SpeakingFaces: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Voice Commands with Visual and Thermal Video Streams
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce SpeakingFaces, a large-scale publicly available dataset of voice commands accompanied by streams of visible and thermal image sequences.
- We prepare the dataset by aligning the video streams to minimize the pixel-to-pixel alignment errors between the visual and thermal images. This procedure allows for automatic annotation of thermal images using facial bounding boxes extracted from their visual pairs.
- We provide full annotations on each utterance of a command.
- We present two baseline tasks to illustrate the utility and reliability of the dataset: a classifier for gender using all the three data streams, and an instance of thermal-to-visual image translation as an example of domain transfer. The data used for the latter experiment is publicly available and can be used as a benchmark for image translation models.
2. Materials and Methods
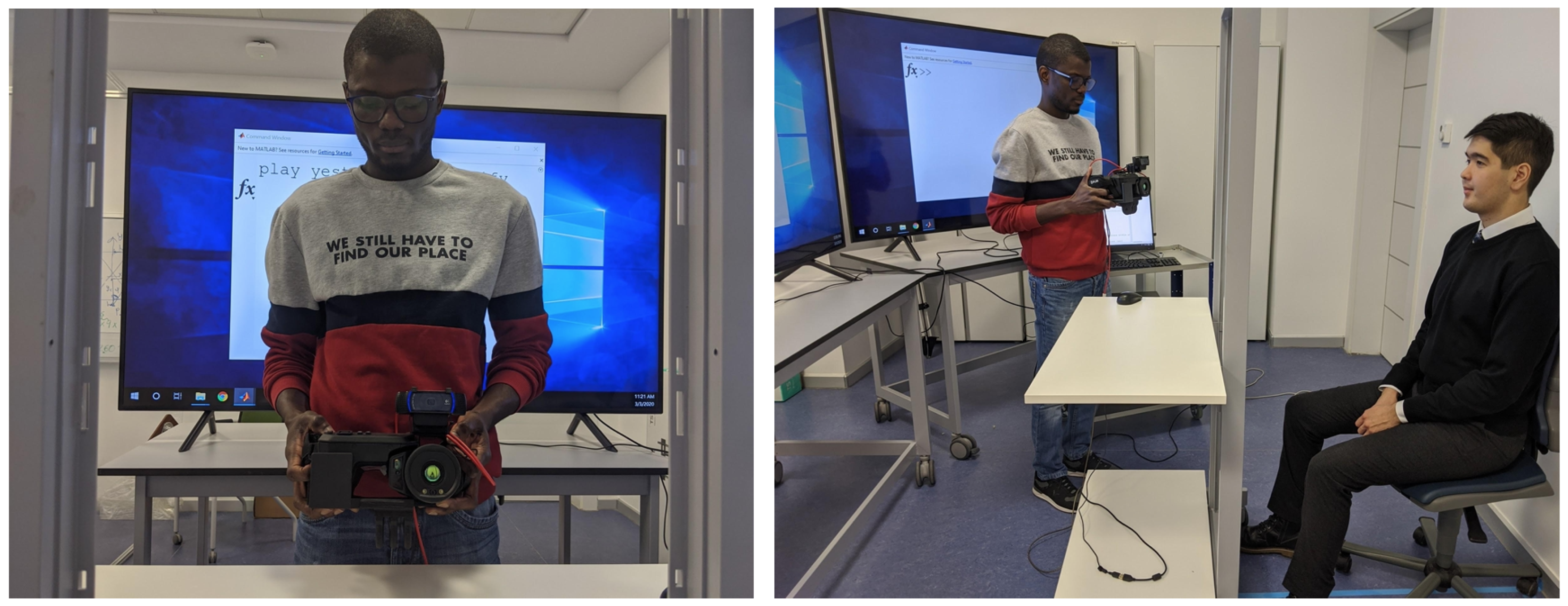
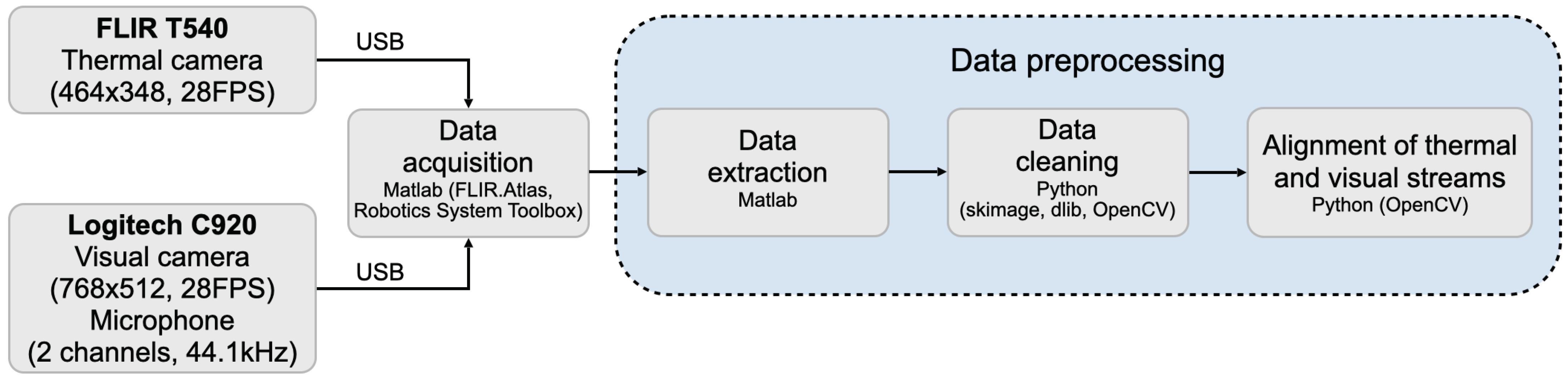
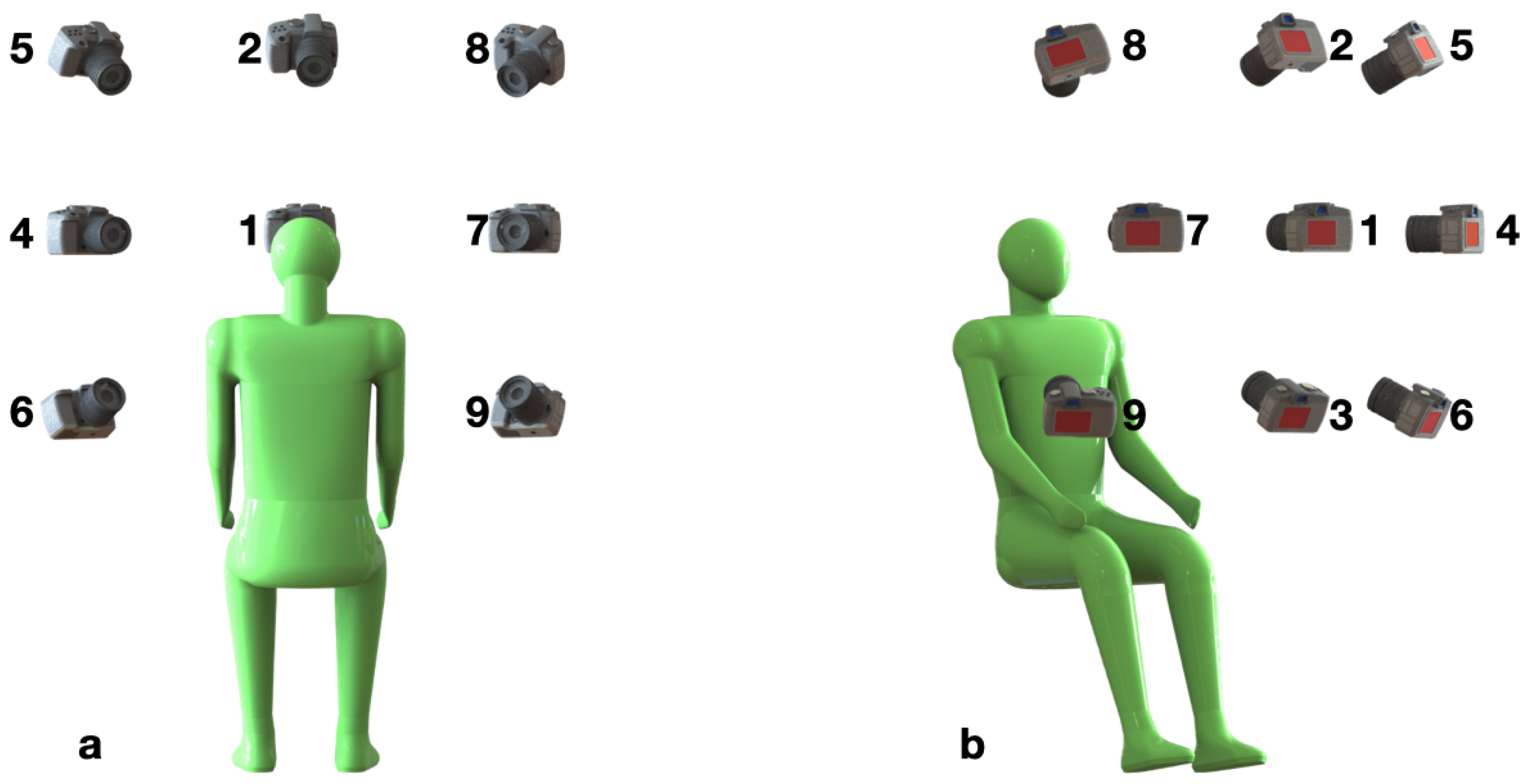
2.1. Data Acquisition
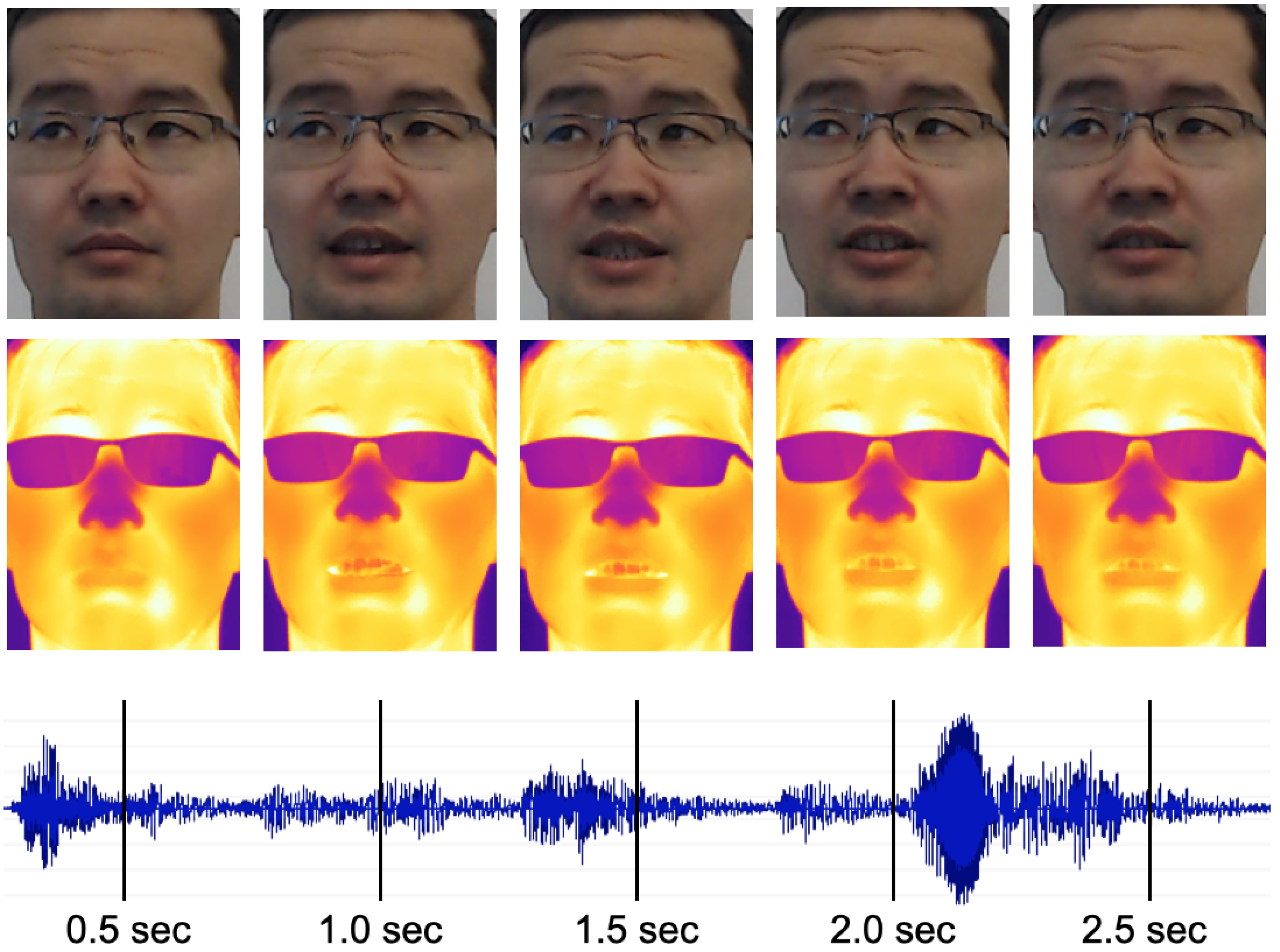
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Database Structure
- subID denotes the subject number.
- trialID denotes the trial number.
- sessionID is 1 if the session does not involve utterances and 2 otherwise.
- posID denotes the camera position.
- commandID denotes the command number.
- frameID the number of an image in a sequence.
- streamID is 1 for thermal images, 2 for visual images, and 3 for the aligned version of the visual images.
- micID is 1 for the left microphone and 2 for the right microphone on the web camera.
3. Results and Discussion
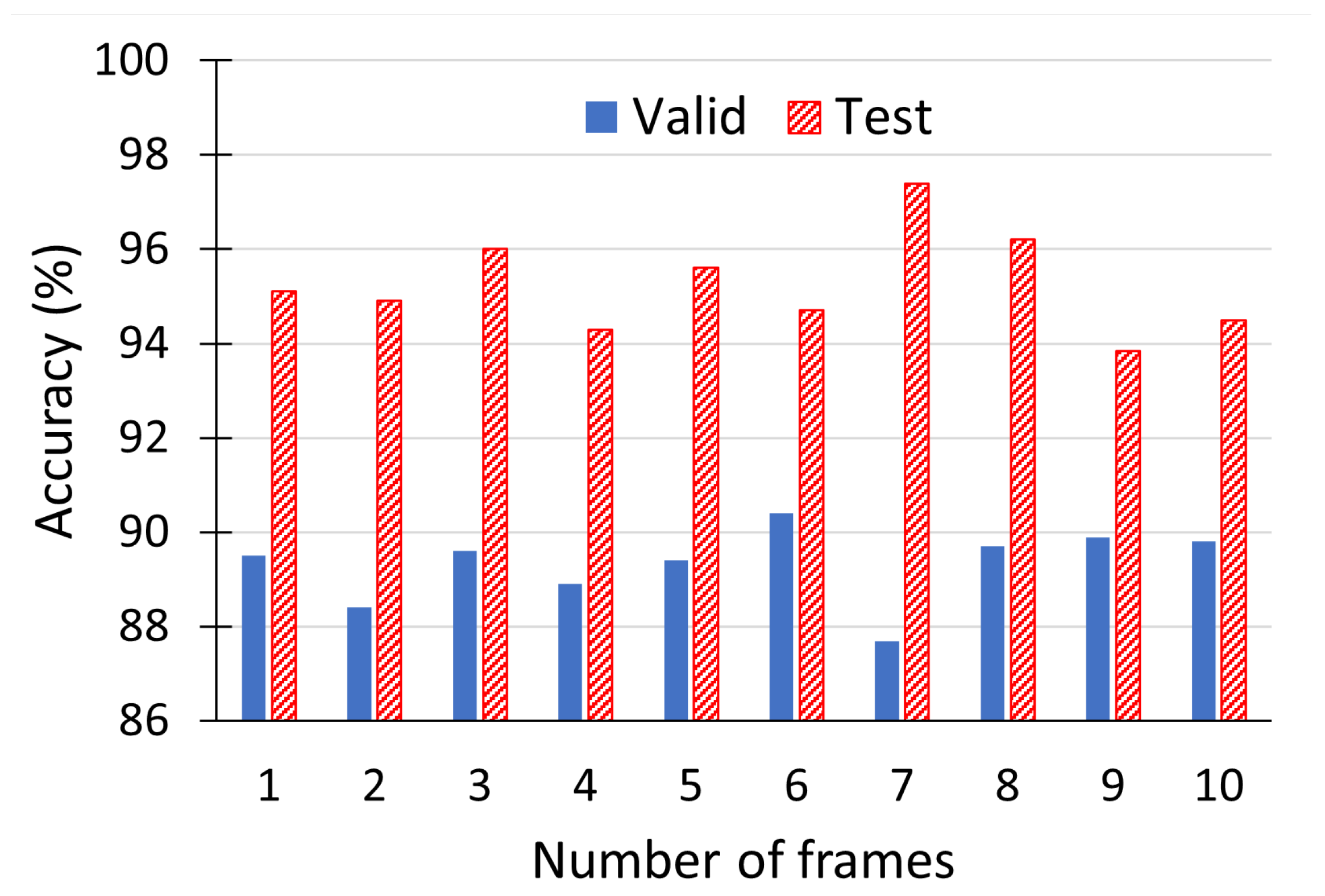
3.1. Gender Classification
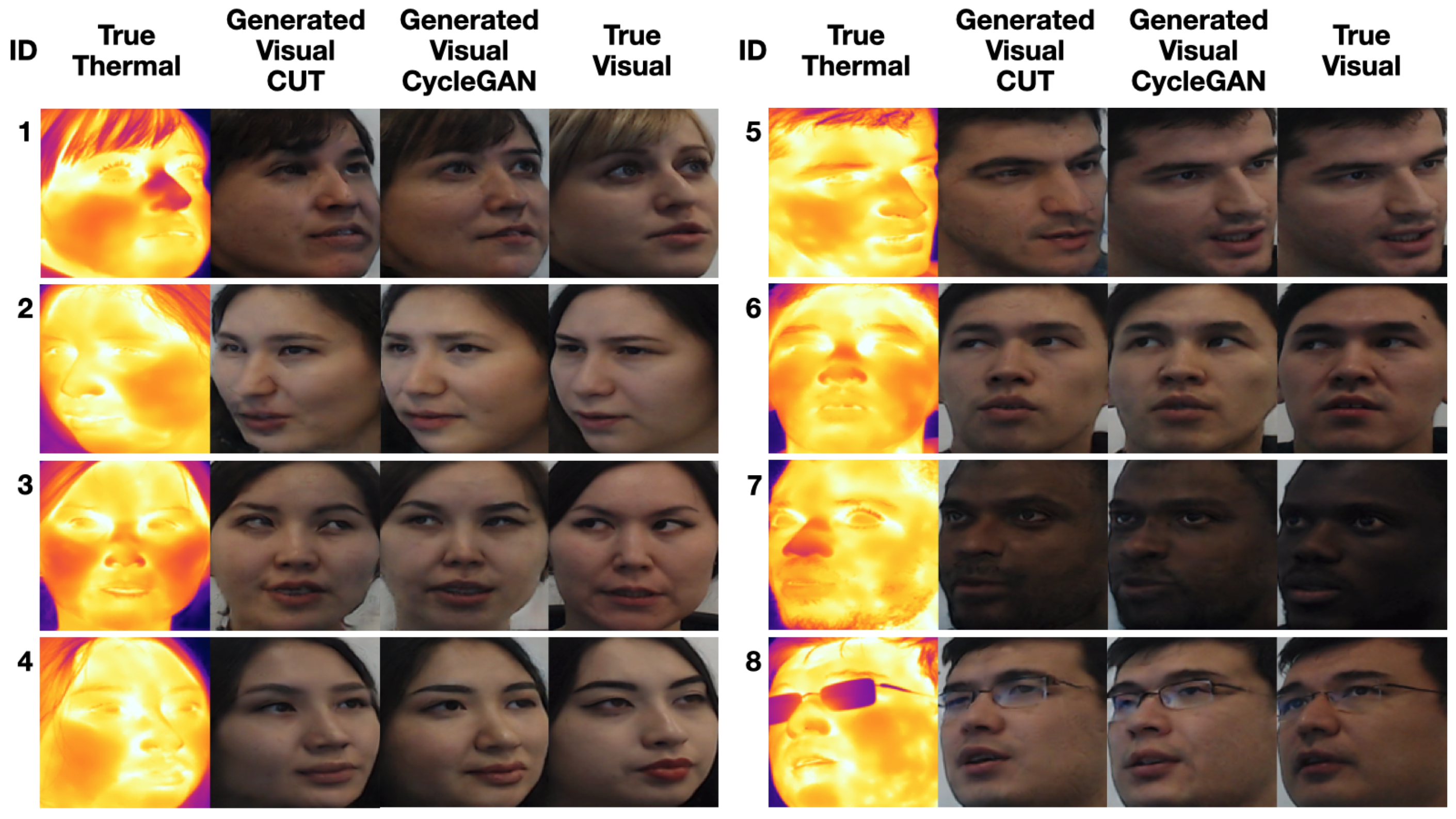
3.2. Thermal-to-Visual Facial Image Translation
- The model may be biased towards young people, due to the observation that of participating subjects were 20–25 years old. As a result, the model in some cases generated a younger version of the subject.
- The model may be biased towards Asian people, given that the majority of the participating subjects were Asians. As an example, in the case of some subjects wearing glasses, the depiction of eyes seems skewed towards an Asian presentation.
3.3. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AWGN | Additive White Gaussian Noise |
| BRNN | Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| DOI | Digital Object Identifier |
| FID | Fréchet Inception Distance |
| FPS | Frames per Second |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Networks |
| HCI | Human-Computer Interaction |
| ID | Identifier |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ISSAI | Institute of Smart Systems and Artificial Intelligence |
| LRS | Lip Reading Sentences |
| LRW | Lip Reading in the Wild |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| RoI | Region-of-Interest |
References
- Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Qian, Y. Multi-modality Matters: A Performance Leap on VoxCeleb. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 2252–2256. [Google Scholar]
- Gade, R.; Moeslund, T.B. Thermal cameras and applications: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, S.; Oh, T.; Glass, J. Noise-tolerant Audio-visual Online Person Verification Using an Attention-based Neural Network Fusion. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afouras, T.; Chung, J.S.; Senior, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A. Deep audio-visual speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, F.; Busso, C. End-to-End Audiovisual Speech Recognition System With Multitask Learning. IEEE Trans. Multim. 2021, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLIR ONE Pro. Available online: https://www.flir.com/products/flir-one-pro/ (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- CAT S62 Pro. Available online: https://www.catphones.com/en-dk/cat-s62-pro-smartphone/ (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Lepton—LWIR Micro Thermal Camera Module. Available online: https://www.flir.com/products/lepton/ (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Espinosa-Duró, V.; Faundez-Zanuy, M.; Mekyska, J. A New Face Database Simultaneously Acquired in Visible, Near-Infrared and Thermal Spectrums. Cogn. Comput. 2013, 5, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, K.; Dugelay, J.L. A benchmark database of visible and thermal paired face images across multiple variations. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group, BIOSIG 2018, Darmstadt, Germany, 26–28 September 2018; pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hammoud, R.I. IEEE OTCBVS WS Series Bench. Available online: http://vcipl-okstate.org/pbvs/bench/ (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Lv, S.; Lv, Y.; Wu, G.; Peng, P.; Chen, F.; Wang, X. A Natural Visible and Infrared Facial Expression Database for Expression Recognition and Emotion Inference. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2010, 12, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, K.; Wan, Q.; Agaian, S.; Rajeev, S.; Kamath, S.; Rajendran, R.; Rao, S.P.; Kaszowska, A.; Taylor, H.A.; Samani, A.; et al. A comprehensive database for benchmarking imaging systems. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 42, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiass, R.S.; Bendada, H.; Maldague, X. Université Laval Face Motion and Time-Lapse Video Database (UL-FMTV); Technical Report; Université Laval: Québec, QC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Poster, D.; Thielke, M.; Nguyen, R.; Rajaraman, S.; Di, X.; Fondje, C.N.; Patel, V.M.; Short, N.J.; Riggan, B.S.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; et al. A Large-Scale, Time-Synchronized Visible and Thermal Face Dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 1559–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, M.; Barker, J.; Cunningham, S.; Shao, X. An audio-visual corpus for speech perception and automatic speech recognition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. Lip Reading in the Wild. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.S.; Senior, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A. Lip reading sentences in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3444–3453. [Google Scholar]
- Campagna, G.; Ramesh, R.; Xu, S.; Fischer, M.; Lam, M.S. Almond: The architecture of an open, crowdsourced, privacy-preserving, programmable virtual assistant. In Proceedings of the International Conference on World Wide Web, Perth, Australia, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- The Best Siri Commands for iOS and MacOS. Available online: https://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/best-siri-commands/ (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- The Complete List of Siri Commands. Available online: https://www.cnet.com/how-to/the-complete-list-of-siri-commands/ (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Garrido-Jurado, S.; Muñoz-Salinas, R.; Madrid-Cuevas, F.J.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J. Automatic generation and detection of highly reliable fiducial markers under occlusion. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROS Toolbox for MATLAB. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Structural Similarity Index. Available online: https://scikit-image.org/docs/dev/auto_examples/transform/plot_ssim.html/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- How-To: Python Compare Two Images. Available online: https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2014/09/15/python-compare-two-images/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Blur Detection with OpenCV. Available online: https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/09/07/blur-detection-with-opencv/ (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- King, D.E. Dlib-ml: A Machine Learning Toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Szeliski, R. Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Camera calibration with OpenCV. Available online: https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/doc/tutorials/calib3d/camera_calibration/camera_calibration.html (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; So Kweon, I. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzdeuov, A.; Rubagotti, M.; Varol, H.A. Neural Network Augmented Sensor Fusion for Pose Estimation of Tensegrity Manipulators. IEEE Sens. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babinec, A.; Jurišica, L.; Hubinský, P.; Duchoň, F. Visual Localization of Mobile Robot Using Artificial Markers. Procedia Eng. 2014, 96, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacik, J.; Durovsky, F.; Fedor, P.; Perdukova, D. Autonomous flying with quadrocopter using fuzzy control and ArUco markers. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2017, 10, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, R.G.; Herghelegiu, P.; Botezatu, N.; Moldoveanu, A.; Ferche, O.; Ilie, C.; Levinta, A. Virtual reality system for stroke recovery for upper limbs using ArUco markers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Sinaia, Romania, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction. Available online: https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/modules/calib3d/doc/camera_calibration_and_3d_reconstruction.html (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Geometric Image Transformations. Available online: https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/modules/imgproc/doc/geometric_transformations.html (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Rai, P.; Khanna, P. Gender classification techniques: A review. In Advances in Computer Science, Engineering & Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Assael, Y.M.; Shillingford, B.; Whiteson, S.; de Freitas, N. LipNet: Sentence-level Lipreading. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01599. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D. Adadelta: an adaptive learning rate method. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate. In Conference Track Proceedings, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y., Eds.; DBLP: Trier, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Efros, A.A.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J.Y. Contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation. In European Conference on Computer Vision, Proceedings of the 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 319–345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Wiliem, A.; Yang, S.; Lovell, B. TV-GAN: Generative adversarial network based thermal to visible face recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Gold Coast, Australia, 20–23 February 2018; pp. 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F. Thermal to visible facial image translation using generative adversarial networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Face Recognition. Available online: https://github.com/opencv/opencv/tree/master/samples/dnn/face_detector (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.08500. [Google Scholar]
- Face Recognition. Available online: https://github.com/ageitgey/face_recognition (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Shon, S.; Glass, J. Multimodal Association for Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH), Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 2247–2251. [Google Scholar]




| Datasets | Subjects | Image Pairs | Thermal Resolution | Poses | Trials | Aligned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carl [9] | 41 | 2460 | 1 | 1 | no | |
| VIS-TH [10] | 50 | 2100 | 4 | 2 | yes | |
| IRIS [11] | 30 | 4228 | 11 | 1 | no | |
| USTC-NVIE [12] | 215 | N/A | 1 | 1 | no | |
| Tufts [13] | 100 | 3600 | 9 | 1 | no | |
| UL-FMTV [14] | 238 | N/A | 1 | >1 | N/A | |
| ARL-VTF [15] | 395 | 549,712 | 3 | 1 | no | |
| SpeakingFaces | 142 | 4,581,595 | 9 | 2 | yes |
| Category | Train | Valid | Test | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | 100 | 20 | 22 | 142 |
| Speaker IDs | 1–100 | 101–120 | 121–142 | 1–142 |
| Commands | 9771 | 1963 | 1977 | 13,711 |
| Unique commands | 1297 | 250 | 250 | 1797 |
| Words | 52,769 | 10,324 | 11,177 | 74,270 |
| Unique words | 683 | 337 | 312 | 823 |
| Visual-thermal image pairs for trials with commands | 1,054,989 | 223,528 | 234,071 | 1,512,588 |
| Visual-thermal image pairs for trials w/o commands | 1,620,000 | 356,400 | 324,000 | 2,268,000 |
| Duration in hours for trials with commands | 16.1 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 22.8 |
| Duration in hours for trials w/o commands | 16.1 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 22.8 |
| Size of raw data in TB | 5.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 7.1 |
| Value | Thermal | Visual | Audio | Text |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Clean | Clean | Clean | Clean |
| 1 | Frozen images | Blurred images | Background noise | Minor text noise |
| 2 | - | Cut chin | - | Invalid |
| 3 | - | Both 1 and 2 | - | - |
| ID | Data streams | Accuracy (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual | Audio | Thermal | Valid | Test | |
| 1 | clean | clean | clean | 89.6 | 96.0 |
| 2 | noisy | 87.9 | 95.6 | ||
| 3 | noisy | clean | 81.9 | 84.4 | |
| 4 | noisy | 76.6 | 82.0 | ||
| 5 | noisy | clean | clean | 89.2 | 93.6 |
| 6 | noisy | 84.5 | 88.2 | ||
| 7 | noisy | clean | 67.5 | 65.8 | |
| 8 | noisy | 55.2 | 50.1 | ||
| 9 | clean | n/a | n/a | 91.5 | 91.3 |
| 10 | n/a | clean | n/a | 90.1 | 94.8 |
| 11 | n/a | n/a | clean | 94.8 | 94.3 |
| Domain | Tolerance | TP | FP | FN | Total | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual (real) | 0.45 | 1110 | 4 | 20 | 1134 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Thermal (real) | 0.45 | 12 | 555 | 567 | 1134 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| CUT (generated visual) | 0.45 | 236 | 382 | 516 | 1134 | 0.38 | 0.31 |
| CycleGAN (generated visual) | 0.45 | 397 | 317 | 420 | 1134 | 0.56 | 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdrakhmanova, M.; Kuzdeuov, A.; Jarju, S.; Khassanov, Y.; Lewis, M.; Varol, H.A. SpeakingFaces: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Voice Commands with Visual and Thermal Video Streams. Sensors 2021, 21, 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103465
Abdrakhmanova M, Kuzdeuov A, Jarju S, Khassanov Y, Lewis M, Varol HA. SpeakingFaces: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Voice Commands with Visual and Thermal Video Streams. Sensors. 2021; 21(10):3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103465
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdrakhmanova, Madina, Askat Kuzdeuov, Sheikh Jarju, Yerbolat Khassanov, Michael Lewis, and Huseyin Atakan Varol. 2021. "SpeakingFaces: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Voice Commands with Visual and Thermal Video Streams" Sensors 21, no. 10: 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103465
APA StyleAbdrakhmanova, M., Kuzdeuov, A., Jarju, S., Khassanov, Y., Lewis, M., & Varol, H. A. (2021). SpeakingFaces: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Voice Commands with Visual and Thermal Video Streams. Sensors, 21(10), 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103465






