Small-Target Complex-Scene Detection Method Based on Information Interworking High-Resolution Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Studies
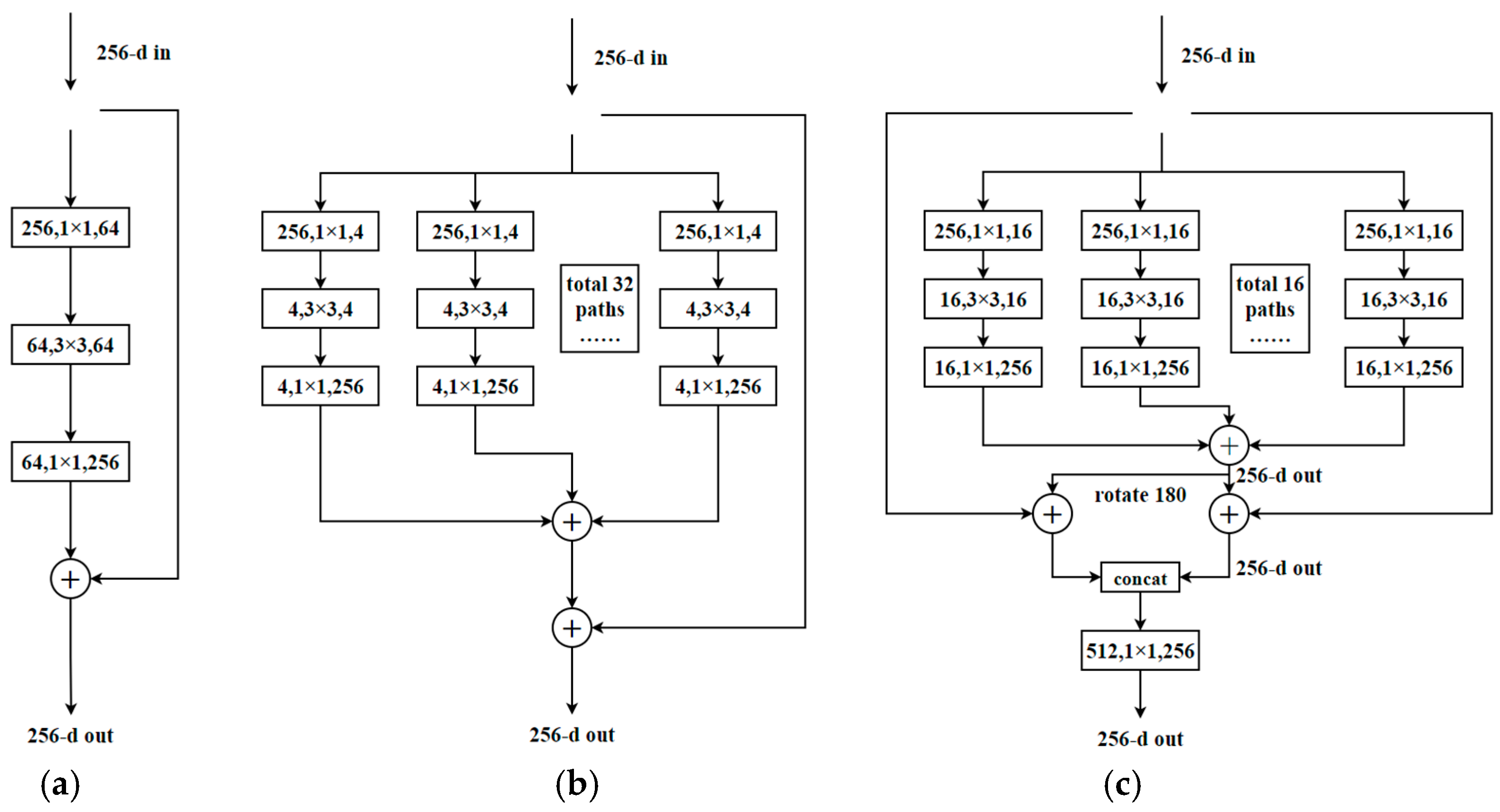
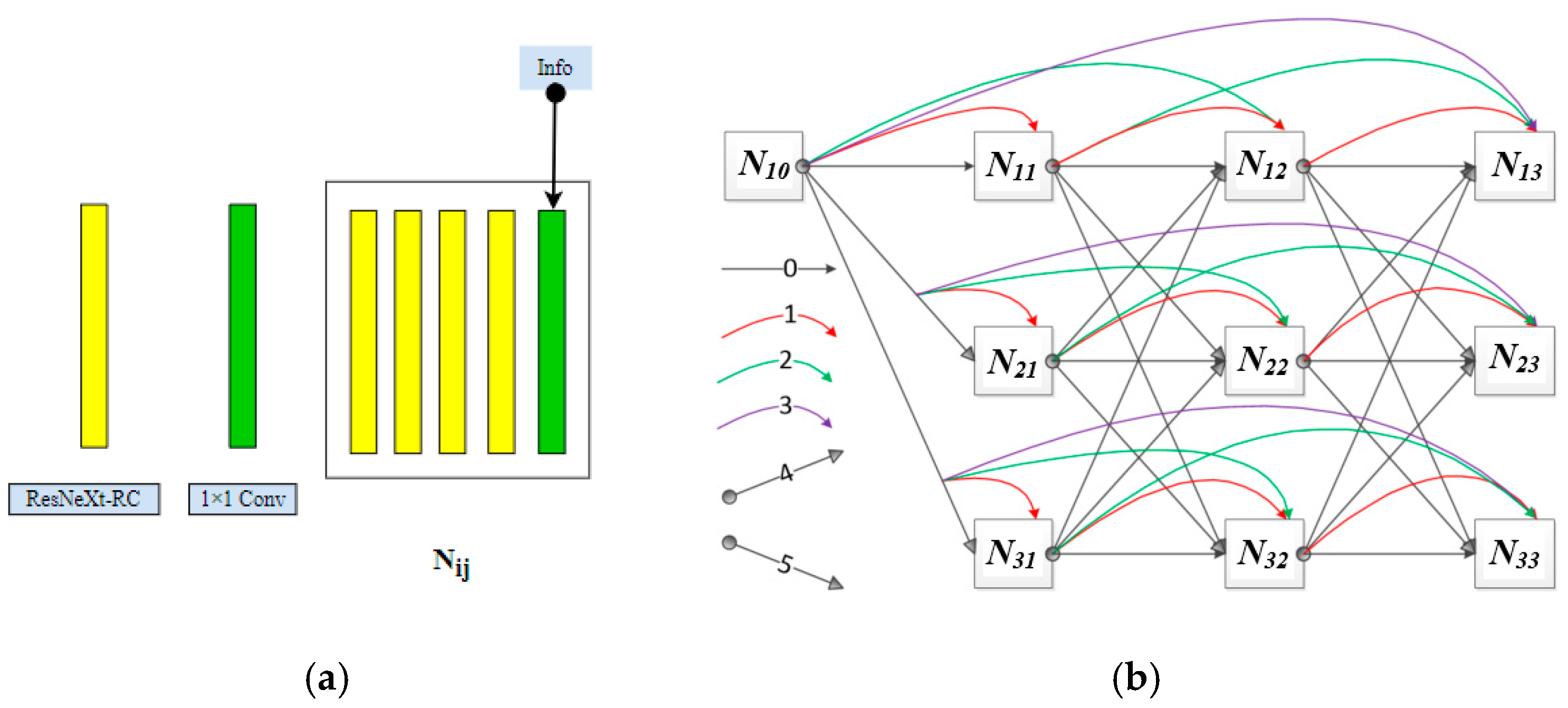
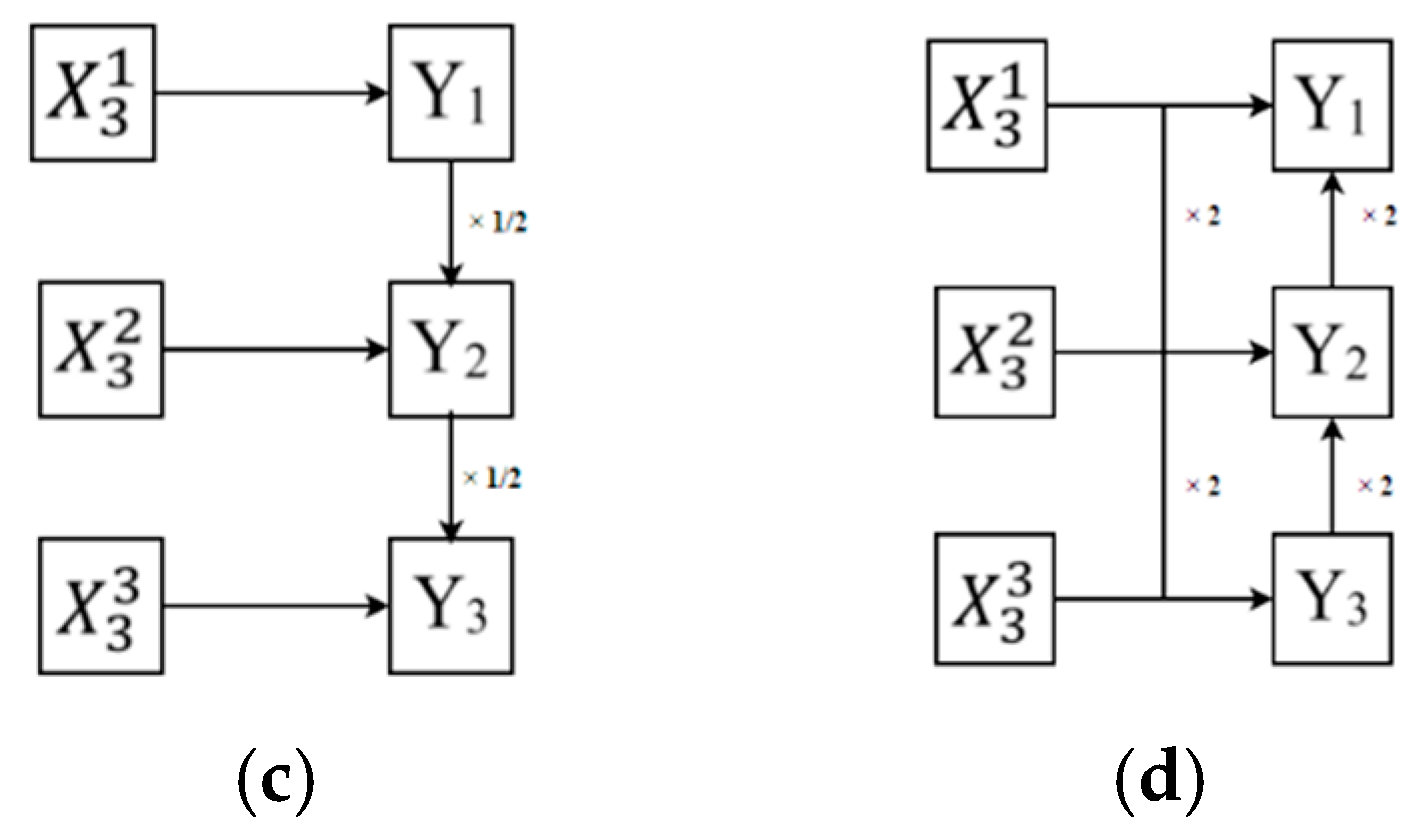
3. Proposed Model
→ N21 → N22 → N23 (sub-resolution)
→ N31 → N32 → N33 (low-resolution)
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.3. Model Training
4.1.4. Infer Metric
4.2. Ablation Study
4.2.1. Model
- (1)
- Classification weights trained on the ImageNet [27] dataset;
- (2)
- Detection weights trained on the PHF COCO (person and head from MSCOCO) dataset [28] consisting of person and head data extracted from the MSCOCO (2014) dataset;
- (3)
- Detection weights trained on 81 categories of the MSCOCO (2014) dataset.
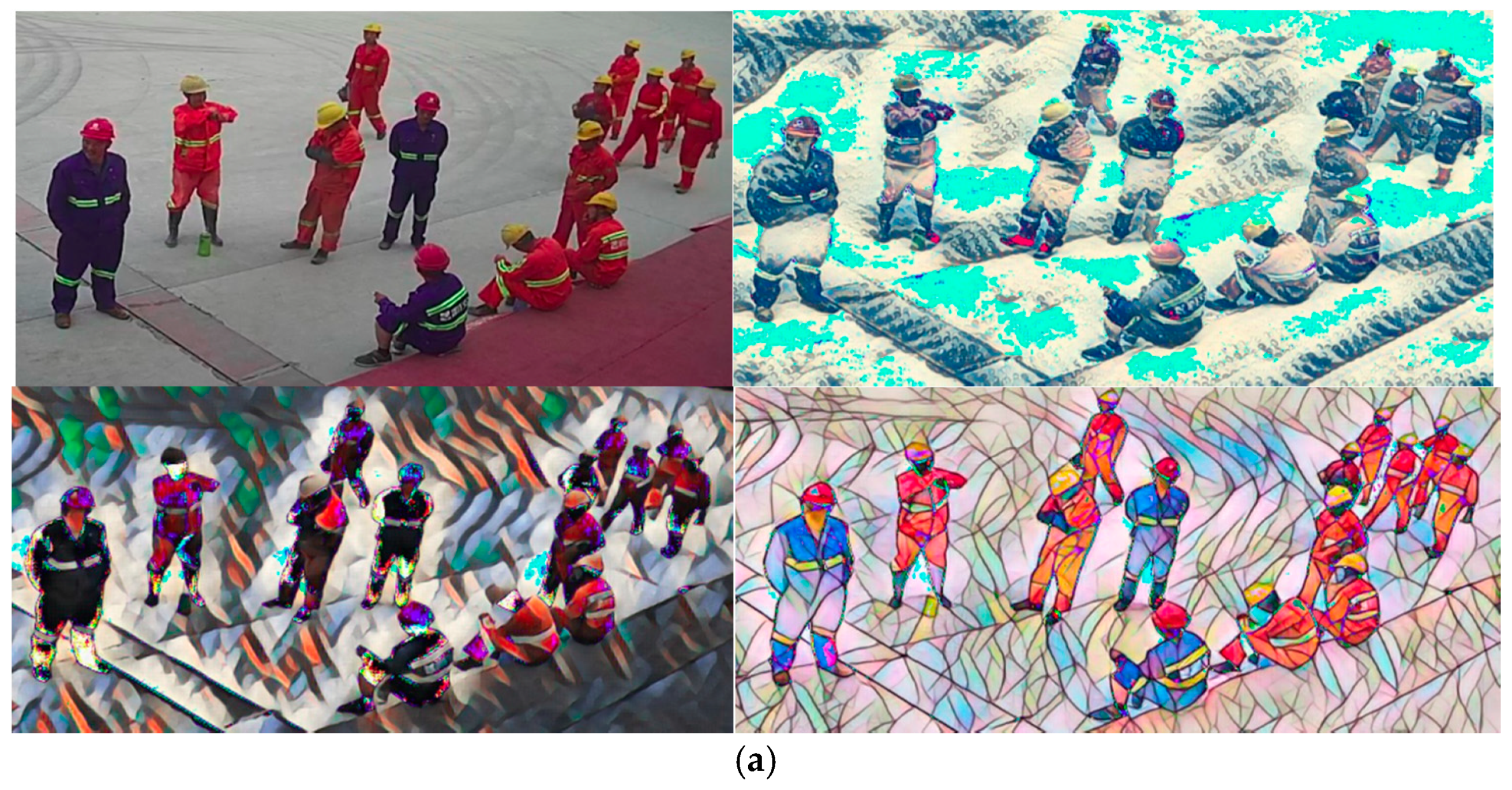
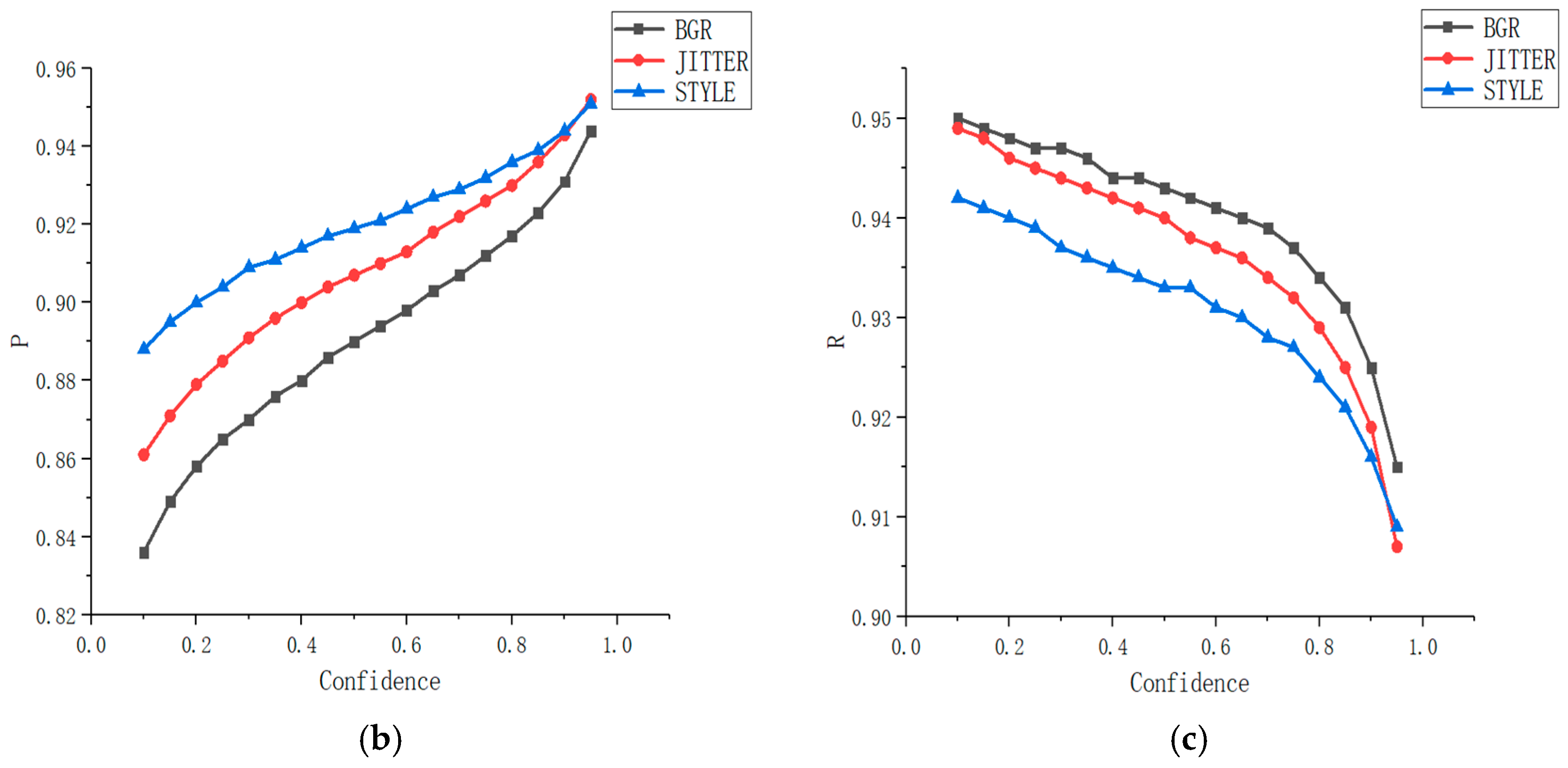
4.2.2. Input Data
4.2.3. Convolution Module
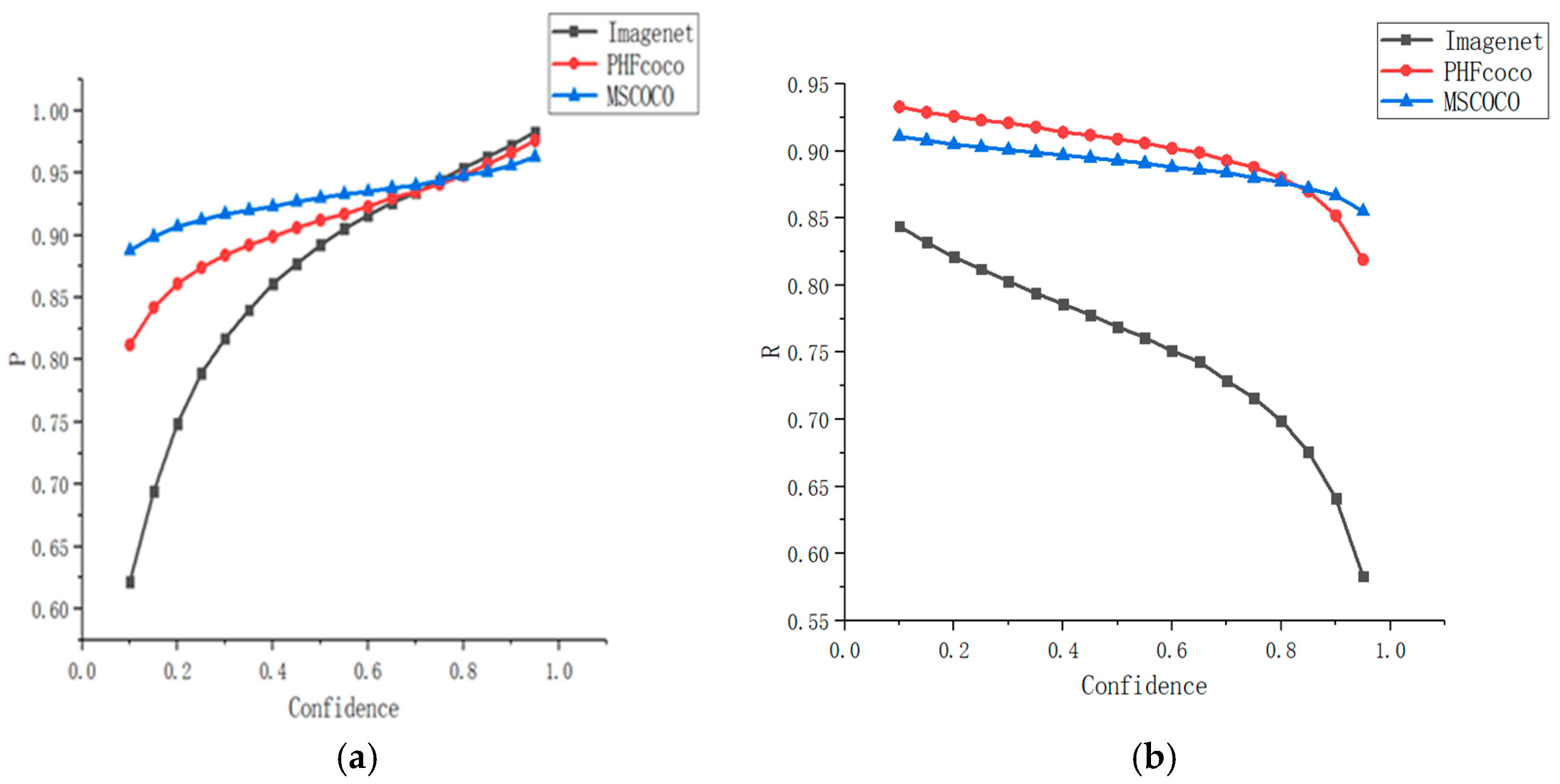
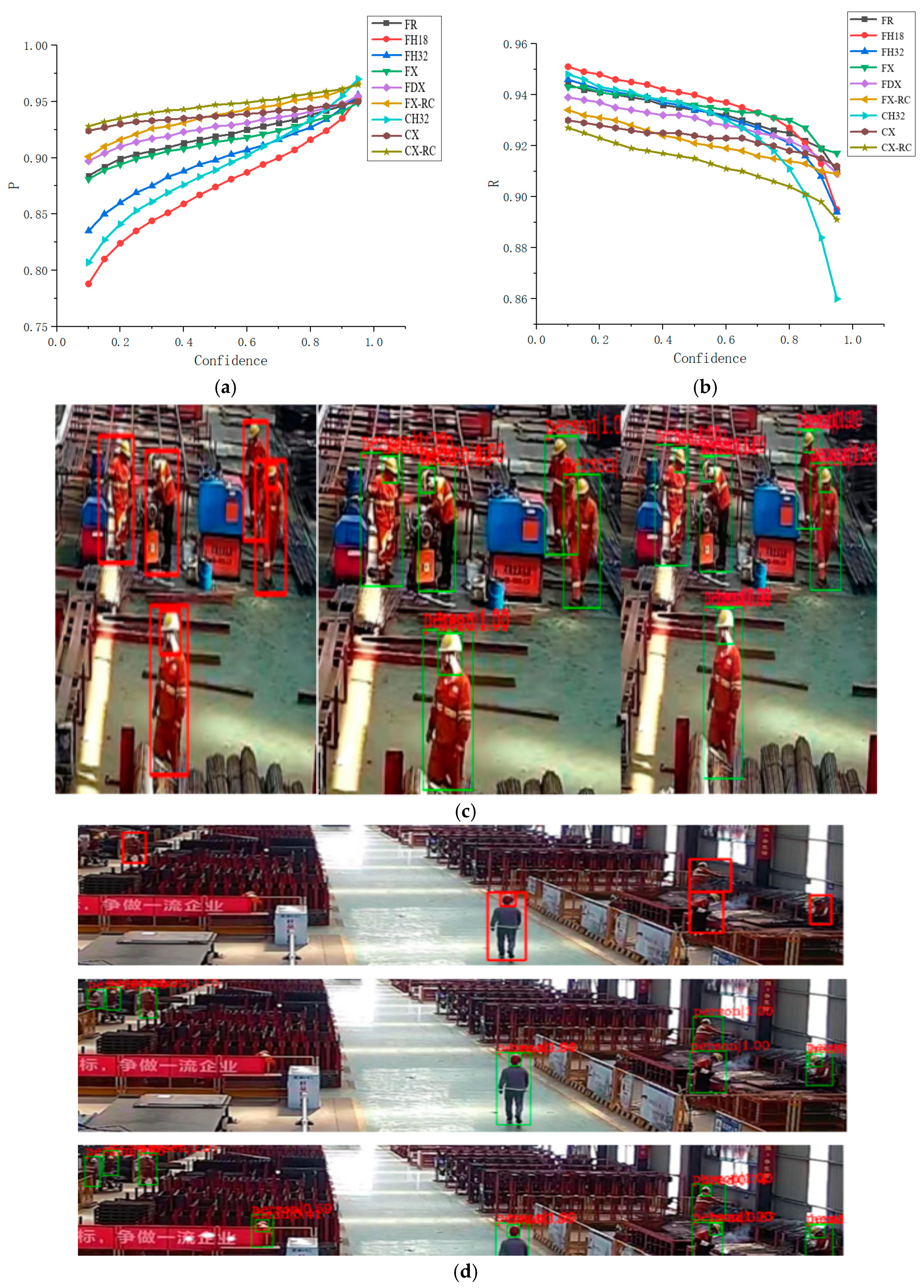
4.2.4. Detection Effect and Reasoning Performance
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5686–5696. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, T.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. High-resolution representations for labeling pixels and regions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.04514. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Lei, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, R. Automatic Detection of Cervical Cells Using Dense-Cascade R-CNN. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision 2020, Nanjing, China, 16–18 October 2020; pp. 602–613. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized Intersection Over Union: A Metric and a Loss for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J. A Detection Method of Safety Helmet Wearing Based on Centernet. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Networks, Xi’an, China, 16–18 October 2020; pp. 1128–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. CenterNet—Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 6568–6577. [Google Scholar]
- Law, H.; Teng, Y.; Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J. Cornernet-lite: Efficient keypoint based object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08900. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, H. Adaptive threshold cascade faster RCNN for domain adaptive object detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 25291–25308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.Q.; Su, H.; Kaichun, M.; Guibas, L.J. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5987–5995. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Sohail, A.; Zahoora, U.; Qureshi, A.S. A survey of the recent architectures of deep convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5455–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.Y.; Liu, W.; Ranga, A.; Tyagi, A.; Berg, A.C. Dssd: Deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06659. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, L.; Bian, X.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Single-Shot Refinement Neural Network for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4203–4212. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F. FSSD: Feature fusion single shot multibox detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00960. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M. A multi-scale target detection method for optical remote sensing images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 8751–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Fieguth, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Pietikäinen, M. Deep learning for generic object de-tection: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 261–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F. Recent advances in small object detection based on deep learning: A review. Image Vis. Comput. 2020, 97, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. A CenterNet++ model for ship detection in SAR images. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 112, 107787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Song, B.; Gao, X. A Rotational Libra R-CNN Method for Ship Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2020, 58, 5772–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosquet, B.; Mucientes, M.; Brea, V.M. STDnet: Exploiting high resolution feature maps for small object detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 91, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, D.; Li, T.; Wu, F.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Multi-scale dense convolutional networks for efficient prediction. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09844v5. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Samy, M.; Amer, K.; Eissa, K.; Shaker, M.; Elhelw, M. NU-Net: Deep Residual Wide Field of View Convolutional Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, S.; Verbeek, J. Convolutional neural fabrics. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 4053–4061. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Li, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Igcv3: Interleaved low-rank group convolutions for efficient deep neural networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00178. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, W. Deeply-fused nets. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]


| Name | Time (ms) | Time (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CUDA memcpy HtoD | 22.341 | 11.02 |
| ROIAlignForward | 24.959 | 12.32 |
| Winnograd128128 | 56.824 | 28.04 |
| Metro | Backbone | Input Size | Infer | AP | AP50 | AP75 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 99.659 | 65.4 | 94.4 | 78.4 | ||
| ResNet101 | B | 65.962 | 63.5 | 93.5 | 73.5 | |
| C | 56.561 | 58.8 | 89.3 | 67.8 | ||
| A | 79.884 | 64.1 | 94.6 | 77.4 | ||
| HRNetv2p_w18 | B | 55.735 | 63.6 | 93.8 | 76.2 | |
| C | 47.603 | 59.7 | 90.5 | 69.6 | ||
| A | 98.435 | 64.3 | 93.9 | 77.1 | ||
| Faster | HRNetv2p_w32 | B | 67.867 | 63.5 | 93.5 | 75.5 |
| C | 59.478 | 58.9 | 88.8 | 68.4 | ||
| A | 118.423 | 66.1 | 95.0 | 80.3 | ||
| ResNeXt101 | B | 80.673 | 64.2 | 93.5 | 76.1 | |
| C | 68.842 | 59.6 | 88.4 | 70.1 | ||
| A | 143.38 | 65.5 | 94.1 | 78.8 | ||
| D_ResNeXt101 | B | 93.274 | 63.7 | 93.1 | 75.5 | |
| C | 77.849 | 59.2 | 88.4 | 69.3 | ||
| A | 75.218 | 65.5 | 94.6 | 78.2 | ||
| ResNeXt-RC | B | 54.026 | 63.4 | 93.5 | 73.2 | |
| C | 46.873 | 58.6 | 88.2 | 67.6 | ||
| Cascade | A | 135.19 | 65.4 | 93.8 | 79.1 | |
| HRNetv2p_w32 | B | 104.731 | 64.5 | 93.5 | 77.7 | |
| C | 96.017 | 62.2 | 91.6 | 73.5 | ||
| A | 147.471 | 66.3 | 94.0 | 79.6 | ||
| ResNeXt101 | B | 113.283 | 63.6 | 92.6 | 76.4 | |
| C | 100.857 | 61.7 | 90.8 | 73.6 | ||
| A | 115.26 | 65.8 | 93.9 | 79.1 | ||
| ResNeXt-RC | B | 96.037 | 64.6 | 93.5 | 77.2 | |
| C | 87.431 | 61.5 | 90.4 | 72.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z. Small-Target Complex-Scene Detection Method Based on Information Interworking High-Resolution Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 5103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155103
Fu Y, Li X, Hu Z. Small-Target Complex-Scene Detection Method Based on Information Interworking High-Resolution Network. Sensors. 2021; 21(15):5103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155103
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yongzhong, Xiufeng Li, and Zungang Hu. 2021. "Small-Target Complex-Scene Detection Method Based on Information Interworking High-Resolution Network" Sensors 21, no. 15: 5103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155103
APA StyleFu, Y., Li, X., & Hu, Z. (2021). Small-Target Complex-Scene Detection Method Based on Information Interworking High-Resolution Network. Sensors, 21(15), 5103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155103






