Temperature Monitoring in Hyperthermia Treatments of Bone Tumors: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Temperature Monitoring: Main Techniques and Applications in Bone HTs
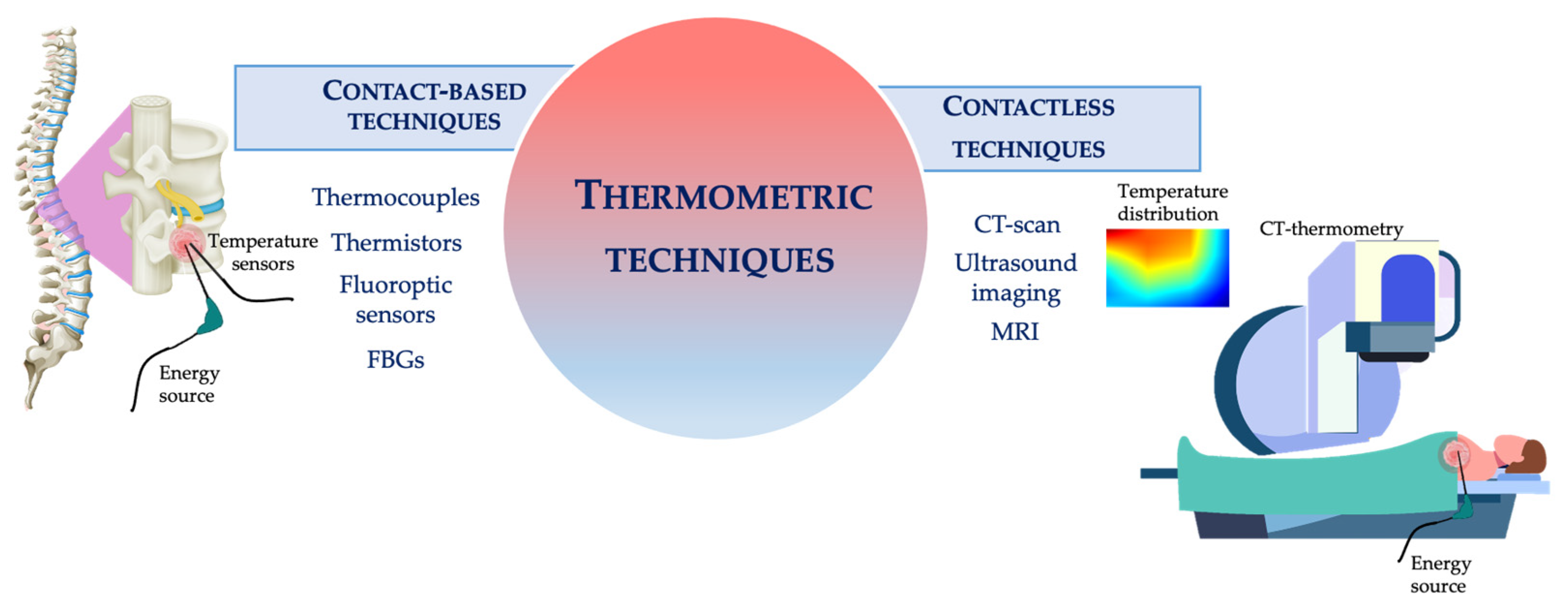
2.1. Most Popular Thermometric Techniques Used during HTs
2.1.1. Contact Based Techniques
2.1.2. Contactless Techniques
2.2. Temperature Monitoring during RFA in Bone
2.3. Temperature Monitoring during LA in Bone
2.4. Temperature Monitoring during MWA in Bone
2.5. Temperature Monitoring during HIFU in Bone
3. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OO | Osteoid osteoma |
| HT | Hyperthermia treatments |
| RFA | Radiofrequency ablation |
| LA | Laser ablation |
| MWA | Microwave ablation |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| MR | Magnetic resonance |
| HIFU | High intensity focused ultrasound |
| CEM | Cumulative equivalent minutes |
| FBG | Fiber Bragg grating sensors |
| emf | Electromotive force |
| PTC | Positive temperature coefficient |
| NTC | Negative temperature coefficient |
| HU | Hounsfield unit |
| PRF | Proton Resonance Frequency |
| TE | Echo time |
| RF | Radiofrequency |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, O.S.; Munro, A.J.; Tannock, I.F. Bone metastases: Pathophysiology and management policy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 9, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazario, J.; Hernandez, J.; Tam, A.L. Thermal ablation of painful bone metastases. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 14, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, C.C.; Piciucchi, S.; Sammarra, M.; Santini, D.; Vincenzi, B.; Tonini, G.; Grasso, R.F.; Zobel, B.B. Bone metastases in breast cancer: Higher prevalence of osteosclerotic lesions. Radiol. Med. 2007, 112, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, T.; Flamini, E.; Mercatali, L.; Sacanna, E.; Serra, P.; Amadori, D. Pathogenesis of osteoblastic bone metastases from prostate cancer. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2010, 116, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuya, A.; Fukuoka, M. Bone metastases in lung cancer. Clin. Calcium 2008, 18, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenspan, A. Benign bone-forming lesions: Osteoma, osteoid osteoma, and osteoblastoma. Skelet. Radiol. 1993, 22, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kransdorf, M.J.; Stull, M.A.; Gilkey, F.W.; Moser, R.P., Jr. Osteoid osteoma. Radiographics 1991, 11, 671–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.A.O. The incidence of vertebral body metastases. Int. Orthop. 1995, 19, 309–311. [Google Scholar]
- Sciubba, D.M.; Gokaslan, Z.L. Diagnosis and management of metastatic spine disease. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 15, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, A.; Alizadeh, H.; Wong, L.; Buy, X.; Dietemann, J.L.; Roy, C. Osteoid osteoma: Percutaneous laser ablation and follow-up in 114 patients. Radiology 2007, 242, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.S. Painful Osseous Metastases. Pain Physician 2011, 14, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripamonti, C.; Fulfaro, F. Malignant bone pain: Pathophysiology and treatments. Curr. Rev. Pain 2000, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasian, A.; Jennings, J.W. Percutaneous minimally invasive thermal ablation for management of osseous metastases: Recent advances. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, B.; Shokek, O.; Frassica, D.A. The role of radiation treatment in the contemporary management of bone tumors. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2007, 5, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.H.; Brown, H.K. Complications of bone metastases: Surgical management. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2000, 88, 2940–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourney, D.R.; Frangou, E.M.; Ryken, T.C.; DiPaola, C.P.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Berven, S.H.; Bilsky, M.H.; Harrop, J.S.; Fehlings, M.G.; Boriani, S. Spinal instability neoplastic score: An analysis of reliability and validity from the spine oncology study group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frassica, D.A. General Principles of External Beam Radiation Therapy for Skeletal Metastases. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, D.; Callstrom, M.R. Critical review and state of the art in interventional oncology: Benign and metastatic disease involving bone. Radiology 2012, 262, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynagh, M.R.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.R. Thermal Ablation of Bone Metastases. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringe, K.I.; Panzica, M.; Von Falck, C. Thermoablation of Bone Tumors. In RoFo Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Rontgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren; Georg Thieme Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 188, pp. 539–550. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasian, A.; Jennings, J.W. Percutaneous Minimally Invasive Thermal Ablation of Osseous Metastases: Evidence-Based Practice Guidelines. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, D. Bone Cancer. 2020. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/patientresources/patient-resources/guidelines-for-patients/guidelines-for-patients-details?patientGuidelineId=51 (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Goldberg, S.N.; Gazelle, G.S.; Mueller, P.R. Thermal Ablation Therapy for Focal Malignancy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palussière, J.; Pellerin-Guignard, A.; Descat, E.; Cornélis, F.; Dixmérias, F. Radiofrequency ablation of bone tumours. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetz, M.P.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Farrell, M.A.; Maus, T.P.; Welch, T.J.; Wong, G.Y.; Sloan, J.A.; Novotny, P.J.; Petersen, I.A. Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of painful metastases involving bone: A multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, A.; Basille, A.; Buy, X.; Alizadeh, H.; Sauer, B.; Bierry, G. Radiofrequency and laser ablation of spinal lesions. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2005, 26, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; de Rubeis, G.; de Marini, P.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Auloge, P.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous microwave ablation of bone tumors: A systematic review. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3530–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, C.; Sotgia, B.; Fele, R.M.; Melis, L. Treatment of bone metastases with microwave thermal ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T.; Goldberg, S.N. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 2011, 258, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.N.; Grassi, C.J.; Cardella, J.F.; Charboneau, J.W.; Dodd, G.D.; Dupuy, D.E.; Gervais, D.; Gillams, A.R.; Kane, R.A.; Lee, F.T.; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 2005, 235, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, T.A.; Kennedy, J.E. High-intensity focused ultrasound principles, current uses, and potential for the future. Ultrasound Q. 2006, 22, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfelice, D.; Gupta, C.; Kucharczyk, W.; Bret, P.; Havill, D.; Clemons, M. Palliative treatment of painful bone metastases with MR imaging–guided focused ultrasound. Radiology 2008, 249, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, A.; Mastantuono, M.; Cavallo Marincola, B.; Anzidei, M.; Zaccagna, F.; Moreschini, O.; Passariello, R.; Catalano, C. Osteoid osteoma: MR-guided focused ultrasound for entirely noninvasive treatment. Radiology 2013, 267, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, M.; Lam, M.K.; Bartels, L.W.; Nijenhuis, R.J.; Moonen, C.T.; Knuttel, F.M.; Verkooijen, H.M.; van Vulpen, M.; van den Bosch, M.A. Feasibility of volumetric MRI-guided high intensity focused ultrasound (MR-HIFU) for painful bone metastases. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2014, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bing, F.; Vappou, J.; de Mathelin, M.; Gangi, A. Targetability of osteoid osteomas and bone metastases by MR-guided high intensity focused ultrasound (MRgHIFU). Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.A. Models for thermal damage in tissues: Processes and Applications. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, H.P.; Cressman, E.N.K.; Ceelen, W.; Brace, C.L.; Ivkov, R.; Grüll, H.; ter Haar, G.; Wust, P.; Crezee, J. Heating technology for malignant tumors: A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 711–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomandi, P.; Schena, E.; Silvestri, S. Techniques for temperature monitoring during laser-induced thermotherapy: An overview. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepetit-Coiffé, M.; Laumonier, H.; Seror, O.; Quesson, B.; Sesay, M.-B.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Grenier, N.; Trillaud, H. Real-time monitoring of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors using thermal-dose calculation by MR temperature imaging: Initial results in nine patients, including follow-up. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupin, S.; Bour, P.; Lepetit-Coiffé, M.; Ozenne, V.; de Senneville, B.D.; Schneider, R.; Vaussy, A.; Chaumeil, A.; Cochet, H.; Sacher, F.; et al. Feasibility of real-time MR thermal dose mapping for predicting radiofrequency ablation outcome in the myocardium in vivo. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2017, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorber, G.; Glamore, M.; Doshi, M.; Jorda, M.; Morillo-Burgos, G.; Leveillee, R.J. Long-term oncologic outcomes following radiofrequency ablation with real-time temperature monitoring for T1a renal cell cancer. In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 32, pp. 1017–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy, D.E.; Hong, R.; Oliver, B.; Goldberg, S.N. Radiofrequency ablation of spinal tumors: Temperature distribution in the spinal canal. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasian, A.; Jennings, J.W. Vertebral Metastases: Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Thermal Ablation. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 23, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornemann, R.; Grötz, S.F.; Pennekamp, P.H.; Wilhelm, K.E.; Sander, K.; Wirtz, D.C.; Pflugmacher, R. Radiofrequency Ablation: Temperature Distribution in Adjacent Tissues. Z. Orthop. Unfall. 2016, 154, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoumakidou, G.; Buy, X.; Garnon, J.; Enescu, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous thermal ablation: How to protect the surrounding organs. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 14, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Yamakado, K.; Maeda, M.; Yasuda, M.; Akeboshi, M.; Takaki, H.; Hamada, A.; Takeda, K. Radiofrequency ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of bone malignancies. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004, 15, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangi, A.; Tsoumakidou, G.; Buy, X.; Quoix, E. Quality improvement guidelines for bone tumour management. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garnon, J.; Cazzato, R.L.; Caudrelier, J.; Nouri-Neuville, M.; Rao, P.; Boatta, E.; Ramamurthy, N.; Koch, G.; Gangi, A. Adjunctive Thermoprotection During Percutaneous Thermal Ablation Procedures: Review of Current Techniques. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.D.; Gangi, A.; Buy, X.; Vieira, R.L.R.; Wittig, J. Thermal ablation of spinal osteoid osteomas close to neural elements: Technical considerations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lecigne, R.; Garnon, J.; Cazzato, R.L.; Auloge, P.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Gangi, A. Transforaminal insertion of a thermocouple on the posterior vertebral wall combined with hydrodissection during lumbar spinal radiofrequency ablation. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figliola, R.S.; Beasley, D.E. Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 20, ISBN 1119723450. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, S.L. Preliminary study of the effect of artificial fever upon hopeless tumor cases. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1935, 33, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Carnochan, P.; Dickinson, R.J.; Joiner, M.C. The practical use of thermocouples for temperature measurement in clinical hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 1986, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schena, E.; Giurazza, F.; Massaroni, C.; Fong, Y.; Park, J.J.; Saccomandi, P. Thermometry based on computed tomography images during microwave ablation: Trials on ex vivo porcine liver. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Turin, Italy, 22–25 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi-Yu, H.; Ping, L.; Xiao-Ling, Y.; Zhi-Gang, C.; Fang-Yi, L.; Jie, Y. A clinical study of thermal monitoring techniques of ultrasound-guided microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in high-risk locations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogan, K.; Roberts, W.W.; Wilhelm, D.M.; Bonnell, L.; Leiner, D.; Lindberg, G.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Cadeddu, J.A. Infrared thermography and thermocouple mapping of radiofrequency renal ablation to assess treatment adequacy and ablation margins. Urology 2003, 62, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liang, P.; Yu, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. A comparison of microwave ablation and bipolar radiofrequency ablation both with an internally cooled probe: Results in ex vivo and in vivo porcine livers. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 79, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Liang, P. Comparison of temperature curve and ablation zone between 915- and 2450-MHz cooled-shaft microwave antenna: Results in ex vivo porcine livers. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, R.; Selig, A.M.; Colucci, V.M.; Jolesz, F.A. Interstitial Nd: YAG laser ablation in normal rabbit liver: Trial to maximize the size of laser-induced lesions. Lasers Surg. Med. 1992, 12, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, J.; Loyd, D. Thermocouples; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Manns, F.; Milne, P.J.; Gonzalez-Cirre, X.; Denham, D.B.; Parel, J.-M.; Robinson, D.S. In Situ temperature measurements with thermocouple probes during laser interstitial thermotherapy (LITT): Quantification and correction of a measurement artifact. Lasers Surg. Med. 1998, 23, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schena, E.; Majocchi, L. Assessment of temperature measurement error and its correction during Nd: YAG laser ablation in porcine pancreas. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.A.; Green, C.B.; Pearson, G.L. Properties and uses of thermistors—Thermally sensitive resistors. Electr. Eng. 1946, 65, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.R. A probe for measuring temperature in radiofrequency heated material. IEEE Trans. Microw. Technol. Tech. 1976, 24, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturesson, C.; Ivarsson, K.; Andersson-Engels, S.; Tranberg, K.G. Changes in local hepatic blood perfusion during interstitial laser-induced thermotherapy of normal rat liver measured by interstitial laser Doppler flowmetry. Lasers Med. Sci. 1999, 14, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, J.A.; McKenzie, A.; McLeod, K. Temperature gradients in pigs during whole-body hyperthermia at 42 degrees C. J. Appl. Physiol. 1979, 47, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.; Zweije, R.; van Tienhoven, G.; Kok, H.P.; Sijbrands, J.; van den Bongard, H.J.G.D.; Rasch, C.R.N.; Crezee, H. Two high-resolution thermal monitoring sheets for clinical superficial hyperthermia. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 175021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiella, S.; Casetti, L.; Ewald, J.; Marchese, U.; D’Onofrio, M.; Garnier, J.; Landoni, L.; Gilabert, M.; Manzini, G.; Esposito, A.; et al. Laser Treatment (imILT) of Pancreatic Cancer: Safety and Feasibility Results From Two Phase 2a Studies. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 259, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehn, F.E.; Neeman, Z.; Hvizda, J.L.; Wood, B.J. Remote Thermometry to Avoid Complications in Radiofrequency Ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuang, M.; Lu, M.D.; Xie, X.Y.; Xu, H.X.; Mo, L.Q.; Liu, G.J.; Xu, Z.F.; Zheng, Y.L.; Liang, J.Y. Liver cancer: Increased microwave delivery to ablation zone with cooled-shaft antenna—Experimental and clinical studies. Radiology 2007, 242, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, F.; Giannetti, A.; Mencaglia, A.A.; Trono, C. Fiber Optic Sensors for Biomedical Applications. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2008, 4, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, D.; Poeggel, S.; Iordachita, I.; Schena, E. Fiber optic sensors for biomedical applications. In Opto-Mechanical Fiber Optic Sensors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 301–333. [Google Scholar]
- Schena, E.; Tosi, D.; Saccomandi, P.; Lewis, E.; Kim, T. Fiber optic sensors for temperature monitoring during thermal treatments: An overview. Sensors 2016, 16, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, P.; Silva, S.; Frazão, O.; Novais, S. Optical fiber temperature sensors and their biomedical applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo Presti, D.; Massaroni, C.; Jorge Leitao, C.S.; De Fatima Domingues, M.; Sypabekova, M.; Barrera, D.; Floris, I.; Massari, L.; Oddo, C.M.; Sales, S.; et al. Fiber bragg gratings for medical applications and future challenges: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 156863–156888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Zaltieri, M.; Lo Presti, D.; Nicolo, A.; Tosi, D.; Schena, E. Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Cardiorespiratory Monitoring: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Finegan, T.M.; Mohsen, P.; Hatton, T.A.; Laibinis, P.E. Fluorescence-based Thermometry Principles and Applications. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 235–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, D.E.; Verow, A.F. Observations on electrode-tissue interface temperature and effect on electrical impedance during radiofrequency ablation of ventricular myocardium. Circulation 1990, 82, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blouin, L.T.; Marcus, F.I.; Lampe, L. Assessment of Effects of a Radiofrequency Energy Field and Thermistor Location in an Electrode Catheter on the Accuracy of Temperature Measurement. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1991, 14, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whayne, J.G.; Nath, S.; Haines, D.E. Microwave catheter ablation of myocardium in vitro. Assessment of the characteristics of tissue heating and injury. Circulation 1994, 89, 2390–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viallon, M.; Terraz, S.; Roland, J.; Dumont, E.; Becker, C.D.; Salomir, R. Observation and correction of transient cavitation-induced PRFS thermometry artifacts during radiofrequency ablation, using simultaneous Ultrasound/MR imaging. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 1491–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Moriarty, J.A.; Derbyshire, J.A.; Peters, R.D.; Trachtenberg, J.; Bell, S.D.; Doyle, J.; Arrelano, R.; Wright, G.A.; Henkelman, R.M. Prostate cancer: MR imaging and thermometry during microwave thermal ablation-initial experience. Radiology 2000, 214, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Converse, M.C.; Mahvi, D.M.; Webster, J.G. Measurement and analysis of tissue temperature during microwave liver ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 54, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bosch, M.; Daniel, B.; Rieke, V.; Butts-Pauly, K.; Kermit, E.; Jeffrey, S. MRI-guided radiofrequency ablation of breast cancer: Preliminary clinical experience. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 27, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, B.S.; Hill, K.O.; Johnson, D.C.; Fujii, Y. Narrow-band Bragg reflectors in optical fibers. Opt. Lett. 1978, 3, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdogan, T. Fiber grating spectra. J. Light. Technol. 1997, 15, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaiola, C.; Saccomandi, P.; Massaroni, C.; Tosi, D.; Giurazza, F.; Frauenfelder, G.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Di Matteo, F.M.; Caponero, M.A.; Polimadei, A.; et al. Error of a temperature probe for cancer ablation monitoring caused by respiratory movements: Ex vivo and in vivo analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Tommasi, F.; Massaroni, C.; Carnevale, A.; Lo Presti, D.; De Vita, E.; Iadicicco, A.; Faiella, E.; Grasso, R.F.; Longo, U.G.; Campopiano, S.; et al. Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Temperature Monitoring During Thermal Ablation Procedure: Experimental Assessment of Artefact Caused by Respiratory Movements. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13342–13349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.; Iadicicco, A.; Tosi, D.; Verze, P.; Carlomagno, N.; Tammaro, V.; Ippolito, J.; Campopiano, S. Temperature profile of ex-vivo organs during radio frequency thermal ablation by fiber Bragg gratings. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 117003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jelbuldina, M.; Korobeinyk, A.V.; Korganbayev, S.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Tosi, D. Fiber Bragg grating based temperature profiling in ferromagnetic nanoparticles-enhanced radiofrequency ablation. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 43, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltieri, M.; Allegretti, G.; Massaroni, C.; Schena, E.; Cauti, F.M. Fiber bragg grating sensors for millimetric-scale temperature monitoring of cardiac tissue undergoing radiofrequency ablation: A feasibility assessment. Sensors 2020, 20, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.L.; Wong, Y.H.; Cheah, P.L.; Tan, D.; Lim, K.S.; Ahmad, A.C.; Sulaiman, N.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Yeong, C.H. Correlation between CT Number shift and tissue temperature change during radiofrequency ablation: An ex-vivo study using bovine liver. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1248, 12039. [Google Scholar]
- Polito, D.; Caponero, M.A.; Polimadei, A.; Saccomandi, P.; Massaroni, C.; Silvestri, S.; Schena, E. A needlelike probe for temperature monitoring during laser ablation based on fiber Bragg grating: Manufacturing and characterization. J. Med. Devices Trans. ASME 2015, 9, 041006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korganbayev, S.; Orrico, A.; Bianchi, L.; De Landro, M.; Wolf, A.; Dostovalov, A.; Saccomandi, P. Closed-loop temperature control based on fiber bragg grating sensors for laser ablation of hepatic tissue. Sensors 2020, 20, 6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, E.; De Landro, M.; Massaroni, C.; Iadicicco, A.; Saccomandi, P.; Schena, E.; Campopiano, S. Fiber optic sensors-based thermal analysis of perfusion-mediated tissue cooling in liver undergoing laser ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassino, R.; Vallan, A.; Perrone, G. Evaluation of temperature measurement errors due to FBG sensors during laser ablation of Ex-Vivo porcine liver. In Proceedings of the I2MTC 2018–2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference: Discovering New Horizons in Instrumentation and Measurement, Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jelbuldina, M.; Korobeinyk, A.; Korganbayev, S.; Tosi, D.; Dukenbayev, K.; Inglezakis, V.J. Real-Time Temperature Monitoring in Liver during Magnetite Nanoparticle-Enhanced Microwave Ablation with Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors: Ex Vivo Analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8005–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomandi, P.; Schena, E.; Massaroni, C.; Fong, Y.; Grasso, R.F.; Giurazza, F.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Buy, X.; Palussiere, J.; Cazzato, R.L. Temperature monitoring during microwave ablation in ex vivo porcine livers. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schena, E.; Villani, S.; Massaroni, C.; Fong, Y.; Saccomandi, P.; Diana, M.; Marescaux, J. Three-Dimensional Temperature Map During Microwave Ablation of Ex Vivo Porcine Liver: Theoretical Prediction and Experimental Validation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Nanotechnology for Instrumentation and Measurement (NANOfIM), Chemnitz, Germany, 8–9 September 2016; pp. 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zaltieri, M.; De Vita, E.; De Tommasi, F.; Massaroni, C.; Faiella, E.; Zobel, B.B.; Iadicicco, A.; Schena, E.; Grasso, R.F.; Campopiano, S. Evaluation of the Thermal Response of Liver Tissue Undergoing Microwave Treatment by Means of Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Sensors, Taiwan, China, 29–30 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jelbuldina, M.; Korganbayev, S.; Seidagaliyeva, Z.; Sovetov, S.; Tuganbekov, T.; Tosi, D. Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor for Temperature Monitoring During HIFU Ablation of Ex Vivo Breast Fibroadenoma. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2019, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.J.; Webb, D.J.; Jackson, D.A.; Zhang, L.; Bennion, I. In-fiber bragg-grating temperature sensor system for medical applications. J. Light. Technol. 1997, 15, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, L.W. Principles of CT and CT technology. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2007, 35, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homolka, P.; Gahleitner, A.; Nowotny, R. Temperature dependence of HU values for various water equivalent phantom materials. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamenhof, R.G.; Sternick, E.S.; Curran, B.M. Non-invasive temperature mapping by computerized tomography. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1981, 7, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallone, B.G.; Moran, P.R.; Podgorsak, E.B. Noninvasive thermometry with a clinical x-ray CT scanner. Med. Phys. 1982, 9, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzen, S.M.; Overgaard, J.; Jørgensen, J. Isotherm mapping in hyperthermia using subtraction X-ray computed tomography. Radiother. Oncol. 1984, 2, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schena, E.; Massaroni, C.; Giurazza, F.; Park, J.; Park, J.; Fong, Y.; Saccomandi, P. Feasibility Assessment and Analysis of Thermal Sensitivity of CT-Thermometry During Microwave Ablation of Ex Vivo Porcine Kidneys. In 2016 Nanotechnology for Instrumentation and Measurement (NANOfIM); Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, J.; Vogl, T.J.; Chacko, A. Dual energy computed tomography thermometry during hepatic microwave ablation in an ex-vivo porcine model. Phys. Med. 2015, 31, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomandi, P.; De Landro, M.; Massaroni, C.; Fong, Y.; Park, J.; Park, J.; Schena, E. Temperature map of kidneys undergoing microwave ablation using computed tomography-thermometry: Ex-vivo experiments and numerical simulations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Istanbul, Turkey, 26–28 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlan, J.; Kress, W.; Hermann, K.-G.; Mews, J.; Kroes, M.; Hamm, B.; Diekhoff, T. Computed tomography thermography for ablation zone prediction in microwave ablation and cryoablation: Advantages and challenges in an ex vivo porcine liver model. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2020, 44, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Lim, K.-S.; Wong, Y.-H.; Abd Raziff, H.H.; Tan, S.-H.; Sulaiman, N.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Ahmad, H.; Yeong, C.-H. Multivariate Regression Between Hounsfield Unit Shift, Tissue Temperature, and Tissue Contraction: A Feasibility Study of Computed Tomography Thermometry. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; Mohamad, N.A.; Wong, Y.H.; Yeong, C.H.; Cheah, P.L.; Sulaiman, N.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Fabell, M.K.; Lim, K.S. Experimental assessment on feasibility of computed tomography-based thermometry for radiofrequency ablation on tissue equivalent polyacrylamide phantom. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, N.; Goldberg, S.N.; Sosna, J.; Azhari, H. Temperature–density hysteresis in X-ray CT during HIFU thermal ablation: Heating and cooling phantom study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, N.; Sosna, J.; Goldberg, S.N.; Azhari, H. Non-invasive temperature monitoring and hyperthermic injury onset detection using X-ray CT during HIFU thermal treatment in ex vivo fatty tissue. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, F.; Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P.; Silvestri, S. CT-based thermometry: An overview. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.N.T. Ultrasound imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivens, I.; Shaw, A.; Civale, J.; Morris, H. Treatment monitoring and thermometry for therapeutic focused ultrasound. Int. J. Hyperth. 2007, 23, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasoni, R.L.; Bowen, T.; Connor, W.G.; Sholes, R.R. In vivo temperature dependence of ultrasound speed in tissue and its application to noninvasive temperature monitoring. Ultrason. Imaging 1979, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurazza, F.; Massaroni, C.; Silvestri, S.; Zobel, B.B.; Schena, E. Preliminary analysis of ultrasound elastography imaging-based thermometry on non-perfused ex vivo swine liver. J. Ultrasound 2020, 23, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, T.; Zagzebski, J.A.; Chen, Q.; Techavipoo, U.; Frank, G.; Johnson, C.; Wright, A.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Ultrasound monitoring of temperature change during radiofrequency ablation: Preliminary in-vivo results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-D.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Yeah, Y.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Tsui, P.-H. Adaptive ultrasound temperature imaging for monitoring radiofrequency ablation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Bai, Y.; Gao, H. Ultrasound monitoring of temperature and coagulation change during tumor treatment with microwave ablation. Front. Biol. China 2009, 4, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.A.; Staruch, R.M.; Chopra, R. Thermometry and ablation monitoring with ultrasound. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlaardingerbroek, M.T.; Boer, J.A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Theory and Practice; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; ISBN 978-3-540-43681-2. [Google Scholar]
- Quesson, B.; de Zwart, J.A.; Moonen, C.T.W. Magnetic resonance temperature imaging for guidance of thermotherapy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 12, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, F.; Mattner, J.; Stehling, M.K.; Müller-Lisse, U.; Peller, M.; Loeffler, R.; Weber, J.; Meßmer, K.; Wilmanns, W.; Issels, R.; et al. Non-invasive temperature mapping using MRI: Comparison of two methods based on chemical shift and T1-relaxation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 16, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis de Senneville, B.; Quesson, B.; Moonen, C.T.W. Magnetic resonance temperature imaging. Int. J. Hyperth. 2005, 21, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, L.; Oberacker, E.; Paul, K.; Ji, Y.; Oezerdem, C.; Ghadjar, P.; Thieme, A.; Budach, V.; Wust, P.; Niendorf, T. Magnetic resonance thermometry: Methodology, pitfalls and practical solutions. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jolesz, F.A.; Bleier, A.R.; Jakab, P.; Ruenzel, P.W.; Huttl, K.; Jako, G.J. MR imaging of laser-tissue interactions. Radiology 1988, 168, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, V.; Kinsey, A.M.; Ross, A.B.; Nau, W.H.; Diederich, C.J.; Sommer, G.; Pauly, K.B. Referenceless MR thermometry for monitoring thermal ablation in the prostate. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2007, 26, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breen, M.S.; Breen, M.; Butts, K.; Chen, L.; Saidel, G.M.; Wilson, D.L. MRI-guided thermal ablation therapy: Model and parameter estimates to predict cell death from MR thermometry images. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccomandi, P.; Massaroni, C.; Silvestri, S.; Giurazza, F.; Frauenfelder, G.; Zobel, B.B.; Schena, E. Feasibility assessment of magnetic resonance-thermometry on pancreas undergoing laser ablation: Sensitivity analysis of three sequences. Measurement 2016, 80, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, C.; Kickhefel, A.; Mensel, B.; Pickartz, T.; Puls, R.; Roland, J.; Hosten, N. PRFS-based MR thermometry versus an alternative T1 magnitude method–comparative performance predicting thermally induced necrosis in hepatic tumor ablation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, R.; Langner, S.; Rosenberg, C.; Hegenscheid, K.; Kuehn, J.P.; Noeckler, K.; Hosten, N. Laser ablation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer with MR thermometry: 5-year survival. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodrum, D.A.; Mynderse, L.A.; Gorny, K.R.; Amrami, K.K.; McNichols, R.J.; Callstrom, M.R. 3.0 T MR-guided laser ablation of a prostate cancer recurrence in the postsurgical prostate bed. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, O.; Lepetit-Coiffé, M.; Le Bail, B.; De Senneville, B.D.; Trillaud, H.; Moonen, C.; Quesson, B. Real time monitoring of radiofrequency ablation based on MR thermometry and thermal dose in the pig liver in vivo. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holbrook, A.B.; Santos, J.M.; Kaye, E.; Rieke, V.; Pauly, K.B. Real-time MR thermometry for monitoring HIFU ablations of the liver. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, Y.; Mulier, S.; Miao, Y.; Michel, L.; Marchal, G. A review of the general aspects of radiofrequency ablation. Abdom. Imaging 2005, 30, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenthal, D.I.; Alexander, A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Springfield, D. Ablation of Osteoid Osteomas with a Percutaneously Placed Electrode: A New Procedure. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 1992, 183, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Tanigawa, N.; Kariya, S.; Komemushi, A.; Shomura, Y.; Sawada, S. Clinical assessment of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for painful metastatic bone tumors. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2006, 29, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.T.; Jakobs, T.F.; Trumm, C.; Weber, C.; Helmberger, T.K.; Reiser, M.F. Radiofrequency ablation in combination with osteoplasty in the treatment of painful metastatic bone disease. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, N.; Naito, A.; Kakizawa, H.; Hieda, M.; Hirai, N.; Tachikake, T.; Kimura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Ito, K. Radiofrequency ablation therapy combined with cementoplasty for painful bone metastases: Initial experience. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2005, 28, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, M.D.; Le, H.B.Q.; Lee, S.; Young, C.; Heran, M.K.S.; Badii, M.; Clarkson, P.W.; Munk, P.L. Combination radiofrequency ablation and cementoplasty for palliative treatment of painful neoplastic bone metastasis: Experience with 53 treated lesions in 36 patients. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.A.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Hornicek, F.J.; Wolfe, M.W.; Jennings, L.C.; Gebhardt, M.C.; Mankin, H.J. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. A 1999, 81, 437–438. [Google Scholar]
- Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Goetz, M.P.; Rubin, J.; Wong, G.Y.; Sloan, J.A.; Novotny, P.J.; Lewis, B.D.; Welch, T.J.; Farrell, M.A. Painful metastases involving bone: Feasibility of percutaneous CT-and US-guided radio-frequency ablation. Radiology 2002, 224, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachbauer, F.; Mangat, J.; Bodner, G.; Eichberger, P.; Krismer, M. Heat distribution and heat transport in bone during radiofrequency catheter ablation. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2003, 123, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitsch, R.G.; Rupp, R.; Bernd, L.; Ludwig, K. Osteoid osteoma in an ex vivo animal model: Temperature changes in surrounding soft tissue during CT-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 2006, 238, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, A.; Kaminou, T.; Ogawa, T.; Kawai, T.; Takaki, Y.; Sugiura, K.; Ohuchi, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Heat distribution in the spinal canal during radiofrequency ablation for vertebral lesions: Study in swine. Radiology 2008, 247, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Yamakado, K.; Takaki, H.; Uraki, J.; Makita, M.; Oshima, F.; Takeda, K. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful spinal tumors adjacent to the spinal cord with real-time monitoring of spinal canal temperature: A prospective study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2009, 32, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groetz, S.F.; Birnbaum, K.; Meyer, C.; Strunk, H.; Schild, H.H.; Wilhelm, K.E. Thermometry during coblation and radiofrequency ablation of vertebral metastases: A cadaver study. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pezeshki, P.S.; Woo, J.; Akens, M.K.; Davies, J.E.; Gofeld, M.; Whyne, C.M.; Yee, A.J.M. Evaluation of a bipolar-cooled radiofrequency device for ablation of bone metastases: Preclinical assessment in porcine vertebrae. Spine J. 2014, 14, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.; Berenstein Weyel, T.; Sosna, J.; Applbaum, J.; Peyser, A. The distribution of heat in bone during radiofrequency ablation of an ex vivo bovine model of osteoid osteoma. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornemann, R.; Pflugmacher, R.; Frey, S.P.; Roessler, P.P.; Rommelspacher, Y.; Wilhelm, K.E.; Sander, K.; Wirtz, D.C.; Grötz, S.F. Temperature distribution during radiofrequency ablation of spinal metastases in a human cadaver model: Comparison of three electrodes. Technol. Health Care 2016, 24, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Peng, Z.H.; Chen, J.Z.; Hu, J.H.; Huang, J.Q.; Jiang, Y.N.; Luo, G.; Yi, G.F.; Wang, H.; Jin, S.; et al. Thermal effect of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with a clustered electrode for vertebral tumors: In vitro and vivo experiments and clinical application. J. Bone Oncol. 2018, 12, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, T.; Cazzato, R.L.; De Marini, P.; Auloge, P.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Spinal metastases treated with bipolar radiofrequency ablation with increased (>70 C) target temperature: Pain management and local tumor control. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2021, 102, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecigne, R.; Cazzato, R.L.; Dalili, D.; Gangi, A.; Garnon, J. Transosseous Temperature Monitoring of the Anterior Epidural Space during Thermal Ablation in the Thoracic Spine. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2021, 44, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P.; Fong, Y. Laser ablation for cancer: Past, present and future. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muller, G.; Roggan, A. Laser-Induced Interstitial Thermotherapy; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gangi, A.; Dietemann, J.-L.; Guth, S.; Vinclair, L.; Sibilia, J.; Mortazavi, R.; Steib, J.P.; Roy, C. Percutaneous laser photocoagulation of spinal osteoid osteomas under CT guidance. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1998, 19, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Ghia, A.J.; Rebueno, N.C.; Li, J.; Brown, P.D.; Rhines, L.D.; Tatsui, C.E. The use of image guided laser interstitial thermotherapy to supplement spine stereotactic radiosurgery to manage metastatic epidural spinal cord compression: Proof of concept and dosimetric analysis. In Practical Radiation Oncology; Spriger Link: Berlin, Germany, 2016; Volume 6, pp. e35–e38. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, T.; Giacomelli, M.-C.; Clavert, J.-M.; Buy, X.; Dietemann, J.-L.; Gangi, A. Image-guided laser ablation of osteoid osteoma in pediatric patients. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2008, 28, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.H.; Gebauer, B.; Wieners, G.; De Bucourt, M.; Renz, D.M.; Hamm, B.; Streitparth, F. Treatment of osteoid osteoma using CT-guided radiofrequency ablation versus MR-guided laser ablation: A cost comparison. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, e1002–e1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkert, C.A.; Nanz, D.; Bootz, F.; Nehrbass, D.; Pospischil, A.; Boos, N.; Pfammatter, T.; Treiber, K.; Hodler, J. Laser-Induced Thermotherapy of the Vertebral Body. Investig. Radiol. 2002, 37, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeiros, R.B.; Hyvönen, P.; Sequeiros, A.B.; Jyrkinen, L.; Ojala, R.; Klemola, R.; Vaara, T.; Tervonen, O. MR imaging-guided laser ablation of osteoid osteomas with use of optical instrument guidance at 0.23 T. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitparth, F.; Gebauer, B.; Melcher, I.; Schaser, K.; Philipp, C.; Rump, J.; Hamm, B.; Teichgräber, U. MR-guided laser ablation of osteoid osteoma in an open high-field system (1.0 T). Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2009, 32, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitparth, F.; Teichgräber, U.; Walter, T.; Schaser, K.D.; Gebauer, B. Recurrent osteoid osteoma: Interstitial laser ablation under magnetic resonance imaging guidance. Skelet. Radiol. 2010, 39, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsui, C.E.; Stafford, R.J.; Li, J.; Sellin, J.N.; Amini, B.; Rao, G.; Suki, D.; Ghia, A.J.; Brown, P.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Utilization of laser interstitial thermotherapy guided by real-time thermal MRI as an alternative to separation surgery in the management of spinal metastasis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatsui, C.E.; Lee, S.-H.; Amini, B.; Rao, G.; Suki, D.; Oro, M.; Brown, P.D.; Ghia, A.J.; Bhavsar, S.; Popat, K. Spinal laser interstitial thermal therapy: A novel alternative to surgery for metastatic epidural spinal cord compression. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, S73–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, C.J.; Dupuy, D.E.; Mayo-Smith, W.W. Microwave ablation: Principles and applications. Radiographics 2005, 25, S69–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ma, B.; Qiu, X.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhou, Y. Preliminary report on treatment of bone tumors with microwave-induced hyperthermia. Bioelectromagn. J. Bioelectromagn. Soc. Soc. Phys. Regul. Biol. Med. Eur. Bioelectromagn. Assoc. 1996, 17, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ma, B.; Guo, A.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, X. Surgical treatment of bone tumors in conjunction with microwave-induced hyperthermia and adjuvant immunotherapy. A preliminary report. Chin. Med. J. 1996, 109, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prud’homme, C.; Nueffer, J.-P.; Runge, M.; Dubut, J.; Kastler, B.; Aubry, S. Prospective pilot study of CT-guided microwave ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteomas. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, C.; Sotgia, B.; Fele, R.M.; Ballicu, N.; Melis, L. Combined microwave ablation and cementoplasty in patients with painful bone metastases at high risk of fracture. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewa, M.; Diezler, P.; Michaely, H.; Rathmann, N.; Attenberger, U.I.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Diehl, S.J. Microwave ablation of osteoid osteomas using dynamic MR imaging for early treatment assessment: Preliminary experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinzler, E.S.; Shivaram, G.M.; Shaw, D.W.; Monroe, E.J.; Koo, K.S.H. Microwave ablation of osteoid osteoma: Initial experience and efficacy. Pediatr. Radiol. 2019, 49, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastler, A.; Alnassan, H.; Aubry, S.; Kastler, B. Microwave thermal ablation of spinal metastatic bone tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ma, B.; Yang, T.; Long, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, Z. Microwave ablation of malignant extremity bone tumors. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kastler, A.; Krainik, A.; Sakhri, L.; Mousseau, M.; Kastler, B. Feasibility of Real-Time Intraprocedural Temperature Control during Bone Metastasis Thermal Microwave Ablation: A Bicentric Retrospective Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, E.; Zaltieri, M.; De Tommasi, F.; Massaroni, C.; Faiella, E.; Zobel, B.B.; Iadicicco, A.; Schena, E.; Grasso, R.F.; Campopiano, S. Multipoint temperature monitoring of microwave thermal ablation in bones through fiber bragg grating sensor arrays†. Sensors 2020, 20, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tommasi, F.; Zaltieri, M.; Schena, E.; Massaroni, C.; Faiella, E.; Grasso, R.F.; Zobel, B.B.; De Vita, E.; Iadicicco, A.; Campopiano, S. Temperature Monitoring during Microwave Thermal Ablation of Ex Vivo Bovine Bone: A Pilot Test. In Proceedings of the MetroInd 4.0 & IoT 2020: 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT, Rome, Italy, 3 June 2020; pp. 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Cheng, S.; Yang, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y. Feasibility of Controlling Metastatic Osseous Pain Using Three Kinds of Image-Guided Procedures for Thermal Microwave Ablation: A Retrospective Study. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Haar, G. HIFU tissue ablation: Concept and devices. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 880, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, W.Z.; Bai, J.; Zou, J.Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.B. Pathological changes in human malignant carcinoma treated with high-intensity focused ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2001, 27, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, M.D.; Ghanouni, P.; Kanaev, S.V.; Iozeffi, D.; Gianfelice, D.; Fennessy, F.M.; Kuten, A.; Meyer, J.E.; LeBlang, S.D.; Roberts, A. Magnetic resonance–guided focused ultrasound for patients with painful bone metastases: Phase III trial results. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Chen, W.; Wei, F. Technique Success, Technique Efficacy and Complications of HIFU Ablation for Palliation of Pain in Patients With Bone Lesions: A Meta-Analysis of 28 Feasibility Studies. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catane, R.; Beck, A.; Inbar, Y.; Rabin, T.; Shabshin, N.; Hengst, S.; Pfeffer, R.M.; Hanannel, A.; Dogadkin, O.; Liberman, B. MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MRgFUS) for the palliation of pain in patients with bone metastases—Preliminary clinical experience. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, B.; Gianfelice, D.; Inbar, Y.; Beck, A.; Rabin, T.; Shabshin, N.; Chander, G.; Hengst, S.; Pfeffer, R.; Chechick, A.; et al. Pain palliation in patients with bone metastases using MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery: A multicenter study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknor, M.D.; Rieke, V.; Do, L.; Majumdar, S.; Link, T.M.; Saeed, M. MRI-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of bone: Evaluation of acute findings with MR and CT imaging in a swine model. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geiger, D.; Napoli, A.; Conchiglia, A.; Gregori, L.; Arrigoni, F.; Bazzocchi, A.; Busacca, M.; Moreschini, O.; Mastantuono, M.; Albisinni, U.; et al. MR-guided Focused Ultrasound ( MRgFUS ) Ablation for the Treatment of Nonspinal Osteoid Osteoma: A prospective multicenter evaluation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2014, 96, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsay, E.; Mougenot, C.; Kazem, M.; Laetsch, T.W.; Chopra, R. Temperature-dependent MR signals in cortical bone: Potential for monitoring temperature changes during high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment in bone. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, M.K.; Huisman, M.; Nijenhuis, R.J.; van den Bosch, M.A.A.J.; Viergever, M.A.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Bartels, L.W. Quality of MR thermometry during palliative MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (MR-HIFU) treatment of bone metastases. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2015, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozhinsky, E.; Han, M.; Bucknor, M.; Krug, R.; Rieke, V. T2-based temperature monitoring in bone marrow for MR-guided focused ultrasound. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2016, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, K.V.; Yarmolenko, P.S.; Celik, H.; Eranki, A.; Partanen, A.; Smitthimedhin, A.; Kim, A.; Oetgen, M.; Santos, D.; Patel, J. Comparison of noninvasive high-intensity focused ultrasound with radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma. J. Pediatr. 2017, 190, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillemin, P.C.; Gui, L.; Lorton, O.; Zilli, T.; Crowe, L.A.; Desgranges, S.; Montet, X.; Terraz, S.; Miralbell, R.; Salomir, R.; et al. Mild hyperthermia by MR-guided focused ultrasound in an ex vivo model of osteolytic bone tumour: Optimization of the spatio-temporal control of the delivered temperature. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lena, B.; Bartels, L.W.; Ferrer, C.J.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Viergever, M.A.; Bos, C. Interleaved water and fat MR thermometry for monitoring high intensity focused ultrasound ablation of bone lesions. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.F.; Dupuy, D.E. Thermal ablation of tumours: Biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, J.; Cornell, D.L.; Mittal, S.K.; Agrawal, D.K. Immunotherapy plus cryotherapy: Potential augmented abscopal effect for advanced cancers. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.; Oebisu, N.; Hoshi, M.; Orita, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Hamamoto, S.; Kageyama, K.; Nakamura, H. Promising abscopal effect of combination therapy with thermal tumour ablation and intratumoural OK-432 injection in the rat osteosarcoma model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fionda, B.; Massaccesi, M.; Tagliaferri, L.; Dinapoli, N.; Iezzi, R.; Boldrini, L. Abscopal effect and interventional oncology: State of art and future perspectives. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Thermometric Techniques | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Thermocouples | Low cost; small size; robustness; wide measurement range; and short response time | Invasive; single point measurement; metallic composition; potential measurement artifacts |
| Thermistors | Low cost; small size; robustness; high sensitivity; short response time; good accuracy | Invasive; single point measurement; potential measurement artifacts |
| Fluoroptic sensors | Biocompatibility; small size, immunity to electromagnetic fields; wide measuring range; high accuracy | Invasive; single point measurement; fragility; potential measurement artifacts |
| FBGs | Biocompatibility; small size; immunity to electromagnetic fields; high accuracy; short response time; multi-point temperature measurements; | Invasive; fragility; cross-sensitivity to strain; high-cost |
| CT-thermometry | Non-invasive; thermal map reconstruction; good spatial resolution; fast acquisition time; temperature precision around 3 °C | Ionizing radiation dose; potential measurement artifacts; quite expensive |
| US-thermometry | Non-invasive; thermal map reconstruction; absence of ionizing radiation; quite inexpensive | Potential measurement artifacts |
| MR-thermometry | Non-invasive; thermal map reconstruction; absence of ionizing radiation; linear relationship between T1 and temperature variations in the range of 30 °C and 70 °C; no tissue type dependence for PRF method | Potential measurement artifacts; lack of MR signal in cortical bone; expensive |
| Authors, Reference and Year | Type of Study | Type of Sensors (Number of Sensors) | Type of Probe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dupuy et al. [43], 2000 | Ex vivo and in vivo animal trial | Thermistors (3) | Monopolar RFA |
| Rachbauer et al. [148], 2003 | Ex vivo trial | Thermocouples (5) | Water-cooled single RF electrode (Radionics Instruments Inc.) |
| Bitsch et al. [149], 2006 | Ex vivo trial | Thermocouples (3) | Monopolar RF electrode (TCM 101; Stryker Leibinger, Freiburg, Germany) |
| Adachi et al. [150], 2008 | Ex vivo and in vivo trials | K-type thermocouples (3 during in vivo and 2 during ex vivo experiments) | 17G monopolar cooled RF electrode |
| Nakatuska et al. [151], 2009 | Clinical trial | Thermocouple (1) | 17G monopolar cooled RF electrode |
| Groetz et al. [152], 2013 | Ex vivo human trial | K-type thermocouples (3) | RFA array electrode (LeV-eenTM Electrode System, Boston Scientific, Natick, USA) Single-needle RFA electrode (SoloistTM Electrode System, Boston Scientific, Natick, USA) |
| Pezeshki et al. [153], 2014 | Ex vivo animal trial | Thermocouple (1) | 17G bipolar cooled RF probe (OsteoCool Baylis Medical Company) |
| Greenberg at al. [154], 2014 | Ex vivo animal trial | Thermocouple (not defined) | Monopolar RF probe (ACT-1510 Cool-tip Ablation System, Valley-lab, Boulder, Colorado) |
| Bornemann et al. [45], 2016 | Ex vivo animal trial | K-type thermocouples (3) | Monopolar RF probe (SpineSTAR, DFINE Inc. San Jose, CA, USA) |
| Bornemann et al. [155], 2016 | In vitro model | K-type thermocouples (3) | Bipolar RF ablation electrode (SpineSTAR, DFINE Inc. San Jose, CA, USA) Two monopolar RF electrodes (Soloist and LeVeen, Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) |
| Wei et al. [156], 2018 | Ex vivo and in vivo animal trials | Not specified in ex vivo trial (2) and thermistors in in vivo (3) | Multipolar RFA (RFA-1315, Beijing Bolai, Beijing, China) |
| Lecigne et al. [51], 2019 | Clinical trial | Thermocouple (1) | Bipolar RFA (OsteoCool Medtronic/STAR Merrit Medical) Monopolar RFA (OsteoCool Medtronic) |
| Mayer et al. [157], 2021 | Clinical trial | Thermocouple (1) | Bipolar RFA (Osteocool medtronic) |
| Lecigne et al. [158], 2021 | Clinical trial | Thermocouple (1) | Monopolar RFA (Multigen Stryker, USA) Bipolar RFA (OsteoCool Medtronic/STAR Merrit Medical) |
| Authors, Reference and Year | Type of Study | Type of Technique | Type of Laser |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binkert et al. [165], 2002 | In vivo animal trial | MR-thermometry | 1064 nm Nd:YAG |
| Sequeiros et al. [166], 2003 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | 1064 nm Nd:YAG |
| Streitparth et al. [167], 2009 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | 1064 nm Nd:YAG |
| Streitparth et al. [168], 2010 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | 1064 nm Nd:YAG |
| Tatsui et al. [169], 2015 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | 980 nm diode |
| Tatsui et al. [170], 2016 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | 980 nm diode |
| Authors, Reference and Year | Type of Study | Type of Sensors (and Number) | Type of Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kastler et al. [178], 2014 | Clinical trial | Thermocouple (1) | 2.45 GHz-MW generator (Microsulis/AngioDynamics, Latham, New York) and 14 cm or 19 cm long of MW antenna. |
| Fan et al. [179], 2016 | Clinical trial | Thermocouples (not specified) | 2.45 GHz MW generator and co-axial antenna (no further details provided). |
| Kastler et al. [180], 2017 | Clinical trial | Thermocouples (1 or more than one in 3 cases) | 2.45 GHz-MW generator (AngioDynamics, Inc, Latham, New York) or Amica (Hospital Service, Rome, Italy). Details about the antenna used were not specified. |
| De Vita et al. [181], 2020 | Ex vivo animal trial | FBGs (40) | 2.45 GHz-MW generator and 15 cm long antenna with an active tip of 31 mm (Microwave Ablation System, Surgnova Healthcare Technologies, Zhejiang) |
| De Tommasi et al. [182], 2020 | Ex vivo animal trial | FBGs (30) | 2.45 GHz-MW generator and 15 cm long antenna with an active tip of 31 mm (Microwave Ablation System, Surgnova Healthcare Technologies, Zhejiang) |
| Authors, Reference and Year | Type of Study | Type of Techniques | Type of Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geiger et al. [191], 2014 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | ExAblate 2100 MR-guided focused ultrasound system (InSightec, Tirat Carmel, Israel) |
| Ramsay et al. [192], 2015 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry and 4 fiber optics | 1.2 MHz-transducer |
| Lam et al. [193], 2016 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | Not specified |
| Ozhinspky et al. [194], 2016 | Ex vivo and in vivo animal trial | MR-thermometry and 3 fiber optics | Ultrasound system operating at 500 kHz (ExAblate 2100, InSightec, Israel) |
| Sharma et al. [195], 2017 | Clinical trial | MR-thermometry | Ultrasound system Sonalleve V2 (Philips, Vantaa, Finland) |
| Guillemin et al. [196], 2019 | Ex vivo animal trial | MR-thermometry and 1 fluoroptic sensor | Phased array HIFU transducer (Imasonic, Besançon, France) |
| Lena et al. [197] | Ex vivo and in vivo trials | MR-thermometry | HIFU Platform (Sonalleve MR-HIFU V2; Profound Medical, Mississauga, ON, Canada Mississauga, ON, Canada) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Tommasi, F.; Massaroni, C.; Grasso, R.F.; Carassiti, M.; Schena, E. Temperature Monitoring in Hyperthermia Treatments of Bone Tumors: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges. Sensors 2021, 21, 5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165470
De Tommasi F, Massaroni C, Grasso RF, Carassiti M, Schena E. Temperature Monitoring in Hyperthermia Treatments of Bone Tumors: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165470
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Tommasi, Francesca, Carlo Massaroni, Rosario Francesco Grasso, Massimiliano Carassiti, and Emiliano Schena. 2021. "Temperature Monitoring in Hyperthermia Treatments of Bone Tumors: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165470
APA StyleDe Tommasi, F., Massaroni, C., Grasso, R. F., Carassiti, M., & Schena, E. (2021). Temperature Monitoring in Hyperthermia Treatments of Bone Tumors: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges. Sensors, 21(16), 5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165470









