Classification Method of Uniform Circular Array Radar Ground Clutter Data Based on Chaotic Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Firstly, the characteristics of ground clutter data measured in different UCA ground-based radar scenarios are studied, and the correlation, non-stationary, and statistical characteristics of the range-Doppler domain of clutter data are analyzed.
- Secondly, a GA clustering method based on chaos theory is proposed to overcome standard GA’s defects, such as premature convergence and weak local optimization ability, and complete the data classification and recognition according to the feature factors extracted from the measured clutter data.
2. Materials and Methods
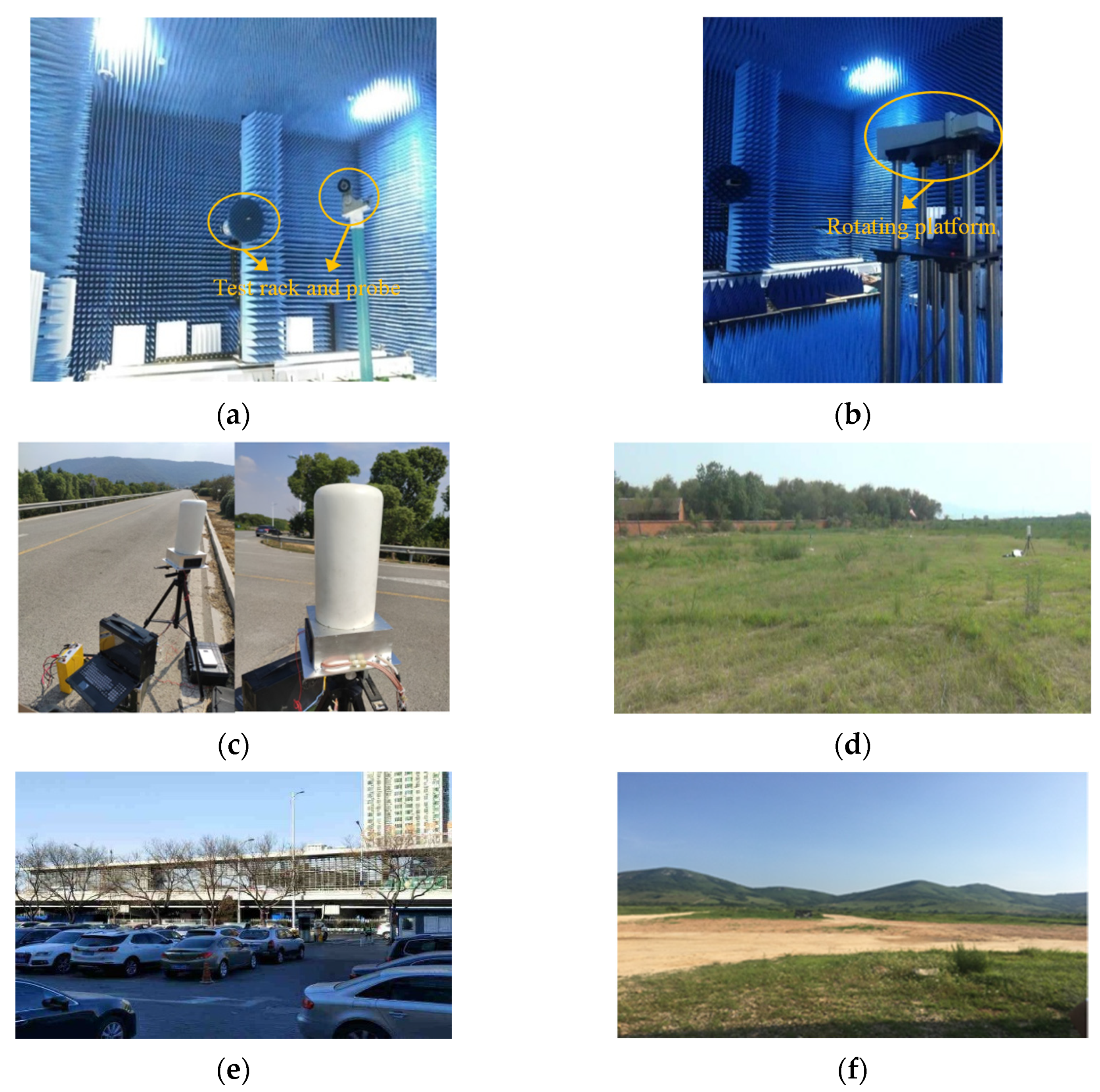
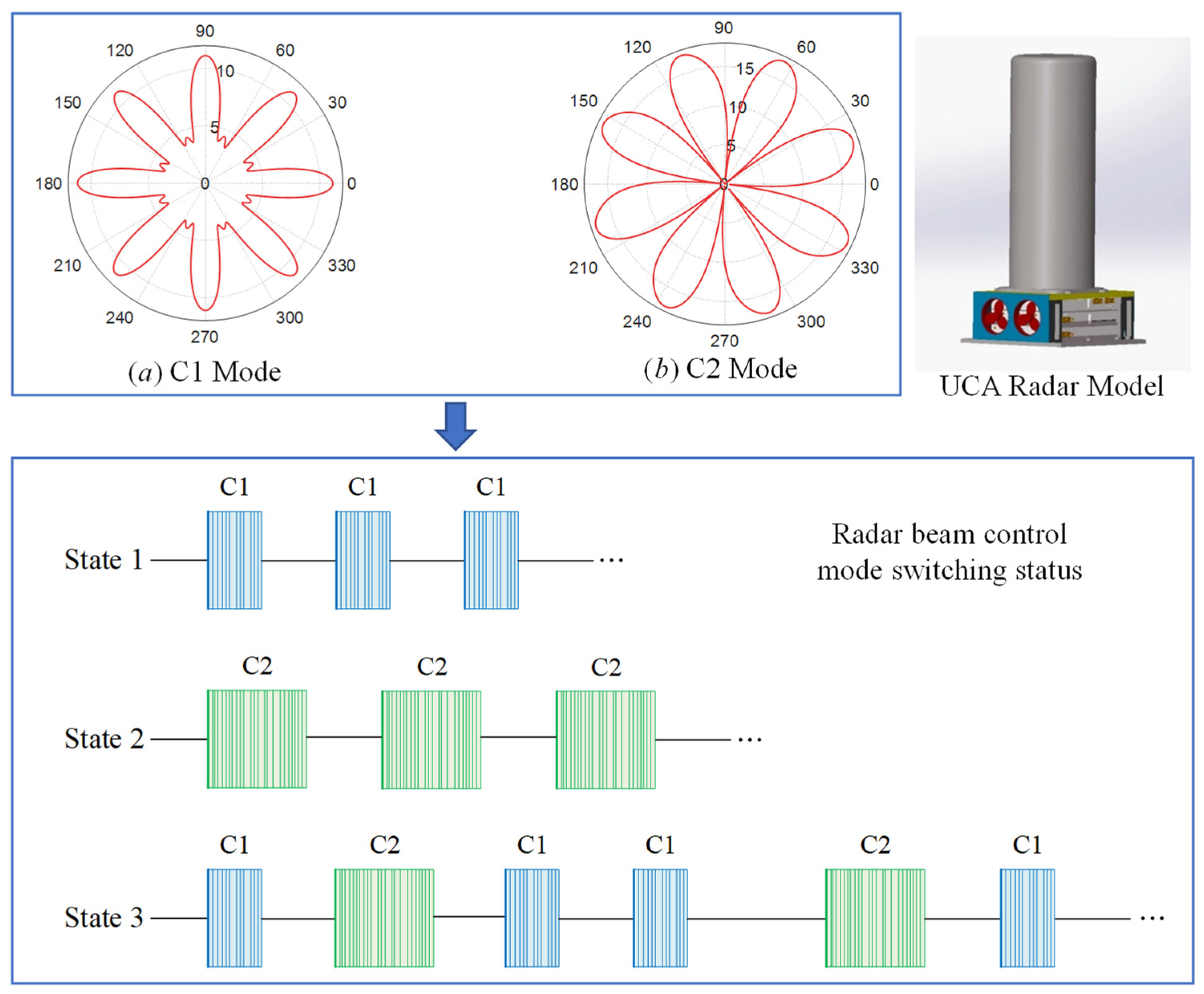
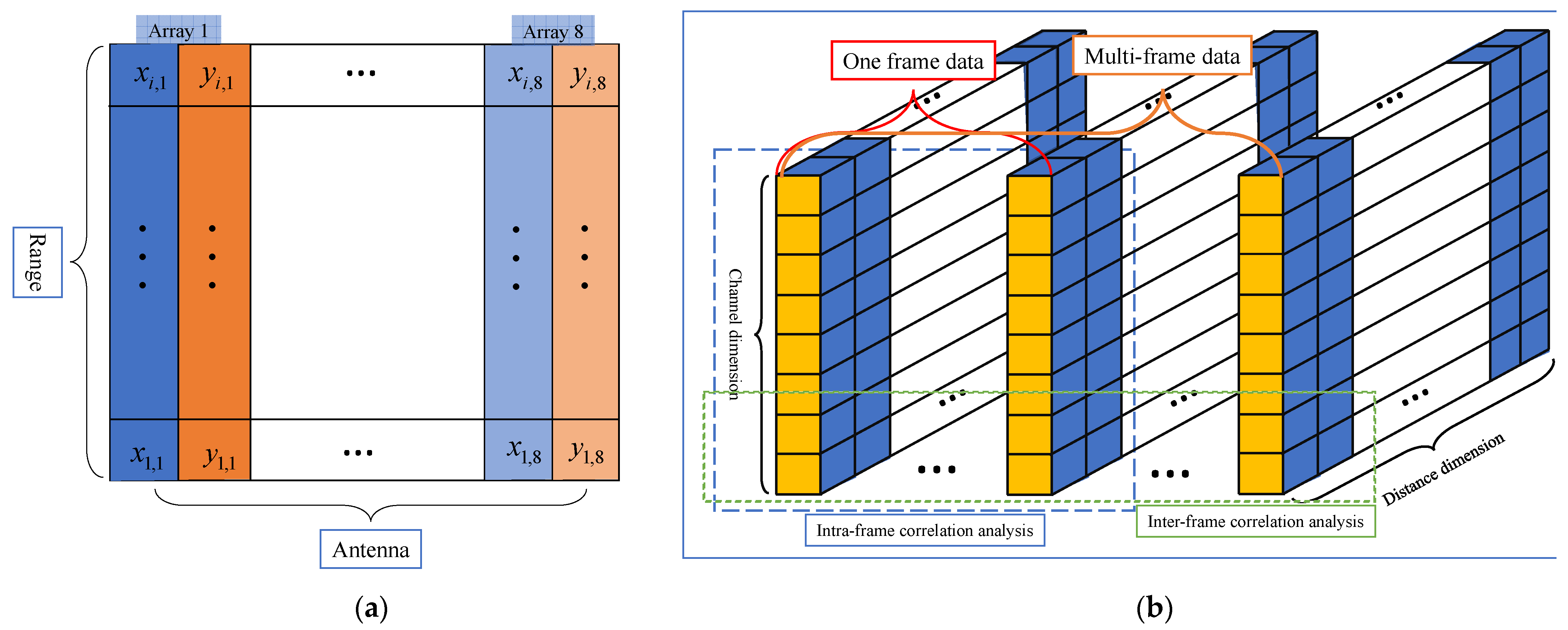
2.1. Uniform Circular Array Radar and Experiment Sites
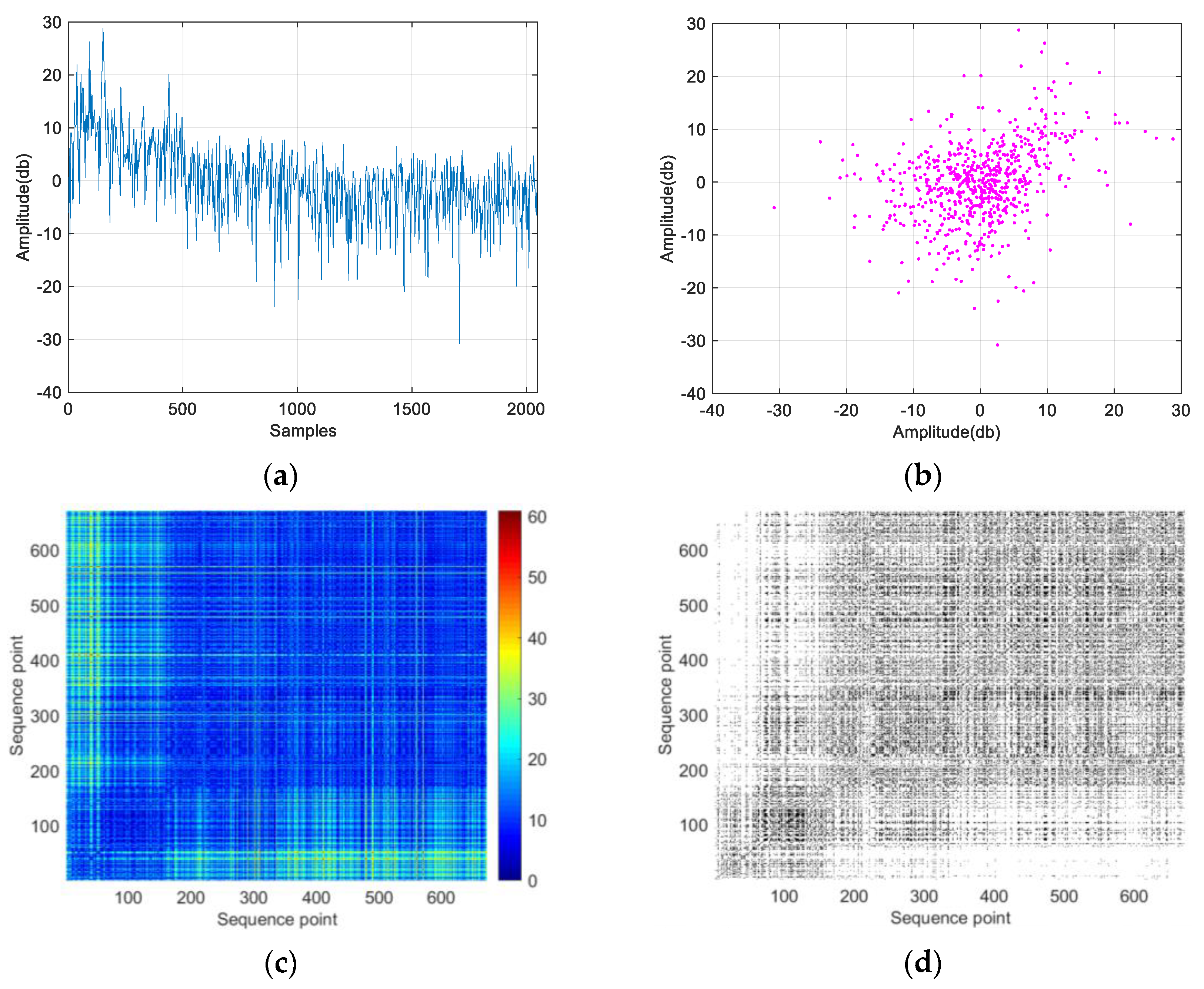
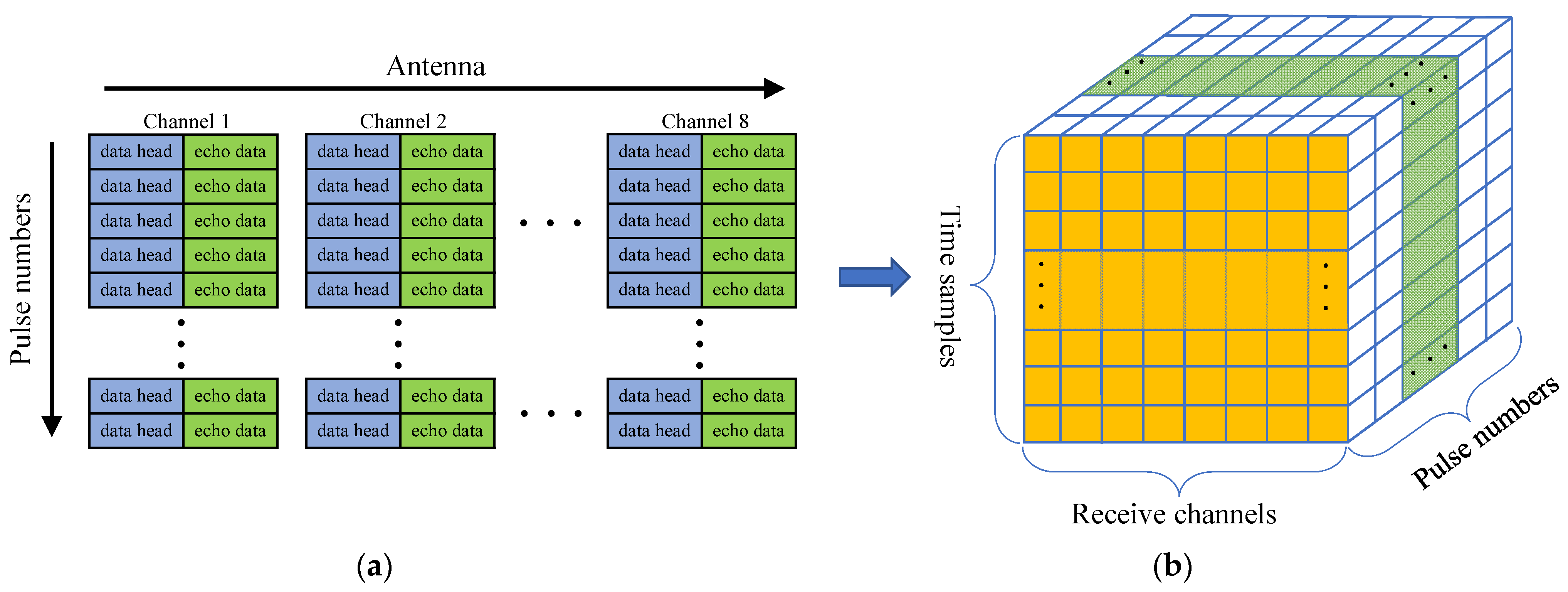
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
2.3. Characteristic Factors
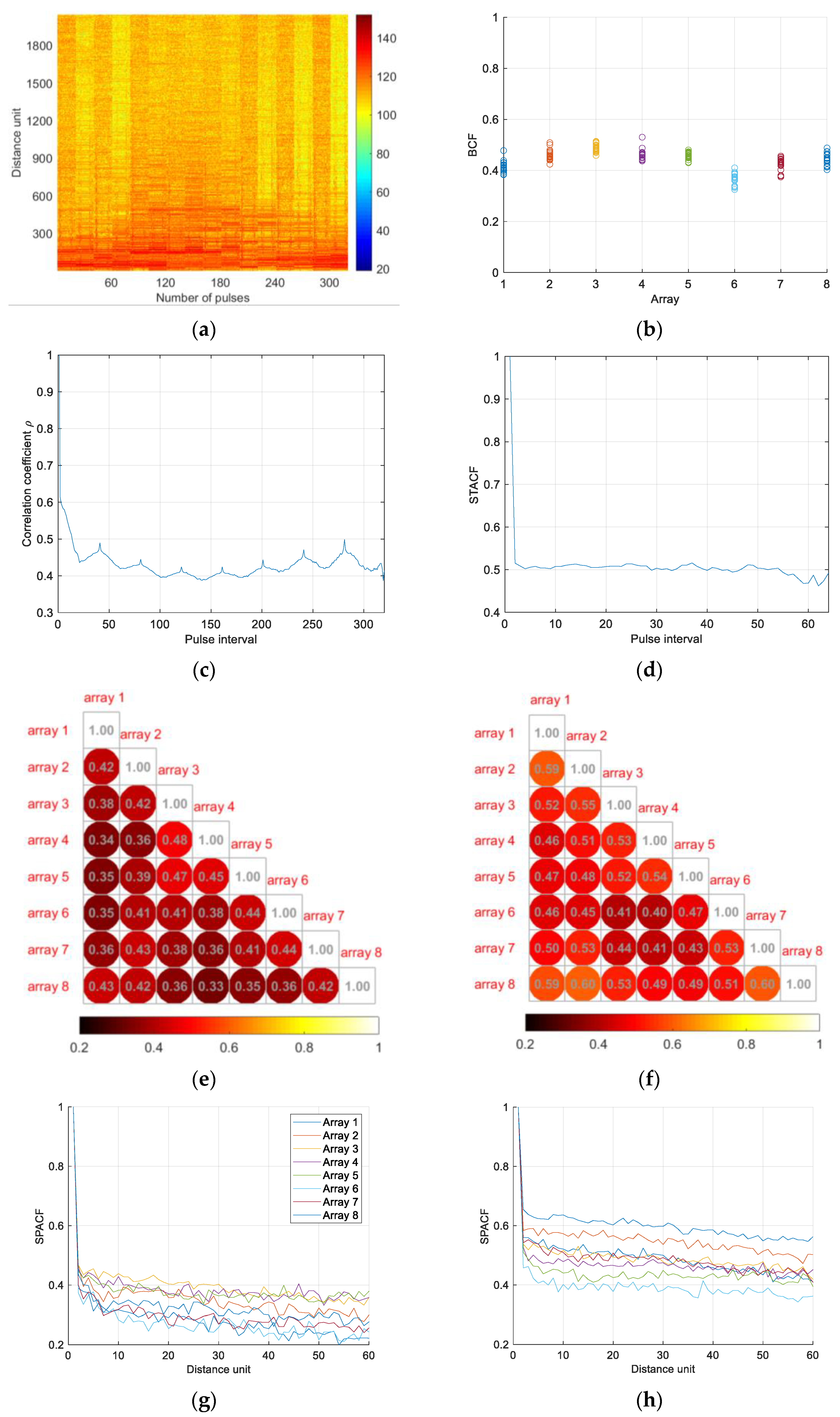
2.3.1. Correlation Analysis of Ground Clutter Data
Radar Beam Correlation
Azimuth Correlation
Range Correlation
2.3.2. Recursive Graph
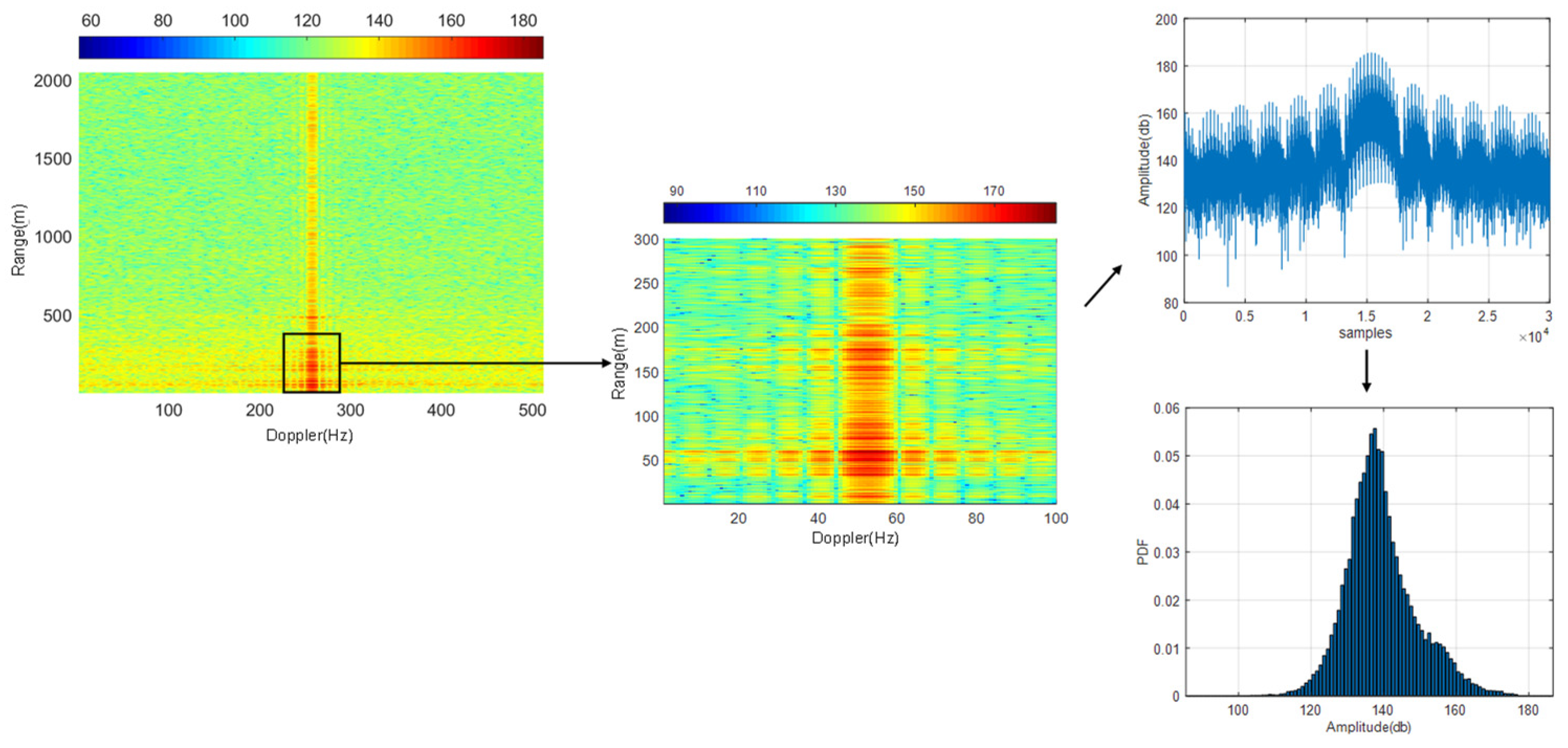
2.3.3. The Range-Doppler Maps
Feature Factor Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Clustering Algorithms
2.4.1. Standard Genetic Algorithm Clustering
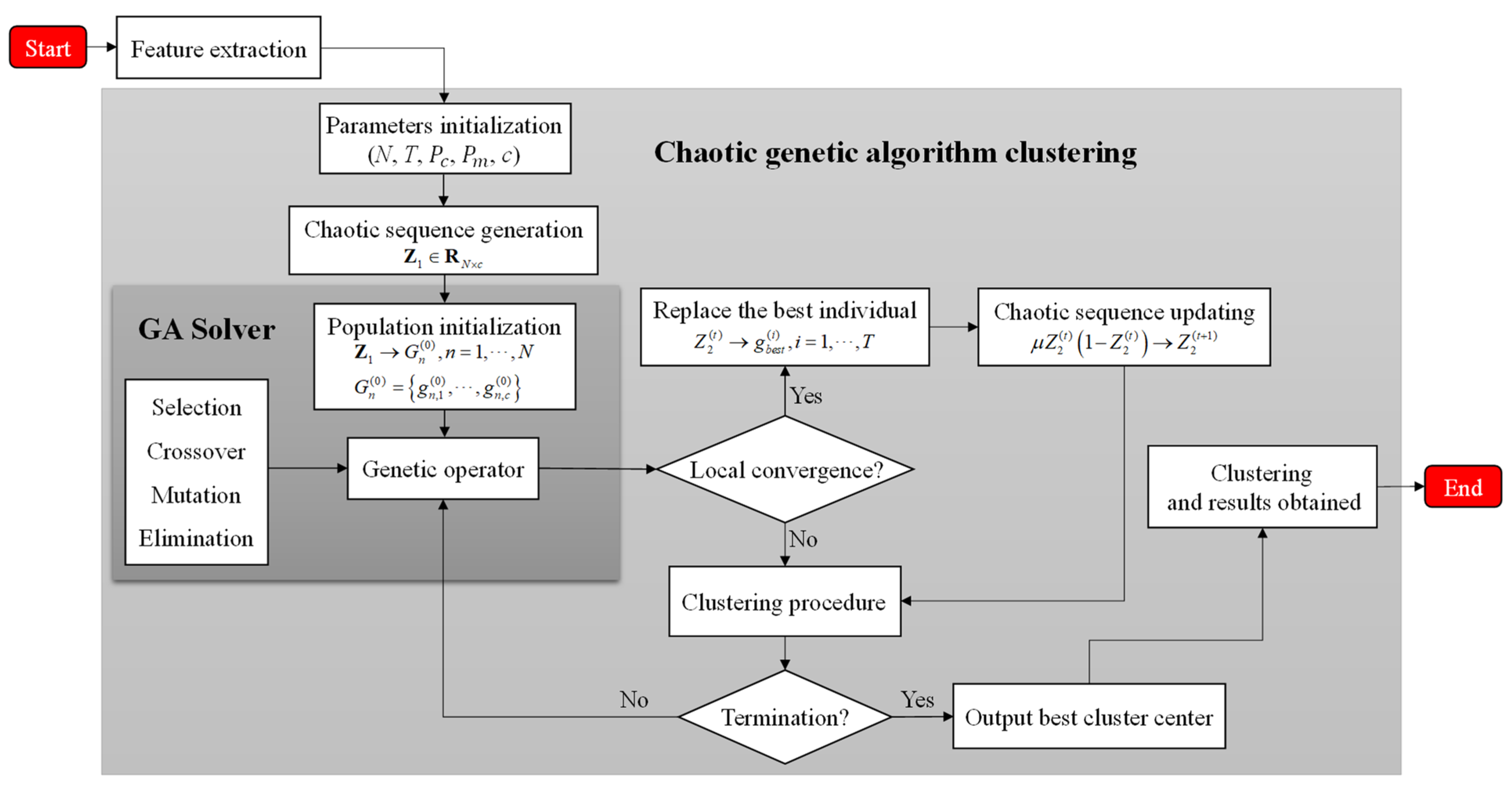
2.4.2. Chaotic Genetic Algorithm Clustering
3. Results
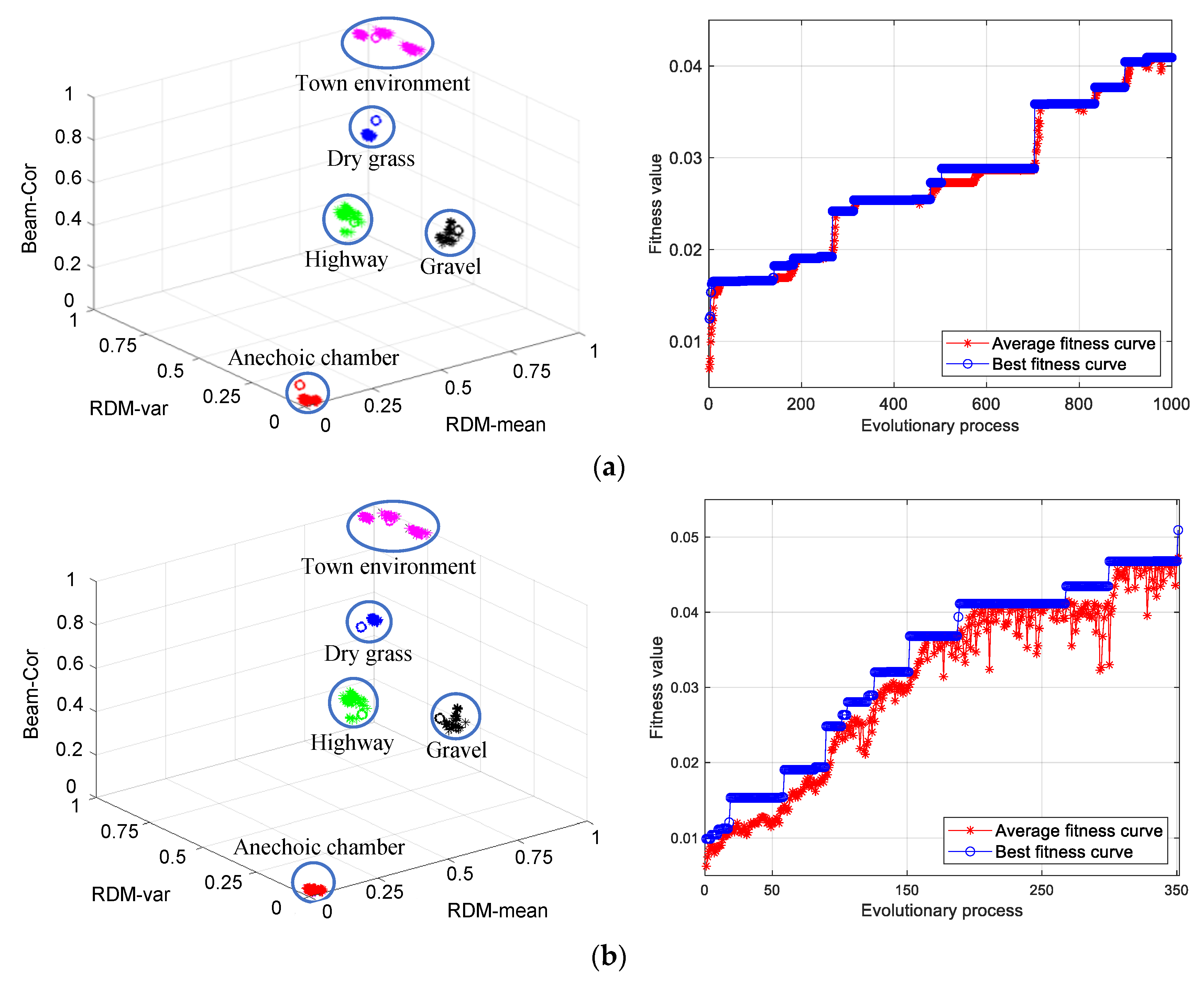
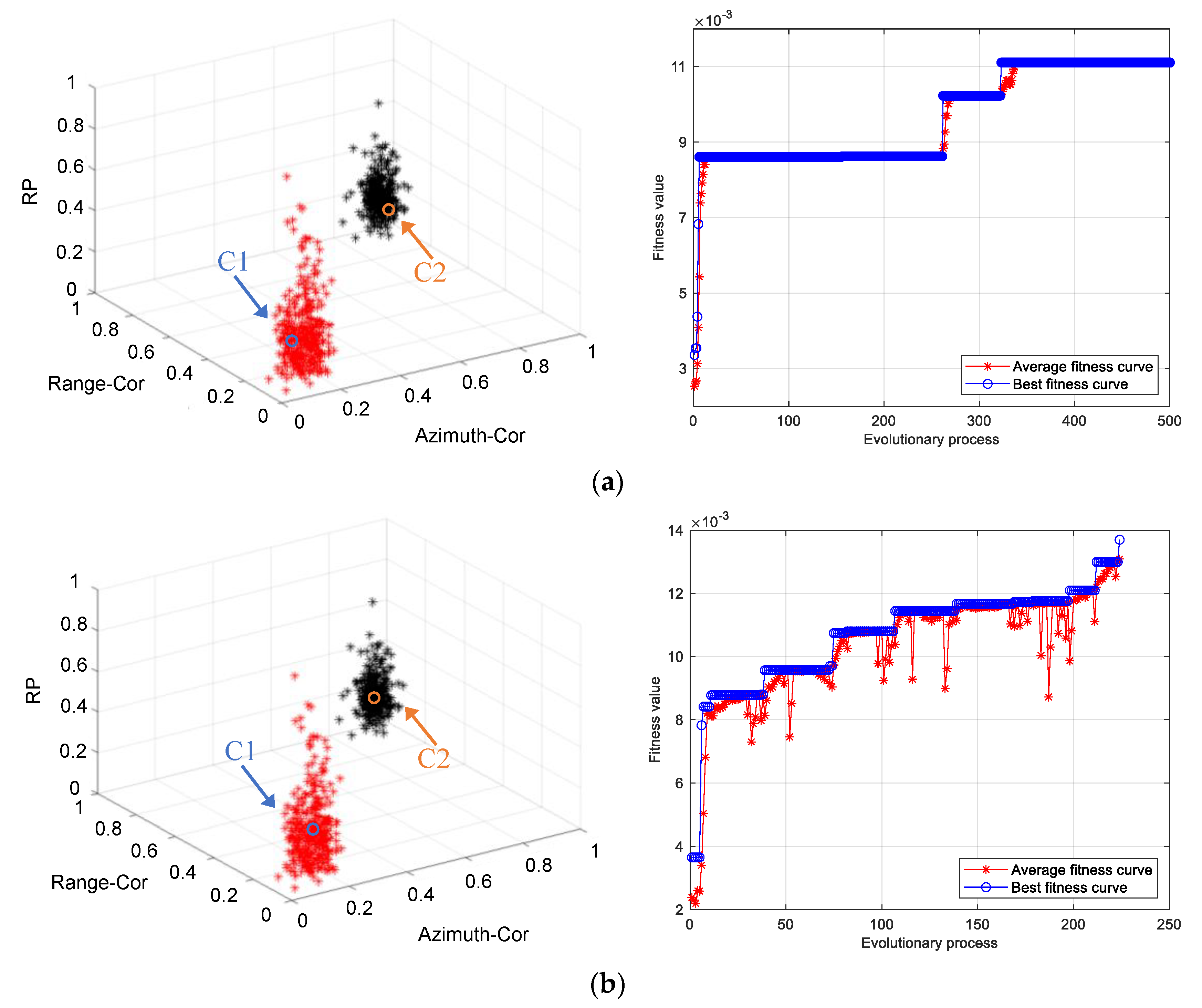
3.1. Clustering of Clutter Data in Different Scene
- It has a faster convergence speed, which can save 34.60% of the time.
- It has a higher classification accuracy, and the average criterion function value is reduced by 42.82%.
3.2. Clutter Data Clustering of Two-Beam Control Modes in The Same Scene
4. Conclusions
- Compared with SGA clustering, the clustering center obtained by chaotic SGA clustering is more consistent with the classification and division of actual characteristic factors. From the scene data, the criterion function values of SGA and chaotic SGA clustering corresponding to scene classification are 38.03 and 21.74, respectively, and the time consumed is 55.57 and 36.34 s, respectively. From the beam control mode of data classification, the criterion functions are 93.99 and 74.45, respectively, and the convergence speeds are 17.47 and 10.01 s, respectively.
- Chaotic SGA clustering has high local search ability and global searchability, realizing the effective classification of data samples.
- The effective classification and analysis of ground clutter data can improve UCA radar adaptability to clutter environments to enhance target detection performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chen, R.; Yang, W.; Xu, H.; Li, J. A 2-D FFT-based transceiver architecture for OAM-OFDM systems with UCA antennas. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5481–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, T.; Wang, C. Two-Stage Fast DOA Estimation Based on Directional Antennas in Conformal Uniform Circular Array. Sensors 2021, 21, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Feng, W.; Jin, Y. Time–Frequency-Analysis-Based Blind Modulation Classification for Multiple-Antenna Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Fu, L.; Chen, K.; Boateng, C.D.; Ge, S. Adaptive ground clutter reduction in ground-penetrating radar data based on principal component analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3271–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont-Smith, T.; Waseda, T.; Rheem, C.K. Measurements of the Doppler spectra of breaking waves. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2007, 1, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont-Smith, T.; Mitomi, M.; Kawamura, T.; Waseda, T. Electromagnetic scattering from wind blown waves and ripples modulated by longer waves under laboratory conditions. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2010, 4, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S. The effects of covariance matrix mismatch on adaptive CFAR performance. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 9–12 September 2013; pp. 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S.; Bakker, R.; Currie, B.W. Uncovering nonlinear dynamics-the case study of sea clutter. Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 860–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Kay, S.; Cogun, F.; Raghavan, R.S. On detection of non-stationarity in radar signal processing. IEEE Radar Conf. 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, W.; Mao, H.; Dong, R. Clutter Suppression Approach for End-Fire Array Airborne Radar Based on Adaptive Segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147094–147105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S.; Li, X.B. Detection of signals in chaos. Proc. IEEE. 1995, 83, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, B. The fractal properties of sea clutter and their applications in maritime target detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Luo, F.; Li, M.; Hu, C.; Chen, S. Fractal properties of autoregressive spectrum and its application on weak target detection in sea clutter background. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhou, F.; Jia, L.; Hou, L. A new two parameter CFAR ship detector in Log-Normal clutter. IEEE Radar Conf. Radar Conf. 2017, 0195–0199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicen-Bueno, R.; Rosa-Zurera, M.; Jarabo-Amores, M.P.; de la Mata-Moya, D. Coherent detection of Swerling 0 targets in sea-ice Weibull-distributed clutter using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 3139–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.; Bocquet, S. The Pareto distribution for high grazing angle sea-clutter. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. IGARSS 2013, 4209–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, G.V. Noncoherent radar detection in correlated Pareto distributed clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 2628–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; De Maio, A.; Galdi, C. Statistical analysis of real clutter at different range resolutions. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.; Crisp, D.J.; Stacy, N.J. Analysis of the KK-distribution with medium grazing angle sea-clutter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2010, 4, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Chuang, L.Z.; Yang, Y.J.; Leu, L.G. The correlation analysis of ionospheric clutter and noise using SeaSonde HF radar. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2017 Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Azevedo Coste, C.; Nierat, M.-C.; Renaux, S.; Similowski, T.; Guiraud, D. Respiratory Monitoring Based on Tracheal Sounds: Continuous Time-Frequency Processing of the Phonospirogram Combined with Phonocardiogram-Derived Respiration. Sensors 2021, 21, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningbo, L.; Yanan, X.; Hao, D.; Yonghua, X.; Jian, G. High-dimensional feature extraction of sea clutter and target signal for intelligent maritime monitoring network. Comput. Commun. 2019, 147, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanes, Y.; Barbaresco, F.; Arnaudon, M.; Bigot, J. Non-supervised Machine Learning Algorithms for Radar Clutter High-Resolution Doppler Segmentation and Pathological Clutter Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Ulm, Germany, 26–28 June 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, D.; Smith, S. Creating a likelihood vector for ground moving targets in the exo-clutter region of airborne radar signals. In Proceedings of the 2012 Workshop on Sensor Data Fusion: Trends, Solutions, Applications (SDF), Bonn, Germany, 4–6 September 2012; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, J. X-Band Radar Cross-Section of Tandem Helicopter Based on Dynamic Analysis Approach. Sensors 2021, 21, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, S.P.; Wang, X.S.; Li, Y.Z. Non-coherent radar detection probability for correlated gamma fluctuating targets in k distributed clutter. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 3824–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Huang, Y.; Guan, J. Adaptive clutter suppression and detection algorithm for radar maneuvering target with high-order motions via sparse fractional ambiguity function. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Shi, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Novel polarimetric detector for target detection in heterogeneous clutter. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2016, 27, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Classification of Radar Clutter using the Maximum-Entropy Method. In Nonlinear Stochastic Problems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nederland, 1983; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Darzikolaei, M.A.; Ebrahimzade, A.; Gholami, E. Classification of radar clutters with artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI), Tehran, Iran, 5–6 November 2015; pp. 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, R. Intelligent suppression method for ionospheric clutter based on clutter cluster and greedy strategy. J. Radars China 2020, 9, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Guo, L.F.; Sima, W.X.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhao, L.J. Hierarchical Fuzzy-clustering Classification of Overvoltages in Power Systems Based on the Genetic Algorithm. Proc. CSEE 2010, 30, 119124. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, S.; Stegall, P.; Edwards, H.; Stirling, L.; Siu, H.C. Ablation Analysis to Select Wearable Sensors for Classifying Standing, Walking, and Running. Sensors 2021, 21, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarra, T.; Galang, M.G.K.; Ballesteros, F.C., Jr.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V. Instrumental Odour Monitoring System Classification Performance Optimization by Analysis of Different Pattern-Recognition and Feature Extraction Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongcui, H.; Fuding, X.; Jun, Y.; Yong, Z. A Method of Semi-supervised Classification for Hyperspectral Images Based on Spatial Information and Genetic Optimization. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2015, 10, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Wei, C.; Yang, Y. Force identification by using SVM and CPSO technique. In International Conference in Swarm Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Xiong, Y. Separation of the Sound Power Spectrum of Multiple Sources by Three-Dimensional Sound Intensity Decomposition. Sensors 2021, 21, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J.; Parmryd, I. Quantifying colocalization by correlation: The Pearson correlation coefficient is superior to the Mander’s overlap coefficient. Cytom. Part A 2010, 77, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, L. Analysis of real sea clutter based on meta recurrence plot. In Proceedings of the 2013 Ninth International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC), Shenyang, China, 23–25 July 2013; pp. 1108–1112. [Google Scholar]


| Feature Factors | Minimum | Maximum | Samples | Categories | Cluster Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDM-mean | 119.3997 | 139.1942 | 320 | 5 | Scene classification |
| RDM-variance | 55.9213 | 166.1000 | |||
| Radar beam correlation | 0.0973 | 0.6299 | |||
| Azimuth correlation | 0.3490 | 0.5171 | 640 | 5 | Beam steering mode classification |
| Range correlation | 0.1528 | 0.4497 | |||
| Recursive rate of recursive graph | 0.1693 | 0.5601 |
| Algorithm | Population Size | Number of Runs | Average Evolutionary Generation | Average of Convergence Rate (s) | Mean Value of Criterion Function | Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGA Clustering | 10 | 5 | 1000 | 29.85 | 49.52 | 20% |
| 15 | 5 | 1000 | 43.18 | 46.27 | 40% | |
| 20 | 5 | 959 | 54.52 | 35.23 | 40% | |
| 25 | 5 | 1000 | 69.99 | 30.53 | 60% | |
| 30 | 5 | 988 | 80.31 | 28.59 | 60% | |
| Chaotic SGA Clustering | 10 | 5 | 933 | 28.14 | 23.63 | 40% |
| 15 | 5 | 827 | 35.00 | 23.11 | 60% | |
| 20 | 5 | 643 | 35.72 | 20.65 | 80% | |
| 25 | 5 | 586 | 39.53 | 20.30 | 100% | |
| 30 | 5 | 530 | 43.31 | 21.03 | 100% |
| Algorithm | Population Size | Number of Runs | Average Evolutionary Generation | Average of Convergence Rate (s) | Mean Value of Criterion Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGA Clustering | 5 | 10 | 500 | 7.76 | 132.24 |
| 10 | 10 | 500 | 12.45 | 89.94 | |
| 15 | 10 | 500 | 17.60 | 86.76 | |
| 20 | 10 | 472 | 21.95 | 81.52 | |
| 25 | 10 | 475 | 27.57 | 79.49 | |
| Chaotic SGA Clustering | 5 | 10 | 340 | 4.91 | 77.82 |
| 10 | 10 | 281 | 7.29 | 73.42 | |
| 15 | 10 | 293 | 11.00 | 74.09 | |
| 20 | 10 | 275 | 13.00 | 73.69 | |
| 25 | 10 | 238 | 13.87 | 73.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Huang, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Rong, Y.; Huang, H.; Duan, T. Classification Method of Uniform Circular Array Radar Ground Clutter Data Based on Chaotic Genetic Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134596
Yang B, Huang M, Xie Y, Wang C, Rong Y, Huang H, Duan T. Classification Method of Uniform Circular Array Radar Ground Clutter Data Based on Chaotic Genetic Algorithm. Sensors. 2021; 21(13):4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134596
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bin, Mo Huang, Yao Xie, Changyuan Wang, Yingjiao Rong, Huihui Huang, and Tao Duan. 2021. "Classification Method of Uniform Circular Array Radar Ground Clutter Data Based on Chaotic Genetic Algorithm" Sensors 21, no. 13: 4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134596
APA StyleYang, B., Huang, M., Xie, Y., Wang, C., Rong, Y., Huang, H., & Duan, T. (2021). Classification Method of Uniform Circular Array Radar Ground Clutter Data Based on Chaotic Genetic Algorithm. Sensors, 21(13), 4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134596









