Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Using Siamese Network and Adversarial Learning
Abstract
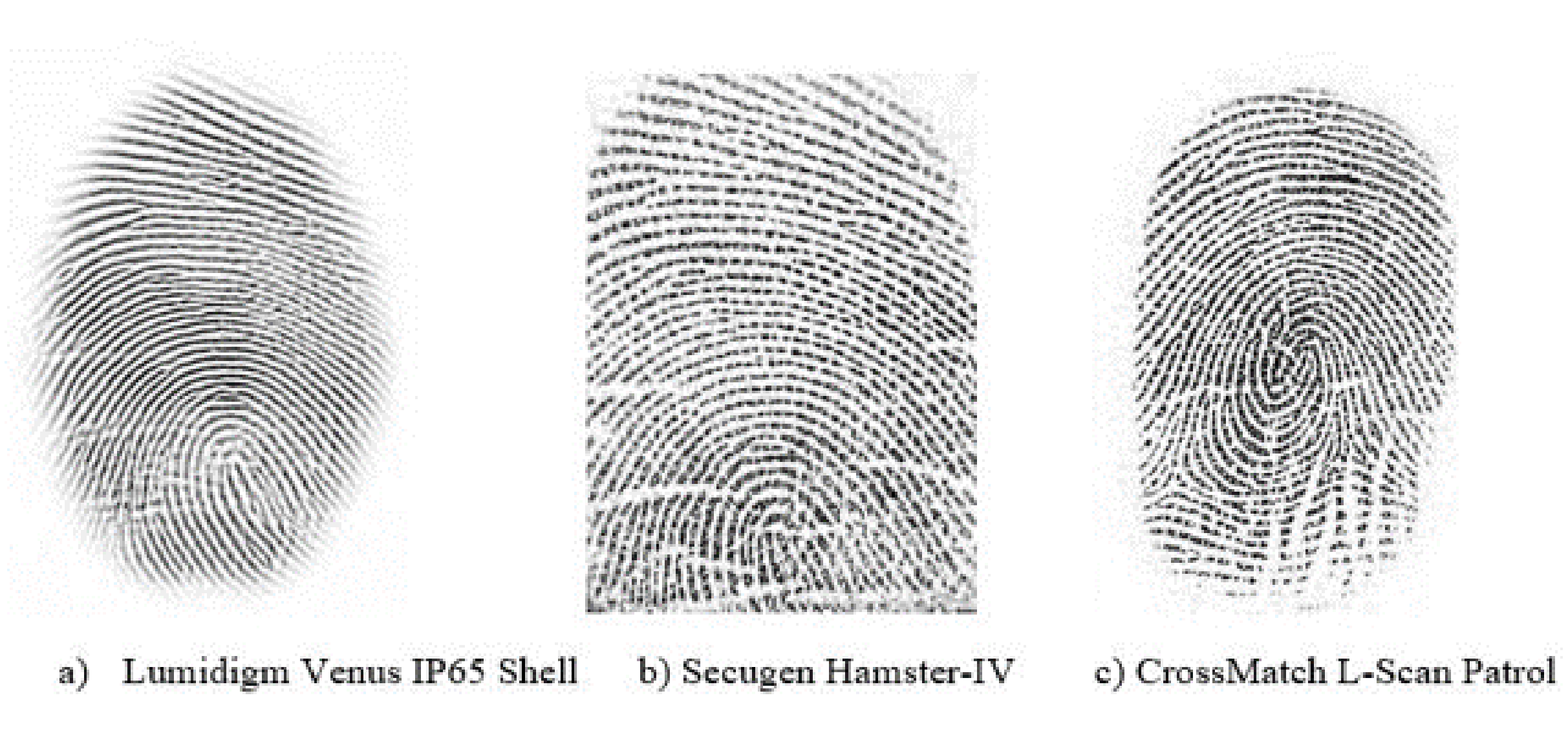
1. Introduction
- A novel deep learning method has been introduced to address the cross-matching problem. The method is alignment free, which reduces the matching time of fingerprints.
- A Siamese network has been proposed to learn fingerprint feature correspondences. The architecture of the Siamese network has been designed specifically to address the cross-matching problem.
- An adversarial learning method has been used to train the Siamese network.
- The method has been evaluated comprehensively using two benchmark datasets and compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Related Work
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Siamese Network for Matching
2.2.1. The Backbone CNN Model
2.2.2. Similarity Module
2.2.3. Loss Functions for Training the Network
2.3. Adversarial Learning and Sensor Discriminator
3. Evaluation Protocol
3.1. Description of Datasets
3.2. Evaluation Procedure
3.3. Training Model
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Results on the FingerPass Database
4.2. Experimental Results on The MOLF Database
4.3. Comparisons with the State-of-the-Art Methods
4.3.1. Results on the MOLF Database
4.3.2. Results on The FingerPass Database
4.4. Model Complexity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross, A.; Jain, A. Biometric sensor interoperability: A case study in fingerprints. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2004, 3087, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Alshehri, H.; Hussain, M.; Aboalsamh, H.A.; Zuair, M.A.A. Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Method Based on Orientation, Gradient, and Gabor-HOG Descriptors with Score Level Fusion. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 28951–28968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-fernandez, F.; Veldhuis, R.N.J.; Bazen, A.M.; Fierrez-Aguilar, J.; Ortega-Garcia, J. Sensor Interoperability and Fusion in Fingerprint Verification: A Case Study using Minutiae- and Ridge-Based Matchers. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, Singapore, 5–8 December 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alshehri, H.; Hussain, M.; Aboalsamh, H.A.; Emad-Ul-Haq, Q.; Alzuair, M.; Azmi, A.M. Alignment-Free Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Based on the Co-Occurrence of Ridge Orientations and Gabor-HOG Descriptor. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86436–86452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Nadgir, R. A thin-plate spline calibration model for fingerprint sensor interoperability. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2008, 20, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Dass, S.; Jain, A. A deformable model for fingerprint matching. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Yang, X.; Jia, X.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J.; Zhu, X. A Coarse-fine Fingerprint Scaling Method. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Yang, X.; Jia, X.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J.; Zhao, J. Evaluation of minutia cylinder-code on fingerprint cross-matching and its improvement with scale. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Ren, C.; Wu, Y. Fingerprint scaling for sensor interoperability. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 303, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Kumar, A. A CNN-Based Framework for Comparison of Contactless to Contact-Based Fingerprints. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Kumar, A. Multi-Siamese networks to accurately match contactless to contact-based fingerprint images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Denver, CO, USA, 1–4 October 2017; Volume 14, pp. 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Yang, X.; Zang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J. A cross-device matching fingerprint database from multi-type sensors. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 3001–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran, A.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. Multisensor Optical and Latent Fingerprint Database. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, L.; Lumini, A. Descriptors for image-based fingerprint matchers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 12414–12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Wan, Y.; Jain, A. Fingerprint image enhancement: Algorithm and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugini, I.G.L.; Marasco, E.; Cukic, B. Interoperability in Fingerprint Recognition: A Large-Scale Empirical Study. In Proceedings of the 2013 43rd Annual IEEE/IFIP Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks Workshop (DSN-W), Budapest, Hungary, 24–27 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, S.; Gashi, I.; Lugini, L.; Marasco, E.; Cukic, B. Interoperability between Fingerprint Biometric Systems: An Empirical Study. In Proceedings of the 2014 44th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, Atlanta, GA, USA, 23–26 June 2014; pp. 586–597. [Google Scholar]
- Rathod, P.; Nangre, M.; Kolhale, P. Contactless Fingerprint Recognition System Based On CNN. Int. J. Future Gener. Commun. Netw. 2020, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; Volume 10, pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015—Conference Track Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the NIPS’14: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2672–2680.
- Ganin, Y.; Lempitsky, V. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation by Backpropagation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 1180–1189. [Google Scholar]
- El-abed, M.; Charrier, C. Evaluation of biometric systems: A study of users’ acceptance and satisfaction. Int. J. Biom. 2012, 4, 265–290. [Google Scholar]
- Shalabi, L.A.; Shaaban, Z.; Kasasbeh, B. Data Mining: A Preprocessing Engine. J. Comput. Sci. 2006, 2, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, R.; Ferrara, M.; Maltoni, D. Minutia Cylinder-Code: A new representation and matching technique for fingerprint recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 2128–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VeriFinger SDK 9. Available online: http//www.neurotechnology.com/verifinger.html (accessed on 30 September 2016).







| Dataset | Sensor | Technology Type | Interaction Type | Image Size (Pixels) | Image Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXOP | FX3000 | Optical | Press | 400 × 560 | 569 dpi |
| V3OP | V300 | Optical | Press | 640 × 480 | 500 dpi |
| UROP | URU4000B | Optical | Press | 500 × 550 | 700 dpi |
| AEOS | AES2501 | Optical | Sweep | Variable | 500 dpi |
| ATCS | ATRUA | Capacitive | Sweep | 124 × 400 | 250 dpi |
| SWCS | SW6888 | Capacitive | Sweep | 288 × 384 | 500 dpi |
| AECP | AES3400 | Capacitive | Press | 144 × 144 | 500 dpi |
| FPCP | FPC1011C | Capacitive | Press | 152 × 200 | 363 dpi |
| TCCP | TCRU2C | Capacitive | Press | 208 × 288 | 500 dpi |
| Gallery Dataset | Probe Dataset | EER | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native-Matching | |||
| UROP | UROP | 3.509 | 96.63% |
| TCCP | TCCP | 2.646 | 97.54% |
| AEOS | AEOS | 1.489 | 98.53% |
| SWCS | SWCS | 2.242 | 97.89% |
| FPCP | FPCP | 1.995 | 98.12% |
| AECP | AECP | 3.738 | 96.33% |
| ATCS | ATCS | 0.998 | 98.97% |
| V3OP | V3OP | 5.167 | 94.77% |
| FXOP | FXOP | 2.638 | 97.43% |
| Cross-Matching | |||
| UROP | TCCP | 7.175 | 92.61% |
| UROP | AECP | 7.177 | 92.56% |
| UROP | FPCP | 5.923 | 94.03% |
| UROP | AEOS | 5.555 | 94.35% |
| UROP | SWCS | 5.694 | 94.43% |
| FPCP | UROP | 6.801 | 93.23% |
| FPCP | AEOS | 3.843 | 96.14% |
| TCCP | AEOS | 4.259 | 95.19% |
| AECP | AEOS | 5.752 | 94.19% |
| TCCP | SWCS | 4.305 | 95.74% |
| AECP | SWCS | 6.426 | 93.86% |
| AECP | ATCS | 4.694 | 95.52% |
| FPCP | TCCP | 5.740 | 94.67% |
| AEOS | SWCS | 2.869 | 96.99% |
| AEOS | FPCP | 4.583 | 95.52% |
| ATCS | AECP | 6.111 | 93.95% |
| AECP | FXOP | 8.840 | 91.66% |
| FXOP | AECP | 8.853 | 91.35% |
| V3OP | AECP | 10.700 | 90.12% |
| AECP | V3OP | 11.433 | 90.71% |
| V3OP | FPCP | 7.591 | 92.23% |
| FPCP | V3OP | 8.240 | 91.89% |
| V3OP | FXOP | 7.601 | 92.50% |
| FXOP | V3OP | 8.555 | 90.75% |
| Gallery/Probe | DB1 | DB2 | DB3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | 1.83 (98.16%) | 10.47 (82.16%) | 10.48 (81.56%) |
| DB2 | 10.23 (83.90%) | 3.52 (96.02%) | 10.29 (82.02%) |
| DB3 | 10.73 (80.18%) | 10.3 (82.82%) | 2.69 (96.78%) |
| Gallery/Probe | SiameseFinger | CrossVFinger (Gabor-HoG) |
|---|---|---|
| DB1, DB2, DB3 | DB1, DB2, DB3 | |
| DB1 | 1.83, 10.47, 10.48 | 6.80, 11.81, 9.93 |
| DB2 | 10.23, 3.52, 10.29 | 11.81, 7.48, 8.79 |
| DB3 | 0.73, 10.3, 2.69 | 9.93, 8.79, 6.59 |
| Gallary | FPCP | AECP | SWCS | AECP | UROP | FPCP | AECP | UROP | AEOS | ATCS | AECP | FPCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe | FPCP | AECP | SWCS | AEOS | FPCP | AEOS | SWCS | AECP | FPCP | AECP | ATCS | UROP |
| MCC | 25.37 | 43.18 | 3.07 | 34.71 | 46.44 | 41.25 | 36.88 | 43.98 | 41.25 | 47.69 | 47.7 | 46.44 |
| Verifinger | 5.2 | 12.87 | 0.45 | 10.62 | 43.3 | 28.99 | 12.81 | 27.81 | 28.98 | 30.32 | 30.33 | 43.35 |
| CrossVFinger | 0.754 | 0.578 | 0.002 | 6.543 | 6.829 | 6.872 | 6.427 | 5.565 | 6.872 | 6.717 | 6.717 | 6.82 |
| SiameseFinger | 1.955 | 3.738 | 1.92 | 5.752 | 5.923 | 3.843 | 6.426 | 7.177 | 4.583 | 6.111 | 4.694 | 6.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrashidi, A.; Alotaibi, A.; Hussain, M.; AlShehri, H.; AboAlSamh, H.A.; Bebis, G. Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Using Siamese Network and Adversarial Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113657
Alrashidi A, Alotaibi A, Hussain M, AlShehri H, AboAlSamh HA, Bebis G. Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Using Siamese Network and Adversarial Learning. Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113657
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrashidi, Adhwa, Ashwaq Alotaibi, Muhammad Hussain, Helala AlShehri, Hatim A. AboAlSamh, and George Bebis. 2021. "Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Using Siamese Network and Adversarial Learning" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113657
APA StyleAlrashidi, A., Alotaibi, A., Hussain, M., AlShehri, H., AboAlSamh, H. A., & Bebis, G. (2021). Cross-Sensor Fingerprint Matching Using Siamese Network and Adversarial Learning. Sensors, 21(11), 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113657






