Investigation on the Sampling Frequency and Channel Number for Force Myography Based Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
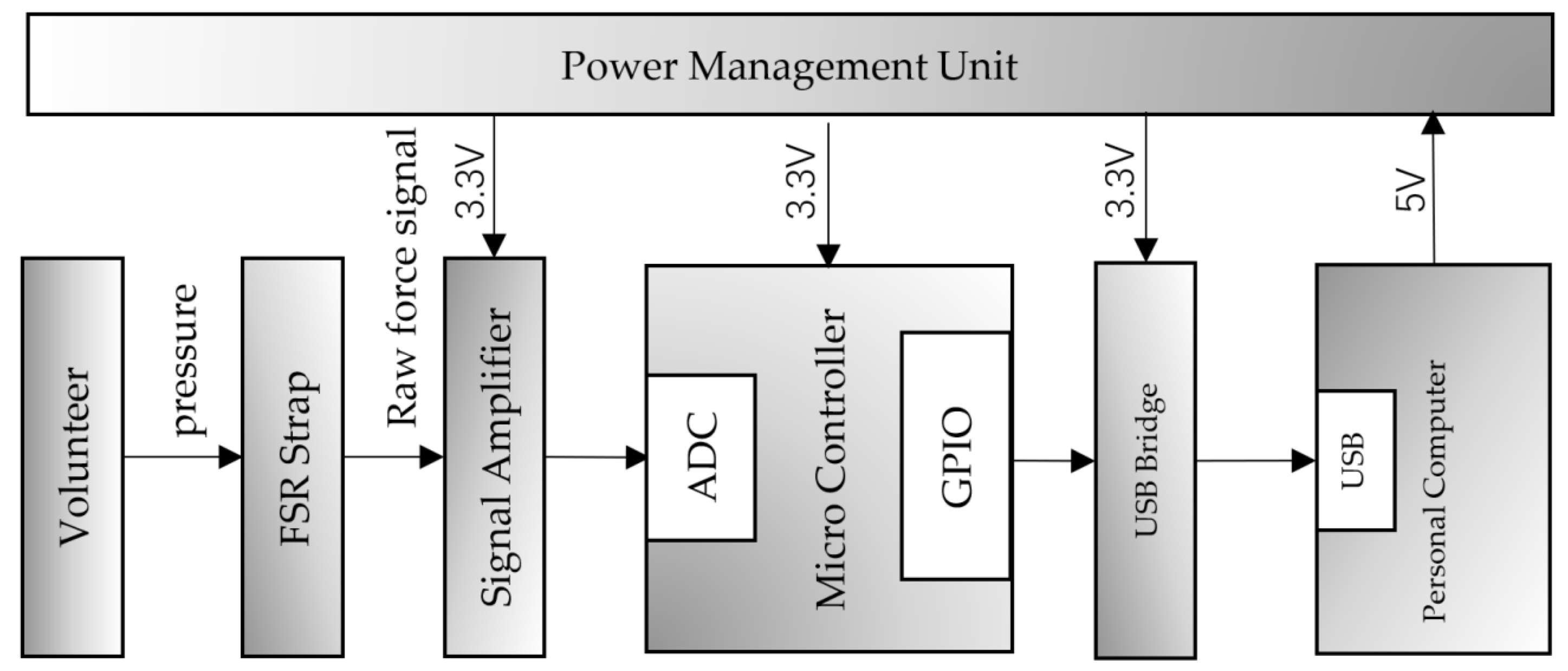
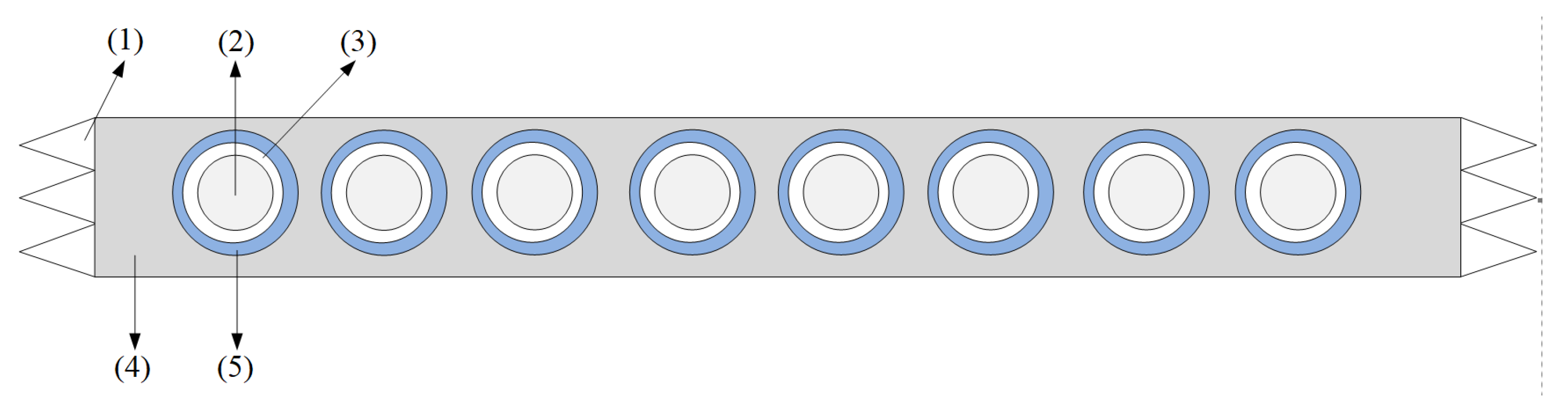
2.1. Sensing Unit
2.2. System Architecture
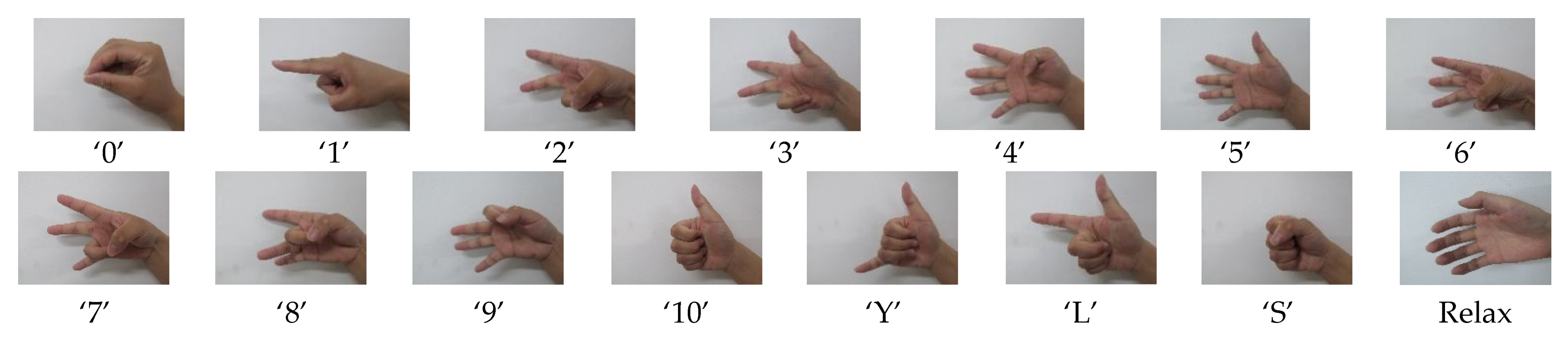
2.3. Experimental Setup
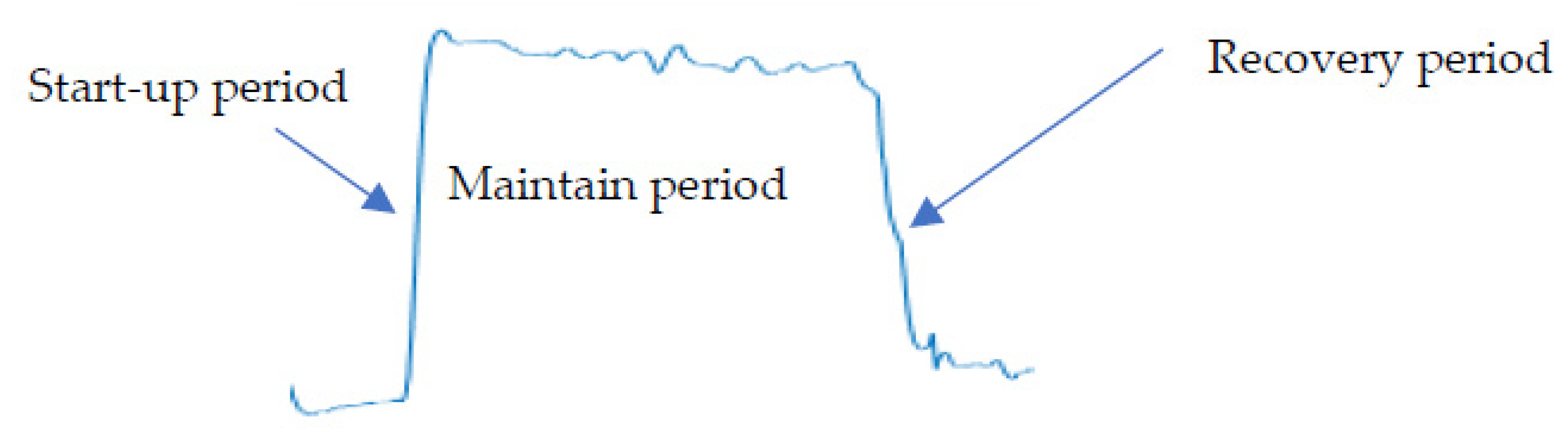
2.4. Data Analysis and Processing
3. Results
3.1. The Impact of Sampling Frequency on Classification Accuracy
3.2. The Impact of Channel Number on Classification Accuracy
3.3. The Impact of Channel Combination on Classification Accuracy
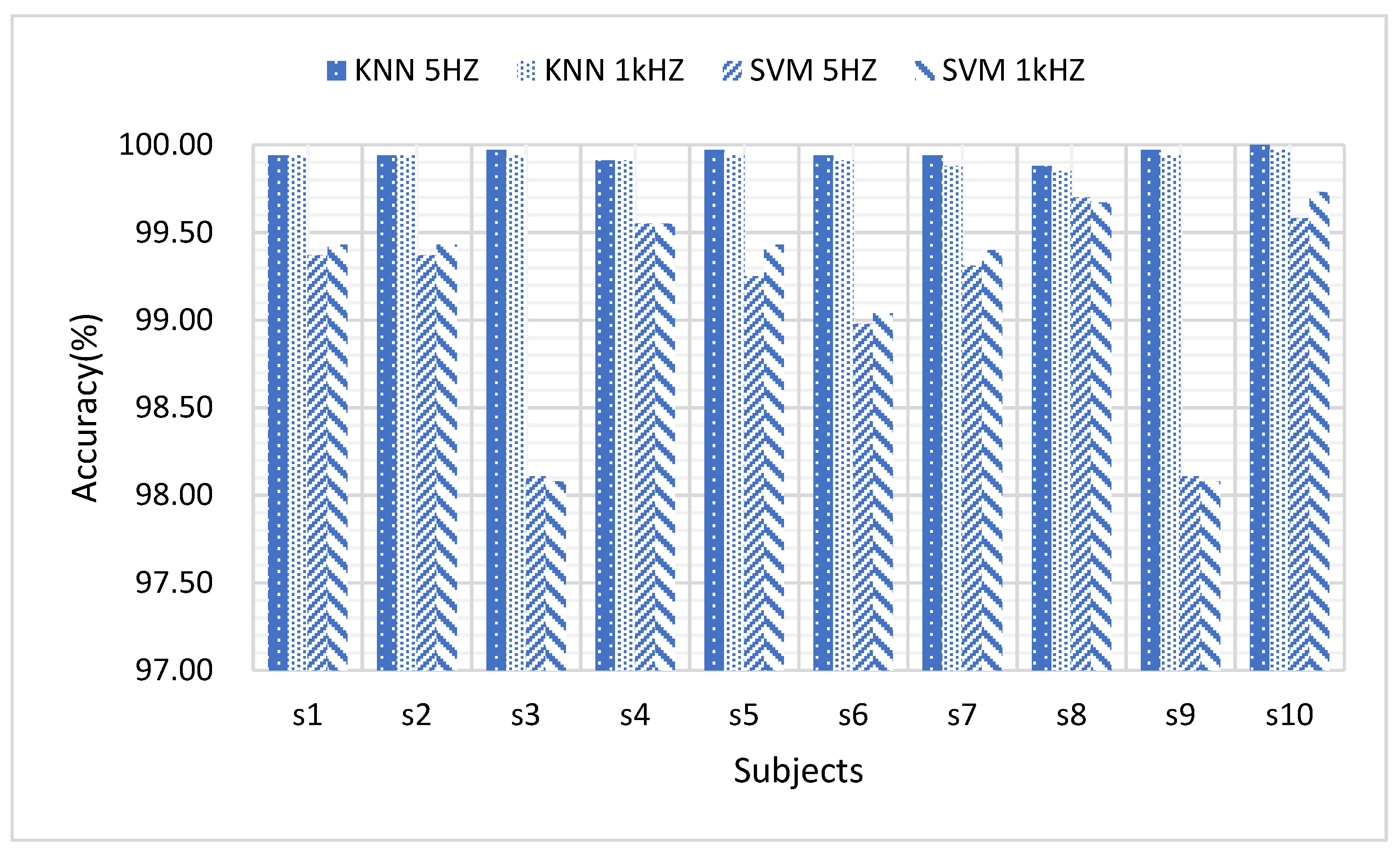
3.4. Individual Differences for FMG Based Hand Gesture Classification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Y.; Hettiarachchi, N.; Zhou, D.; Liu, H. Multi-Modal Sensing Techniques for Interfacing Hand Prostheses: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 6065–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, A.; Sahi, A.K.; Sharma, N. Force myography controlled multifunctional hand prosthesis for upper-limb amputees. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyea, A.; Englehart, K.; Scheme, E. FMG vs. EMG: A Comparison of Usability for Real-time Pattern Recognition Based Control. IEEE Trans. Med. Eng. 2019, 66, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connan, M.; Ruiz Ramírez, E.; Vodermayer, B.; Castellini, C. Assessment of a Wearable Force- and Electromyography Device and Comparison of the Related Signals for Myocontrol. Front. Neurorobotics 2016, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Merhi, L.K.; Xiao, Z.G. Exploration of Force Myography and surface Electromyography in hand gesture classifica-tion. Med Eng. Phys. 2017, 41, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucaccini, L.F. The french electric hand: Some observations and conclusions. Bull. Prosthet. Res. 1966, 10, 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Abboudi, R.L.; Glass, C.A.; Newby, N.A.; Flint, J.A.; Craelius, W. A biomimetic controller for a multifinger prosthesis. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1999, 7, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wininger, M.; Kim, N.H.; Craelius, W. Pressure signature of forearm as predictor of grip force. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2008, 45, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yang, D.; Jiang, L.; Liu, H.; Cai, H. Combined Use of FSR Sensor Array and SVM Classifier for Finger Motion Recognition Based on Pressure Distribution Map. J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.; Withanachchi, G.P.; Yihun, Y. Force Myography Signal-Based Hand Gesture Classification for the Implementation of Real-Time Control System to a Prosthetic Hand. In Proceedings of the 2018 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Graduate Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Zhen, G.X.; Menon, C. Virtual Grasps Recognition using Fusion of Leap Motion and Force Myography. Virtual Real. 2018, 22, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.X.; Menon, C. Towards the development of a wearable feedback system for monitoring the activities of the up-per-extremities. J. Neuro Eng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, G.X.; Carlo Menon, C.M. Performance of forearm FMG and sEMG for estimating elbow, forearm and wrist positions. J. Bionic Eng. 2017, 14, 284–295. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkan, R.; Erik, S.; Kevin, E. High-density force myography: A possible alternative for upper-limb prosthetic control. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2016, 53, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Merhi, L.K.; Menon, C. Force Exertion Affects Grasp Classification Using Force Myography. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2018, 48, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegani, R.S.; Menon, C. Regressing grasping using force myography: An exploratory study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadizadeh, C.; Merhi, L.K.; Pousett, B. Toward Intuitive Prosthetic Control: Solving Common Issues Using Force My-ography, Surface Electromyography, and Pattern Recognition in a Pilot Case Study. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2017, 24, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeetinder Ghataurah, J.; Diego Ferigo, D.; Lukas-Karim Merhi, L.K.; Brittany Pousett, B.P.; Carlo Menon, C.M. A Multi-Sensor Approach for Biomimetic Control of a Robotic Prosthetic Hand; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chengani, R.; Delva, M.L.; Sakr, M. Pilot study on strategies in sensor placement for robust hand/wrist gesture classification based on movement related changes in forearm volume. In Proceedings of the Healthcare Innovation Point-of-Care Technologies Conference, Cancun, Mexico, 9–11 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Delva, M.L.; Menon, C. FSR based force myography (FMG) stability throughout non-stationary upper extremity tasks [C]. In Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29–30 November 2017; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Anvaripour, M.; Saif, M. Hand gesture recognition using force myography of the forearm activities and optimized features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Lyon, France, 20–22 February 2018; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadizadeh, C.; Pousett, B.; Menon, C. Investigation of Channel Selection for Gesture Classification for Prosthesis Control Using Force Myography: A Case Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiyal, A.K.; Singh, U.; Anand, S. Analysis of Force Myography based locomotion patterns. Measurement 2019, 140, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Chen, R.; Merhi, L.K.; Xiao, Z.; Pousett, B.; Menon, C. Force Myography to Control Robotic Upper Extremity Prostheses: A Feasibility Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dlugosz, R.; Iniewski, K. Ultra low power current-mode algorithmic analog-to-digital converter implemented in 0.18/spl mu/m CMOS technology for wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the International Conference Mixed Design of In-tegrated Circuits and System, Gdynia, Poland, 22–24 June 2006; pp. 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.G.; Menon, C. An Investigation on the Sampling Frequency of the Upper-Limb Force Myographic Signals. Sensors 2019, 19, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Chu, K.H.T.; Khoshnam, M.A. Wearable Gait Phase Detection System Based on Force Myography Techniques. Sensors 2018, 18, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delva, M.L.; Sakr, M.; Chegani, R.L.; Khoshnam, M.; Menon, C. Investigation into the Potential to Create a Force Myogra-phy-based Smart-home Controller for Aging Populations. In Proceedings of the IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Enschede, The Netherlands, 26–29 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, R.; Claudio, C. A Comparative Analysis of Three Non-Invasive Human-Machine Interfaces for the Disabled. Front. Neurorobotics 2014, 8, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanou, T.; Chance, G.; Assaf, T. Wearable Tactile Sensor Brace for Motion Intent Recognition in Upper-Limb Rehabilita-tion. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (Biorob), Enschede, The Netherlands, 26–29 August 2018; pp. 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kargov, A.; Pylatiuk, C.; Martin, J.; Schulz, S. A comparison of the grip force dis-tribution in natural hands and in prosthetic hands. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 26, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.W.; Jiang, X.; Merhi, L.K. Investigation of the Feasibility of Strain Gages as Pressure Sensors for Force Myography. In Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, IWBBIO; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, C.; Allmendinger, R.; Climent, R. New Interfaces and Approaches to Machine Learning When Classifying Gestures within Music. Entropy 2020, 22, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinyomark, A.; Quaine, F.; Charbonnier, S.; Serviere, C.; Tarpin-Bernard, F.; Laurillau, Y. EMG feature evaluation for im-proving myoelectric pattern recognition robustness. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 4832–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, K.; Liu, H. Bio-signal based elbow angle and torque simultaneous prediction during isokinetic contraction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D. Improve Inter-day Hand Gesture Recognition Via Convolutional Neural Network-based Feature Fusion. Int. J. Hum. Robot. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, L.; Ju, Z.; Liu, H. Attribute-driven granular model for EMG-based pinch and fingertip force grand recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Studies | Sampling Frequency (Hz) | Number of Channels | Number of Gestures | Features | Classifiers | Classification Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li, 2012 [9] | 100 | 32 | 17 | - | SVM | 99 |
| Ha, 2018 [10] | 25 | - | - | - | SVM | 95 |
| Carlo, 2018 [11] | 50 | 10 | 6 | - | LDA, SVM, TB 4 and NN 5 | 87.7 |
| Carlo, 2014 [12] | 1000 | 8 | 6 | - | ELM 11 | 92.33 |
| Carlo, 2017 [13] | 1000 | 8 | 45 | RMS 1 | LDA 2 and SVM 3 | 84.3 |
| Radmand, 2016 [14] | 20 | 126 | 8 | - | LDA | 99.7 |
| Jiang, 2018 [15] | 15 | 16 | 16 | - | LDA | 82 |
| Carlo, 2018 [16] | 15 | 18 | 15 | RMSE 6 and R 2–7 | LDA, SVM and RF 8 | 90 |
| Ahmadizadeh, 2017 [17] | 10 | 16 | 10 | - | KNN 9, SVM and LDA | 81.1 |
| Ghataurah, 2017 [18] | 10 | 16 × 5 | 11 | - | LDA | - |
| Chengani, 2016 [19] | 10 | 16 | 8 | - | LDA | 95 |
| Mena, 2017 [20] | 10 | 16 | 7 | RMS | - | 94 |
| Anvaripour, 2018 [21] | 10 | 8 | 6 | PSD 10 | SVM | 93 |
| Ahmadizadeh, 2019 [22] | 10 | 16 | 6 | - | LDA | 79.2 |
| Kant, 2019 [23] | 100 | 8 | 8 | VR 12 | - | - |
| Cho, 2016 [24] | 10 | 88 | 11 | - | LDA | 89 |
| Sensor Model | Studies |
|---|---|
| FSR 400 | [9,27,28] |
| FSR 400 short | [4,23,28,29] |
| FSR 402 | [2,11,12,30] |
| Accuracy (%) | 1 kHz | 100 Hz | 10 Hz | 5 Hz | 3 Hz | 2 Hz | 1 Hz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16_KNN | 99.92 | 99.91 | 99.90 | 99.95 | 99.77 | 99.63 | 99.33 |
| 16_SVM | 99.18 | 99.18 | 99.20 | 99.13 | 98.86 | 98.54 | 97.41 |
| 8_KNN | 99.85 | 99.81 | 99.49 | 99.42 | 99.01 | 98.50 | 97.16 |
| 8_SVM | 98.13 | 98.71 | 98.49 | 98.18 | 93.11 | 96.01 | 93.11 |
| 4_KNN | 99.33 | 99.28 | 99.95 | 98.93 | 98.32 | 97.58 | 95.73 |
| 4_SVM | 93.78 | 93.76 | 93.50 | 93.47 | 86.32 | 90.29 | 86.32 |
| 2_KNN | 93.00 | 92.03 | 91.94 | 92.02 | 90.33 | 88.77 | 85.97 |
| 2_SVM | 78.33 | 78.30 | 77.97 | 77.92 | 70.20 | 74.65 | 70.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, G.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Investigation on the Sampling Frequency and Channel Number for Force Myography Based Hand Gesture Recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113872
Lei G, Zhang S, Fang Y, Wang Y, Zhang X. Investigation on the Sampling Frequency and Channel Number for Force Myography Based Hand Gesture Recognition. Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113872
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Guangtai, Shenyilang Zhang, Yinfeng Fang, Yuxi Wang, and Xuguang Zhang. 2021. "Investigation on the Sampling Frequency and Channel Number for Force Myography Based Hand Gesture Recognition" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113872
APA StyleLei, G., Zhang, S., Fang, Y., Wang, Y., & Zhang, X. (2021). Investigation on the Sampling Frequency and Channel Number for Force Myography Based Hand Gesture Recognition. Sensors, 21(11), 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113872







