Assessing Automated Facial Action Unit Detection Systems for Analyzing Cross-Domain Facial Expression Databases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Facial Datasets
2.1.1. In-the-Wild SNS Data
2.1.2. Data from Posed Expression of Emotions
2.1.3. Conversation Data
2.2. Automatic Facial Detection Systems
2.2.1. Face Reader
2.2.2. OpenFace
2.2.3. AFAR
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Aff-Wild2 (in-the-Wild)
3.2. DISFA+ (Posed)
3.3. GFT (Conversational)
3.4. Bias Evaluation
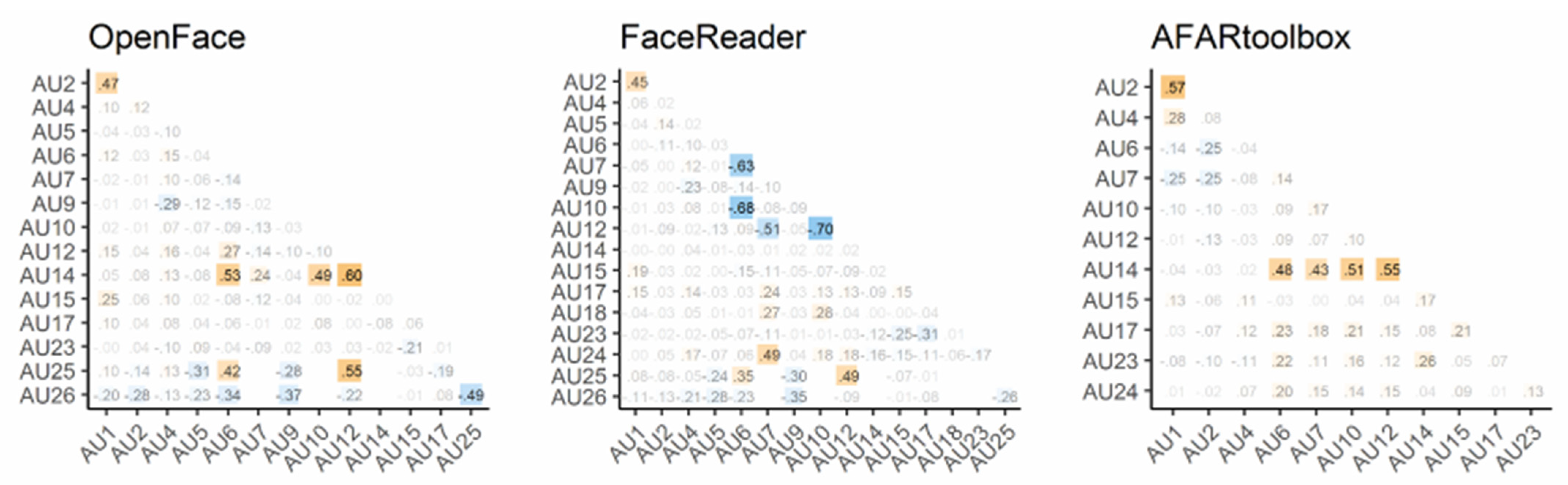
3.5. Within-System Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, M.K.; Awasthi, A. Understanding Facial Expressions in Communication: Cross-Cultural and Multidisciplinary Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V.; Hager, J.C. Facial Action Coding System, 2nd ed.; Research Nexus eBook: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Rosenberg, E.L. What the Face Reveals: Basic and Applied Studies of Spontaneous Expression Using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS), 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Namba, S.; Makihara, S.; Kabir, R.S.; Miyatani, M.; Nakao, T. Spontaneous facial expressions are different from posed facial expressions: Morphological properties and dynamic sequences. Curr. Psychol. 2017, 36, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugrul, I.O.; Cohn, J.F.; Jeni, L.A.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, L.; Ji, Q. Crossing domains for AU coding: Perspectives, approaches, and measures. IEEE Trans. Biom. Behav. Identity Sci. 2020, 2, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Mahmoud, M.; Robinson, P. Cross-dataset learning and person-specific normalisation for automatic action unit detection. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Zadeh, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Morency, L.P. OpenFace 2.0: Facial behavior analysis toolkit. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ertugrul, I.O.; Cohn, J.F.; Jeni, L.A.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, L.; Ji, Q. Cross-domain AU detection: Domains, learning approaches, and measures. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ertugrul, I.O.; Jeni, L.A.; Ding, W.; Cohn, J.F. AFAR: A deep learning based tool for automated facial affect recognition. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lewinski, P.; den Uyl, T.M.; Butler, C. Automated facial coding: Validation of basic emotions and FACS AUs in FaceReader. J. Neurosci. Psychol. Econ. 2014, 7, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skiendziel, T.; Rösch, A.G.; Schultheiss, O.C. Assessing the convergent validity between the automated emotion recognition software Noldus FaceReader 7 and Facial Action Coding System Scoring. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, K. The face of time: Temporal cues in facial expressions of emotion. Psychol. Sci. 1998, 9, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumhuber, E.G.; Kappas, A.; Manstead, A.S. Effects of dynamic aspects of facial expressions: A review. Emot. Rev. 2013, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perusquía-Hernández, M.; Ayabe-Kanamura, S.; Suzuki, K. Human perception and biosignal-based identification of posed and spontaneous smiles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perusquia-Hernandez, M. Are people happy when they smile? Affective assessments based on automatic smile genuineness identification. Emot. Stud. 2021, 6, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Krumhuber, E.G.; Küster, D.; Namba, S.; Shah, D.; Calvo, M.G. Emotion recognition from posed and spontaneous dynamic expressions: Human observers versus machine analysis. Emotion 2019, 21, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, X.H.; Liang, J.; Yan, W.J. The dynamic features of lip corners in genuine and posed smiles. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemamou, L.; Felhi, G.; Vandenbussche, V.; Martin, J.C.; Clavel, C. Hirenet: A hierarchical attention model for the automatic analysis of asynchronous video job interviews. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23 July 2019; pp. 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Perusquia-Hernandez, M.; Dollack, F.; Tan, C.K.; Namba, S.; Ayabe-Kanamura, S.; Suzuki, K. Facial movement synergies and action unit detection from distal wearable electromyography and computer vision. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.08791. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, J.F.; Ertugrul, I.O.; Chu, W.S.; Girard, J.M.; Jeni, L.A.; Hammal, Z. Affective facial computing: Generalizability across domains. Multimodal Behav. Anal. Wild 2019, 407–441. [Google Scholar]
- Jeni, L.A.; Cohn, J.F.; De La Torre, F. Facing imbalanced data—Recommendations for the use of performance metrics. In Proceedings of the Humaine Association Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Washington, DC, USA, 2–5 September 2015; pp. 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.; Chong, L.Y.; Baltrusaitis, T.; Morency, L.P. Convolutional experts constrained local model for 3d facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2519–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrusaitis, T.; Robinson, P.; Morency, L.P. Constrained local neural fields for robust facial landmark detection in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Kotsia, I.; Zhao, G.; Zafeiriou, S. Recognition of affect in the wild using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Zafeiriou, S. Aff-wild2: Extending the Aff-wild database for affect recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07770. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Zafeiriou, S. A multi-task learning & generation framework: Valence–arousal, action units & primary expressions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07771. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Zafeiriou, S. Expression, affect, action unit recognition: Aff-wild2, multi-task learning and ArcFace. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.04855. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Tzirakis, P.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Papaioannou, A.; Zhao, G.; Schuller, B.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. Deep affect prediction in-the-wild: Aff-wild database and challenge, deep architectures, and beyond. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 907–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zafeiriou, S.; Kollias, D.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Papaioannou, A.; Zhao, G.; Kotsia, I. Aff-wild: Valence and arousal ‘n-the-Wild’ challenge. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mavadati, M.; Sanger, P.; Mahoor, M.H. Extended DISFA dataset: Investigating posed and spontaneous facial expressions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, J.M.; Chu, W.S.; Jeni, L.A.; Cohn, J.F. Sayette group formation task (GFT) spontaneous facial expression database. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- McKeown, G.; Valstar, M.; Cowie, R.; Pantic, M.; Schroder, M. The semaine database: Annotated multimodal records of emotionally colored conversations between a person and a limited agent. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, L.; Cohn, J.F.; Canavan, S.; Reale, M.; Horowitz, A.; Liu, P.; Girard, J.M. Bp4d-spontaneous: A high-resolution spontaneous 3D dynamic facial expression database. Image Vis. Comput. 2014, 32, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savran, A.; Alyüz, N.; Dibeklioğlu, H.; Çeliktutan, O.; Gökberk, B.; Sankur, B.; Akarun, L. Bosphorus database for 3D face analysis. In Proceedings of the European Workshop on Biometrics and Identity Management, Roskilde, Denmark, 7–8 May 2008; pp. 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mavadati, S.M.; Mahoor, M.H.; Bartlett, K.; Trinh, P.; Cohn, J.F. DISFA: A spontaneous facial action intensity database. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2013, 4, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valstar, M.F.; Jiang, B.; Mehu, M.; Pantic, M.; Scherer, K. The first facial expression recognition and analysis challenge. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Prkachin, K.M.; Solomon, P.E.; Matthews, I. Painful data: The UNBC-McMaster shoulder pain expression archive database. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jeni, L.A.; Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T. Dense 3D face alignment from 2D video for real-time use. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 58, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Girard, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Ciftci, U.; Canavan, S.; Reale, M.; Horowitz, A.; Yang, H.; et al. Multimodal spontaneous emotion corpus for human behavior analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3438–3446. [Google Scholar]
- Dowle, M.; Srinivasan, A. data.table: Extension of ‘data.frame’. R Package, Version 1.13.2. 2020. Available online: Https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=data.table (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, A.S.; Keltner, D.; Schroff, F.; Jou, B.; Adam, H.; Prasad, G. Sixteen facial expressions occur in similar contexts worldwide. Nature 2021, 589, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, P. Emotions Revealed; Times Books: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Reisenzein, R.; Studtmann, M.; Horstmann, G. Coherence between emotion and facial expression: Evidence from laboratory experiments. Emot. Rev. 2013, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.G.; Nummenmaa, L. Perceptual and affective mechanisms in facial expression recognition: An integrative review. Cogn. Emot. 2016, 30, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, J.M.; Cohn, J.F.; Yin, L.; Morency, L.P. Reconsidering the Duchenne smile: Formalizing and testing hypotheses about eye constriction and positive emotion. Affect. Sci. 2021, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etcoff, N.; Stock, S.; Krumhuber, E.G.; Reed, L.I. A novel test of the Duchenne marker: Smiles after botulinum toxin treatment for crow’s feet wrinkles. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, N.; Messinger, D.; Gao, A.Y.L.; Krumhuber, E.; Mattson, W.; Joober, R.; Tabbane, K.; Martinez-Trujillo, J.C. Generalizing Duchenne to sad expressions with binocular rivalry and perception ratings. Emotion 2019, 19, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.J.; Krumhuber, E.G.; Dawel, A. Observers perceive the Duchenne marker as signaling only intensity for sad expressions, not genuine emotion. Emotion 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, H.; Iwanaga, S.; Asada, M. Comparison between the facial flow lines of androids and humans. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, A.L.; Crewther, D.P. The 4D space-time dimensions of facial perception. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotardo, P.; Riviere, J.; Bradley, D.; Ghosh, A.; Beeler, T. Practical dynamic facial appearance modeling and acquisition. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, S.; Matsui, H.; Zloteanu, M. Distinct temporal features of genuine and deliberate facial expressions of surprise. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, E.; Tamarit, L.; Reveret, L.; Grandjean, D.M.; Sander, D.; Scherer, K.R. FACSGen: A tool to synthesize emotional facial expressions through systematic manipulation of facial action units. J. Nonverbal Behav. 2011, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumhuber, E.G.; Tamarit, L.; Roesch, E.B.; Scherer, K.R. FACSGen 2.0 animation software: Generating three-dimensional FACS-valid facial expressions for emotion research. Emotion 2012, 12, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitzhak, N.; Giladi, N.; Gurevich, T.; Messinger, D.S.; Prince, E.B.; Martin, K.; Aviezer, H. Gently does it: Humans outperform a software classifier in recognizing subtle, nonstereotypical facial expressions. Emotion 2017, 17, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumhuber, E.G.; Küster, D.; Namba, S.; Skora, L. Human and machine validation of 14 databases of dynamic facial expressions. Behav. Res. Methods 2021, 53, 686–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, K.; Xue, J.; Gao, P.; Lyu, J. Feafa: A well-annotated dataset for facial expression analysis and 3D facial animation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Dupré, D.; Krumhuber, E.G.; Küster, D.; McKeown, G.J. A performance comparison of eight commercially available automatic classifiers for facial affect recognition. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmour, N.; Masmoudi, S.; Abdelkrim, A. A New Video Based Emotions Analysis System (VEMOS): An Efficient Solution Compared to iMotions Affectiva Analysis Software. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2021, 6, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, D.; Wu, Z.; Tan, Z.X.; Reddan, M.; Kahhale, I.; Mattek, A.; Zaki, J. Modeling emotion in complex stories: The Stanford Emotional Narratives Dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.H.; Xie, T.; Byrne, S.; Chang, L.J. Py-Feat: Python Facial Expression Analysis Toolbox. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03509. [Google Scholar]





| AU | FACS Name | |
|---|---|---|
| AU1 | Inner brow raiser |  |
| AU2 | Outer brow raiser |  |
| AU4 | Brow lowerer |  |
| AU5 | Upper lid raiser |  |
| AU6 | Cheek raiser |  |
| AU7 | Lid tightener |  |
| AU9 | Nose wrinkler |  |
| AU10 | Upper lip raiser |  |
| AU12 | Lip corner puller |  |
| AU14 | Dimpler |  |
| AU15 | Lip corner depressor |  |
| AU17 | Chin raiser |  |
| AU20 | Lip stretcher |  |
| AU23 | Lip tightener |  |
| AU24 | Lip pressor |  |
| AU25 | Lips part |  |
| AU26 | Jaw drop |  |
| OpenFace/In-the-Wild | OpenFace/Posed | OpenFace/Conversation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU | CE-CLM | CE-CLM_s | CLNF | CLNF_s | CE-CLM | CE-CLM_s | CLNF | CLNF_s | CE-CLM | CE-CLM_s | CLNF | CLNF_s |
| AU1 | 0.748 | 0.690 | 0.696 | 0.632 | 0.791 | 0.847 | 0.786 | 0.841 | 0.782 | 0.653 | 0.763 | 0.647 |
| AU2 | 0.648 | 0.698 | 0.632 | 0.720 | 0.689 | 0.911 | 0.702 | 0.912 | 0.637 | 0.665 | 0.625 | 0.643 |
| AU4 | 0.778 | 0.780 | 0.743 | 0.743 | 0.917 | 0.917 | 0.920 | 0.920 | 0.597 | 0.596 | 0.578 | 0.578 |
| AU5 | - | - | - | - | 0.688 | 0.946 | 0.680 | 0.937 | 0.762 | 0.741 | 0.761 | 0.715 |
| AU6 | 0.769 | 0.770 | 0.759 | 0.759 | 0.976 | 0.976 | 0.981 | 0.981 | 0.879 | 0.878 | 0.870 | 0.870 |
| AU7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.687 | 0.687 | 0.685 | 0.685 |
| AU9 | - | - | - | - | 0.775 | 0.984 | 0.767 | 0.988 | 0.671 | 0.745 | 0.663 | 0.743 |
| AU10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.834 | 0.833 | 0.824 | 0.824 |
| AU12 | 0.874 | 0.875 | 0.831 | 0.831 | 0.894 | 0.894 | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.933 | 0.932 | 0.927 | 0.927 |
| AU14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.654 | 0.655 | 0.627 | 0.627 |
| AU15 | 0.803 | 0.723 | 0.600 | 0.688 | 0.756 | 0.945 | 0.757 | 0.943 | 0.627 | 0.690 | 0.618 | 0.692 |
| AU17 | - | - | - | - | 0.817 | 0.867 | 0.853 | 0.869 | 0.712 | 0.652 | 0.710 | 0.641 |
| AU20 | 0.622 | 0.534 | 0.582 | 0.525 | 0.760 | 0.718 | 0.742 | 0.668 | - | - | - | - |
| AU23 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.544 | 0.563 | 0.547 | 0.558 |
| AU25 | 0.544 | 0.603 | 0.521 | 0.541 | 0.935 | 0.959 | 0.936 | 0.957 | - | - | - | - |
| AU26 | - | - | - | - | 0.736 | 0.722 | 0.759 | 0.757 | - | - | - | - |
| Mean | 0.723 | 0.709 | 0.670 | 0.680 | 0.811 | 0.891 | 0.816 | 0.890 | 0.717 | 0.715 | 0.708 | 0.704 |
| AFAR/In-the-Wild | AFAR/Posed | AFAR/Conversation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU | HOG | HOG_s | SIFT | SIFT_s | HOG | HOG_s | SIFT | SIFT_s | HOG | HOG_s | SIFT | SIFT_s |
| AU1 | 0.569 | 0.501 | 0.569 | 0.501 | 0.789 | 0.780 | 0.790 | 0.780 | 0.780 | 0.640 | 0.778 | 0.636 |
| AU2 | 0.521 | 0.524 | 0.523 | 0.523 | 0.756 | 0.833 | 0.756 | 0.834 | 0.713 | 0.616 | 0.717 | 0.608 |
| AU4 | 0.677 | 0.625 | 0.676 | 0.624 | 0.870 | 0.828 | 0.869 | 0.828 | 0.707 | 0.703 | 0.702 | 0.712 |
| AU6 | 0.663 | 0.666 | 0.662 | 0.666 | 0.919 | 0.949 | 0.919 | 0.949 | 0.829 | 0.810 | 0.841 | 0.846 |
| AU7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.744 | 0.735 | 0.745 | 0.757 |
| AU10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.824 | 0.843 | 0.846 | 0.873 |
| AU12 | 0.706 | 0.743 | 0.706 | 0.743 | 0.823 | 0.851 | 0.823 | 0.850 | 0.832 | 0.838 | 0.857 | 0.863 |
| AU14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.581 | 0.561 | 0.612 | 0.605 |
| AU15 | 0.761 | 0.722 | 0.760 | 0.722 | 0.720 | 0.801 | 0.720 | 0.802 | 0.664 | 0.726 | 0.664 | 0.732 |
| AU17 | - | - | - | - | 0.675 | 0.776 | 0.676 | 0.776 | 0.641 | 0.612 | 0.633 | 0.648 |
| AU23 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.646 | 0.620 | 0.662 | 0.643 |
| AU24 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.696 | 0.707 | 0.709 | 0.764 |
| Mean | 0.649 | 0.630 | 0.649 | 0.630 | 0.793 | 0.831 | 0.793 | 0.831 | 0.721 | 0.701 | 0.730 | 0.724 |
| FaceReader/In-the-Wild | FaceReader/Posed | FaceReader/Conversation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU | Default | Calibration | Default | Calibration | Default | Calibration |
| AU1 | 0.656 | 0.656 | 0.533 | 0.533 | 0.649 | 0.649 |
| AU2 | 0.746 | 0.746 | 0.513 | 0.513 | 0.606 | 0.606 |
| AU4 | 0.663 | 0.663 | 0.549 | 0.549 | 0.551 | 0.551 |
| AU5 | - | - | 0.596 | 0.596 | 0.645 | 0.645 |
| AU6 | 0.579 | 0.579 | 0.561 | 0.561 | 0.747 | 0.747 |
| AU7 | - | - | - | - | 0.507 | 0.507 |
| AU9 | - | - | 0.504 | 0.504 | 0.510 | 0.510 |
| AU10 | - | - | - | - | 0.506 | 0.506 |
| AU12 | 0.800 | 0.800 | 0.583 | 0.583 | 0.877 | 0.877 |
| AU14 | - | - | - | - | 0.513 | 0.513 |
| AU15 | 0.607 | 0.607 | 0.639 | 0.639 | 0.505 | 0.505 |
| AU17 | - | - | 0.530 | 0.530 | 0.508 | 0.508 |
| AU20 | 0.579 | 0.579 | 0.498 | 0.498 | - | - |
| AU23 | - | - | - | - | 0.500 | 0.500 |
| AU24 | - | - | - | - | 0.506 | 0.506 |
| AU25 | 0.711 | 0.711 | 0.592 | 0.592 | - | - |
| AU26 | - | - | 0.501 | 0.501 | - | - |
| Mean | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.550 | 0.550 | 0.581 | 0.581 |
| System | In-the-Wild | Posed | Conversational | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FaceReader | C | D | D | This system also can estimate emotional states (emotion category, valence and arousal). |
| OpenFace | B | A | B | For analyzing posed facial data, static mode is better than dynamic mode. |
| AFAR toolbox | C | B | B | For analyzing posed facial data, static mode is better than dynamic mode. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Namba, S.; Sato, W.; Osumi, M.; Shimokawa, K. Assessing Automated Facial Action Unit Detection Systems for Analyzing Cross-Domain Facial Expression Databases. Sensors 2021, 21, 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124222
Namba S, Sato W, Osumi M, Shimokawa K. Assessing Automated Facial Action Unit Detection Systems for Analyzing Cross-Domain Facial Expression Databases. Sensors. 2021; 21(12):4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124222
Chicago/Turabian StyleNamba, Shushi, Wataru Sato, Masaki Osumi, and Koh Shimokawa. 2021. "Assessing Automated Facial Action Unit Detection Systems for Analyzing Cross-Domain Facial Expression Databases" Sensors 21, no. 12: 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124222
APA StyleNamba, S., Sato, W., Osumi, M., & Shimokawa, K. (2021). Assessing Automated Facial Action Unit Detection Systems for Analyzing Cross-Domain Facial Expression Databases. Sensors, 21(12), 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124222







