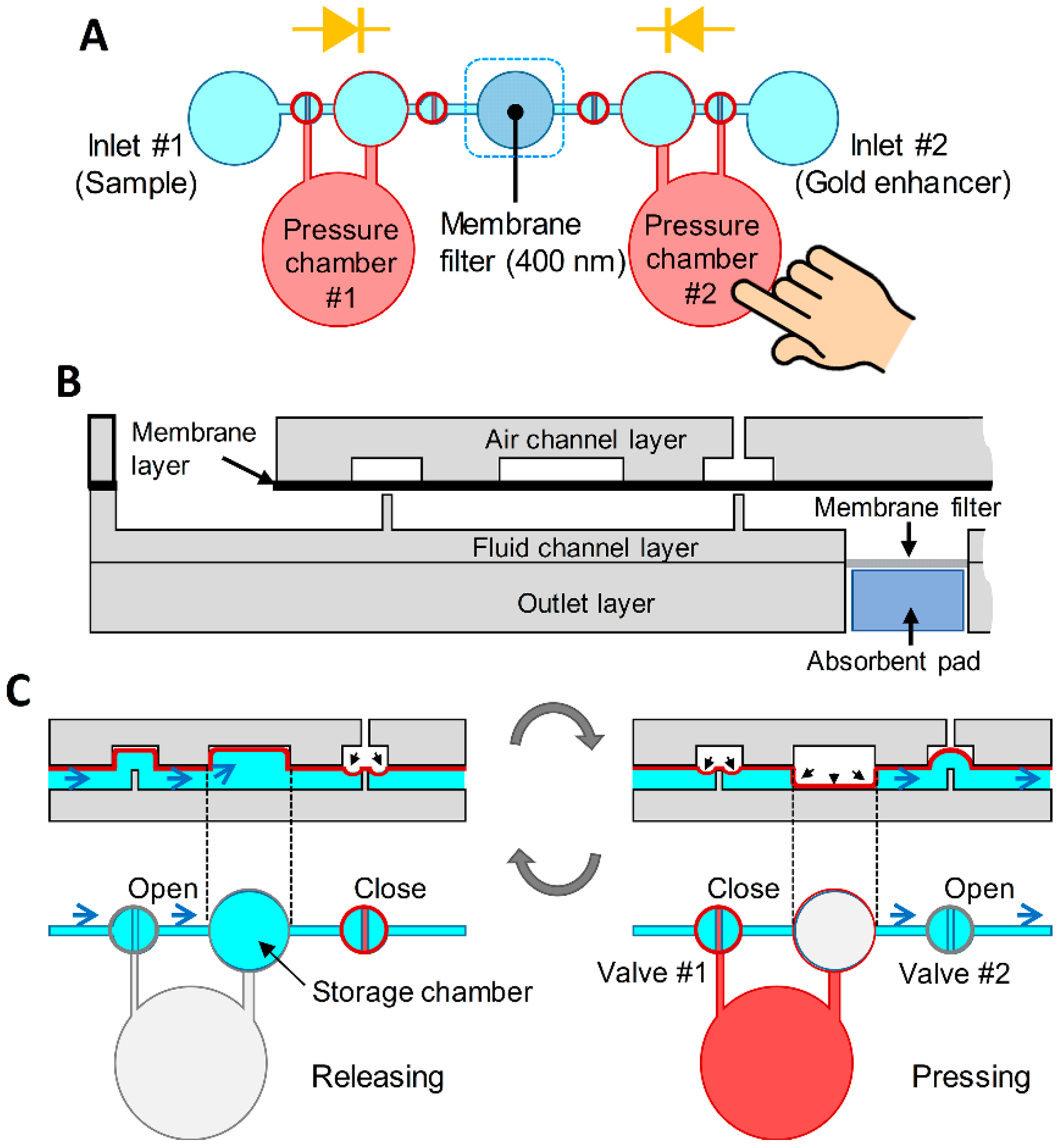
2.1. Device Fabrication
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Signal Measurement
3. Results & Discussion
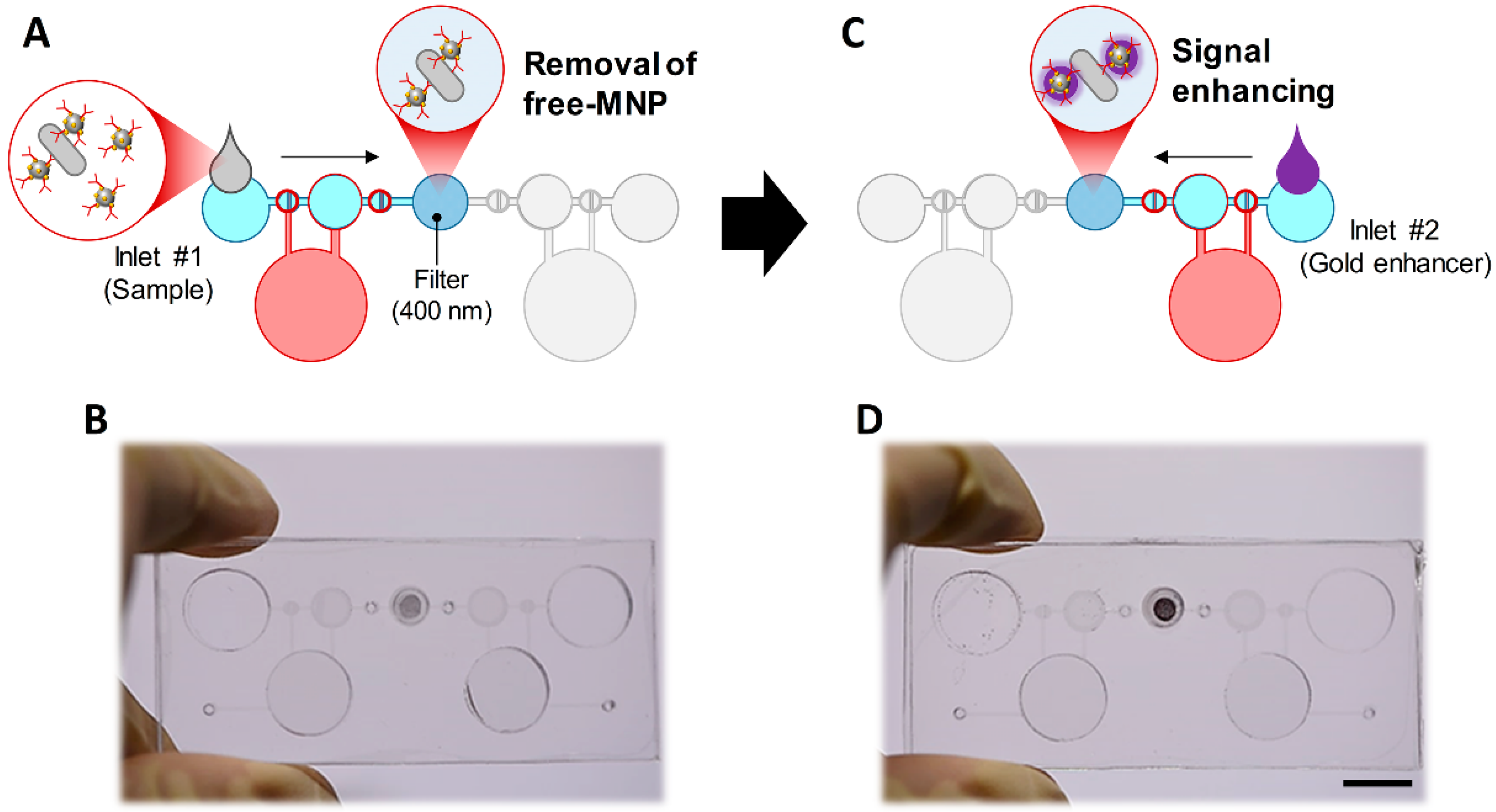
3.1. Design and Concept
3.2. Effect of the Pore Size of the Membrane Filter on the Negative Control
3.3. Comparison of E. coli O157:H7 Detection Signals According to the Pore Size Difference
3.4. Signal Enhancement Using Gold-Coated MNPs and Gold Enhancer
3.5. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 with Signal Enhancement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elaine, S.; Robert, M.H.; Frederick, J.A.; Robert, V.T.; Marc-Alain, W.; Sharon, L.R.; Jeffery, L.J.; Patricia, M.G. Foodborne illness acquired in the united states—major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, H.P.; Jaykus, L.-A. Detection of pathogens in foods: The current state-of-the-art and future directions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 37, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracias, K.S.; McKillip, J.L. A review of conventional detection and enumeration methods for pathogenic bacteria in food. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.D.; Ladd, J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; Homola, J.; Jiang, S. Quantitative and simultaneous detection of four foodborne bacterial pathogens with a multi-channel SPR sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torun, Ö.; Hakkı Boyacı, İ.; Temür, E.; Tamer, U. Comparison of sensing strategies in SPR biosensor for rapid and sensitive enumeration of bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 37, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, R.M.; Goodacre, R. Characterisation and identification of bacteria using SERS. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premasiri, W.R.; Moir, D.T.; Klempner, M.S.; Krieger, N.; Jones, G.; Ziegler, L.D. Characterization of the surface enhanced raman scattering (SERS) of bacteria. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Pla, M.; Scortti, M.; Monzó, H.J.; Vázquez-Boland, J.A. A novel real-time PCR for Listeria monocytogenes that monitors analytical performance via an internal amplification control. Appl. Environ. Microiol. 2005, 71, 9008–9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deisingh, A.K.; Thompson, M. Strategies for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in foods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, C.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Immunobiosensor chips for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4814–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.D.; Zheng, J.; Swager, T.M.; Seeberger, P.H. Detection of bacteria with carbohydrate-functionalized fluorescent polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13343–13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Qu, X.; Zhang, K.; Rong, Z.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. A rapid SERS method for label-free bacteria detection using polyethylenimine-modified Au-coated magnetic microspheres and Au@Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 2016, 141, 6226–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Ku, S.K.; Seo, D.; Hur, K.; Jeon, H.; Shvartsman, D.; Seok, H.-K.; Mooney, D.J.; Lee, K. Label-free bacterial detection using polydiacetylene liposomes. Chem. Comm. 2016, 52, 10346–10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Li, B.; Yao, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Qu, H.; Li, Q.; Li, N.; Chi, H.; et al. Intuitive label-free SERS detection of bacteria using aptamer-based in situ silver nanoparticles synthesis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9836–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Xu, D.; Feng, Y.; Sui, G.; Fu, H.; Valev, V.K.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Klarite as a label-free SERS-based assay: A promising approach for atmospheric bioaerosol detection. Analyst 2020, 145, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ravindranath, S.; Irudayaraj, J. Separation and detection of multiple pathogens in a food matrix by magnetic SERS nanoprobes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cha, R.; Sun, J.; Jiang, X. One-Step Detection of Pathogens and Viruses: Combining Magnetic Relaxation Switching and Magnetic Separation. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3184–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, M.; Chao, Q.; Jia, N.; Ge, Y.; Shen, H. Simultaneous detection of multifood-borne pathogenic bacteria based on functionalized quantum dots coupled with immunomagnetic separation in food samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kwon, D.; Choi, W.; Jung, G.Y.; Au, A.K.; Folch, A.; Jeon, S. 3D-printed microfluidic device for the detection of pathogenic bacteria using size-based separation in helical channel with trapezoid cross-section. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.J.; Suk, H.-J.; Sung, H.Y.; Li, T.; Poo, H.; Kim, M.-G. Novel antibody/gold nanoparticle/magnetic nanoparticle nanocomposites for immunomagnetic separation and rapid colorimetric detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, J.-K. Finger-actuated microfluidic device for the blood cross-matching test. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, J.-K. Finger-actuated microfluidic display for smart blood typing. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11636–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, K.; Shih, K.C.; Lin, X.; Brubaker, T.A.; Sochol, R.D.; Lin, L. Finger-powered microfluidic systems using multilayer soft lithography and injection molding processes. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z.; Fei, P.; Yu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Huang, Y. Squeeze-chip: A finger-controlled microfluidic flow network device and its application to biochemical assays. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, M.T.; Kinahan, D.J.; Ducrée, J. Rapid, low-cost and instrument-free CD4+ cell counting for HIV diagnostics in resource-poor settings. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, Y.; Park, J.; Park, J.-K. Colorimetric Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with Signal Enhancement Using Size-Based Filtration on a Finger-Powered Microfluidic Device. Sensors 2020, 20, 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082267
Jo Y, Park J, Park J-K. Colorimetric Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with Signal Enhancement Using Size-Based Filtration on a Finger-Powered Microfluidic Device. Sensors. 2020; 20(8):2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082267
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Younggeun, Juhwan Park, and Je-Kyun Park. 2020. "Colorimetric Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with Signal Enhancement Using Size-Based Filtration on a Finger-Powered Microfluidic Device" Sensors 20, no. 8: 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082267
APA StyleJo, Y., Park, J., & Park, J.-K. (2020). Colorimetric Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with Signal Enhancement Using Size-Based Filtration on a Finger-Powered Microfluidic Device. Sensors, 20(8), 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082267






