A Low-Cost Surge Current Detection Sensor with Predictive Lifetime Display Function for Maintenance of Surge Protective Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
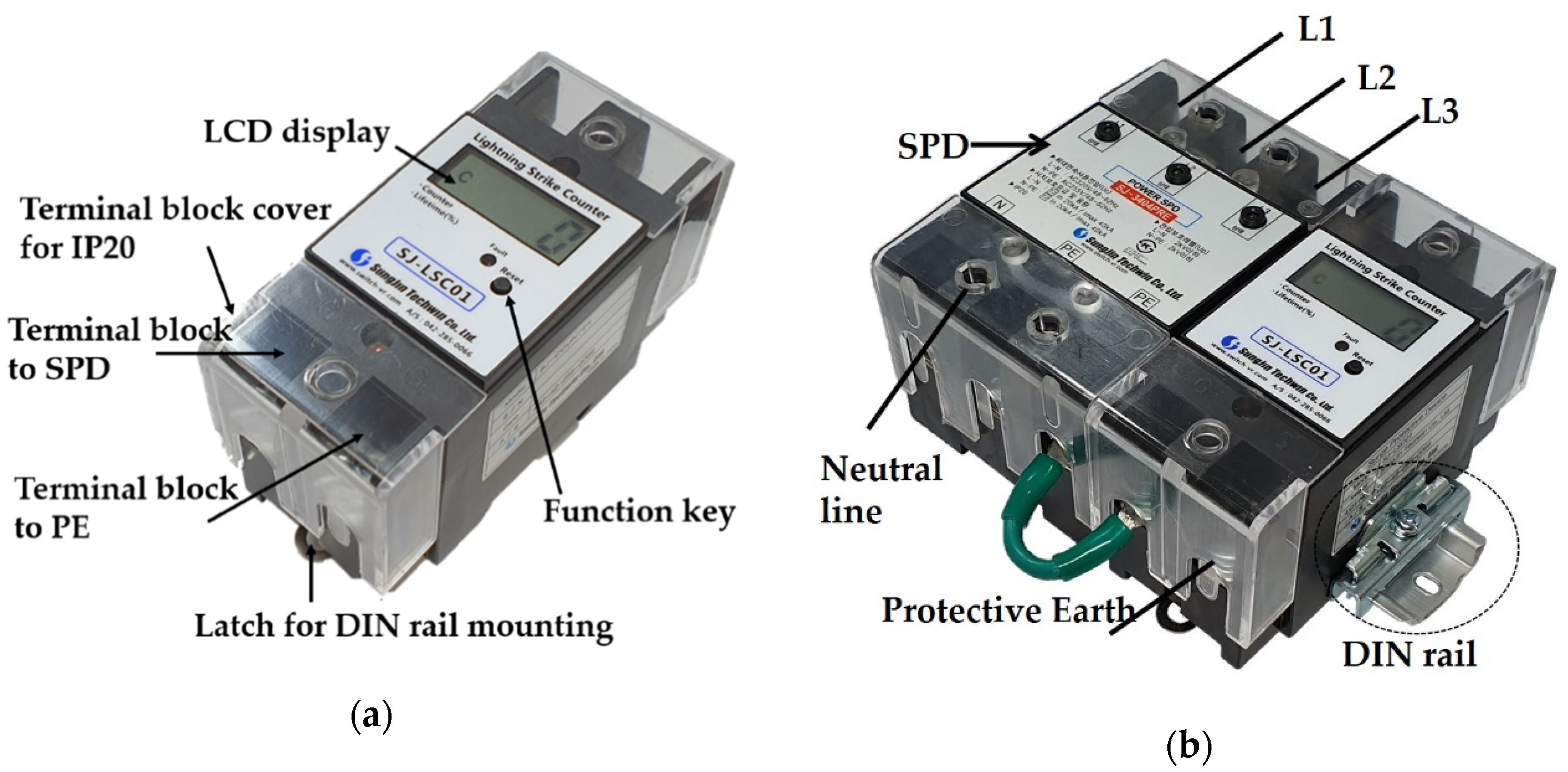
2.1. Mechanical Design
2.2. Block Diagram
2.3. Lightning Surge
2.3.1. Classification of Surges
2.3.2. Lifetime of MOV
2.4. Toroidal Coil Type Current Sensor and Signal Conditioning Circuit Design
2.4.1. Toroidal Coil Type Current Sensor
2.4.2. Signal Conditioning Circuit
2.5. Calculation Principle of the Predictive Lifetime and Software Algorithm for the Expected Lifetime of the SPD
2.5.1. Calculation Principle of the Predictive Lifetime of the SPD
2.5.2. Software Algorithm for the Predictive Lifetime of the SPD
3. Results
3.1. Expected Lifetime of the SPD
IEC62561-6 Test Results
3.2. Results of the Predictive Lifetime Test of the SPD
3.3. Battery Power Consumption Test Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wetter, M.; Finis, G.; Sander, C.; Joerres, S. Smart IoT monitoring system for surge protective devices (SPDs). In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th Asia-Pacific International Conference on Lightning (APL), Hong Kong, China, 12–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chiste, A.; Kladar, D. Electronic systems protection via advanced surge protective devices. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, 37th IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No. 02CH37344), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–18 October 2002; Volume 3, pp. 2244–2247. [Google Scholar]
- Jeoung, T.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Nam, S.P.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, S.G. Development of thermal runaway preventing ZnO varistor for surge protective device. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 8957–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanmiri, D.T.; Ball, R.; Lehman, B. Degradation Effects on Energy Absorption Capability and Time to Failure of Low Voltage Metal Oxide Varistors. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 32, 2272–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Li, F. Effect of the injected number and amplitude of 8/20 [us] impulse current on the life of ZnO varistors. J. Korean Inst. Illum. Electr. Install. Eng. 2007, 21, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, N.; Ishii, M. Repetitive Impulse Withstand Performance of Metal-Oxide Varistors. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 32, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Salles, C.; Martinez, M.L.; de Queiroz, Á.A. Ageing of metal oxide varistors due to surges. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Lightning Protection, Fortaleza, Brazil, 3–7 October 2011; pp. 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Amicucci, G.L.; D’Elia, B. Reliability of surge protective devices stressed by lightning. J. Electrostat. 2004, 60, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, K.W.; Wingate, M.; Pham, E. Application and safety issues for transient voltage surge suppressors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar]
- The International Electrotechnical Commission. IEC 61643-331, Components For-Low-Voltage Surge Protective Devices—Part 331: Performance Requirements and Test Method for Metal Oxide Varistors (MOV); IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- The International Electrotechnical Commission. IEC 61643-11, Low-Voltage Surge Protective Devices—Part 11: Surge Protective Devices Connected to Low-Voltage Power Systems—Requirements and Tests; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- The International Electrotechnical Commission. IEC 61643-12, Low-Voltage Surge Protective Devices—Part 12: Surge Protective Devices Connected to Low-Voltage Power Systems—Selection and Application Principles; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata, T.; Yanagawa, S.; Takahashi, H.; Yamamoto, K. A development of a shunt lightning current measuring system using a Rogowski coil. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Lightning Protection (XII SIPDA), Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 7–11 October 2013; pp. 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, L.; Visacro, S. Low-cost Systems for Measurement of Lightning-Currents Provided with Remote Access. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Lightning Protection (ICLP), Rzeszow, Poland, 2–7 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.M.; Janischewskyj, W.; Milewski, M.; Shostak, V.; Chisholm, W.; Chang, J.S. Current waveform parameters of CN tower lightning return strokes. J. Electr. 2004, 60, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.A.; Exon, J.L.T. Using Rogowski coils for transient current measurements. Eng. Sci. Educ. J. 1993, 2, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Long, Y.; Yao, C.; Mi, Y.; Wu, J. Novel lightning current sensor based on Printed Circuit Board Rogowski coil. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application, Shanghai, China, 17–20 September 2012; pp. 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Alibaba. Available online: https://korean.alibaba.com/trade/search?fsb=y&IndexArea=product_en&CatId=&SearchText=surge+protective+device (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Sungjin Techwin Co., Ltd. Available online: http://www.switch-vr.com/eng/sub/prodcut_protection.php?checkfi=73 (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Otowa Electric Co., Ltd. Available online: https://www.otowadenki.co.jp/eng/products/spd3/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Datasheet of Metal Oxide Varistor. Available online: https://www.tdk-electronics.tdk.com/en/1321012/products/product-catalog/protection-devices/voltage-protection/strap-varistors--epcos- (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Core Electronics Co., Ltd. Available online: http://www.emicore.co.kr/EN/index.php?mm_code=78&sm_code=89&board_no=1 (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistivity_and_conductivity (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Kirchhoff’s Current Law. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kirchhoff%27s_circuit_laws (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Lightning Surge Simulator LSS-15AX. Available online: http://www.noiseken.com/modules/products/index.php?content_id=194 (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Impulse Current Generator SSG Series. Available online: http://www.haefely.com/2133781.html (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- The International Electrotechnical Commission. IEC 62561-6, Lightning Protection System Components (LPSC)—Part 6: Requirements for Lightning Strike Counters (LSC); IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Battery Life Calculator. Available online: https://www.digikey.kr/en/resources/conversion-calculators/conversion-calculator-battery-life (accessed on 2 November 2019).
















| Lightning Surge Current | T1 [μs] | T2 [μs] | SPD Class | SPD Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | 10 | 350 | class I | |
| Induced | 8 | 20 | class II |
| Part No. | Inner Diameter | Outer Diameter | Height | Material | Frequency Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C27-B11 | 14.48 mm | 26.92 mm | 11.1 × 3 mm | Iron powder and small other mixtures | 500 kHz |
| AWG | Cross-Sectional Area (mm2) | Resistance (Ω/m) | Cable Length (mm) | Connection Resistance (Ω) | Current Distribution Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 6.63 | 0.0026 | 30 | 0.001 | ≅97 |
| 24 | 0.205 | 0.0842 | 60 | 0.029 | ≅3 |
| Description | Number of Power Lines | Maximum Surge Current (Induced, 8/20 μs, In 20 kA) | Maximum Surge Current (Direct, 10/350 μs, Iimp 25 kA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-phase | 2 (line, neutral): i3 | Total 40 kA | Total 50 kA |
| I | 38.67 kA | 48.34 kA | |
| i | 1.33 kA | 1.66 kA | |
| Three-phase | 4 (R, S, T, neutral): i5 | Total 80 kA | Total 100 kA |
| I | 77.34 kA | 96.67 kA | |
| i | 2.66 kA | 3.33 kA |
| Lightning Surge Current (kA) | T (ms) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 5.29 | 5.4 | 0.3 |
| 0.5 | 18.00 | 11.1 | 0.85 |
| 1 | 32.00 | 22 | 2.24 |
| 2 | 39.00 | 42.2 | 5.24 |
| 3 | 47.50 | 66.2 | 7.7 |
| 4 | 50.00 | 90 | 10.6 |
| 5 | 52.00 | 130 | 13.7 |
| 6 | 53.50 | 151 | 16.2 |
| 7 | 56.00 | 175 | 19.6 |
| 10 | 62.00 | 235 | 28.6 |
| 20 | 74.09 | 435 | 58.6 |
| 30 | 79.48 | 635 | 88.6 |
| 40 | 83.29 | 835 | 118.6 |
| 50 | 86.23 | 1035 | 148.6 |
| 60 | 88.63 | 1235 | 178.6 |
| 70 | 90.65 | 1435 | 208.6 |
| 80 | 92.40 | 1635 | 238.6 |
| 90 | 93.95 | 1835 | 268.6 |
| 100 | 95.46 | 2035 | 301.6 |
| Test Equipment | Maker | Model | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning surge simulator | Noiseken | LSS-15AX | Voc (1.2/50 μs): 15 kV Isc (8/20 μs): 7.5 kA |
| Impulse current generator | HAEFELY | SSG series | Isc (8/20 μs): 120 kA |
| High voltage differential probe | Sapphire Instruments | SI-9010 | ±7000 V |
| Oscilloscope | Yokogawa | DLM2054 | 2.5 Gs, 500 MHz |
| Scope probe | Yokogawa | 701939 | 600 V, 600 MHz |
| Surge Current (A) | Endurable Number of Surges | |
|---|---|---|
| 90 | 1.235 × 10−4 | 1,000,000 |
| 200 | 2.500 × 10−5 | 100,000 |
| 500 | 4.000 × 10−6 | 10,000 |
| 2000 | 2.500 × 10−7 | 1000 |
| 7000 | 2.041 × 10−8 | 100 |
| 20,000 | 2.500 × 10−9 | 10 |
| 40,000 | 6.250 × 10−10 | 1 |
| Application | Value | Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPS conductor | - | 1 kA 8/20 μs | - | - | - | - | 100 kA 10/350 μs |
| SPD conductor | 500 A 8/20 μs | - | 20 kA 8/20 μs | 40 kA 8/20 μs | 60 kA 8/20 μs | 80 kA 8/20 μs | 100 kA 8/20 μs |
| LPS and SPD conductors | - | 1 kA 8/20 μs | - | - | - | - | 100 kA 10/350 μs |
| Surge Current 8/20 μs | Number of Surge Tests | Count Results | Test Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 A (positive) | 10 | X (no count) | Pass |
| 250 A (negative) | 10 | X (no count) | Pass |
| 400 A (positive) | 10 | X (no count) | Pass |
| 400 A (negative) | 10 | X (no count) | Pass |
| 500 A (positive) | 10 | O (10 times) | Pass |
| 500 A (negative) | 10 | O (10 times) | Pass |
| Surge Current 8/20 μs | Surge Current Per Path | Decreased Predictive Lifetime (%) | Sample #1 (%) | Sample #2 (%) | Sample #3 (%) | Sample #4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 kA | 250 A | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 kA | 1.25 kA | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 10 kA | 2.5 kA | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| 20 kA | 5 kA | 0.50 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.51 |
| 30 kA | 7.5 kA | 1.15 | 1.06 | 1.11 | 1.22 | 1.19 |
| 40 kA | 10 kA | 2.08 | 1.95 | 2.01 | 2.24 | 2.15 |
| 50 kA | 12.5 kA | 3.32 | 3.06 | 3.14 | 3.52 | 3.44 |
| 60 kA | 15 kA | 4.93 | 4.52 | 4.67 | 5.35 | 5.20 |
| 70 kA | 17.5 kA | 6.96 | 6.35 | 6.50 | 7.53 | 7.23 |
| 80 kA | 20 kA | 9.49 | 8.78 | 9.19 | 10.23 | 9.79 |
| 90 kA | 22.5 kA | 12.66 | 11.66 | 12.05 | 13.69 | 12.98 |
| 100 kA | 25 kA | 16.61 | 15.30 | 15.87 | 17.59 | 17.20 |
| SCDS | Surge Count | Current Measurement | Polarity | SPD Predictive Lifetime | Cost | General Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed SCDS | O | O | X | O | Very low (tens of USD) | Applicable |
| Surge counter | O | X | X | X | Very low (tens of USD) | Applicable |
| SCDS with Rogowski coil | O | O | O | O | High (hundreds of USD) | Not applicable |
| SCDS with expensive CT | O | O | O | O | Very high(thousands of USD) | Not applicable |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.S. A Low-Cost Surge Current Detection Sensor with Predictive Lifetime Display Function for Maintenance of Surge Protective Devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082310
Lee Y, Lee YS. A Low-Cost Surge Current Detection Sensor with Predictive Lifetime Display Function for Maintenance of Surge Protective Devices. Sensors. 2020; 20(8):2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082310
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Youngjun, and Young Sam Lee. 2020. "A Low-Cost Surge Current Detection Sensor with Predictive Lifetime Display Function for Maintenance of Surge Protective Devices" Sensors 20, no. 8: 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082310
APA StyleLee, Y., & Lee, Y. S. (2020). A Low-Cost Surge Current Detection Sensor with Predictive Lifetime Display Function for Maintenance of Surge Protective Devices. Sensors, 20(8), 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082310





