A Data-Driven Long Time-Series Electrical Line Trip Fault Prediction Method Using an Improved Stacked-Informer Network
Abstract
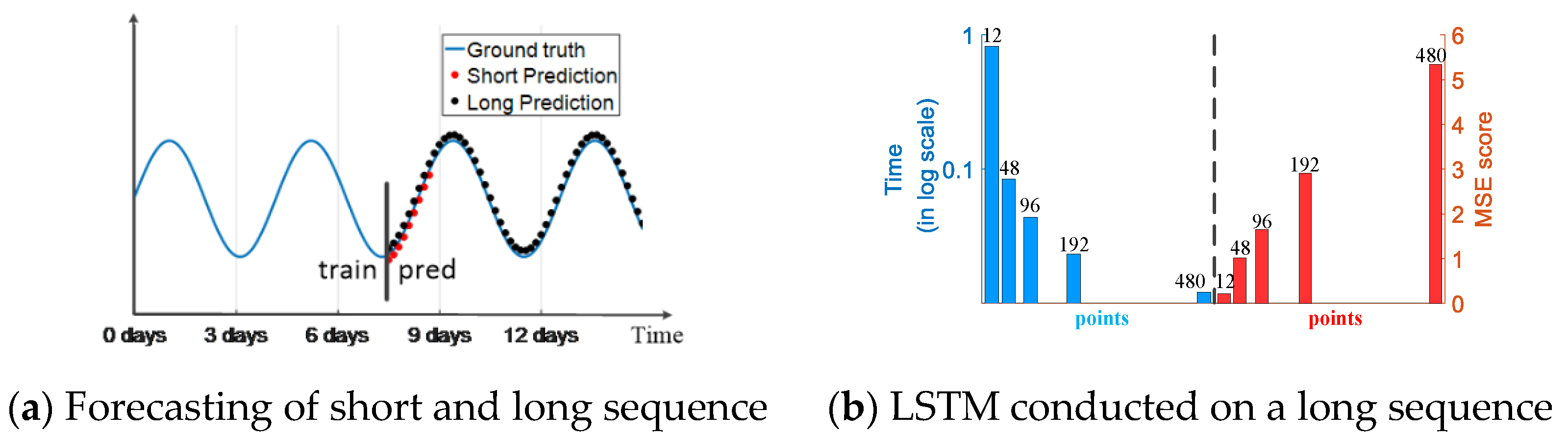
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The long time-series line trip fault prediction method using the improved stacked-Informer network is adopted; it exploits more comprehensive temporal information of long sequence input measurement data, includes normal and abnormal current and voltage data of power lines, and then predicts the short sequence output fault. This method achieves a superior generalization performance.
- (2)
- The strategy of gradient centralization (GC) technology is introduced and embedded into the optimizer, replacing the original Adam optimizer usually used in the DNN model for a GC+Adam optimization. GC can be viewed as a projected gradient descent method with a constrained loss function; it operates directly on gradients by centralizing the gradient vectors in order to have zero means. This technology improves the training time of the long sequence time-series fault prediction markedly and improves the accuracy and efficiency of the presented methodology.
- (3)
- Real measurement long sequence data is collected by electrical sensors at a wind solar hybrid power station, which is located in Zhangjiakou City, China. The recorded long sequence data is divided into two datasets, and both of them are conducted on the proposed methodology in order to prove a superior performance in real-scenario application.
2. Related Work
3. The Proposed Methodology of Long Sequence Time-Series Fault Prediction
3.1. Architecture
3.2. The Improved GC + Adam Optimizer
4. Evaluated Experiments
4.1. Data Description and Experimental Setting
4.2. Different Optimizer Validation
4.3. Comparative Results of the Presented Method and the Original Informer Network
4.4. Comparative Result of the Different Lengths of the Prediction Output Sequence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, M.Q.; Bao, Z.J. Data-based Line Trip Fault Prediction in Power Systems using LSTM Networks and SVM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 7675–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Qian, G.J.; Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Dou, X.H.; Pei, H.W. A New Trip Fault of Transmission Line Caused by Lightning Striking to Ground Wire and Conductor Simultaneously. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 701–702, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Kim, H.S. A Research on Dynamic Service Function Chaining based on Reinforcement Learning using Resource Usage. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Milan, Italy, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 582–586. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, M.N.; Werneck, M.M. Optical Voltage Transformer Based on FBG-PZT for Power Quality Measurement. Sensors 2021, 21, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K. A Condition-based Failure-Prediction and Processing-Scheme for Preventive Maintenance. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2003, 52, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wen, F.; Ledwich, G.; Liao, Z.; He, X.; Liang, J. An Analytic Model for Fault Diagnosis in Power Systems Considering Malfunctions of Protective Relays and Circuit Breakers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z. Power System Fault Reasoning and Diagnosis based on the Improved Temporal Constraint Network. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hink, R.C.B.; Beaver, J.M.; Buckner, M.A.; Morris, T.; Adhikari, U.; Pan, S. Machine Learning for Power System Disturbance and Cyber-attack Discrimination. In Proceedings of the 2014 7th International symposium on resilient control systems (ISRCS), Denver, CO, USA, 19–21 August 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Sinha, A. Intelligent Fault Analysis in Electrical Power Grids. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 29th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 November 2017; pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Andresen, C.A.; Torsæter, B.N.; Haugdal, H.; Uhlen, K. Fault Detection and Prediction in Smart Grids. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th International Workshop on Applied Measurements for Power Systems (AMPS), Bologna, Italy, 26–28 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jalil, B.; Leone, G.R.; Martinelli, M.; Moroni, D.; Pascali, M.A.; Berton, A. Fault Detection in Power Equipment via An Unmanned Aerial Systems using Multi Modal Data. Sensors 2019, 19, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al Mhdawi, A.K.; Al-Raweshidy, H.S. Smart Optimization of Fault Diagnosis in Electrical Grid Using Distributed Software-Defined IoT System. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 14, 2780–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, V.; Michalowska, K.; Andresen, C.; Torsaeter, B. Incipient Fault Prediction in Power Quality Monitoring. In Proceedings of the CIRED 2019, Madrid, Spain, 3–6 June 2019; Volume 6, pp. 1535–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Jinglong, Z.; Changzhan, H.; Xiangming, W.; Jiakun, A.; Chunguang, H.; Jinglin, H. Research on Fault Prediction of Distribution Network Based on Large Data. In Proceedings of the 2017 3th International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Engineering (ICMITE 2017), Chengdu, China, 16–17 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Veljko, M.T.; Predrag, R.T.; Zeljko, M.D. Expert System for Fault Detection and Isolation of Coal-shortage in Thermal Power Plants. In Proceedings of the 2010 Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (SysTol), Nice, France, 6–8 October 2010; pp. 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.-Q.; He, C.-F.; Cai, Z.-Q.; Wen, L.; Ren, T. Track Circuit Fault Prediction Method based on Grey Theory and Expert System. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 58, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Polavarapu, V.A.; Kumar, V.; Aruna, E.; Sumathi, V. Anomaly Detection in Smart Grid using Rough Set Theory and K Cross Validation. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Circuits, Power and Computing Technologies [ICCPCT-2014], Nagercoil, India, 20–21 March 2014; pp. 479–483. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; He, L.M.; Lin, J.L. Bayesian Networks-based Approach for Power Systems Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 634–639. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Monti, A.; Ponci, F. Fault Detection and Classification in Medium Voltage DC Ship Board Power Systems with Wavelets and Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2651–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zou, L.; Li, R.; Wang, S.; Zou, J. A New Controlled Fault Limiting Algorithm for Vacuum Fault Current Limiter based on Fault Current Zero-crossing Prediction Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Electric Power Equipment-Switching Technology (ICEPE-ST), Xi’an, China, 22–25 October 2017; pp. 519–522. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gu, M.; Xu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Wang, W.; Cheng, M. Fault-Tolerant Control of Common Electrical Faults in Dual Three-Phase PMSM Drives Fed by T-Type Three-Level Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 57, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.P.; Ryan, H.M.; Tindle, J. Power system fault prediction using artificial neural networks. In Progress in Neural Information Processing. SET.; Amari, S.-I., Xu, L., Chan, L.-W., King, I., Leung, K.-S., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 1996; pp. 1181–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Moustapha, A.I.; Selmic, R.R. Wireless Sensor Network Modeling using Modified Recurrent Neural Networks: Application to Fault Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Guo, D.; Liu, T.-Y. Health Status Assessment and Failure Prediction for Hard Drives with Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 65, 3502–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Fan, H.; Blasch, E.; Ling, H. Combining Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks for Human Skin Detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yu, K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF Models for Sequence Tagging. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.01991. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.07436. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, H.; Huang, J.; Hua, X.; Zhang, L. Gradient Centralization: A New Optimization Technique for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2020), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 635–652. [Google Scholar]








| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Length of input sequence | 200 |
| Length of predicting short sequence | 50 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Dropout rate | 0.05 |
| Decay | 0.001 |
| Datasets | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset 1 | 885.26 | 538.86 | 539.23 | 384.85 |
| Dataset 2 | 381.52 | 267.26 | 572.89 | 496.34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, L.; Li, R.; Jiang, B. A Data-Driven Long Time-Series Electrical Line Trip Fault Prediction Method Using an Improved Stacked-Informer Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134466
Guo L, Li R, Jiang B. A Data-Driven Long Time-Series Electrical Line Trip Fault Prediction Method Using an Improved Stacked-Informer Network. Sensors. 2021; 21(13):4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134466
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Li, Runze Li, and Bin Jiang. 2021. "A Data-Driven Long Time-Series Electrical Line Trip Fault Prediction Method Using an Improved Stacked-Informer Network" Sensors 21, no. 13: 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134466
APA StyleGuo, L., Li, R., & Jiang, B. (2021). A Data-Driven Long Time-Series Electrical Line Trip Fault Prediction Method Using an Improved Stacked-Informer Network. Sensors, 21(13), 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134466







