Remote Monitoring of Heart Failure in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Current Status and Future Needs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
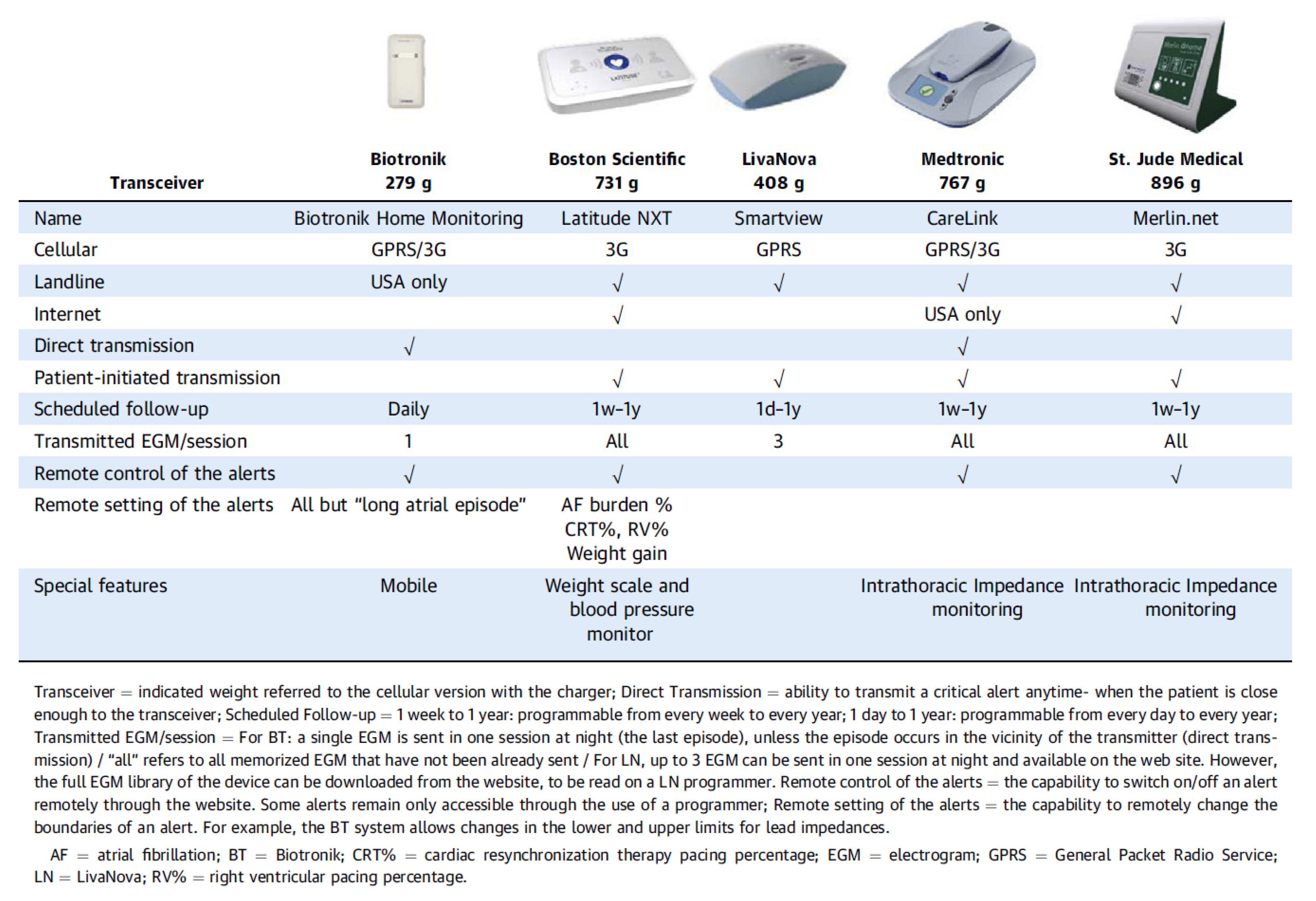
2. Remote Monitoring Systems
3. Remote Patient Management
4. Intrathoracic Impedance Monitoring
4.1. Single Vector Analysis
4.2. Multiple Vector Analysis
5. Monitoring Multiple Device Diagnostic Parameters
6. Randomized Clinical Trials and Remote Monitoring
7. Remote Monitoring, Atrial Fibrillation, and Heart Failure Hospitalization
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statemen
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ponikowski, P.; Anker, S.D.; AlHabib, K.F.; Cowie, M.R.; Force, T.L.; Hu, S.; Jaarsma, T.; Krum, H.; Rastogi, V.; Rohde, L.E.; et al. Heart failure: Preventing disease and death worldwide. ESC Heart Fail. 2014, 1, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Roger, V.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013, 127, e6–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Vaduganathan, M.; Fonarow, G.C.; Bonow, R.O. Rehospitalization for heart failure: Problems and perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martirosyan, M.; Caliskan, K.; Theuns, D.; Szili-Torok, T. Remote monitoring of heart failure: Benefits for therapeutic decision making. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2017, 15, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploux, S.; Swerdlow, C.D.; Strik, M.; Lazarus, A.; Bordachar, P. Towards eradication of inappropriate therapies for ICD lead failure by combining comprehensive remote monitoring and lead noise alerts. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubner, S.; Auricchio, A.; Steinberg, J.S.; Vardas, P.; Stone, P.; Brugada, J.; Piotrowicz, R.; Hayes, D.L.; Kirchhof, P.; Breithardt, G.; et al. ISHNE/EHRA expert consensus on remote monitoring of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIEDs). Europace 2012, 14, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.M.; Wang, L.I.; Chau, E.; Chan, R.H.W.; Kong, S.L.; Tang, M.O.; Christensen, J.; Stadler, R.W.; Lau, C.P. Intrathoracic impedance monitoring in patients with heart failure: Correlation with fluid status and feasibility of early warning preceding hospitalization. Circulation 2005, 112, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vollmann, D.; Nägele, H.; Schauerte, P.; Wiegand, U.; Butter, C.; Zanotto, G.; Quesada, A.; Guthmann, A.; Hill, M.R.; Lamp, B. Clinical utility of intrathoracic impedance monitoring to alert patients with an implanted device of deteriorating chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conraads, V.M.; Tavazzi, L.; Santini, M.; Oliva, F.; Gerritse, B.; Yu, C.M.; Cowie, M.R. Sensitivity and positive predictive value of implantable intrathoracic impedance monitoring as a predictor of heart failure hospitalizations: The SENSE-HF trial. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Braunschweig, F.; Conraads, V.; Ford, I.; Cowie, M.R.; Jondeau, G.; Kautzner, J.; Munoz Aguilera, R.; Lunati, M.; Yu, C.M.; et al. Intrathoracic impedance monitoring, audible patient alerts, and outcome in patients with heart failure. Circulation 2011, 124, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binkley, P.F.; Porterfield, J.G.; Porterfield, L.M.; Beau, S.L.; Corbisiero, R.; Greer, G.S.; Love, C.J.; Turkel, M.; Bjorling, A.; Qu, F.; et al. Feasibility of using multivector impedance to monitor pulmonary congestion in heart failure patients. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forleo, G.B.; Panattoni, G.; Schirripa, V.; Papavasileiou, L.P.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Politano, A.; Ticconi, F.; Biscione, C.; Sergi, D.; Di Molfetta, A.; et al. Device monitoring of heart failure in cardiac resynchronization therapy device recipients: A single-center experience with a novel multivector impedance monitoring system. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2013, 14, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heist, E.K.; Herre, J.M.; Binkley, P.F.; Van Bakel, A.B.; Porterfield, J.G.; Porterfield, L.M.; Qu, F.; Turkel, M.; Pavri, B.B.; DEFEAT-PE Study Investigators. Analysis of different device-based intrathoracic impedance vectors for detection of heart failure events (from the Detect Fluid Early from Intrathoracic Impedance Monitoring study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palfy, J.A.; Benezet-Mazuecos, J.; Martinez Milla, J.; Iglesias, J.A.; de la Vieja, J.J.; Sanchez-Borque, P.; Miracle, A.; Rubio, J.M. CorVue algorithm efficacy to predict heart failure in real life: Unnecessary and potentially misleading information? Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whellan, D.J.; Ousdigian, K.T.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Pu, W.; Sarkar, S.; Porter, C.B.; Pavri, B.B.; O’Connor, C.M.; PARTNERS Study Investigators. Combined heart failure device diagnostics identify patients at higher risk of subsequent heart failure hospitalizations: Results from PARTNERS HF (Program to Access and Review Trending Information and Evaluate Correlation to Symptoms in Patients With Heart Failure) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowie, M.R.; Sarkar, S.; Koehler, J.; Whellan, D.J.; Crossley, G.H.; Tang, W.H.W.; Abraham, W.T.; Sharma, V.; Santini, M. Development and validation of an integrated diagnostic algorithm derived from parameters monitored in implantable devices for identifying patients at risk for heart failure hospitalization in an ambulatory setting. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.A.; Sharma, V.; McCann, M.; Koehler, J.; Tsang, B.; Zieroth, S. Prospective evaluation of integrated device diagnostics for heart failure management: Results of the TRIAGE-HF study. ESC Heart Fail. 2018, 5, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.Z.; Taylor, J.K.; Green, C.; Moore, L.; Goode, A.; Black, P.; Howard, L.; Fullwood, C.; Zaidi, A.; Seed, A.; et al. Triage-HF Plus: A novel device-based remote monitoring pathway to identify worsening heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehmer, J.P.; Hariharan, R.; Devecchi, F.G.; Smith, A.L.; Molon, G.; Capucci, A.; An, Q.; Averina, V.; Stolen, C.M.; Thakur, P.H.; et al. A Multisensor Algorithm Predicts Heart Failure Events in Patients With Implanted Devices: Results From the MultiSENSE Study. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, A.; Santini, L.; Favale, S.; Pecora, D.; Petracci, B.; Calò, L.; Molon, G.; Cipolletta, L.; Bianchi, V.; Schirripa, V.; et al. Preliminary experience with the multisensor HeartLogic algorithm for heart failure monitoring: A retrospective case series report. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varma, N.; Epstein, A.E.; Irimpen, A.; Schweikert, R.; Love, C.; Trust Investigators. Efficacy and safety of automatic remote monitoring for implantable cardioverter-defibrillator follow-up: The Lumos-T Safely Reduces Routine Office Device Follow-up (TRUST) trial. Circulation 2010, 122, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crossley, G.H.; Boyle, A.; Vitense, H.; Chang, Y.; Mead, R.H.; CONNECT Investigators. The CONNECT (Clinical Evaluation of Remote Notification to Reduce Time to Clinical Decision) trial: The value of wireless remote monitoring with automatic clinician alerts. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landolina, M.; Perego, G.B.; Lunati, M.; Curnis, A.; Guenzati, G.; Vicentini, A.; Parati, G.; Borghi, G.; Zanaboni, P.; Valsecchi, S.; et al. Remote monitoring reduces healthcare use and improves quality of care in heart failure patients with implantable defibrillators: The evolution of management strategies of heart failure patients with implantable defibrillators (EVOLVO) study. Circulation 2012, 125, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guédon-Moreau, L.; Lacroix, D.; Sadoul, N.; Clémenty, J.; Kouakam, C.; Hermida, J.S.; Aliot, E.; Boursier, M.; Bizeau, O.; Kacet, S.; et al. A randomized study of remote follow-up of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: Safety and efficacy report of the ECOST trial. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hindricks, G.; Taborsky, M.; Glikson, M.; Heinrich, U.; Schumacher, B.; Katz, A.; Brachmann, J.; Lewalter, T.; Goette, A.; Block, M.; et al. Implant-based multiparameter telemonitoring of patients with heart failure (IN-TIME): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthje, L.; Vollmann, D.; Seegers, J.; Sohns, C.; Hasenfuss, G.; Zabel, M. A randomized study of remote monitoring and fluid monitoring for the management of patients with implanted cardiac arrhythmia devices. Europace 2015, 17, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Böhm, M.; Drexler, H.; Oswald, H.; Rybak, K.; Bosch, R.; Butter, C.; Klein, G.; Gerritse, B.; Monteiro, J.; Israel, C.; et al. Fluid status telemedicine alerts for heart failure: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, J.M.; Kitt, S.; Gill, J.; McComb, J.M.; Ng, G.A.; Raftery, J.; Roderick, P.; Seed, A.; Williams, S.G.; Witte, K.K.; et al. Remote management of heart failure using implantable electronic devices. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boriani, G.; Da Costa, A.; Quesada, A.; Ricci, R.P.; Favale, S.; Boscolo, G.; Clementy, N.; Amori, V.; Mangoni di SStefano, L.; Burri, H.; et al. Effects of remote monitoring on clinical outcomes and use of healthcare resources in heart failure patients with biventricular defibrillators: Results of the MORE-CARE multicentre randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parthiban, N.; Esterman, A.; Mahajan, R.; Twomey, D.J.; Pathak, R.K.; Lau, D.H.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Young, G.D.; Sanders, P.; Ganesan, A.N. Remote Monitoring of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Varma, N.; Kacet, S.; Lewalter, T.; Søgaard, P.; Guédon-Moreau, L.; Proff, J.; Gerds, T.A.; Anker, S.D.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Daily remote monitoring of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: Insights from the pooled patient-level data from three randomized controlled trials (IN-TIME, ECOST, TRUST). Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, M.; Gasparini, M.; Landolina, M.; Lunati, M.; Proclemer, A.; Padeletti, L.; Catanzariti, D.; Molon, G.; Botto, G.L.; La Rocca, L.; et al. Device-detected atrial tachyarrhythmias predict adverse outcome in real-world patients with implantable biventricular defibrillators. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, S.; Koehler, J.; Crossley, G.H.; Tang, W.H.; Abraham, W.T.; Warman, E.N.; Whellan, D.J. Burden of atrial fibrillation and poor rate control detected by continuous monitoring and the risk for heart failure hospitalization. Am. Heart J. 2012, 164, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, R.; Morgan, J.M.; Phillips, P.; Kitt, S.; Ng, G.A.; McComb, J.M.; Williams, S.; Wright, D.J.; Gill, J.S.; Seed, A.; et al. Impact of remote monitoring on clinical outcomes for patients with heart failure and atrial fibrillation: Results from the REM-HF trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotwiner, D.; Varma, N.; Akar, J.G.; Annas, G.; Beardsall, M.; Fogel, R.I.; Galizio, N.O.; Glotzer, T.V.; Leahy, R.A.; Love, C.J.; et al. HRS Expert Consensus Statement on remote interrogation and monitoring for cardiovascular implantable electronic devices. Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, e69–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Stevenson, L.W.; Bourge, R.C.; Lindenfeld, J.A.; Bauman, J.G.; Adamson, P.B.; CHAMPION Trial Study Group. Sustained efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure to guide adjustment of chronic heart failure therapy: Complete follow-up results from the CHAMPION randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Study | FU (Months) | Sample Size (n) | RM (n) | IO (n) | Age (yrs) | Male (%) | LVEF (%) | ICM (%) | NYHA II (%) | NYHA III-IV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRUST [21] | 12 | 1,339 | 908 | 431 | 64 | 73 | 29 | 67 | 57 | 30 |
| CONNECT [22] | 15 | 1,997 | 1014 | 983 | 65 | 71 | 29 | 62 | 40 | 50 |
| EVOLVO [23] | 16 | 200 | 99 | 101 | 67 | 79 | 31 | 46 | 70 | 19 |
| ECOST [24] | 24 | 433 | 221 | 212 | 62 | 88 | 35 | 65 | 62 | 9 |
| IN-TIME [25] | 12 | 664 | 333 | 331 | 65 | 82 | 26 | 70 | 43 | 57 |
| CONNECT OptiVol [26] | 15 | 176 | 87 | 89 | 66 | 77 | 32 | 53 | 46 | 43 |
| OptiLink HF [27] | 18 | 1,002 | 505 | 497 | 66 | 80 | 27 | 54 | 19 | 81 |
| REM-HF [28] | 34 | 1,650 | 824 | 826 | 70 | 86 | 30 | 68 | 70 | 30 |
| MORE-CARE [29] | 24 | 865 | 437 | 428 | 66 | 76 | 27 | 44 | 38 | 60 |
| Study | Parameters | Telemedicine-Based Disease Management |
|---|---|---|
| TRUST [21] | VT, VF, SVT, ineffective 30-J shock, mode switch duration >10% in 24 h | No |
| CONNECT [22] | AT/AF burden, ventricular rate during AT/AF, number of shocks delivered, all therapies exhausted in a zone | No |
| EVOLVO [23] | Thoracic impedance (OptiVol), AT/AF burden, number of shocks delivered | Yes |
| ECOST [24] | VT, VF, SVT, ineffective 30-J shock, >75% (18 h) spent in mode switch | No |
| IN-TIME [25] | VT, VF, SVT, % biventricular pacing, PVC/h, patient activity | Yes |
| CONNECT OptiVol [26] | Thoracic impedance (OptiVol) | Yes |
| OptiLink HF [27] | Thoracic impedance (OptiVol) | Yes |
| REM-HF [28] | Thoracic impedance, % biventricular pacing, AT/AF burden, ventricular arrhythmias, activity level, heart rate variability | Yes |
| MORE-CARE [29] | Thoracic impedance (OptiVol), AT/AF burden | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theuns, D.A.M.J.; Radhoe, S.P.; Brugts, J.J. Remote Monitoring of Heart Failure in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Current Status and Future Needs. Sensors 2021, 21, 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113763
Theuns DAMJ, Radhoe SP, Brugts JJ. Remote Monitoring of Heart Failure in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Current Status and Future Needs. Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113763
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheuns, Dominic A. M. J., Sumant P. Radhoe, and Jasper J. Brugts. 2021. "Remote Monitoring of Heart Failure in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Current Status and Future Needs" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113763
APA StyleTheuns, D. A. M. J., Radhoe, S. P., & Brugts, J. J. (2021). Remote Monitoring of Heart Failure in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Current Status and Future Needs. Sensors, 21(11), 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113763






